若尔盖盆地阿米欧拉-南剖面粒度端元特征及其记录的15 ka来气候变化
Particle endmembers characteristics of Amiola-South profile in the Zoige Basin and recorded climate change since 15 ka BP
若尔盖盆地阿米欧拉-南剖面粒度端元特征及其记录的15 ka来气候变化 |
| 翟颖, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 查小春, 周亚利, 李瑜琴, 张玉柱, 孙雪晴, 赵晓康 |
|
Particle endmembers characteristics of Amiola-South profile in the Zoige Basin and recorded climate change since 15 ka BP |
| Ying Zhai, Jiangli Pang, Chunchang Huang, Xiaochun Zha, Yali Zhou, Yuqin Li, Yuzhu Zhang, Xueqing Sun, Xiaokang Zhao |
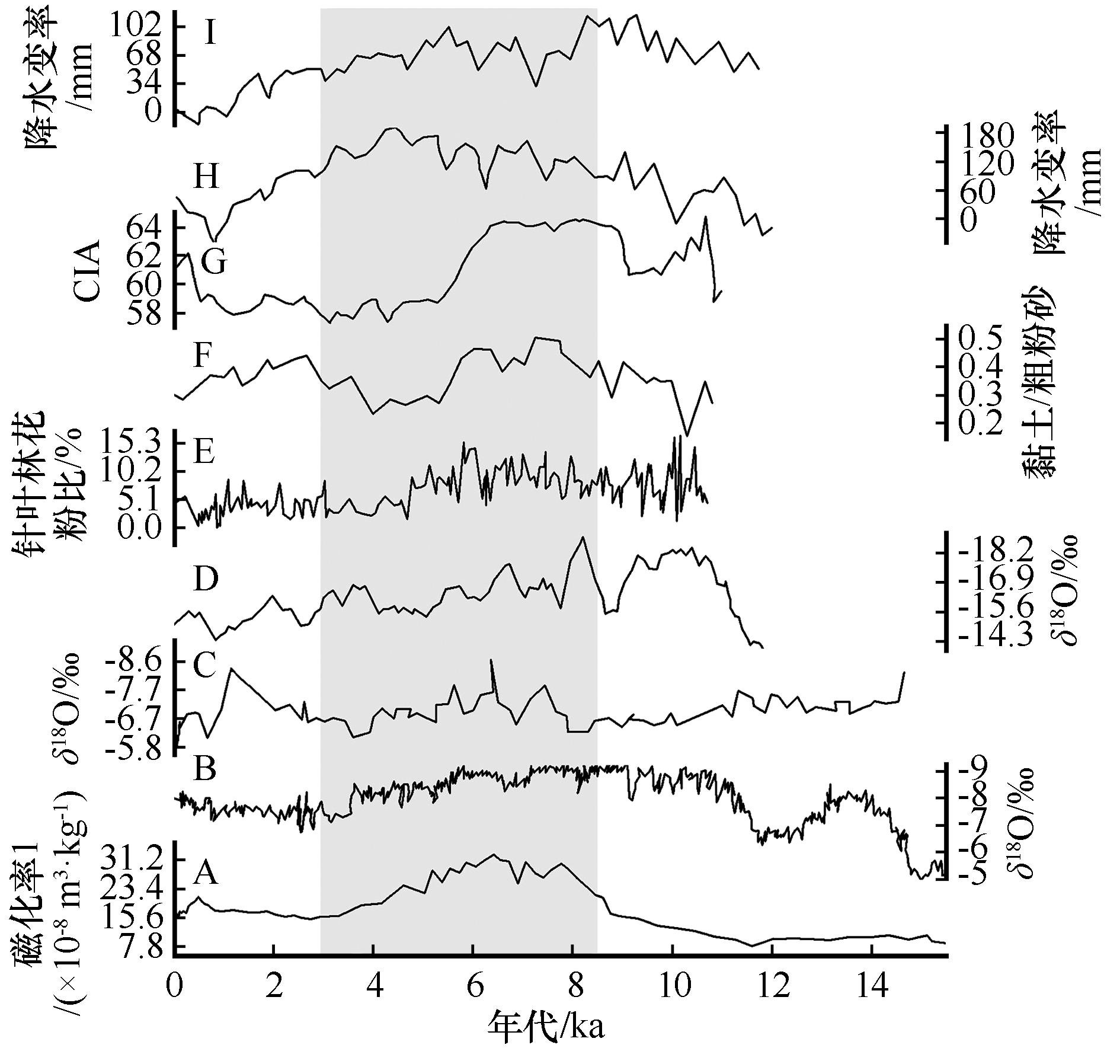
| 图5 AMOL-S剖面磁化率与其他区域气候变化代用指标的比较 |
| Fig.5 Comparison of magnetic susceptibility of AMOL-Sprofile (A) with Guizhou Dongge Cave stalagmites δ18O (B), Sediments from the Dalianhai Sea on the Tibetan Plateau δ18O (C), Guliya core on the Tibetan Plateau δ18O (D), pollen content of z10-C14 coniferous forest in red plain peat core (E), Maqu ZHK profile clay / coarse silt(F), Maqu DEQ-E profile CIA (G), holocene precipitation variability in northern China(H), and water variability in southern China in the Holocene (I) |

|