基于文献记录的敦煌地区历史时期沙尘天气序列重建
|
|
王伊蒙, 范亚秋, 龙川, 柳本立
|
Historical dust event sequence reconstruction in Dunhuang based on history records
|
|
Yimeng Wang, Yaqiu Fan, Chuan Long, Benli Liu
|
|
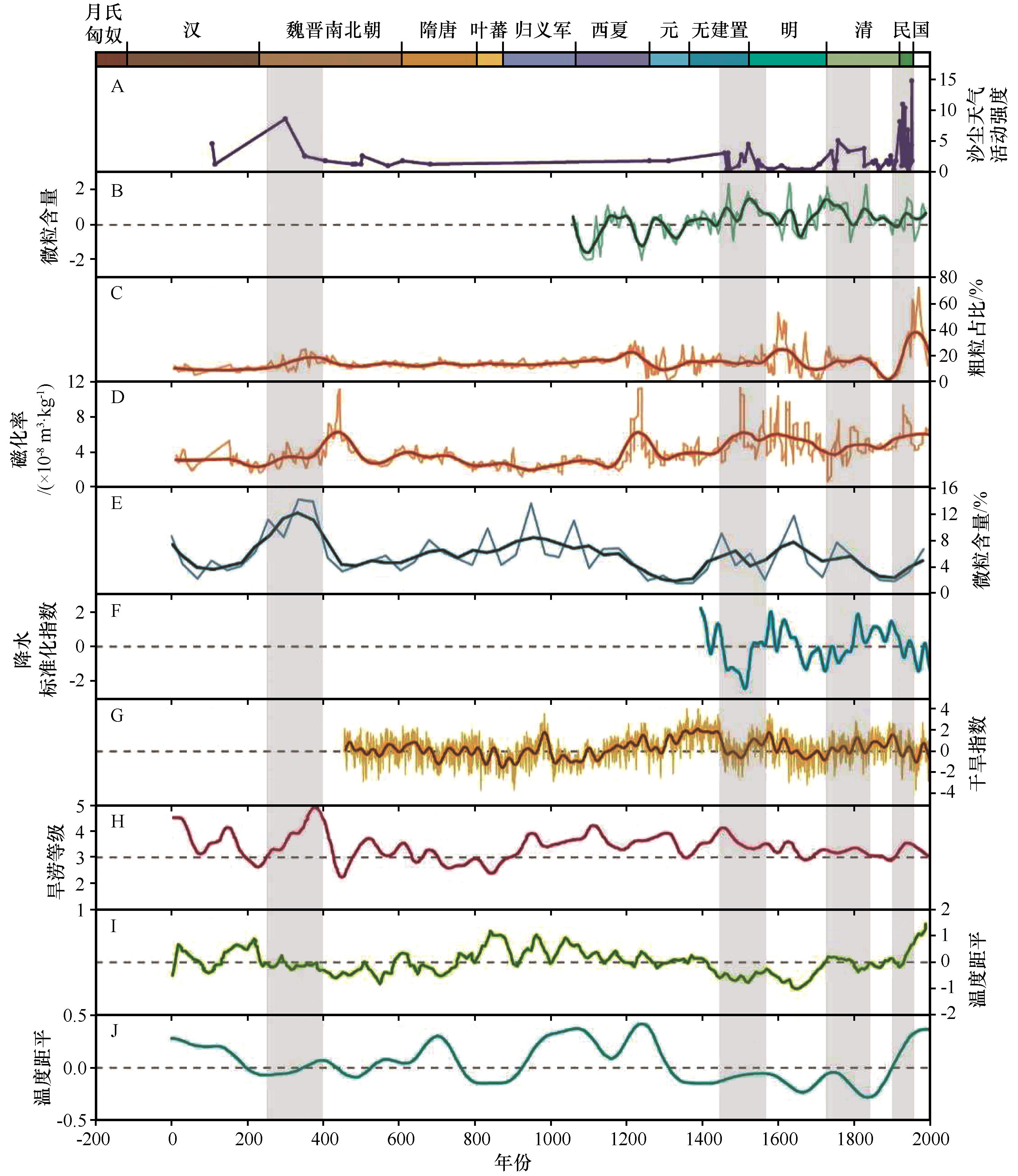
图3 敦煌历史时期沙尘天气活动强度序列(A本文),敦德冰芯微粒含量[30](B),苏干湖沉积物粗粒含量[31](C),苏干湖沉积物磁化率[31](D),巴里坤湖沉积物组分含量[32](E),河西走廊近600年降水序列[33](F),河西走廊帕尔默干旱度指数(scPDSI)序列[34](G),黑河流域近2 000年旱涝序列[35](H),Yang等[36]重建的中国2 000年温度序列(I),Ge等[37]重建的中国2 000年温度序列(J)
|
Fig.3 Activity intensity series of dust event during the historical period of Dunhuang (A in this paper), particulate content of the ice core of Dunde[30] (B), coarse-grained content of the sediments of Sugan lake[31] (C), magnetization rate of the sediments of Sugan lake[31] (D), content of the sedimentary fractions of Balikun lake[32] (E), precipitation sequence of Hexi Corridor in recent 600 years[33] (F), palmer drought severity index (scPDSI ) sequence in Hexi Corridor[34] (G), Heihe River basin nearly 2 000 years drought and flooding sequence[35] (H), Yang et al. reconstructed China's 2,000 years temperature sequence[36] (I), Ge et al. reconstructed China's 2 000 years temperature sequence[37] (J)
|
|
|
|
|

