


Macrobenthos community structure and water quality evaluation in Gansu section of Yellow River Basin
Received date: 2022-10-01
Revised date: 2023-03-14
Online published: 2023-08-14
To explore the impact of human activities on the aquatic ecosystem in the upper reaches of the Yellow River, the species composition, inhabit density, biomass, dominant species and the aquatic physiochemical parameters were investigated in August 2021 of the Gansu section of the Yellow River. A total of 32 macrozoobenthos species including 25 species of arthropods (78.13%), 5 species of mollusks (15.63%) and 2 species of annelids (6.25%) were identified. The dominant species were Sigara substriata, Ampumixis sp., Palaemon modestus, Gammarus sp., Radix Auricularia and Radix ovata in the whole study area. An obvious spatial heterogeneity in existing stock, with the values the density and biomass to be 271 ind.·m2 and 18.0105 g·m2 in the downstream section, and 95 ind.·m2 and 4.1275 g·m2 in the upstream section, respectively. The Shannon-Wiener diversity index and Margalef richness index were showed the downstream section greater than the upstream section, but the Pielou evenness index have little change along the way. The water quality was observed better in the upstream section sites than in the downstream section sites based on the evaluation results of integrated biological index and comprehensive pollution index, and the best water quality site is Y6. The water quality of Gansu section of the Yellow River generally reaches the limit of Class II surface water, the water quality of rivers is significantly improved after being purified by reservoirs and wetlands. According to the correlation matrix analysis between macrozoobenthos and environmental factors and RDA analysis, altitude and potassium permanganate are the key environmental factors affecting the benthos community structure in Gansu section of the Yellow River. Comprehensive macrozoobenthos community structure and water quality analysis, it shows that the water environment in the reservoir area and wetland is the best water. The water quality in the upstream natural reach is better than that in the downstream natural reach, but the biodiversity and abundance in the downstream reach are higher than that in the upstream reach.
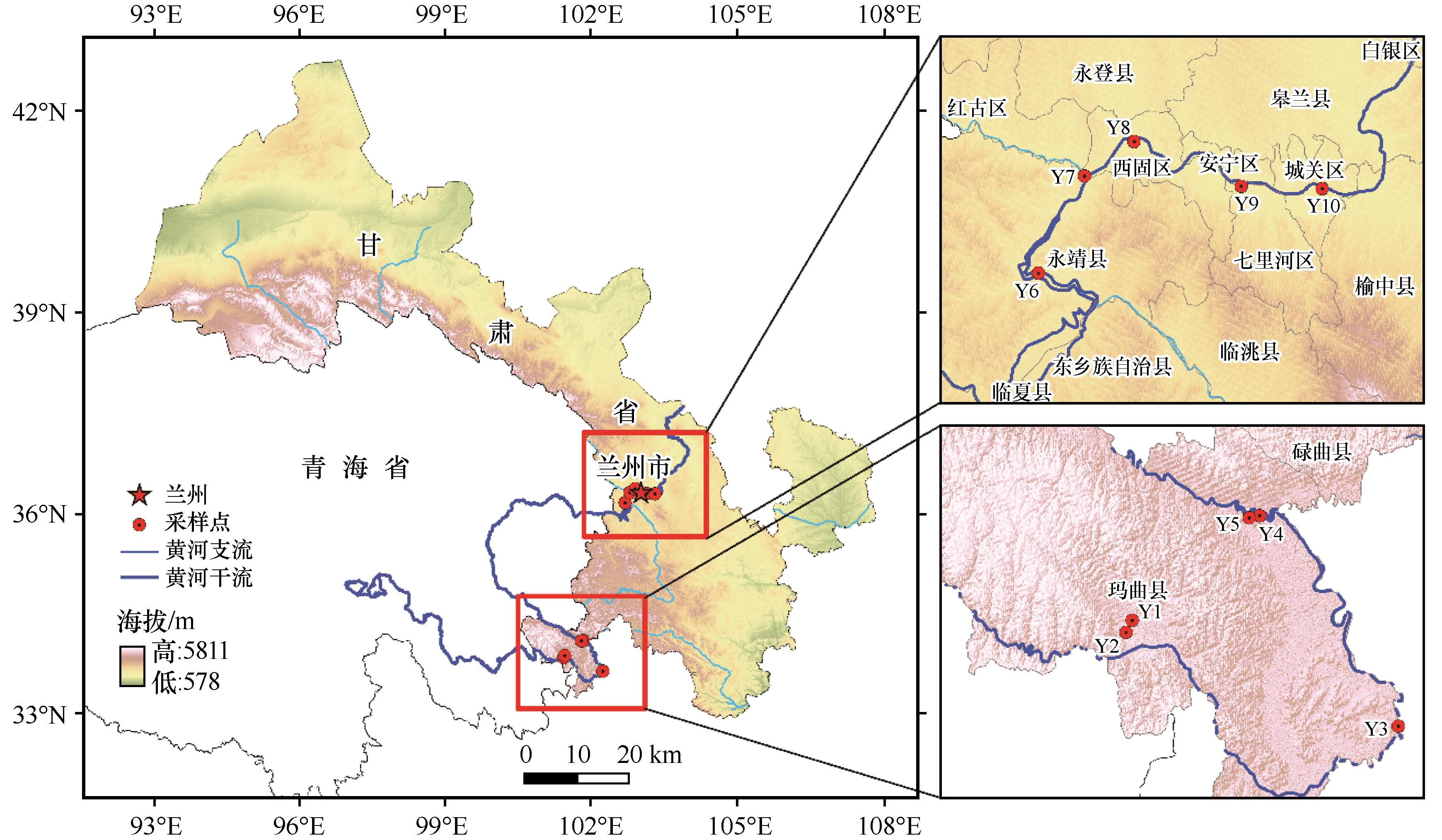
Yu Wang , Xu Wang , Qi Feng , Wei Liu , Yuhua He , Jiale Zhu , Yupeng Wang . Macrobenthos community structure and water quality evaluation in Gansu section of Yellow River Basin[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023 , 43(4) : 146 -156 . DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00024
| 1 | 黄建平,张国龙,于海鹏,等.黄河流域近40年气候变化的时空特征[J].水利学报,2020,51(9):1048-1058. |
| 2 | 周广胜,周莉,汲玉河,等.黄河水生态承载力的流域整体性和时空连通性[J].科学通报,2021,66(22):2785-2792. |
| 3 | 殷万东,吴明可,田宝良,等.生物入侵对黄河流域生态系统的影响及对策[J].生物多样性,2020,28(12):1533-1545. |
| 4 | 左倬,陈煜权,成必新,等.不同植物配置下人工湿地大型底栖动物群落特征及其与环境因子的关系[J].生态学报,2016,36(4):953-960. |
| 5 | 王昱,刘娟娟,冯起,等.黑河流域底栖动物群落结构及水质评价[J].中国环境科学,2020,40(3):1305-1319. |
| 6 | 丁一桐,潘保柱.黄河流域水生生物资源评估及问题诊断[J].中国环境监测,2022,38(1):1-13. |
| 7 | 马宝珊,徐滨,魏开金,等.安宁河中游底栖动物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J].水生生物学报,2019,43(3):643-653. |
| 8 | 张敏,蔡庆华,渠晓东,等.三峡成库后香溪河库湾底栖动物群落演变及库湾纵向分区格局动态[J].生态学报,2017,37(13):4483-4494. |
| 9 | 胡小红,左德鹏,刘波,等.北京市北运河水系底栖动物群落与水环境驱动因子的关系及水生态健康评价[J].环境科学,2022,43(1):247-255. |
| 10 | 李雪迎,杨曦,乔琦,等.黄河流域甘肃段工业行业水污染物空间排放特征[J].环境科学,2022,43(5):2459-2466. |
| 11 | 张金良.黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展水战略思考[J].人民黄河,2020,42(4):1-6. |
| 12 | 李永春.黄河上游流域梯级电站检修项目管理研究[D].兰州:兰州交通大学,2016. |
| 13 | 曲修杰.黄河玛曲段水产种质资源保护区的调查研究[D].北京:中国农业科学院,2009. |
| 14 | 谢元,蒋晓辉,王婷,等.黄河典型支流入干区底栖动物群落结构特征比较研究[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2018,54(5):1067-1076. |
| 15 | 黄旭蕾,李天宏,蒋晓辉.基于大型底栖无脊椎动物指数的黄河水质评价研究[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2015,51(3):553-561. |
| 16 | 龙诗颖,修玉娇,李瑶,等.黄河三角洲水质对底栖动物群落结构的影响[J].环境科学学报,2022,42(1):104-110. |
| 17 | 李姗泽,崔保山,谢湉,等.黄河三角洲沼泽中大型底栖动物的分布特征[J].湿地科学,2015,13(6):759-764. |
| 18 | 彭少明,尚文绣,王煜,等.黄河上游梯级水库运行的生态影响研究[J].水利学报,2018,49(10):1187-1198. |
| 19 | 杨金虎,张强,杨博成,等.黄河上游暖湿化的多时间尺度特征及对生态植被的影响[J].高原气象,2023,42(4):1018-1030. |
| 20 | 叶培龙,张强,王莺,等.1980-2018年黄河上游气候变化及其对生态植被和径流量的影响[J].大气科学学报,2020,43(6):967-979. |
| 21 | 韦军.黄河流域甘肃段土地利用功能时空变化及其权衡/协同关系研究[D].兰州:甘肃农业大学,2021. |
| 22 | 王益民.黄河兰州段水环境污染对鱼类毒性效应研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2007. |
| 23 | 张培栋,介小兵.黄河上游甘肃段草地退化的现状及机理研究[J].草业科学,2007(9):1-4. |
| 24 | 赵映东.黄河甘肃段干支流输沙情况及治理保护建议[J].中国水利,2019(23):56-58. |
| 25 | 苏贤保.黄河上游径流复杂性多尺度特征及其驱动机制研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2019. |
| 26 | 国家环境保护总局.水和废水监测分析方法[M].北京:中国环境科学出版社,2002. |
| 27 | 王备新,杨莲芳.我国东部底栖无脊椎动物主要分类单元耐污值[J].生态学报,2004,24(12):2768-2775. |
| 28 | 王昱,刘娟娟,冯起,等.黑河底栖动物群落结构及生物多样性[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(1):125-135. |
| 29 | 环境保护部.生物多样性观测技术导则淡水底栖大型无脊椎动物:HJ710.8-2014[P].2014. |
| 30 | 王备新.大型底栖无脊椎动物水质生物评价研究[D].南京:南京农业大学,2003. |
| 31 | 王欢欢,白洁,刘世存,等.白洋淀近30年水质时空变化特征[J].农业环境科学学报,2020,39(5):1051-1059. |
| 32 | 曹占琪.典农河上游段水生态系统健康诊断与评价[D].银川:宁夏大学,2022. |
| 33 | 徐梦珍,王兆印,潘保柱,等.雅鲁藏布江流域底栖动物多样性及生态评价[J].生态学报,2012,32(8):2351-2360. |
| 34 | 许栋,张博曦,及春宁,等.梯级水库对南渡江干流底栖动物丰枯水期沿程变化的影响[J].水资源保护,2019,35(2):60-66. |
| 35 | 宋玉珍,马正学,王珪.黄河兰州段大型底栖无脊椎动物调查[J].甘肃科学学报,1995(2):79-81. |
| 36 | 殷旭旺,徐宗学,高欣,等.渭河流域大型底栖动物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J].应用生态学报,2013,24(1):218-226. |
| 37 | 贾秋红,白海锋,袁永锋,等.黄河兰州市区段秋季大型底栖动物群落结构调查[J].河北渔业,2015(8):31-32. |
| 38 | 褚可成,陈锷,许淑青.2018年黄河兰州段底栖动物监测及其评价[J].甘肃科技,2019,35(11):1-3. |
| 39 | 王玥劼,张世敏,张宁,等.小浪底水库建库前后生物种群数量变化调查与分析[J].安徽农业科学,2013,41(18):7916. |
| 40 | 简东,黄道明,常秀岭,等.拉萨河中下游底栖动物群落结构特征分析[J].水生态学杂志,2015,36(1):40-46. |
| 41 | 赵伟华,刘学勤.西藏雅鲁藏布江雄村河段及其支流底栖动物初步研究[J].长江流域资源与环境,2010,19(3):281-286. |
| 42 | 李正飞,王军,谢志才,等.南腊河底栖动物多样性与环境因子的关系[J].生态学杂志,2016,35(12):3364-3373. |
| 43 | 池仕运,王瑞,魏秘,等.基于2010-2019年监测数据的金沙江上中段大型底栖无脊椎动物的群落结构特征和多样性分析[J].生态学报,2022,42(21):1-16. |
| 44 | 张莉红.黄河上游兰州水源水污染风险调查与评估[D].兰州:兰州交通大学,2016. |
| 45 | 赵梦瑶,梁恩航,陈颖,等.黄河玛曲至临河段硅藻群落组成及水质评价[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2022,58(1):169-176. |
| 46 | 魏晓燕,王浩,郜建军,等.基于聚类分析的黄河兰州段监测断面水质执行标准优化[J].兰州交通大学学报,2021,40(5):79-84. |
| 47 | 杨海强,潘保柱,朱朋辉,等.渭河干流和秦岭北麓典型支流底栖动物群落结构及水质生物评价[J].湖泊科学,2020,32(6):1793-1805. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |