


Management regionalization and zoning management tasks of battle against desertification in the core area of Hexi Corridor-Taklimakan Desert edge
Received date: 2024-02-05
Revised date: 2024-04-13
Online published: 2024-08-29
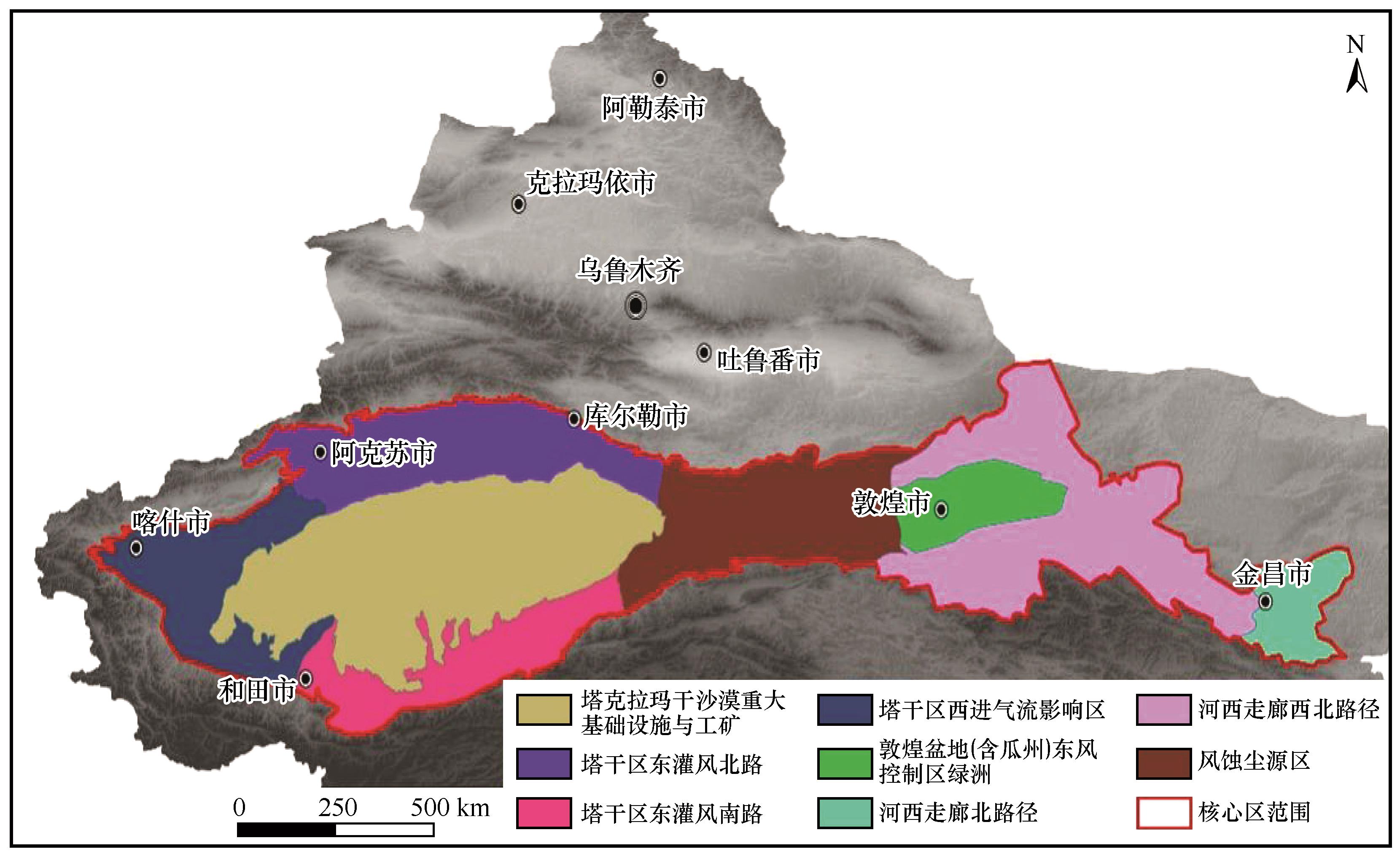
In order to implement the spirit of General Secretary Xi Jinping's speech on strengthening comprehensive prevention and control of desertification, further promote the construction of the "Three North" and other key ecological projects and win the battle against desertification in the core area of the Hexi Corridor-Taklimakan Desert edge (defined as “Battle Zone”), the study of the management regionalization and the zoning management tasks in the core area of the Battle Zone were presented in this paper. According to the characteristics of sandy land and sand activities in the region, using "sand source is no longer causing damage and dust source is effectively controlled " as the goal, this paper systematically sorted out and analyzed the sources of wind, sand and dust, the law and path of sand transmission and its influence range, the natural geographical characteristics and the spatial distribution of the source of dust, wind and sand, protection gap between oasis, encroachment of sand outside oasis. Based on the above analyses, the management regionalization and the key zoning management tasks in the region were presented, so as to provide scientific support for the battle against desertification in the core area of the Hexi Corridor-Taklimakan Desert edge.
Yiming Feng , Qi Lu , Bin Yao , Lei Xi , Xiaoming Cao , Yongping Liu , Huseng Ning . Management regionalization and zoning management tasks of battle against desertification in the core area of Hexi Corridor-Taklimakan Desert edge[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024 , 44(4) : 91 -101 . DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00050
| 1 | 雷加强,高鑫,赵永成,等.河西走廊-塔克拉玛干沙漠边缘阻击战:风沙形势与防治任务[J].中国科学院院刊,2023,38(7):966-977. |
| 2 | 罗晓玲,李岩瑛,严志明,等.近60年河西走廊地区沙尘暴发生演变特征及其气象影响因子[J].水土保持研究,2021,28(5):254-267. |
| 3 | 杨显玉,朱俊橙,文军,等.南疆大风气候特征分析及其对沙尘天气的影响[J].高原气象,2023,42(1):186-196. |
| 4 | 李志鹏,曹晓明,丁杰,等.MODIS 卫星影像显示的2001-2017 年中国荒漠化年度状况[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(6):135-140. |
| 5 | Du H Q, Wang T, Xue X,et al.Modelling of sand/dust emission in Northern China from 2001 to 2014[J].Geoderma,2018,330:162-176. |
| 6 | Song H Q, Zhang K S, Piao S L,et al.Soil organic carbon and nutrient losses resulted from spring dust emissions in Northern China[J].Atmospheric Environment,2019,213:585-596. |
| 7 | 杨德保,尚可政,王式功.影响沙尘暴的中小尺度系统[M]//沙尘暴.北京:气象出版,2003. |
| 8 | 姜学恭,陈受钧.地形影响沙尘传输的观测和模拟研究[J].气象学报,2008,66(1):1-12. |
| 9 | 王旭,马禹.新疆大风的时空统计特征[J].新疆气象,2002(1):1-3. |
| 10 | 王旭,王健,马禹.新疆大风天气过程的特点[J].新疆气象,2002(2):4-6. |
| 11 | 霍文,杨青,何清,等.新疆大风区沙尘暴气候特征分析[J].干旱区地理,2011,34(5):753-761. |
| 12 | 马禹,肖开提,王旭.塔里木盆地沙尘天气的气候特征[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2006(6):784-790. |
| 13 | 宋阳,刘连友,严平,等.中国北方5种下垫面对沙尘暴的影响研究[J].水土保持学报,2005,19(6):17-20. |
| 14 | 陈洪武,王旭,马禹.大风对新疆沙尘暴的影响[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2003,39(2):187-193. |
| 15 | 郑新江,徐建芬,罗敬宁,等.利用风云-1C气象卫星监测南疆沙尘暴研究[J].中国沙漠,2000,20(3):286-287. |
| 16 | 赵兴梁.甘肃特大沙尘暴的危害与对策[J].中国沙漠,1993,13(3):1-5. |
| 17 | 张存杰,汤绪,李耀辉.河西走廊沙尘暴特征及气候成因分析[J].干旱气象,2003,21(4):18-22. |
| 18 | 董安祥,胡文超,张宇,等.河西走廊特殊地形与大风的关系探讨[J].冰川冻土,2014,36(2):347-351. |
| 19 | 宋敏红,钱正安,蔡英.金昌特强沙尘暴爆发诱因再分析[J].高原气象,2020,39(5):1102-1109. |
| 20 | 孙钦珂,周亮,唐相龙,等.干旱区绿洲城镇扩张对耕地空间影响及预测:以河西走廊区域为例[J].自然资源学报,2021,36(4):1008-1020. |
| 21 | 赵文智,任珩,杜军,等.河西走廊绿洲生态建设和农业发展的若干思考与建议[J].中国科学院院刊,2023,38(3):424-434. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |