东亚沙尘气候效应对地面温度日较差影响的数值模拟
Influence of dust aerosol on land surface diurnal temperature range over East Asia Simulated with the WRF-Chem model
东亚沙尘气候效应对地面温度日较差影响的数值模拟 |
| 陈思宇, 贯雅雯, 赵丹, 娄高僮, 陈渔 |
|
Influence of dust aerosol on land surface diurnal temperature range over East Asia Simulated with the WRF-Chem model |
| Siyu Chen, Yawen Guan, Dan Zhao, Gaotong Lou, Yu Chen |
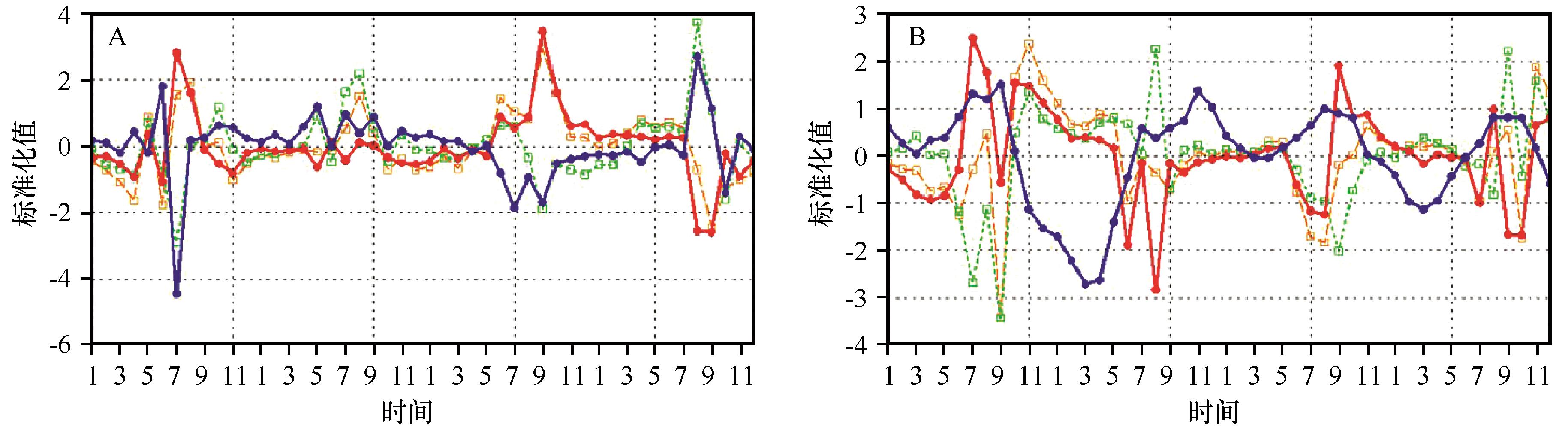
| 图11 WRF-Chem模拟的2002-2005年沙尘气候效应在中国东北地区(48°—55°N, 118°—135°E,A)和青藏高原(26°—40°N, 73°—105°E,B)导致的日最高温度(橙色线)、日最低温度(绿色线)、地面温度日较差(红色线)以及云水含量(蓝色线,A)和积雪当量(蓝色线,B)月变化的区域平均标准化序列 |
| Fig.11 The normalization of monthly variations of liquid water path (blue line in A), snow cover (blue line in B), maximum diurnal temperature (orange line), minimum diurnal temperature (green line) and dinurnal temperature range (red line) in the northeast of China (A) and the Tibetan Plateau (B) |

|