中国沙漠 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 220-230.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00007
• • 上一篇
王金凤1( ), 刘小玲1, 李庆2(
), 刘小玲1, 李庆2( ), 王仁德2, 王盛1
), 王仁德2, 王盛1
收稿日期:2022-12-02
修回日期:2023-02-11
出版日期:2023-07-20
发布日期:2023-08-14
通讯作者:
李庆
作者简介:李庆(E-mail: qingli2020@outlook.com)基金资助:
Jinfeng Wang1( ), Xiaoling Liu1, Qing Li2(
), Xiaoling Liu1, Qing Li2( ), Rende Wang2, Sheng Wang1
), Rende Wang2, Sheng Wang1
Received:2022-12-02
Revised:2023-02-11
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-08-14
Contact:
Qing Li
摘要:
黄土高原北部是黄河流域土壤风蚀典型区,评估防风固沙服务对黄河流域生态安全屏障建设具有重要意义。基于京津风沙源治理工程效益评价中的风蚀模型估算黄土高原北部风蚀区固沙量,定量评估2000—2020年防风固沙服务,并结合土地利用、植被覆盖度与气候变化分析其驱动机制。结果表明:(1)2000—2020年黄土高原北部风蚀区年均固沙量5.52亿t,年际变化总体呈减少趋势,平均变化率-0.12 t·hm-2·a-1;而防风固沙服务保有率以每年0.50%的速率增加,研究区植被防风固沙服务增强。空间分布上榆林北部风沙区、宁夏东部风沙区、甘肃庆阳、毛乌素沙地中南部及沙地北部达拉特旗植被防风固沙服务有所增强。(2)草地是控制土壤风蚀、发挥防风固沙作用的主要土地利用类型。荒漠化逆转与退耕还草明显增强了防风固沙能力,草地退化将造成固沙服务显著减弱。(3)风速是引起黄土高原北部风蚀区防风固沙服务变化的主要驱动因子,植被恢复对库布齐沙漠和毛乌素沙地等关键区域的防风固沙起到了不可忽视的作用。
中图分类号:
王金凤, 刘小玲, 李庆, 王仁德, 王盛. 黄土高原北部风蚀区防风固沙服务时空分异及驱动因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 220-230.
Jinfeng Wang, Xiaoling Liu, Qing Li, Rende Wang, Sheng Wang. Spatio-temporal differentiation and driving factors of windbreak and sand fixation services in wind erosion area of the northern Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 220-230.
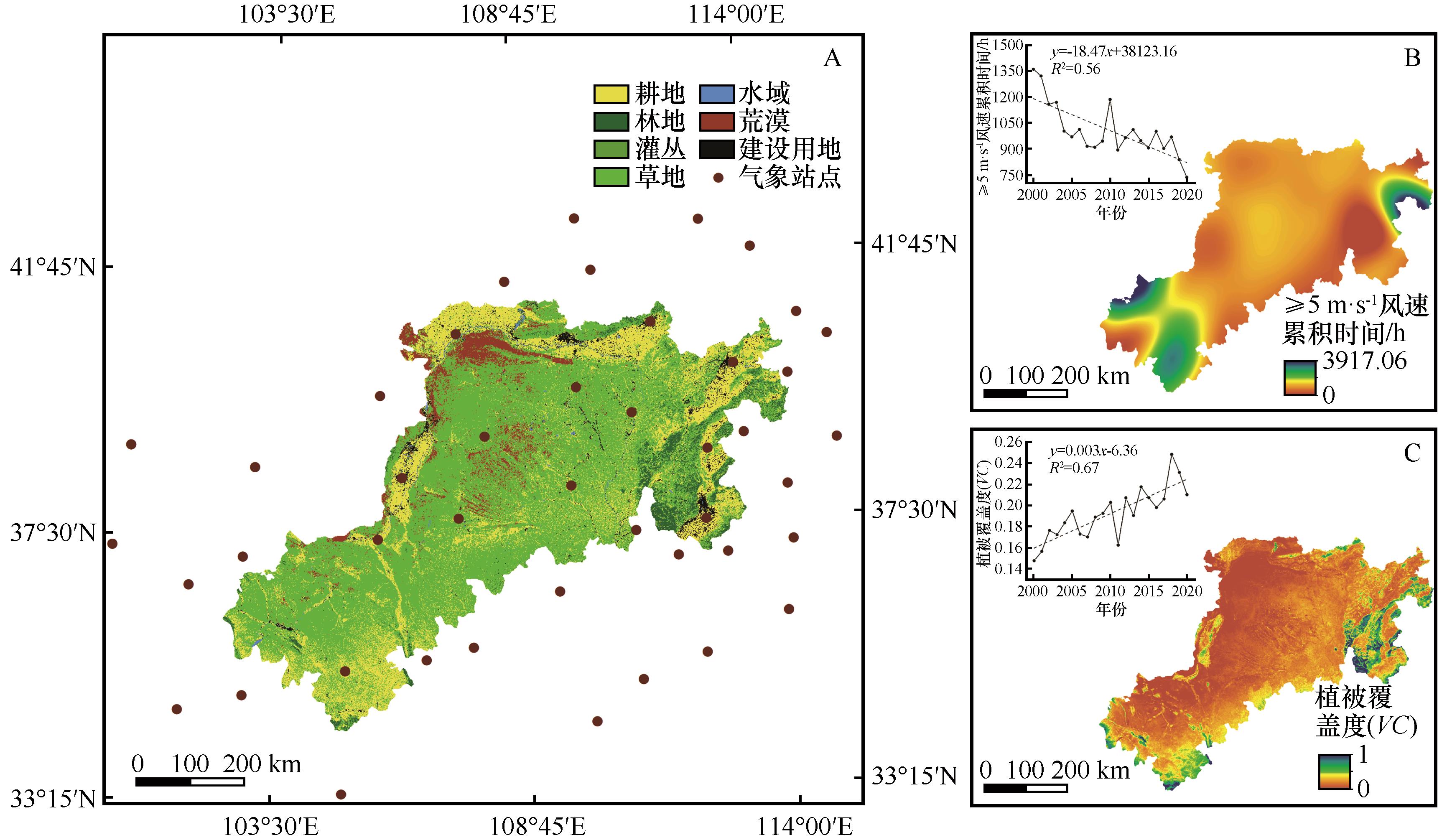
图1 黄土高原北部风蚀区(A)土地利用、(B)≥5 m·s-1风速累积时间和(C)植被覆盖度的空间格局
Fig.1 Spatial patterns of (A) land use, (B) cumulative time of wind speed (≥5 m·s-1) and (C) vegetation coverage in wind erosion area of the northern Loess Plateau
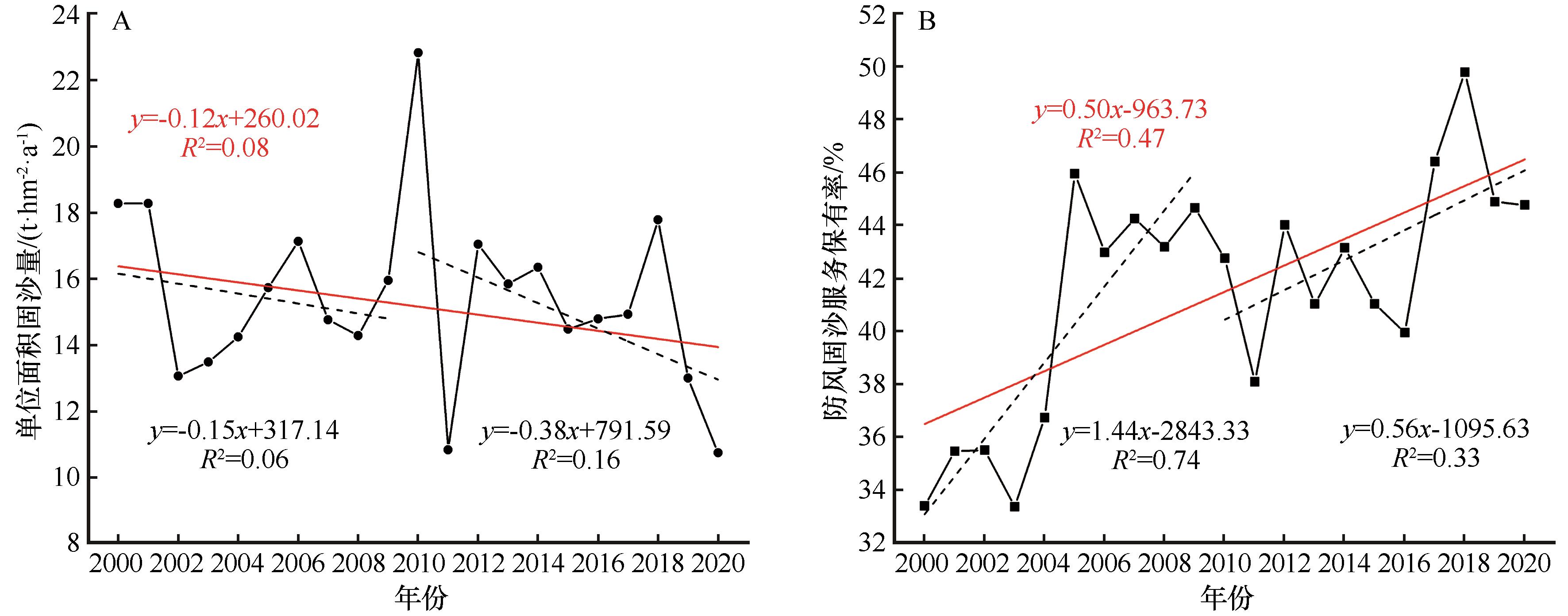
图2 2000—2020年黄土高原北部风蚀区单位面积固沙量和防风固沙服务保有率的年际变化
Fig.2 Annual variation of sand fixation per unit area and windbreak and sand fixation services retention rate in wind erosion area of the northern Loess Plateau during 2000-2020
| 等级 | 分级标准 /(t·hm-2) | 平均单位面积固沙量/(t·hm-2·a-1) | 面积占比/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000—2020年 | 2000—2009年 | 2010—2020年 | 2000—2020年 | 2000—2009年 | 2010—2020年 | ||
| 低 | 0~2 | 0.46 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 62.67 | 63.25 | 61.48 |
| 较低 | 2~10 | 4.48 | 4.50 | 4.56 | 16.40 | 15.94 | 17.43 |
| 中 | 10~25 | 16.27 | 16.23 | 16.27 | 5.53 | 5.28 | 5.93 |
| 较高 | 25~80 | 52.11 | 51.25 | 50.57 | 6.42 | 6.18 | 6.69 |
| 高 | >80 | 112.16 | 112.38 | 117.23 | 8.97 | 9.35 | 8.47 |
表1 不同时段黄土高原北部风蚀区单位面积固沙量的等级划分及面积占比
Table 1 Classification and proportion of sand fixation per unit area in the wind erosion area of the northern Loess Plateau in three periods
| 等级 | 分级标准 /(t·hm-2) | 平均单位面积固沙量/(t·hm-2·a-1) | 面积占比/% | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000—2020年 | 2000—2009年 | 2010—2020年 | 2000—2020年 | 2000—2009年 | 2010—2020年 | ||
| 低 | 0~2 | 0.46 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 62.67 | 63.25 | 61.48 |
| 较低 | 2~10 | 4.48 | 4.50 | 4.56 | 16.40 | 15.94 | 17.43 |
| 中 | 10~25 | 16.27 | 16.23 | 16.27 | 5.53 | 5.28 | 5.93 |
| 较高 | 25~80 | 52.11 | 51.25 | 50.57 | 6.42 | 6.18 | 6.69 |
| 高 | >80 | 112.16 | 112.38 | 117.23 | 8.97 | 9.35 | 8.47 |
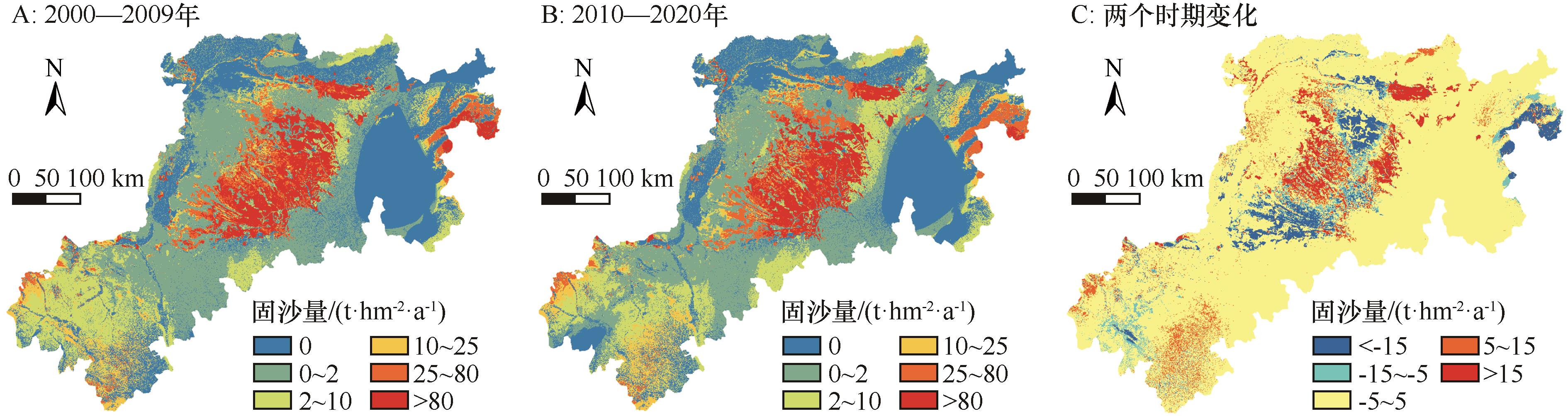
图3 黄土高原北部风蚀区单位面积固沙量空间分布格局和变化特征
Fig.3 Spatial pattern and variation characteristics of sand fixation per unit area in wind erosion area of the northern Loess Plateau
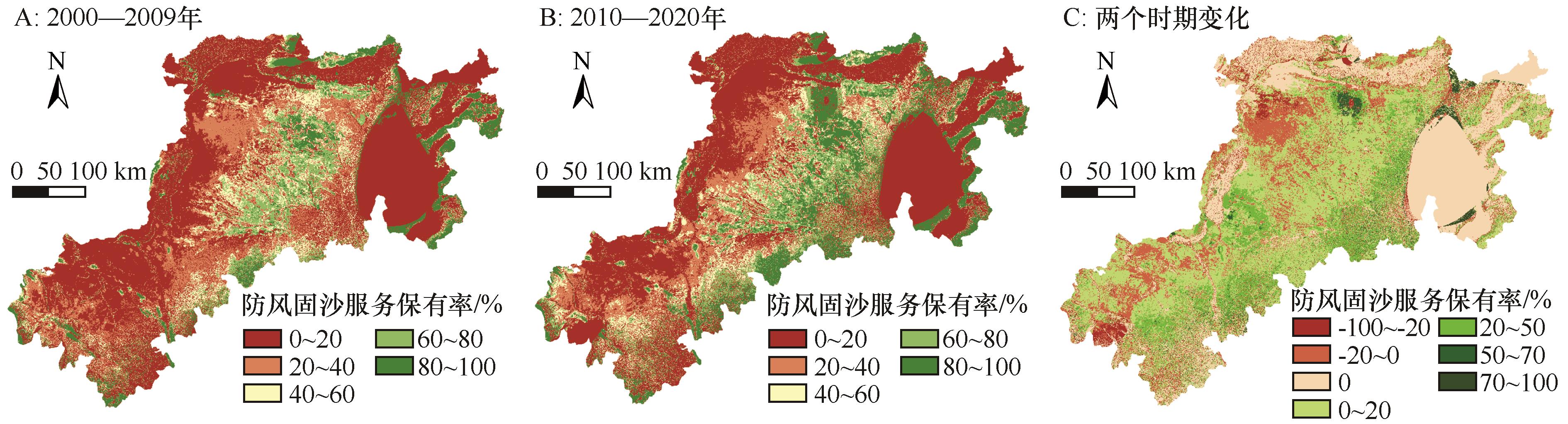
图4 黄土高原北部风蚀区防风固沙服务保有率空间分布格局和变化特征
Fig.4 Spatial pattern and change characteristics of windbreak and sand fixation services retention rate in wind erosion area of the northern Loess Plateau
| 项目 | 研究时段 | 耕地 | 林地 | 灌丛 | 草地 | 荒漠 | 建设用地 | 水域 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土地利用/万km2及变化率 | P1(2000—2009年) | 9.41 | 1.10 | 0.07 | 22.11 | 2.47 | 0.47 | 0.16 |
| P2(2010—2020年) | 8.81 | 1.25 | 0.05 | 22.94 | 1.86 | 0.70 | 0.18 | |
| P1-P2变化量 | -0.60 | 0.15 | -0.02 | 0.83 | -0.61 | 0.24 | 0.02 | |
| P1-P2变化率/% | -6.42 | 13.85 | -31.93 | 3.77 | -24.85 | 50.72 | 12.00 | |
| 平均单位面积固沙量 /(t·hm-2·a-1) 及变化率 | P1(2000—2009年) | 7.20 | 15.50 | 15.89 | 18.31 | 24.63 | 3.48 | 2.82 |
| P2(2010—2020年) | 7.85 | 11.61 | 12.67 | 18.73 | 16.99 | 3.68 | 2.36 | |
| P1-P2变化量 | 0.65 | -3.89 | -3.22 | 0.42 | -7.65 | 0.20 | -0.46 | |
| P1-P2变化率/% | 8.98 | -25.11 | -20.26 | 2.30 | -31.04 | 5.70 | -16.25 | |
平均固沙量/(亿t·a-1) 及贡献率 | P1(2000—2009年) | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.012 | 4.04 | 0.61 | 0.02 | 0.0045 |
| P1贡献率/% | 12.23 | 3.06 | 0.21 | 73.05 | 11.09 | 0.29 | 0.08 | |
| P2(2010—2020年) | 0.69 | 0.18 | 0.006 | 4.30 | 0.32 | 0.03 | 0.0043 | |
| P2贡献率/% | 12.52 | 3.26 | 0.11 | 77.82 | 5.74 | 0.47 | 0.08 | |
| 年均防风固沙服务 保有率/% | P1(2000—2009年) | 27.50 | 95.05 | 98.41 | 47.05 | 20.88 | 29.38 | 31.37 |
| P2(2010—2020年) | 31.51 | 95.53 | 99.23 | 54.78 | 13.18 | 33.19 | 34.70 | |
| P1-P2变化量 | 4.01 | 0.48 | 0.82 | 7.73 | -7.70 | 3.80 | 3.33 |
表2 2000—2009年和2010—2020年黄土高原北部风蚀区不同土地利用类型的固沙量及防风固沙服务保有率
Table 2 Sand fixation and annual average windbreak and sand fixation services retention rate of different land use types in wind erosion area of the northern Loess Plateau in 2000-2009 and 2010-2020
| 项目 | 研究时段 | 耕地 | 林地 | 灌丛 | 草地 | 荒漠 | 建设用地 | 水域 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土地利用/万km2及变化率 | P1(2000—2009年) | 9.41 | 1.10 | 0.07 | 22.11 | 2.47 | 0.47 | 0.16 |
| P2(2010—2020年) | 8.81 | 1.25 | 0.05 | 22.94 | 1.86 | 0.70 | 0.18 | |
| P1-P2变化量 | -0.60 | 0.15 | -0.02 | 0.83 | -0.61 | 0.24 | 0.02 | |
| P1-P2变化率/% | -6.42 | 13.85 | -31.93 | 3.77 | -24.85 | 50.72 | 12.00 | |
| 平均单位面积固沙量 /(t·hm-2·a-1) 及变化率 | P1(2000—2009年) | 7.20 | 15.50 | 15.89 | 18.31 | 24.63 | 3.48 | 2.82 |
| P2(2010—2020年) | 7.85 | 11.61 | 12.67 | 18.73 | 16.99 | 3.68 | 2.36 | |
| P1-P2变化量 | 0.65 | -3.89 | -3.22 | 0.42 | -7.65 | 0.20 | -0.46 | |
| P1-P2变化率/% | 8.98 | -25.11 | -20.26 | 2.30 | -31.04 | 5.70 | -16.25 | |
平均固沙量/(亿t·a-1) 及贡献率 | P1(2000—2009年) | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.012 | 4.04 | 0.61 | 0.02 | 0.0045 |
| P1贡献率/% | 12.23 | 3.06 | 0.21 | 73.05 | 11.09 | 0.29 | 0.08 | |
| P2(2010—2020年) | 0.69 | 0.18 | 0.006 | 4.30 | 0.32 | 0.03 | 0.0043 | |
| P2贡献率/% | 12.52 | 3.26 | 0.11 | 77.82 | 5.74 | 0.47 | 0.08 | |
| 年均防风固沙服务 保有率/% | P1(2000—2009年) | 27.50 | 95.05 | 98.41 | 47.05 | 20.88 | 29.38 | 31.37 |
| P2(2010—2020年) | 31.51 | 95.53 | 99.23 | 54.78 | 13.18 | 33.19 | 34.70 | |
| P1-P2变化量 | 4.01 | 0.48 | 0.82 | 7.73 | -7.70 | 3.80 | 3.33 |
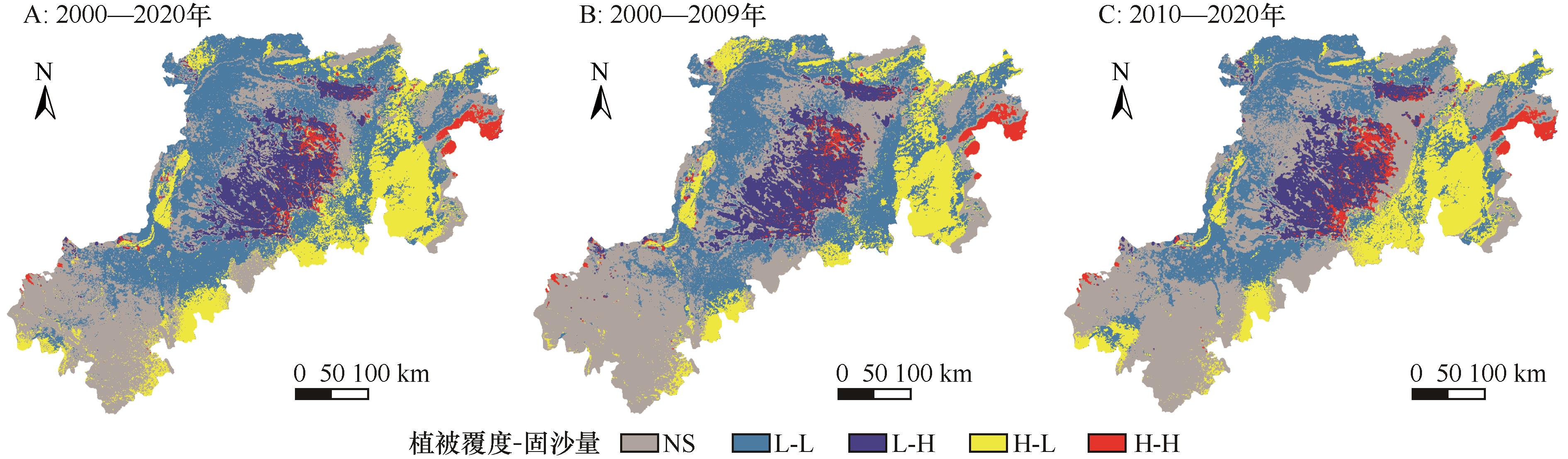
图7 2000—2020年黄土高原北部风蚀区植被覆盖度与单位面积固沙量的局部LISA图
Fig.7 Local LISA plots of vegetation coverage and sand fixation per unit area in wind erosion area of the northern Loess Plateau from 2000 to 2020
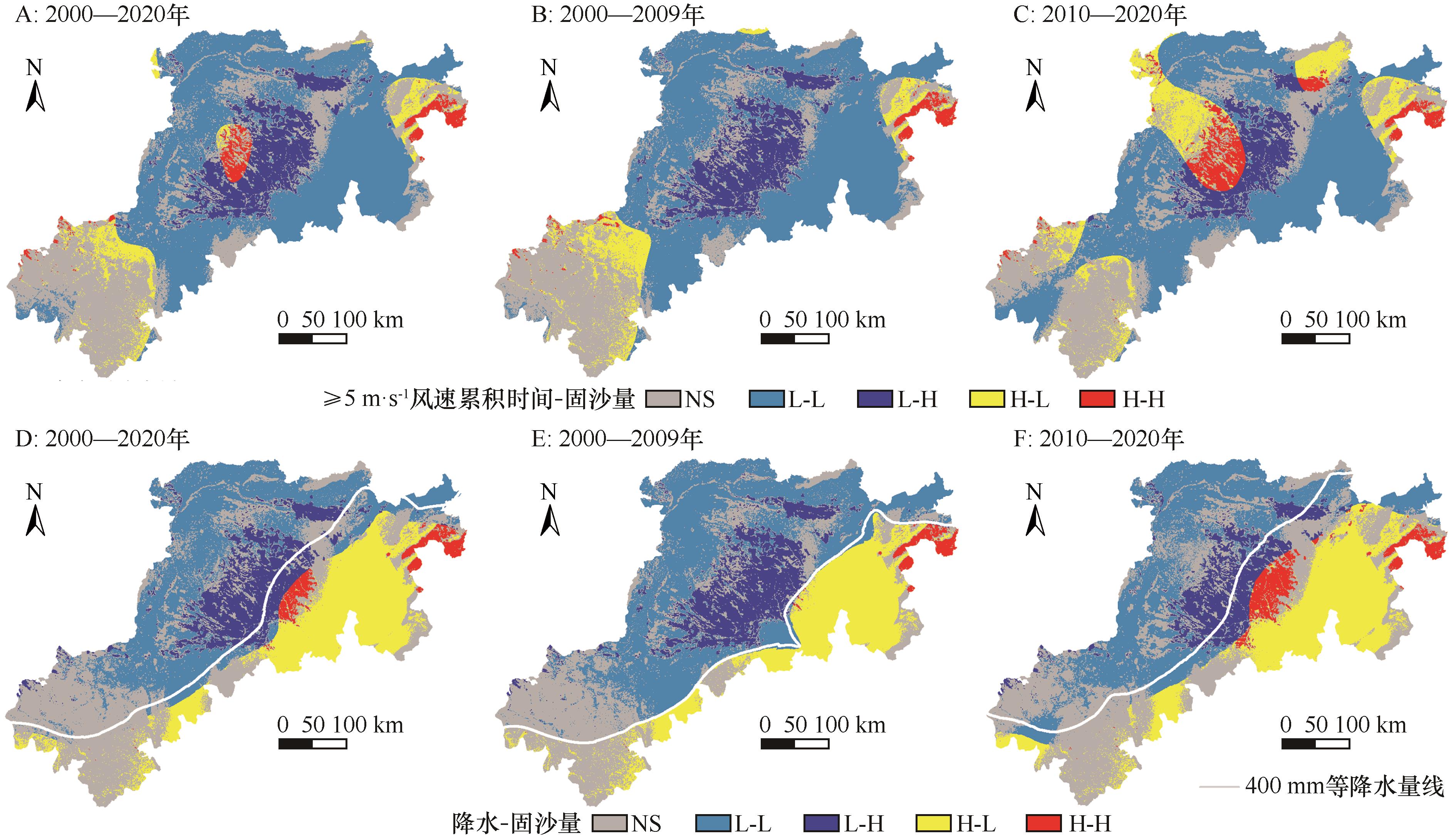
图8 2000—2020年黄土高原北部风蚀区≥5 m·s-1风速累积时间/降水与单位面积固沙量的局部LISA图
Fig.8 Local LISA plots for cumulative time of wind speed(≥5 m·s-1)/precipitation and sand fixation per unit area in wind erosion area of the northern Loess Plateau during 2000-2020
| 1 | 肖玉,谢高地,甄霖,等.北麓草原生态功能区防风固沙服务受益范围识别[J].自然资源学报,2018,33(10):1742-1754. |
| 2 | Li D J, Xu D Y, Wang Z Y,et al.The dynamics of sand-stabilization services in Inner Mongolia,China from 1981 to 2010 and its relationship with climate change and human activities[J].Ecological Indicators,2018,88:351-360. |
| 3 | 元天刚,陈思宇,康丽泰,等.1961-2010年中国北方沙尘源区沙尘强度时空分布特征及变化趋势[J].干旱气象,2016,34(6):927-935. |
| 4 | 张彪,李庆旭,王爽,等.京津风沙源区防风固沙功能的时空变化及其区域差异[J].自然资源学报,2019,34(5):1041-1053. |
| 5 | 张彪,王爽,李庆旭,等.基于防风固沙服务空间流动的区域关联度:以京津风沙源治理工程区为例[J].资源科学,2020,42(5):969-979. |
| 6 | 张照营.北方防沙屏障带防风固沙生态系统服务功能变化评估[D].西安:长安大学,2017. |
| 7 | Xu J, Xiao Y, Xie G D,et al.Assessment of the benefit diffusion of windbreak and sand fixation service in National Key Ecological Function areas in China[J].Aeolian Research,2021,52:100728. |
| 8 | Hu W, Wu X, Zhang K.Spatiotemporal change of beneficiary area from wind erosion prevention service in the Ulan Buh Desert in 2008 and 2018[J].Geography and Sustainability,2022,3(2):119-128. |
| 9 | Li D J, Xu D Y.Sand fixation function response to climate change and land use in northern China from 1981 to 2015[J].Aeolian Research,2019,40:23-33. |
| 10 | 江凌,肖燚,饶恩明,等.内蒙古土地利用变化对生态系统防风固沙功能的影响[J].生态学报,2016,36(12):3734-3747. |
| 11 | 朱趁趁,龚吉蕊,杨波,等.内蒙古荒漠草原防风固沙服务变化及其驱动力[J].生态学报,2021,41(11):4606-4617. |
| 12 | 王夏青,张秀云,周强,等.清末“回民起义”时期黄土高原中部土壤侵蚀和人地关系演变[J].地理科学,2022,42(2):303-313. |
| 13 | 王夏青,夏梦婷,许建伟,等.黄土高原北部丘陵沟壑区近160年土壤侵蚀量演变及其对ENSO事件的响应[J].地理科学,2019,39(7): 1174-1183. |
| 14 | 李晶,任志远.陕北黄土高原土地利用防风固沙功能价值时空研究[J].干旱区资源与环境,2011,25(7):183-187. |
| 15 | Chi W F, Zhao Y Y, Kuang W H,et al.Impacts of anthropogenic land use/cover changes on soil wind erosion in China[J].Science of the Total Environment,2019,668:204-215. |
| 16 | Meng Z, Dang X, Gao Y,et al.Interactive effects of wind speed,vegetation coverage and soil moisture in controlling wind erosion in a temperate desert steppe,Inner Mongolia of China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2018,10(2):1-14. |
| 17 | 张彪,王爽,史芸婷.京津风沙源区防风固沙功能对植被覆盖度变化的时空响应研究[J].生态科学,2022,41(1):110-119. |
| 18 | Huang T, Yu D.Water-soil conservation services dynamic and its implication for landscape management in a fragile semiarid landscape[J].Ecological Indicators,2021,130:108150. |
| 19 | Bu C F, Zhao Y, Hill R L,et al.Wind erosion prevention characteristics and key influencing factors of bryophytic soil crusts[J].Plant and Soil,2015,397(1/2):163-174. |
| 20 | Bergametti G, Rajot J L, Pierre C,et al.How long does precipitation inhibit wind erosion in the Sahel?[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2016,43(12):6643-6649. |
| 21 | Teng Y M, Zhan J Y, Liu W,et al.Spatiotemporal dynamics and drivers of wind erosion on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau,China[J].Ecological Indicators,2021,123:107340. |
| 22 | 彭婉月,兆云,李海东,等.黑河中下游防风固沙功能时空变化及影响因子分析[J].环境科学研究,2020,33(12):2734-2744. |
| 23 | 韩柳,王静璞,王光镇,等.中国北方风蚀区风速变化时空特征分析[J].干旱区地理,2018,41(5):963-971. |
| 24 | 顾朝军,穆兴民,高鹏,等.1961-2014年黄土高原地区降水和气温时间变化特征研究[J].干旱区资源与环境,2017,31(3):136-143. |
| 25 | 李相儒,金钊,张信宝,等.黄土高原近60年生态治理分析及未来发展建议[J].地球环境学报,2015,6(4):248-254. |
| 26 | 王旭洋,郭中领,常春平,等.中国北方农牧交错带土壤风蚀时空分布[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(1):12-22. |
| 27 | 于宝勒,吴文俊,赵学军,等.内蒙古京津风沙源治理工程土壤风蚀控制效益研究[J].干旱区研究,2016,33(6):1278-1286. |
| 28 | 高尚玉.京津风沙源治理工程效益[M].北京:科学出版社,2012. |
| 29 | Zhai T L, Wang J, Jin Z F,et al.Did improvements of ecosystem services supply-demand imbalance change environmental spatial injustices?[J].Ecological Indicators,2020,111:106068. |
| 30 | 赵雪雁,马平易,李文青,等.黄土高原生态系统服务供需关系的时空变化[J].地理学报,2021,76(11):2780-2796. |
| 31 | 何旭宁,于皓,王宗明.基于多源数据的内蒙古东部地区防风固沙能力变化研究[J].测绘与空间地理信息,2019,42(7):138-141. |
| 32 | 宁佳,邵全琴.黄土高原土地利用及生态系统服务时空变化特征研究[J].农业环境科学学报,2020,39(4):774-785. |
| 33 | 王晓峰,马嘉豪,冯晓明,等.黄河流域生态安全屏障的防风固沙服务时空变化及驱动因素分析[J].生态学报,2023,43(2):1-13. |
| 34 | Xavier R L, Wouter B, Gerardo B.Land use can offset climate change induced increases in erosion in Mediterranean watersheds[J].CATENA,2016,143:244-255. |
| 35 | 张华,季媛,苗苗.科尔沁沙地土地利用与耕作方式对土壤风蚀的影响[J].干旱区地理,2006,29(6):861-866. |
| 36 | Zhao Y Y, Wu J G, He C Y,et al.Linking wind erosion to ecosystem services in drylands:a landscape ecological approach[J].Landscape Ecology,2017,32(12):2399-2417. |
| 37 | 秦丽娟.河北坝上地区植树造林防风固沙效果研究[D].石家庄:河北师范大学,2020. |
| 38 | 谭勇,王长如,梁宗锁,等.黄土高原半干旱区林草植被建设措施[J].草业学报,2006,15(4):4-11. |
| 39 | 杨钦,郭中领,王仁德,等.河北坝上不同土地利用方式对土壤风蚀的影响[J].干旱区资源与环境,2017,31(2):185-190. |
| 40 | Cao S X, Zhang J Z, Chen L,et al.Ecosystem water imbalances created during ecological restoration by afforestation in China,and lessons for other developing countries[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2016,183:843-849. |
| 41 | 韩永伟,拓学森,高吉喜,等.黑河下游重要生态功能区防风固沙功能辐射效益[J].生态学报,2010,30(19):5185-5193. |
| 42 | 宋超,余琦殷,王瑞霞,等.基于植被覆盖度的宁夏灵武白芨滩自然保护区防风固沙功能时空变化研究[J].生态学报,2021,41(8):3131-3143. |
| 43 | Zhang M M, Wu X Q.The rebound effects of recent vegetation restoration projects in Mu Us Sandy Land of China[J].Ecological Indicators,2020,113:106228. |
| 44 | Zhao C N, Zhang H B, Wang M,et al.Impacts of climate change on wind erosion in Southern Africa between 1991 and 2015[J].Land Degradation & Development,2021,32(6):2169-2182. |
| 45 | 卢珊,胡泽勇,付春伟,等.黄土高原夏季极端降水及其成因分析[J].高原气象,2022,41(1):241-254. |
| 46 | 马芹,张晓萍,万龙,等.1957-2009年黄土高原地区风速变化趋势[J].自然资源学报,2012,27(12):2123-2134. |
| [1] | 刘珺, 郭中领, 常春平, 王仁德, 李继峰, 李庆, 王旭洋. 基于RWEQ和WEPS模型的中国北方农牧交错带潜在风蚀模拟[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 27-37. |
| [2] | 王旭洋, 郭中领, 常春平, 王仁德, 李继峰, 李庆, 秦丽娟. 中国北方农牧交错带土壤风蚀时空分布[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(1): 12-22. |
| [3] | 文海燕, 吴淑娟, 傅华. 氮添加对黄土高原草原生态系统净碳交换的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(3): 34-40. |
| [4] | 韩致文, 郭彩贇, 钟帅, 李爱敏. 库布齐沙漠HDPE网和植物纤维网沙障防沙试验效应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(4): 681-689. |
| [5] | 王斌, 曾琳, 赵万苍, 张文防, 段克勤. 对黄土高原风尘搬运动力与沉积控制因素的新认识[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(2): 237-246. |
| [6] | 张剑挥, 方峨天, 杨自辉, 王强强, 郭树江, 王多泽, 詹科杰, 李易珺. 沙石质建筑垃圾不同覆盖方式防风固沙效益[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(5): 1247-1251. |
| [7] | 王鹏涛, 延军平, 蒋冲, 曹永旺. 2000-2012年陕甘宁黄土高原区地表蒸散时空分布及影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(2): 499-507. |
| [8] | 张婧, 张仁陟, 左小安. 保护性耕作对黄土高原农田土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(1): 137-143. |
| [9] | 潘留杰, 张宏芳, 周毓荃, 宁志谦, 张科翔, 王从军. 1979-2012年夏季黄土高原空中云水资源时空分布[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(2): 456-463. |
| [10] | 何玉惠, 刘新平, 谢忠奎. 氮素添加对黄土高原荒漠草原草本植物物种多样性和生产力的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(1): 66-71. |
| [11] | 李小英, 段争虎. 基于SMOS的黄土高原区域尺度表层土壤水分时空变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(1): 133-139. |
| [12] | 李德帅, 王金艳, 王式功, 李振朝, 尚可政, 闭建荣. 陇中黄土高原土壤水分变化特征及其机理分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(1): 140-147. |
| [13] | 李小英, 段争虎, 谭明亮, 陈小红. 黄土高原西部人工灌木生长季土壤水分变异特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(6): 1759-1765. |
| [14] | 孙智辉1,2, 王治亮1,2, 曹雪梅1,2, 杨 琼1,2, 刘志超1,2, 雷延鹏1,2. 基于标准化降水指数的陕西黄土高原地区1971—2010年干旱变化特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(5): 1560-1567. |
| [15] | 王 胜1, 张 强1, 王 兴2, 李宏宇1, 张之贤1. 黄土高原不同气候区裸地水、热特征对比[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(4): 1166-1173. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
