巴丹吉林沙漠湖泊对浅层沙含水量的影响
Interdune lakes affects the water content of shallow sand layer: a situ observation from the Badain Jaran Sand Sea, China
巴丹吉林沙漠湖泊对浅层沙含水量的影响 |
| 牛震敏, 王乃昂, 温鹏辉, 苏贤保, 于昕冉, 张文佳 |
|
Interdune lakes affects the water content of shallow sand layer: a situ observation from the Badain Jaran Sand Sea, China |
| Zhenmin Niu, Naiang Wang, Penghui Wen, Xianbao Su, Xinran Yu, Wenjia Zhang |
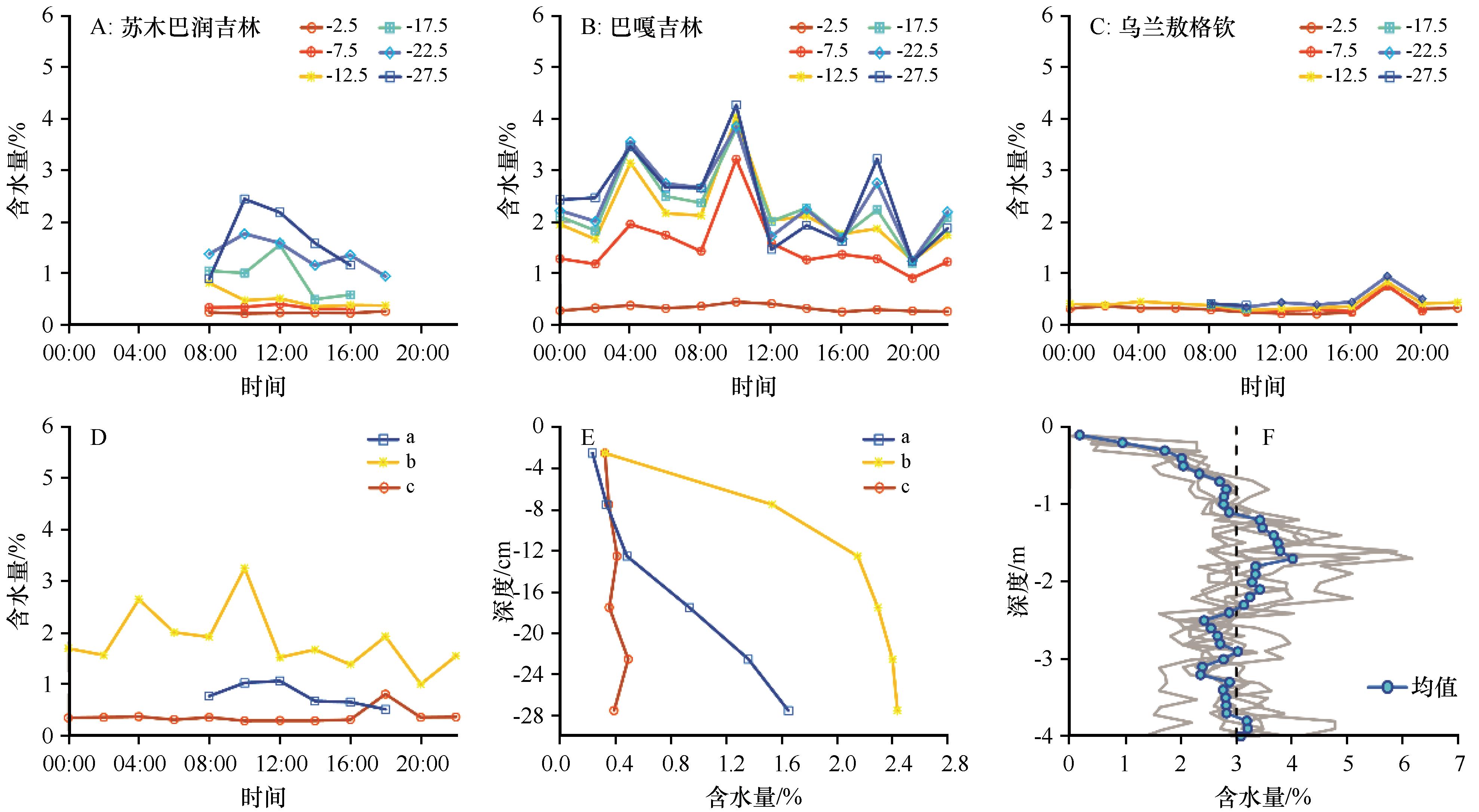
| 图5 沙层含水量随时间和深度的变化。A、B、C分别为苏木巴润吉林、巴嘎吉林和乌兰敖格钦30 cm内各层次的含水量,其中,“-2.5”代表0—5 cm深度,“-7.5”代表5—10 cm深度,以此类推;D为苏木巴润吉林、巴嘎吉林和乌兰敖格钦30 cm内平均含水量随时间的变化;E为苏木巴润吉林、巴嘎吉林和乌兰敖格钦30 cm内各层次的平均含水量随深度的变化;在D和E中,a为苏木巴润吉林,b为巴嘎吉林,c为乌兰敖格钦;F高大沙山背风坡0—4 m深度内6个剖面含水量随深度的变化及其均值(据文献[ |
| Fig.5 Variation of soil water content over time and depth. A, B and C are the soil water content at different depths within 30 cm in Sumubarunjilin, Bagajilin and Wulanaogeqin, respectively, where "-2.5" represents 0-5 cm depths, "-7.5" represents 5-10 cm depths, and so on; D is variation of the average soil water content within 30 cm over time in Sumubarunjilin, Bagajilin and Wulanaogeqin; E is variation of the average soil water content with depth of each layer within 30 cm in Sumubarunjilin, Bagajilin and Wulanaogeqin; in D and E, “a” represents Sumubarunjilin, “b” represents Bagajilin and “c” represents Wulanaogeqin; F is the variation of soil water content with depth and the average value of 6 profiles within the leeward slope of mega-dunes from 0 to 4 m (revised from literature [35]) |

|