中国沙漠 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 252-263.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00149
• • 上一篇
刘俊贺1( ), 迟云平1,2(
), 迟云平1,2( ), 谢远云1,2, 康春国3, 魏振宇1, 吴鹏1, 孙磊1
), 谢远云1,2, 康春国3, 魏振宇1, 吴鹏1, 孙磊1
收稿日期:2022-11-16
修回日期:2022-12-28
出版日期:2023-05-20
发布日期:2023-05-31
通讯作者:
迟云平
作者简介:迟云平(E-mail: 1982cyp@163.com)基金资助:
Junhe Liu1( ), Yunping Chi1,2(
), Yunping Chi1,2( ), Yuanyun Xie1,2, Chunguo Kang3, Zhenyu Wei1, Peng Wu1, Lei Sun1
), Yuanyun Xie1,2, Chunguo Kang3, Zhenyu Wei1, Peng Wu1, Lei Sun1
Received:2022-11-16
Revised:2022-12-28
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-05-31
Contact:
Yunping Chi
摘要:
中国北部沙漠-沙地作为亚洲风尘系统的重要组成部分,是亚洲重要的粉尘源区。对松嫩沙地和欧亚黄土带最东端黄土沉积的源-汇系统进行研究,有利于了解松嫩平原冰期-间冰期大气环流模式与粉尘传输路径之间的关系,并为区域生态环境和沙尘天气治理提供科学依据。本研究采集了松嫩沙地全范围的47件样品(<63 μm)进行元素地球化学分析(常量元素、微量元素和稀土元素),建立了完整的松嫩沙地地球化学数据库,并通过主成分分析和频率模型进行物源定量重建,结合物源判别图解探讨松嫩沙地对下风向区域风尘物质的贡献度。结果表明:松嫩沙地处于化学风化初级阶段,沉积物的成熟度较低,由大多数初次循环和少数再循环沉积混合组成。定量重建结果将松嫩沙地划分为西北部、西南-W部、西南-E部3个分区,对哈尔滨黄土的贡献度依次为西南-E部(即松花江水系沉积物)40.5%~66.3%、西南-W部24.9%~48.9%、西北部1.9%~13.2%。物源判别图解表明哈尔滨黄土与现代尘暴粉尘有相似的源区,揭示了松嫩平原冰期-间冰期粉尘传输路径一直以西南方向为主,与冰期以西北风为主导的环流模式存在差异。哈尔滨西北方向粉尘源区(松嫩沙地西北部和呼伦贝尔沙地)植被覆盖度高、沙地暴露面积小且受地形阻挡是导致其粉尘排放量受限的主要原因,而西南方向源区(主要是松嫩沙地西南区域)植被覆盖度低、沙地暴露面积大且地形平坦开阔使其粉尘排放量持续增高。应加强对松嫩沙地西南区域的生态环境治理,以改善哈尔滨地区频发的沙尘天气和日益严重的大气污染问题。对于区域沙尘天气的防治,其根本在于应重视潜在物源区的生态环境治理而非仅局限于发生区域本身。
中图分类号:
刘俊贺, 迟云平, 谢远云, 康春国, 魏振宇, 吴鹏, 孙磊. 松嫩沙地地球化学特征及其对风尘物质贡献的指示[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 252-263.
Junhe Liu, Yunping Chi, Yuanyun Xie, Chunguo Kang, Zhenyu Wei, Peng Wu, Lei Sun. Geochemical characteristics of Songnen Sandy Land and its indication of contribution to aeolian dust[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 252-263.
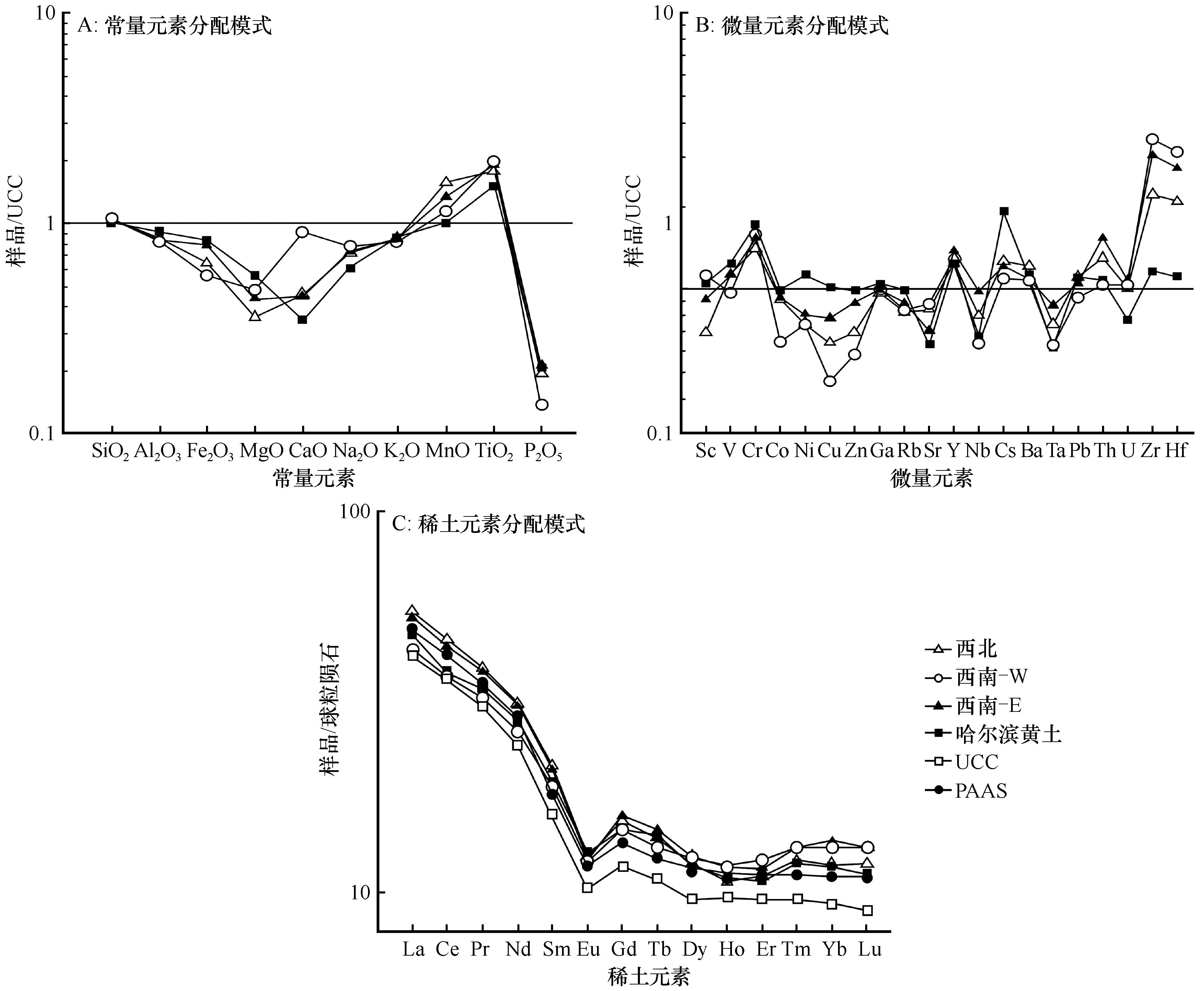
图2 松嫩沙地沉积物的元素标准化模式图解
Fig.2 The normalized patterns for elements of the sediments in Songnen Sandy Land. A, major elements; B, trace elements; C, rare earth elements
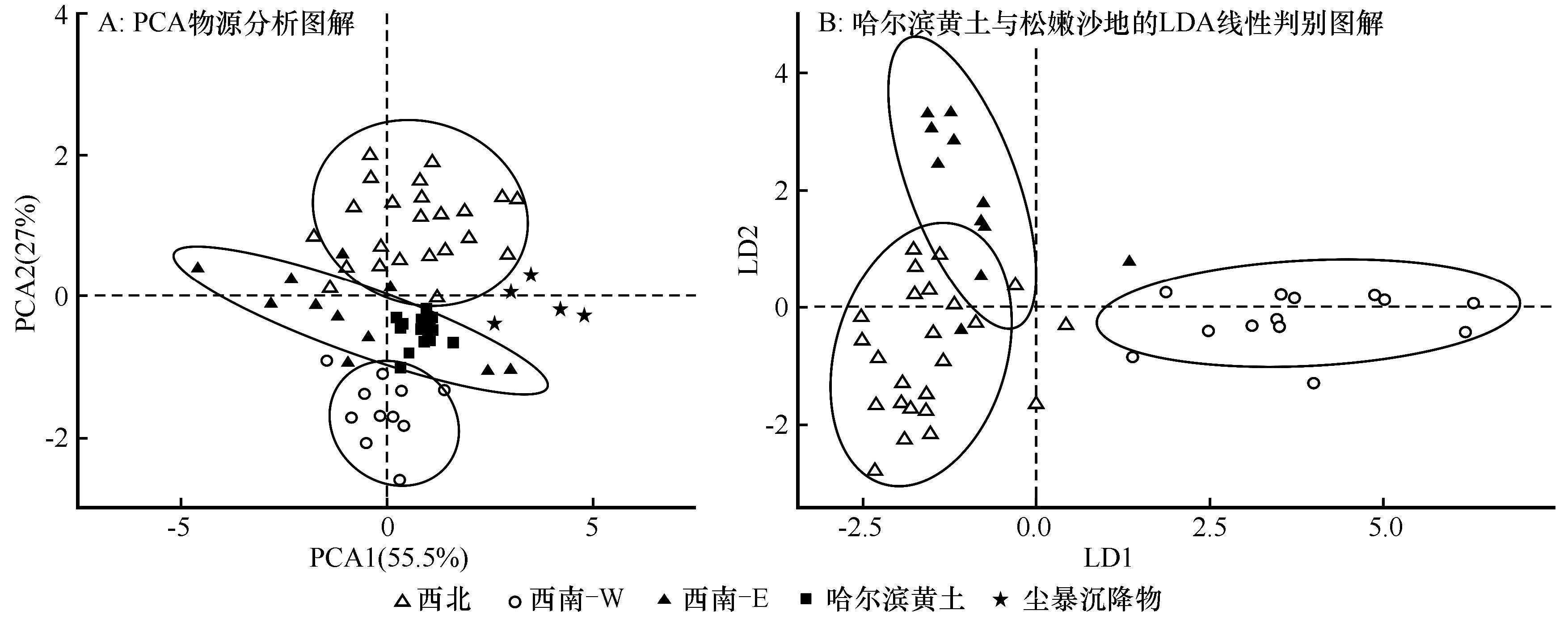
图3 松嫩沙地定量源区划分图解
Fig.3 Quantitative source area division diagram of Songnen Sandy Land. A, PCA material source analysis diagram; B, LDA linear discriminant diagram of Harbin loess and Songnen Sandy Land
| 分区 | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H4 | H6 | H7 | H8 | H9 | H10 | H11 | H12 | H13 | H14 | H15 | 平均 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 西北部 | 12.5 | 8.0 | 6.6 | 13.2 | 7.4 | 12.6 | 10.1 | 8.4 | 11.8 | 8.7 | 6.9 | 4.6 | 4.1 | 6.8 | 1.9 | 8.2 |
| 西南-W部 | 28.9 | 41.3 | 36.9 | 37.8 | 42.6 | 46.8 | 36.5 | 47.4 | 24.9 | 48.9 | 42.7 | 29.1 | 29.4 | 46.7 | 39.1 | 38.6 |
| 西南-E部 | 58.6 | 50.6 | 56.4 | 48.9 | 49.9 | 40.5 | 53.2 | 44.0 | 63.2 | 42.3 | 50.2 | 66.2 | 66.3 | 46.4 | 58.8 | 53.0 |
表1 基于Frequentist模型定量重建3个源区对哈尔滨黄土贡献度(%)
Table 1 Quantitatively reconstructing the contribution of three source areas to Harbin loess by Frequentist model
| 分区 | H1 | H2 | H3 | H4 | H4 | H6 | H7 | H8 | H9 | H10 | H11 | H12 | H13 | H14 | H15 | 平均 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 西北部 | 12.5 | 8.0 | 6.6 | 13.2 | 7.4 | 12.6 | 10.1 | 8.4 | 11.8 | 8.7 | 6.9 | 4.6 | 4.1 | 6.8 | 1.9 | 8.2 |
| 西南-W部 | 28.9 | 41.3 | 36.9 | 37.8 | 42.6 | 46.8 | 36.5 | 47.4 | 24.9 | 48.9 | 42.7 | 29.1 | 29.4 | 46.7 | 39.1 | 38.6 |
| 西南-E部 | 58.6 | 50.6 | 56.4 | 48.9 | 49.9 | 40.5 | 53.2 | 44.0 | 63.2 | 42.3 | 50.2 | 66.2 | 66.3 | 46.4 | 58.8 | 53.0 |
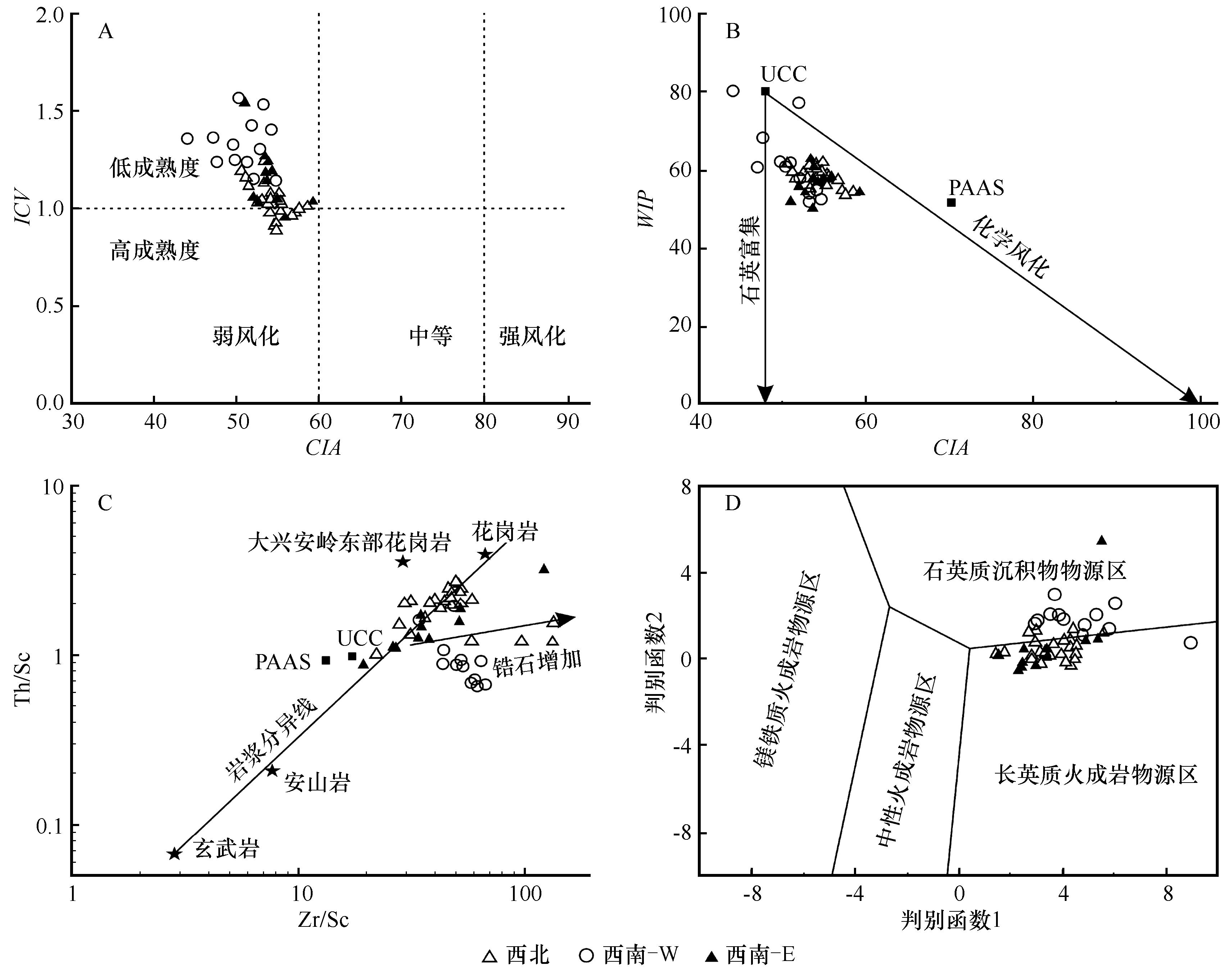
图5 松嫩沙地地表沉积物的成熟度与沉积再循环判别图解判别函数1=30.638×TiO2/Al2O3-12.541×Fe2O3/Al2O3+7.329×MgO/Al2O3+12.031×Na2O/Al2O3+35.42×K2O/Al2O3-6.382;判别函数2=56.500×TiO2/Al2O3-10.879×Fe2O3/Al2O3+30.875×MgO/Al2O3-5.404×Na2O/Al2O3+11.112×K2O/Al2O3-3.89
Fig.5 Maturity and discrimination diagram of the sediment recycling in the Songnen Sandy Land
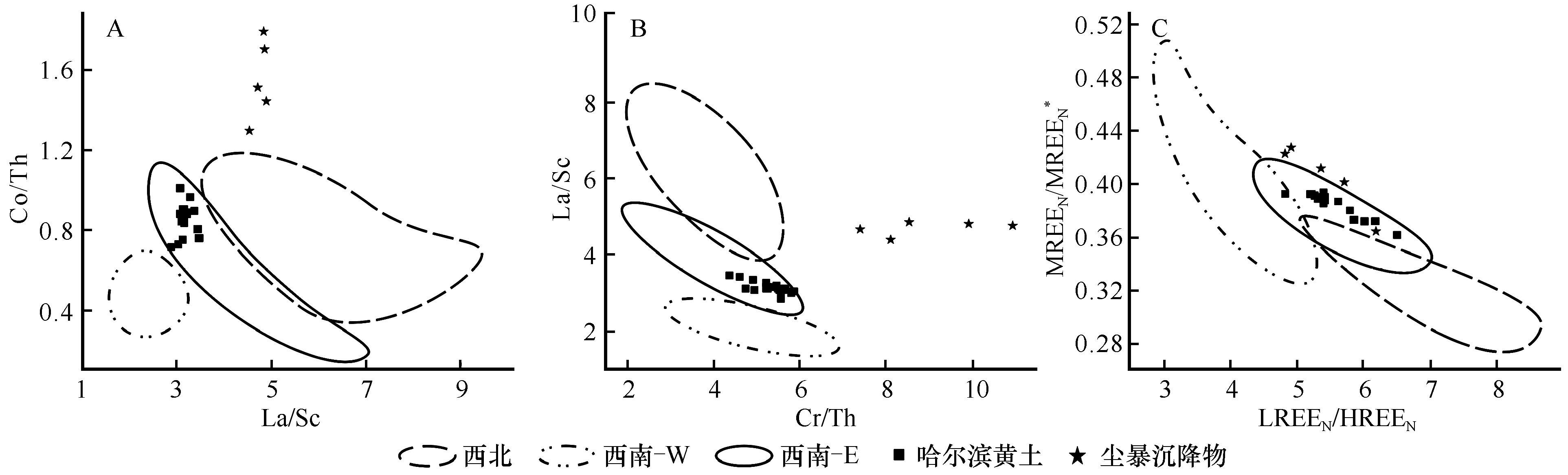
图6 松嫩沙地不活动元素比值物源判别图解LREEN=(LaN+CeN+PrN+NdN); HREEN=(ErN+TmN+YbN+LuN); MREEN=(SmN+EuN+GdN+TbN+DyN+HoN); MREEN*=2×MREEN/(LREEN+HREEN)
Fig.6 Provenance discrimination diagrams involving immobile elements of Songnen Sandy Land
| 1 | Zhang X Y, Arimoto R, An Z S.Dust emission from Chinese desert sources linked to variations in atmospheric circulation [J].Journal of Geophysical Research,1997,102:28041-28047. |
| 2 | Zhang H Z, Lu H Y, Xu X S,et al.Quantitative estimation of the contribution of dust sources to Chinese loess using detrital zircon U-Pb age patterns [J].Journal of Geophysical Research,2016,121(11):2085-2099. |
| 3 | Ding Z L, Sun J M, Yang S L,et al.Geochemistry of the pliocene red clay formation in the Chinese Loess Plateau and implications for its origin,source provenance and paleoclimate change[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2001,65(6):901-913. |
| 4 | Li G J, Chen J, Ji J F,et al.Natural and anthropogenic sources of East Asian dust[J].Geology,2009,37(8):727-730. |
| 5 | Xu D R, Gu X X, Li P C,et al.Mesoproterozoic-Neoproterozoic transition:geochemistry,provenance and tectonic setting of clastic sedimentary rocks on the SE margin of the Yangtze Block,South China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2007,29(5/6):637-650. |
| 6 | Sun J M.Provenance of loess material and formation of loess deposits on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2002,203(3/4):845-859. |
| 7 | Cullers R L.The controls on the major and trace element evolution of shales,siltstones and sandstones of Ordovician to Tertiary age in the Wet Mountains region,Colorado,USA[J].Chemical Geology,1995,123(1/4):107-131. |
| 8 | Chen J, Li G J.Geochemical studies on the source region of Asian dust[J].Science China Earth Sciences,2011,54(9):1279-1301. |
| 9 | Cox R, Lowe D R, Cullers R L.The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in the southwestern United States[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1995,59(14):2919-2940. |
| 10 | Sun J M.Source regions and formation of the loess sediments on the high mountain regions of northwestern China[J].Quaternary Research,2002,58(3):341-351. |
| 11 | Xie Y Y, Kang C G, Chi Y P,et al.The loess deposits in Northeast China:the linkage of loess accumulation and geomorphic-climatic features at the easternmost edge of the Eurasian loess belt[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2019,181:103914. |
| 12 | Song Y G, Chen X L, Qian L B,et al.Distribution and composition of loess sediments in the Ili Basin,Central Asia[J].Quaternary International,2014,334/335:61-73. |
| 13 | Jiang Q D, Hao Q Z, Peng S Z,et al.Grain-size evidence for the transport pathway of the Xiashu loess in northern subtropical China and its linkage with fluvial systems [J].Aeolian Research,2020 46:100613. |
| 14 | Zhang H B, Nie J S, Liu X J,et al.Spatially variable provenance of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Geology,2021,49(10):1155-1159. |
| 15 | 赵万苍,刘连文,陈骏,等.中国沙漠元素地球化学区域特征及其对黄土物源的指示意义[J].中国科学:地球科学,2019,49(9):1425-1438. |
| 16 | Dehghani S, Moore F, Vasiluk L,et al.The geochemical fingerprinting of geogenic particles in road deposited dust from Tehran metropolis,Iran:implications for provenance tracking[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration,2018,190:411-423. |
| 17 | 毛光周,刘池洋.地球化学在物源及沉积背景分析中的应用[J].地球科学与环境学报,2011,33(4):337-348. |
| 18 | García-Comendador J, Martínez-Carreras N, Fortesa J,et al.Combining sediment fingerprinting and hydro-sedimentary monitoring to assess suspended sediment provenance in a mid-mountainous Mediterranean catchment[J].Journal of Environ Manage,2021,299:113593. |
| 19 | Song Y G, Chen X L, Li Y,et al.Quantifying the provenance of dune sediments in the Taklimakan Desert using machine learning,multidimensional scaling and sediment source fingerprinting[J].Catena,2021,210:105902. |
| 20 | Lizaga I, Latorre B, Gaspar L,et al.FingerPro mixing model:an R package for sediment tracing[C]//EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts.EGUGA,2018. |
| 21 | 裘善文.中国东北西部沙地与沙漠化[M].北京:科学出版社,2008. |
| 22 | Xie Y Y, Yuan F, Zhan T,et al.Geochemistry of loess deposits in northeastern China:constraint on provenance and implication for disappearance of the large Songliao palaeolake[J].Journal of the Geological Society,2018,175:146-162. |
| 23 | Xie Y Y, Chi Y P.Geochemical investigation of dry-and wet-deposited dust during the same dust-storm event in Harbin,China:constraint on provenance and implications for formation of aeolian loess[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2016,120:43-61. |
| 24 | Yang X P, Liu Y S, Li C Z,et al.Rare earth elements of aeolian depositions in Northern China and their implications for determining the provenance of dust storms in Beijing[J].Geomorphology,2007,87(4):365-377. |
| 25 | 熊聪慧,王雪莲.电感耦合等离子体发射光谱法测定地质样品中K、Ca等常量元素的前处理方法对比[J].分析测试技术与仪器,2020,26(1):30-36. |
| 26 | 谢远云,孟杰,郭令芬,等.松嫩平原杜蒙沙地地表物质的地化组成及风化特征[J].中国沙漠,2013,33(4):1009-1018. |
| 27 | Yang P H, Yuan D X, Yuan W H,et al.Formations of groundwater hydrogeochemistry in a karst system during storm events as revealed by PCA[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2010,55(14):1412-1422. |
| 28 | Li Y, Gholami H, Song Y G,et al.Source fingerprinting loess deposits in Central Asia using elemental geochemistry with Bayesian and GLUE models[J].Catena,2020,194:104808. |
| 29 | Hu W J, Du S S, Tan L H,et al.Provenance and formation mechanism of aeolian sands on the eastern bank of Co Nag Lake on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J].Catena,2021,208:105786. |
| 30 | Collins A L, Zhang Y, Walling D E,et al.Tracing sediment loss from eroding farm tracks using a geochemical fingerprinting procedure combining local and genetic algorithm optimisation[J].Science of the Total Environment,2010,408(22):5461-5471. |
| 31 | Gholami H, Rahimi S, Fathabadi A,et al.Mapping the spatial sources of atmospheric dust using GLUE and Monte Carlo simulation[J].Science of the Total Environment,2020,723(3):138090. |
| 32 | Collins A L, Walling D E, Leeks G J L.Fingerprinting the origin of fluvial suspended sediment in larger river basins:combining assessment of spatial provenance and source type[J].Geografiska Annaler:Series A Physcial Geography,1997,79(4):239-254. |
| 33 | Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J].Nature,1982,299:715-717. |
| 34 | Cullers R L, Podkovyrov V N.Geochemistry of the Mesoproterozoic Lakhanda shales in southeastern Yakutia,Russia:implications for mineralogical and provenance control,and recycling [J].Precambrian Research,2000,104(1):77-93. |
| 35 | Garzanti E, Padoan M, Andò S,et al.Weathering and relative durability of detrital minerals in equatorial climate:sand petrology and geochemistry in the East African Rift[J].The Journal of Geology,2013,121(6):547-580. |
| 36 | McLennan S M.Weathering and global denudation[J].Journal of Geology,1993,101(2):295-303. |
| 37 | Fedo C M, Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and Paleosols,with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance[J].Geology,1995,23(10):921-924. |
| 38 | Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1984,48(7):1523-1534. |
| 39 | Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Formation and diagenesis of weathering profiles[J].Journal of Geology,1989,97(2):129-147. |
| 40 | Nesbitt H W, Fedo C M, Young G M.Quartz and feldspar stability,steady and non-steady-state weathering,and petrogenesis of siliciclastic sands and muds[J].Journal of Geology,1997,105(2):173-191. |
| 41 | Roser B P, Coombs D S, Korsch R J,et al.Whole-rock geochemical variations and evolution of the arc-derived Murihiku Terrane,New Zealand[J].Geological Magazine,2002,139(6):665-685. |
| 42 | Ohta T.Measuring and adjusting the weathering and hydraulic sorting effects for rigorous provenance analysis of sedimentary rocks:a case study from the Jurassic Ashikita Group,southwest Japan[J].Sedimentology,2008,55(6):1687-1701. |
| 43 | Ohta T, Arai H.Statistical empirical index of chemical weathering in igneous rocks:a new tool for evaluating the degree of weathering[J].Chemical Geology,2007,240(3/4):280-297. |
| 44 | Floyd P A, Leveridge B E.Tectonic environment of the Devonian Gramscatho Basin,South Cornwall:framework mode and geochemical evidence from turbiditic sandstones[J].Journal of the Geological Society,1987,144(4):531-542. |
| 45 | Xie Y Y, Yuan F, Zhan T,et al.Geochemical and isotopic characteristics of sediments for the Hulun Buir Sandy Land,Northeast China:implication for weathering,recycling and dust provenance[J].Catena,2018,160:170-184. |
| 46 | Garzanti E, Padoan M, Setti M,et al.Weathering geochemistry and Sr-Nd fingerprints of equatorial upper Nile and Congo muds[J].Geochem Geophys Geosyst,2013,14(2):292-316. |
| 47 | McLennan S M, Hemming S, McDaniel D K,et al.Geochemical approaches to sedimentation,provenance,and tectonics[J].Geological Society of America,1993,284:21-40. |
| 48 | Asiedu D K, Suzuki S, Nogami K,et al.Geochemistry of Lower Cretaceous sediments,Inner zone of Southwest Japan:constraints on provenance and tectonic environment[J].Geochemical Journal,2000,34(2):155-173. |
| 49 | 袁方,谢远云,詹涛,等.地球化学组成揭示的杜蒙沙地化学风化和沉积再循环特征及其对风尘物质贡献的指示[J].地理科学,2017,37(12):1885-1893. |
| 50 | Roser B P, Korsch R J.Provenance signatures of sandstone mudstone suite determined using discriminant function analysis of major element data[J].Chemical Geology,1988,67:119-139. |
| 51 | Bhatia M R.Rare earth element geochemistry of Australian Paleozoic graywackes and mudrocks:provenance and tectonic control[J].Sedimentary Geology,1985,45:97-113. |
| 52 | Bhatia M R, Crook K A W.Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basins[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,1986,92:181-193. |
| 53 | Condie K C.Another look at rare earth elements in shales[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1991,55(9):2527-2531. |
| 54 | 谢远云,孙磊,康春国,等.松嫩沙地Sr-Nd同位素组成特征[J].沉积学报,2020,38(4):771-780. |
| 55 | Xie Y Y, Meng J, Guo L F.REE geochemistry of modern eolian dust deposits in Harbin city,Heilongjiang Province,China:implications for provenance[J].Catena,2014,123:70-78. |
| 56 | 刘东生.黄土与环境[M].北京:科学出版社,1985. |
| 57 | Sun D H, Bloemendal J, Rea D K,et al.Bimodal grain-size distribution of Chinese loess,and its palaeoclimatic implications[J].Catena,2004,55:325-340. |
| 58 | 刘东生,郑绵平,郭正堂.亚洲季风系统的起源和发展及其与两极冰盖和区域构造运动的时代耦合性[J].第四纪研究,1998(3):194-204. |
| 59 | An Z S.The history and variability of the East Asian paleomonsoon climate[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2000,19:171-187. |
| 60 | Sun J M, Ding Z L, Xia X P,et al.Detrital zircon evidence for the ternary sources of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2018,155:21-34. |
| 61 | 刘东生.黄土的物质成分和结构[M].北京:科学出版社,1966. |
| 62 | Xie Y Y, Liu L, Kang C G,et al.Sr-Nd isotopic characteristics of the northeast sandy land,China and their implications for tracing sources of regional dust[J].Catena,2020,184(3):104303. |
| 63 | Nosrati K, Moradian H, Dolatkordestani M,et al.The efficiency of elemental geochemistry and weathering indices as tracers in aeolian sediment provenance fingerprinting[J].Catena,2022,210:105932. |
| 64 | 裘善文,张柏,王志春.中国东北平原西部荒漠化现状、成因及其治理途径研究[J].第四纪研究,2005,25(1):63-73. |
| 65 | 刘志民,余海滨.“山水林田湖草沙生命共同体” 理念下的科尔沁沙地生态治理[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(1):34-40. |
| 66 | 韩梅,邬晗,韩柏,等.鄂尔多斯地区毛乌素沙地荒漠化形成因素及治理措施[J].农业与技术,2021,41(18):111-115. |
| 67 | 张宝珠,金维林,葛士林,等.呼伦贝尔沙地治理布局及治理模式[J].中国沙漠,2013,33(5):1310-1313. |
| [1] | 张思悦, 李继彦, 张姚姚, 徐德华. 柴达木盆地西南缘山前沙丘区沉积物地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 222-233. |
| [2] | 王晓枝, 董治宝, 南维鸽, 李超, 高冲, 张欣. 拉萨河谷爬坡沙丘沉积物特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 22-31. |
| [3] | 高冲, 董治宝, 南维鸽, 刘铮瑶, 朱春鸣, 王晓枝, 肖南, 张欣. 古尔班通古特沙漠蜂窝状沙丘沉积物理化特征及沉积环境[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 14-24. |
| [4] | 周维鑫, 温小浩, 李保生, 王晨, 田梦圆, 邱明昆. 萨拉乌苏河流域干沟子剖面全新世湖相沉积的地球化学元素特征及其反映的物源变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 114-122. |
| [5] | 陈东雪, 鲁瑞洁, 丁之勇, 刘小槺. 青海湖湖东沙地河湖-风成沉积记录的中晚全新世以来环境变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(6): 99-110. |
| [6] | 郜学敏, 屈欣, 王萌, 张思悦, 张姚姚, 李继彦. 柴达木盆地西北部长垄状雅丹沉积物地球化学元素组成及指示意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 127-136. |
| [7] | 曾方明, 薛红盼. 青藏高原东北部晚第四纪黄土-古土壤的元素组成及其物源指示[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(6): 105-117. |
| [8] | 杜慧荣, 谢远云, 康春国, 迟云平, 王嘉新, 孙磊. 哈尔滨黄土的粒度与地球化学特征及其对粉尘物源的指示[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(1): 64-76. |
| [9] | 李继彦, 周玲, 刘益, 张倩, 蔡莹莹, 张宝贵. 晋西北地区表层土壤粒度与地球化学元素组成[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(5): 155-162. |
| [10] | 凌智永, 王建萍, 陈亮, 芦宝良. 柴达木盆地灌丛沙丘稀土元素地球化学特征与物源[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(5): 963-971. |
| [11] | 陈国祥, 董治宝, 崔徐甲, 肖巍强, 李露露, 杨军怀, 石唯康. 毛乌素沙地中部风成沙的组成与微形态特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(3): 473-483. |
| [12] | 丁之勇, 马龙, 吉力力·阿不都外力, 刘文, 葛拥晓. 新疆艾比湖湖泊沉积物元素地球化学记录及其生态环境意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(1): 101-110. |
| [13] | 曹乐, 聂振龙, 刘学全, 王哲, 孟令群, 姜高磊. 巴丹吉林沙漠湖泊钙华的水化学成因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(5): 1026-1034. |
| [14] | 崔徐甲, 孙虎, 董治宝, 李继彦, 郜学敏, 李超. 巴丹吉林沙漠高大沙山沉积物地球化学元素组成及其环境意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(1): 17-25. |
| [15] | 胡梦珺, 杨爱丽, 张文丽. 常量元素氧化物含量及其比值揭示的中晚全新世以来玛曲高原的环境演变[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(2): 313-321. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
