The Datong Basin developed thick fluvio-lacustrine sediments in Quaternary period and aeolian loess overlied, which recorded an abundant information on past climatic and environmental changes. To analyze the climate changes, we mainly use the primary oxides as climate proxies to establish the age framework according to stratigraphic dating data, combining formation susceptibility and particle size. The results showed that:(1)The average content of chemical elements of the sediments in the constant formation was SiO2 > Al2O3 > CaO > Na2O > TOFE > K2O > MgO from high to low,the sedimentary facies of different elements are obviously different, reflecting elements vary with climate change. (2) The Datong Basin climate change experienced the following 5 stages:The research area climate was warm-humid during the Middle Pleistocene of 220-199 ka BP, and cold-dry climate occurrenced during the Middle Pleistocene of 199-138 ka BP, and warm-humid climate occurrenced during the last interglacial period of 138-71 ka BP, and cold-dry climate was showed during the last glacial stage of 71-11 ka BP, and the Holocene periodclimate was alternate variationsof warm-wet and cold-dry. However, during each period there is still less-grade climate fluctuation level. (3) These climatic changes is similar with Salawusu River and Inner Mongolia Daihai region roughly in the same latitude, and are well accordant with the global climatic change reflected by the deep-sea oxygen isotope and the polar ice core, showing a consistency in time of climatic change between the study area and the global. The climate change in this area is regional response of global climate change influenced by the East Asian winter and summer monsoon.
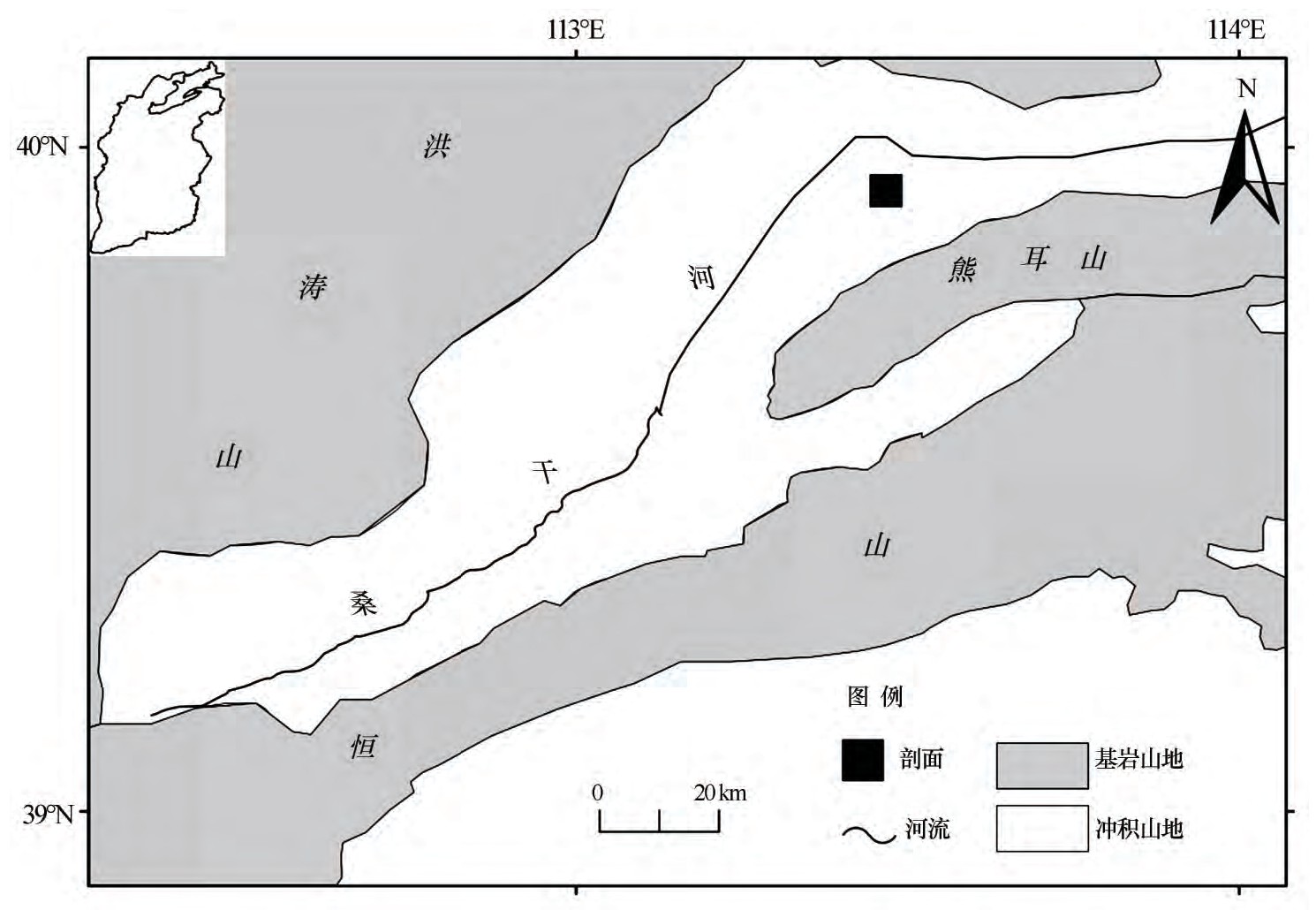
[1] 卫奇,张畅耕,解廷琦.大同湖——雁北历史上的一个湖泊[C]//泥河湾研究论文选编.北京:文物出版社,1989:537-541.
[2] 王乃樑,杨景春,夏正楷,等.山西地堑系新生代沉积与构造地貌[M].北京:科学出版社,1996:1-7.
[3] 杨小强,李华梅,李海涛.华北泥河湾盆地黄土沉积及其古地理意义[J].古地理学报,2003,5(2):209-216.
[4] 迟振卿,闵隆瑞,王志明,等.河北省阳原盆地井儿洼钻孔磁化率、粒度反映的环境意义[J].地质力学学报,2002,8(1):87-96.
[5] 迟振卿,闵隆瑞,武志军.河北阳原盆地井儿洼钻孔岩心氧化铁变化的古环境记录[J].地质通报,2002,21(10):632-637.
[6] 闵隆瑞,迟振卿.河北阳原盆地西部第四纪地质[M].北京:地质出版社,2003:94-100.
[7] 吉云平,杨振京,赵华,等.河北阳原盆地井儿洼剖面常量元素地球化学特征揭示的中更新世晚期以来气候变化[J].古地理学报,2016,18(3):487-496.
[8] 李润兰,朱峰,许清海.大同-阳原盆地的形成与演变[J].古地理学报,2000,2(2):92-96.
[9] 苏志珠,杨宗园,李晋昌.距今220 ka以来大同盆地沉积物磁化率反映的气候变化[J].冰川冻土,2015,37(2):401-407.
[10] 靳鹤龄,李明启,苏志珠,等.220 ka BP来萨拉乌苏河流域地质剖面地球化学特征及其对全球气候变化的响应[J].冰川冻土,2005,27(6):861-868.
[11] 陈渭南,高尚玉,孙忠.毛乌素沙地全新世地层化学元素特点及其古气候意义[J].中国沙漠,1994,14(1):22-30.
[12] 高尚玉,董光荣,李保生,等.萨拉乌苏河第四纪地层中化学元素的迁移和聚集与古气候的关系[J].地球化学,1985(3):269-276.
[13] 靳鹤龄,苏志珠,孙良英,等.气候与环境变化[C]//董光荣,李保生.萨拉乌苏晚第四纪地质与古人类综合研究[M].北京:科学出版社,2017:293-296.
[14] 夏正楷.大同-阳原盆地古泥河湾湖的岸线变化[J].地理研究,1992,11(2):52-59.
[15] 范淑贤,童国榜,郑宏瑞.山西大同地区0.8 Ma以来植物群及古气候变化[J].地质力学学报,1998,4(4):64-68.
[16] Imbrie J,Hays J D,Matinson D G,et al.The Orbital of Pleistocene Climate:Support from a Revised Chronology of the Marine δ18O record[M].New York,USA:Reidel Publication Company,1984:269-305.
[17] Petit J R,Jouzel J,Raynaud D,et al.Climate and atmospheric history of the past 420000 years from the Vostok ice core,Antarctica[J].Nature,1999,39(9):429-436.
[18] 靳鹤龄,李明启,苏志珠,等.萨拉乌苏河流域地层沉积时代及其反映的气候变化[J].地质学报,2007,81(3):307-315.
[19] 郑洪汉,黄宝林,乔玉楼,等.中国北方晚更新世环境[M].重庆:重庆出版社,1991:1-137.
[20] Dansgaard W,Johnsen S J,Clausen H B,et al.Evidence for general instability of past climate from a 250-kyr ice-corerecord[J].Nature,1993,36(4):218-220.
[21] 杨景春,孙建中,李树德,等.大同盆地古冰楔(砂楔)和晚更新世自然环境[J].地理科学,1988,8(4):339-344.
[22] 崔之久,赵亮,Vandenberghe J,等.山西大同、内蒙古鄂尔多斯冰楔、砂楔群的发现及其环境意义[J].冰川冻土,2002,24(6):708-716.
[23] 赵晓红.桑干河河流阶地特征及其年代学初步研究[D].北京:首都师范大学:54-80.
[24] 王苏民,吴瑞金,蒋新禾.内蒙古岱海末次冰期以来的环境变迁与古气候[J].第四纪研究,1990,21(3):223-232.
[25] 贾兰坡,盖培,尤玉柱.山西峙峪旧石器时代遗址发掘报告[J].考古学报,1972(1):39-58.
[26] 范淑贤,刘海坤,周建柱,等.大同盆地全新世以来孢粉特征与环境演变[J].地球学报,2007,28(6):535-540.
[27] 陈一萌,陈发虎,陈兴盛,等.中国干旱、半干旱区末次冰期以来气候变化规律[J].干旱区地理,2004,27(2):161-165.
[28] 苏志珠,董光荣,李小强,等.晚冰期以来毛乌素沙漠环境特征的湖沼相沉积记录[J].中国沙漠,1999,19(2):104-109.
[29] 李保生,吴正,Zhang D D,等.中国季风沙区晚更新世以来环境及其变化[J].地质学报,2001,75(1):127-137.
[30] 牛东风,李保生,王丰年,等.微量元素记录的毛乌素沙漠全新世气候波动[J].沉积学报,2015,33(4):735-743.
[31] 王苏民,冯敏.内蒙古岱海湖泊环境变化与东南季风强弱的关系[J].中国科学B辑,1991,21(7):759-768.



