
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 12-25.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2025.00013
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xinru Deng1( ), Qiang Bie1,2,3(
), Qiang Bie1,2,3( ), Chunlin Huang4, Ying Shi1, Xinzhang Li1
), Chunlin Huang4, Ying Shi1, Xinzhang Li1
Received:2024-12-24
Revised:2025-02-25
Online:2025-11-20
Published:2025-11-26
Contact:
Qiang Bie
CLC Number:
Xinru Deng, Qiang Bie, Chunlin Huang, Ying Shi, Xinzhang Li. Cold island effect of typical oasis landscape pattern in arid region[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(6): 12-25.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2025.00013
| 指数 | 分类标准 | 分类方法 |
|---|---|---|
| OCIE | 无绿洲冷岛效应 | LSTo≥LSTd |
| 弱绿洲冷岛效应 | LSTd-2.5 ℃≤LSTo<LSTd | |
| 中绿洲冷岛效应 | LSTd-5 ℃≤LSTo<LSTd-2.5 ℃ | |
| 强绿洲冷岛效应 | LSTo<LSTd-5 ℃ |
Table 1 Classification standard and classification method of OCIE
| 指数 | 分类标准 | 分类方法 |
|---|---|---|
| OCIE | 无绿洲冷岛效应 | LSTo≥LSTd |
| 弱绿洲冷岛效应 | LSTd-2.5 ℃≤LSTo<LSTd | |
| 中绿洲冷岛效应 | LSTd-5 ℃≤LSTo<LSTd-2.5 ℃ | |
| 强绿洲冷岛效应 | LSTo<LSTd-5 ℃ |
| 指数名称 | 缩写 | 生态学含义 |
|---|---|---|
| 斑块面积百分比 | PLAND | 某一类型斑块占景观总面积百分比,反映景观类型的相对重要性和覆盖程度 |
| 最大斑块指数 | LPI | 衡量景观中最大斑块的相对重要性和占主导地位的程度 |
| 斑块密度 | PD | 单位面积内景观斑块的数量,反映景观的破碎程度 |
| 边缘密度 | ED | 斑块的周长总和与景观总面积的比值,反映斑块形状及边缘效应 |
| 平均斑块面积 | AREA_MN | 反映景观中斑块的平均大小,影响生态过程的规模和强度 |
| 平均形状指标 | SHAPE_MN | 描述斑块的平均形状复杂度,形状越复杂,形状指数越高 |
| 斑块内聚力指数 | COHESION | 描述斑块的空间结构,值越高,斑块内部越连贯 |
Table 2 Landscape pattern index and its ecological implications
| 指数名称 | 缩写 | 生态学含义 |
|---|---|---|
| 斑块面积百分比 | PLAND | 某一类型斑块占景观总面积百分比,反映景观类型的相对重要性和覆盖程度 |
| 最大斑块指数 | LPI | 衡量景观中最大斑块的相对重要性和占主导地位的程度 |
| 斑块密度 | PD | 单位面积内景观斑块的数量,反映景观的破碎程度 |
| 边缘密度 | ED | 斑块的周长总和与景观总面积的比值,反映斑块形状及边缘效应 |
| 平均斑块面积 | AREA_MN | 反映景观中斑块的平均大小,影响生态过程的规模和强度 |
| 平均形状指标 | SHAPE_MN | 描述斑块的平均形状复杂度,形状越复杂,形状指数越高 |
| 斑块内聚力指数 | COHESION | 描述斑块的空间结构,值越高,斑块内部越连贯 |
| 绿洲 | 参数 | PLAND | LPI | PD | ED | AREA_MN | SHAPE_MN | COHESION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阿克苏 | Moran's I | -0.340** | -0.028** | 0.101** | 0.094** | 0.055** | -0.139** | -0.032** |
| 相关系数 | -0.054* | -0.047* | 0.127** | 0.125** | 0.060** | -0.184** | -0.049* | |
| 和田 | Moran's I | 0.268** | 0.248** | -0.194** | -0.385** | 0.343** | -0.301** | 0.048** |
| 相关系数 | 0.362** | 0.344** | -0.241** | -0.468** | 0.412** | -0.372** | 0.239** | |
| 武威 | Moran's I | 0.332** | 0.324** | -0.180** | -0.410** | 0.397** | -0.339** | 0.225** |
| 相关系数 | 0.375** | 0.364** | -0.159** | -0.461** | 0.439** | -0.415** | 0.236** | |
| 张掖 | Molan's I | 0.195** | 0.207** | -0.048** | -0.175** | 0.255** | -0.299** | 0.144** |
| 相关系数 | 0.202** | 0.216** | -0.004** | -0.176** | 0.278** | -0.389** | 0.142** |
Table 3 Correlation analysis and bivariate spatial autocorrelation between landscape index and OCIE
| 绿洲 | 参数 | PLAND | LPI | PD | ED | AREA_MN | SHAPE_MN | COHESION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阿克苏 | Moran's I | -0.340** | -0.028** | 0.101** | 0.094** | 0.055** | -0.139** | -0.032** |
| 相关系数 | -0.054* | -0.047* | 0.127** | 0.125** | 0.060** | -0.184** | -0.049* | |
| 和田 | Moran's I | 0.268** | 0.248** | -0.194** | -0.385** | 0.343** | -0.301** | 0.048** |
| 相关系数 | 0.362** | 0.344** | -0.241** | -0.468** | 0.412** | -0.372** | 0.239** | |
| 武威 | Moran's I | 0.332** | 0.324** | -0.180** | -0.410** | 0.397** | -0.339** | 0.225** |
| 相关系数 | 0.375** | 0.364** | -0.159** | -0.461** | 0.439** | -0.415** | 0.236** | |
| 张掖 | Molan's I | 0.195** | 0.207** | -0.048** | -0.175** | 0.255** | -0.299** | 0.144** |
| 相关系数 | 0.202** | 0.216** | -0.004** | -0.176** | 0.278** | -0.389** | 0.142** |
| 绿洲 | PLAND | LPI | PD | ED | AREA_MN | SHAPE_MN | COHESION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阿克苏 | 显著 | 显著 | 不显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 不显著 |
| 和田 | 显著 | 不显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 不显著 | 显著 | 显著 |
| 武威 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 不显著 |
| 张掖 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 |
Table 4 Comparison of the significance of landscape indices of each oasis
| 绿洲 | PLAND | LPI | PD | ED | AREA_MN | SHAPE_MN | COHESION |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阿克苏 | 显著 | 显著 | 不显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 不显著 |
| 和田 | 显著 | 不显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 不显著 | 显著 | 显著 |
| 武威 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 不显著 |
| 张掖 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 | 显著 |
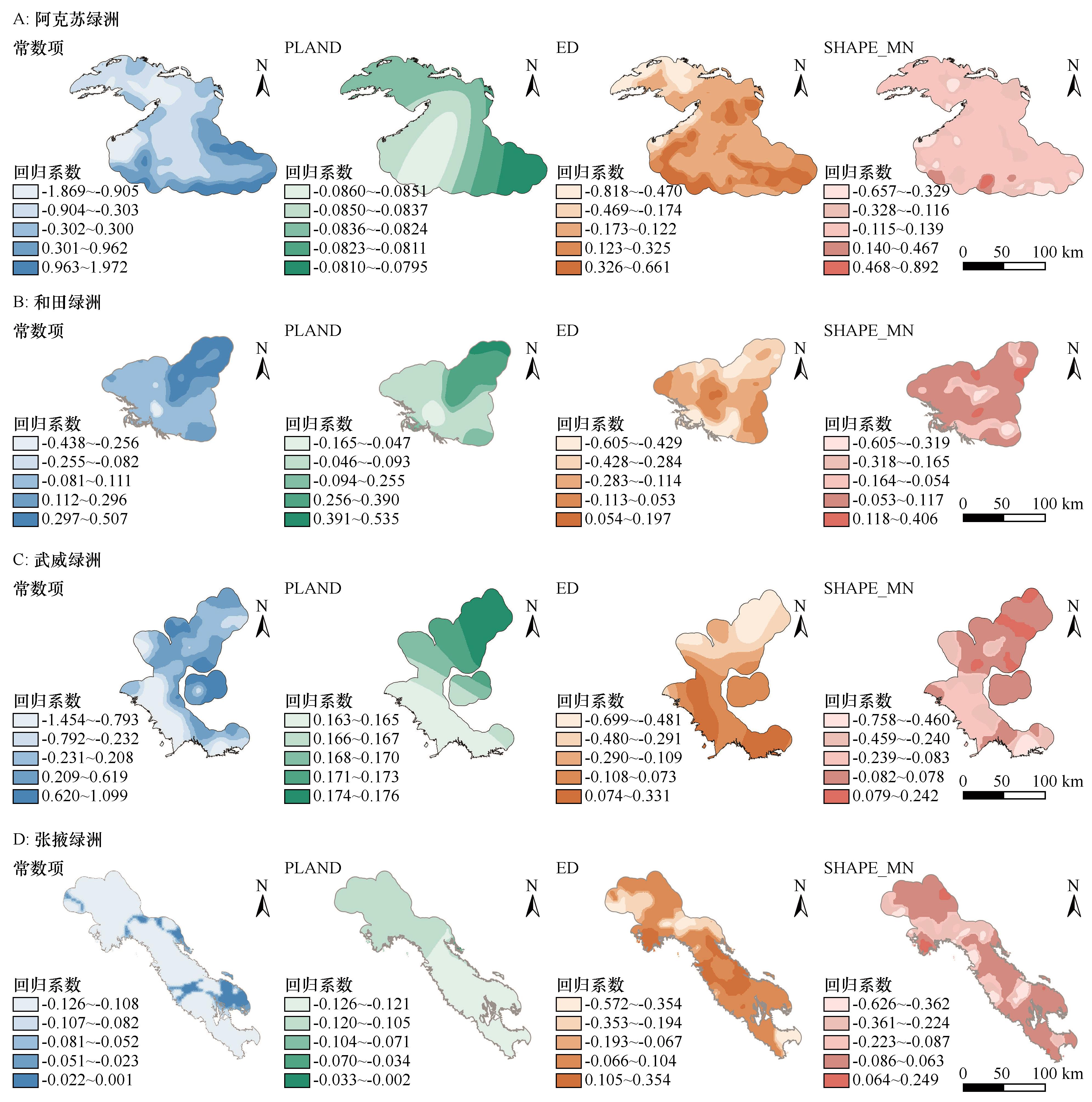
Fig.10 Distribution of regression coefficients between (OCIE) and patch area percentage (PLAND), edge density (ED) and average shape indexes (SHAPE_MN)
| [1] | Ahriz A, Fezzai S, Mady A A M.Predicting the limits of the oasis effect as a cooling phenomenon in hot deserts[J].Desert,2019,24(2):255-266. |
| [2] | 焦岩,闫峰,卢琦,等.西北干旱区绿洲时空变化及驱动力[J].应用生态学报,2024,35(8):2206-2216. |
| [3] | 苏从先,胡隐樵,张永丰,等.河西地区绿洲的小气候特征和“冷岛效应”[J].大气科学,1987,11(4):390-396. |
| [4] | Hao X, Li W.Oasis cold island effect and its influence on air temperature: a case study of Tarim Basin,Northwest China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2016,8(2):172-183. |
| [5] | 毋兆鹏,牛苏娟,毛敏,等.精河流域绿洲“冷岛效应”时空格局遥感研究[J].国土资源遥感,2020,32(3):106-113. |
| [6] | Hao X, Hao H, Zhang J.Soil moisture influenced the variability of air temperature and oasis effect in a large inland basin of an arid region[J].Hydrological Processes,2021,35(6):e14246. |
| [7] | 潘竟虎,张伟强.张掖绿洲冷岛效应时空格局的遥感分析[J].干旱区研究,2010,27(4):481-486. |
| [8] | 李润林,时永杰,姚艳敏,等.基于LandsatTM/ETM+的张掖市甘州区绿洲冷岛效应时空变化研究[J].干旱区资源与环境,2014,28(9):139-144. |
| [9] | Ruehr S, Lee X, Smith R,et al.A mechanistic investigation of the oasis effect in the Zhangye cropland in semiarid western China[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2020,176:104120. |
| [10] | 卢调雪,杨林山,冯起,等.近20年张掖盆地绿洲结构和规模变化及其影响因素[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(6):131-141. |
| [11] | 杨丽萍,潘雪萍,刘晶,等.基于Landsat影像的额济纳绿洲地表温度及冷岛效应时空格局研究[J].干旱区资源与环境,2019,33(2):116-121. |
| [12] | 高原,刘普幸,姚玉龙,等.基于遥感的石河子绿洲冷岛效应时空变化特征及其影响因子分析[J].自然资源学报,2015,30(8):1319-1331. |
| [13] | 侯文兵,李开明,黄卓.近20 a河西地区绿洲效应时空变化特征及归因分析[J].干旱区研究,2023,40(12):2031-2042. |
| [14] | Hao X, Li W, Deng H.The oasis effect and summer temperature rise in arid regions-case study in Tarim Basin[J].Scientific Reports,2016,6(1):35418. |
| [15] | 马勇刚,贡璐,丁建丽.塔里木南缘绿洲“冷岛”效应时空变化研究:以于田地区为例[J].中国沙漠,2007,27(5):866-869. |
| [16] | 孙帆,王弋,陈亚宁.塔里木盆地荒漠-绿洲过渡带动态变化及其影响因素[J].生态学杂志,2020,39(10):3397-3407. |
| [17] | 陈亚宁,李忠勤,徐建华,等.中国西北干旱区水资源与生态环境变化及保护建议[J].中国科学院院刊,2023,38(3):385-393. |
| [18] | Zhang M, Luo G, Hamdi R,et al.Numerical simulations of the impacts of mountain on oasis effects in Arid Central Asia[J].Atmosphere,2017,8(11):212. |
| [19] | 国家气象信息中心.中国国家级地面气象站基本气象要素日值数据集(V3.0)(1951-2010)[Z].时空三极环境大数据平台,2019. |
| [20] | Yang J, Huang X.The 30 m annual land cover and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019[J].Earth System Science Data,2021,13(8):3907-3925. |
| [21] | 石莹,别强,苏晓杰,等.中国西北地区地表覆被变化对太阳辐射吸收的影响[J].自然资源遥感,2024,36(4):260-271. |
| [22] | 李春强,高永刚,徐涵秋.Landsat新型热红外地表温度产品与MODIS地表温度产品的交互对比[J].光谱学与光谱分析,2023,43(3):940-948. |
| [23] | Bie Q, Xie Y, Wang X,et al.Understanding the attributes of the dual oasis effect in an arid region using remote sensing and observational data[J].Ecosystem Health and Sustainability,2020,6(1):1696153. |
| [24] | Schwarz N, Lautenbach S, Seppelt R.Exploring indicators for quantifying surface urban heat islands of european cities with MODIS land surface temperatures[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2011,115(12):3175-3186. |
| [25] | 阿里木江·卡斯木,张雪玲,梁洪武.天山北坡城市群季节性地表温度与景观格局空间关系分析[J].地理研究,2024,43(5):1267-1287. |
| [26] | 王振国,杨国福,聂文彬,等.乡村地表温度对富春江流域景观格局演变的多尺度响应[J].生态学杂志,2025,44(2):575-589. |
| [27] | 韩晓佳,刘小鹏,王亚娟,等.基于景观格局的干旱区绿洲生态风险评价与管理:以青铜峡市为例[J].水土保持研究,2017,24(5):285-290. |
| [28] | 徐炳先,彭雨欣,李兰海,等.基于景观格局的玛纳斯河流域生境质量及生态风险研究[J].水土保持研究,2025,32(1):328-335. |
| [29] | Wu W, Chen R.Finding oasis cold island footprints based on a logistic model:a case study in the Ejina Oasis[J].Remote Sensing,2024,16(16):2895. |
| [30] | 王一航,夏沛,刘志锋,等.中国绿洲城市土地利用/覆盖变化研究进展[J].干旱区地理,2019,42(2):341-353. |
| [31] | Zhang F, Tiyip T, Kung H,et al.Dynamics of land surface temperature (LST) in response to land use and land cover (LULC) changes in the Weigan and Kuqa river oasis,Xinjiang,China[J].Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2016,9:499. |
| [32] | Cao B, Zhang Y, Zhao Y,et al.Influence of the low-level jet on the intensity of the nocturnal oasis cold island effect over Northwest China[J].Theoretical and Applied Climatology,2020,139:689-699. |
| [33] | Zhao H, Fang Y, Xu X.Quantifying morphology evolutions of urban heat islands and assessing their heat exposure in a metropolis[J].Sustainable Cities and Society,2024,102:105244. |
| [34] | 沈中健,曾坚,梁晨.闽南三市绿地景观格局与地表温度的空间关系[J].生态学杂志,2020,39(4):1309-1317. |
| [1] | Zhiwei Jiang, Zhibo Yang, Qing Yang, Jie Hu, Qianya Liu, Lingling Yu, Honghong Zhang, Zhaojing Dan, Lei Tian. Temporal and spatial variation of vegetation cover in Kubuqi Desert from 2000 to 2022 and its driving factors [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(5): 124-133. |
| [2] | Caixia Li, Xue Wu, Yang Hu. Land use and landscape pattern changes in Qingyang, Gansu, China: a typical Loess Plateau gully region [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(5): 172-180. |
| [3] | Xueping Chen, Xueyong Zhao, Haiyan Zhuang, Yulai Qiao, Hongmei Yu, Jing Zhang. Characteristics of groundwater depth in Naiman, Inner Mongolia in 1985-2020 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(4): 166-175. |
| [4] | Haifu Fang, Yulin Li, Yanqing Li, Yuyin Mo, Jin Zhan, Zhijia Luo. Changes in landscape patterns and their driving factors of the typical dune alternated with meadow area in the Horqin Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(4): 285-294. |
| [5] | Mingyu Cai, Biao Jia, Xueli Chang. Impact of interaction of landscape pattern factors on desertification status in Kerqin Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(2): 99-108. |
| [6] | Ziyan Han, Jijun Meng, Yi Zou, Likai Zhu. Vegetation dynamics and their response to climate change and ecological protection projects in the Heihe River Basin from 1982 to 2017 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 96-106. |
| [7] | Changsheng Li, Zhishan Zhang, Jinlin Zhang, Xiufeng Zhang, Bingxin Xu, Yafei Shi, Jianqiang Huo. Transition characteristics of soil properties in desert-oasis [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 209-218. |
| [8] | Lizhu Xing, Fangmin Zhang, Kaicheng Xing, Yunpeng Li, Qi Lu, Feifei Lu. Change of soil wind erosion and attribution in Bayannur, Inner Mongolia based on the Revised Wind Erosion Equation [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(5): 111-119. |
| [9] | Chang Xi, Lu Huayu, Lü Nana, Cui Mengchun, Li Haiyu. Variation of desert and sandy field in China on the basis of remote sensing analysis and the relationship with climate change during 1992-2015 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(1): 57-63. |
| [10] | Bai Xuelian, Wang Lixiang, Ji Shuxin, Chen Zhengxin, Chang Xueli. Assessment of ecosystem health in grassland-desert ecotone in northern Ordos: a case study of Ten Tributaries Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(1): 187-194. |
| [11] | Wang Yu, Li Xiaomei, Feng Qi, Liu Yuqing. Landscape Pattern and Variation of Riverine Sand Dunes in the Kunye River Basin, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(1): 52-61. |
| [12] | Zhang Fuping, Li Xiaojuan, Feng Qi, Wang Huwei, Wei Yongfen, Bai Hao. Spatial and Temporal Variation of Water Conservation in the Upper Reaches of Heihe River Basin Based on InVEST Model [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(6): 1321-1329. |
| [13] | Song Jie, Chun Xi. The Spatial Variation and Grain Size Character of Different Land Cover Types in the Ulanbuh Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2018, 38(2): 243-251. |
| [14] | Niu Ruixue, Liu Jiliang, Hu Yanping, Fu Ying. Soil Respiration Characters and Its Response to Hydrothermic Factors over Different Land Cover Types in the Middle Reaches of the Heihe River Basin [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2017, 37(5): 961-969. |
| [15] | Yu Qiang, Yue Depeng, Zhang Qibin, Lv Qi, Li Ning, Hou Hongbing. The Evolution of Landscape Pattern and the Construction of Ecological Infrastructure Network in Dengkou, Inner Mongolia, China [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2017, 37(3): 601-609. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech