短期增温和降水减少对沙质草地土壤微生物量碳氮和酶活性的影响
Effects of short-term warming and precipitation reduction on soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and enzyme activity in sandy grassland
短期增温和降水减少对沙质草地土壤微生物量碳氮和酶活性的影响 |
| 王怀海, 黄文达, 何远政, 牛亚毅, 朱远忠 |
|
Effects of short-term warming and precipitation reduction on soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and enzyme activity in sandy grassland |
| Huaihai Wang, Wenda Huang, Yuanzheng He, Yayi Niu, Yuanzhong Zhu |
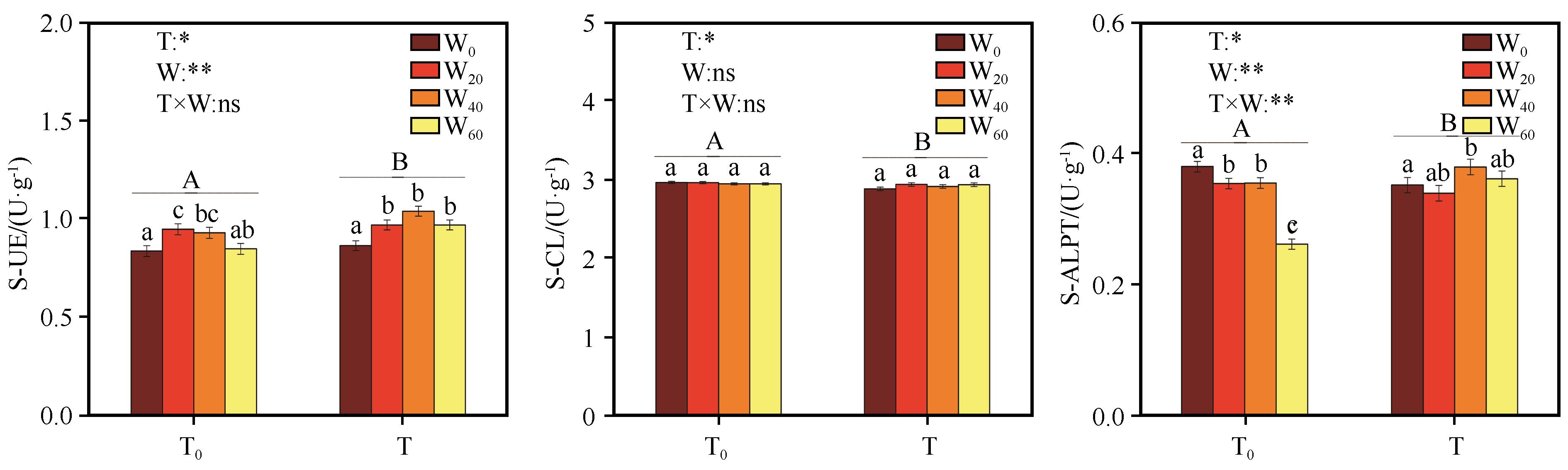
| 图3 短期增温和降水减少对沙质草地土壤酶活性的影响(T0表示自然温度;T表示增温;W0、W20、W40、W60分别表示降水减少0、20%、40%、60%。不同大写字母表示相同降水减少条件下增温处理之间的差异显著,小写字母表示相同温度条件下降水减少处理之间的差异显著,P<0.05;*,处理效应显著,P<0.05;**,处理效应极显著,P<0.01;ns,处理效应不显著) |
| Fig.3 Effects of short-term warming and precipitation reduction on soil enzyme activities in sandy grassland (T0, natural temperature; T, warming; W0, W20, W40 and W60, precipitation decreased by 0, 20%, 40% and 60%, Different capital letters indicate a significant difference between temperature treatments at the same precipitation conditions, and small letters show a significant differencebetween precipitation reduction treatments at the same temperature conditions, P<0.05) |

|