中国沙漠 ›› 2020, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 105-117.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2020.00078
收稿日期:2020-05-08
修回日期:2020-07-24
出版日期:2020-12-09
发布日期:2020-12-09
作者简介:曾方明(1982—),男,湖南邵阳人,博士,副研究员,研究方向为黄土地球化学。E-mail: fmzeng@163.com
基金资助:
Fangming Zeng1( ), Hongpan Xue1,2
), Hongpan Xue1,2
Received:2020-05-08
Revised:2020-07-24
Online:2020-12-09
Published:2020-12-09
摘要:
青藏高原东北部的晚第四纪黄土-古土壤记录了该区环境变化的信息,以往的物源研究样品空间覆盖度不足,仍需进一步研究。在青藏高原东北部较大范围地采集了黄土-古土壤、风成砂、河流沉积、湖相沉积样品,并对这些样品小于75 μm组分的元素组成进行了X射线荧光光谱(XRF)分析。结果表明:(1)青藏高原东北部晚第四纪黄土-古土壤的元素组成以SiO2、Al2O3、Fe2O3、CaO为主;与UCC(上地壳)相比,青藏高原东北部晚第四纪黄土-古土壤的CaO、MgO含量较高,Na2O、K2O含量较低。(2)具有物源指示意义的K2O/Al2O3(摩尔比)、TiO2/Al2O3(摩尔比)、Zr/Nb和Zr/Ti比值图解显示青藏高原东北部青海湖地区的晚第四纪黄土-古土壤与当地的河流沉积、湖相沉积存在较大差异,揭示它们来自青海湖地区以外的区域。(3)K2O/Al2O3(摩尔比)、TiO2/Al2O3(摩尔比)、Zr/Nb和Zr/Ti比值图解显示青藏高原东北部的晚第四纪黄土-古土壤与柴达木盆地的风成砂、河流沉积和湖相沉积重叠在一起,表明柴达木盆地的风化细碎屑物质在近地面西北风、高空西风环流的作用下很可能为青藏高原东北部黄土-古土壤的堆积提供了主要物源。
中图分类号:
曾方明, 薛红盼. 青藏高原东北部晚第四纪黄土-古土壤的元素组成及其物源指示[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(6): 105-117.
Fangming Zeng, Hongpan Xue. Elemental compositions of the late Quaternary loess-paleosol on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and their implications for provenance[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(6): 105-117.
| 样品 编号 | 岩性 | 纬度 /(°) | 经度 /(°) | 测试 组分 | 原始 总浓 度/% | SiO2/% | Al2O3/% | Fe2O3/% | CaO /% | Na2O /% | K2O /% | MgO /% | TiO2/% | P2O5/% | MnO /% | Zr/ (mg·kg-1) | Nb/ (mg·kg-1) | Hf/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZYC-18 | 古土壤 | 36.63 | 100.87 | <75 μm | 89.25 | 62.96 | 13.94 | 5.60 | 9.54 | 1.35 | 2.94 | 2.32 | 0.73 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 255.04 | 17.80 | 7.46 |
| ZYC-25 | 古土壤 | 36.63 | 100.87 | <75 μm | 88.60 | 60.44 | 13.86 | 5.62 | 12.17 | 1.27 | 2.80 | 2.55 | 0.70 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 213.58 | 17.17 | 7.14 |
| ZYC-30 | 古土壤 | 36.63 | 100.87 | <75 μm | 88.81 | 58.50 | 13.74 | 5.40 | 14.06 | 1.51 | 2.68 | 2.87 | 0.65 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 195.11 | 16.47 | 6.78 |
| ZYC-43 | 黄土 | 36.63 | 100.87 | <75 μm | 87.89 | 58.60 | 12.64 | 4.89 | 15.69 | 1.60 | 2.50 | 2.84 | 0.65 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 234.78 | 15.47 | 6.77 |
| ZYC-46 | 黄土 | 36.63 | 100.87 | <75 μm | 87.71 | 59.35 | 12.60 | 4.77 | 15.17 | 1.58 | 2.46 | 2.85 | 0.63 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 257.75 | 14.86 | 6.85 |
| HYW-2 | 黄土 | 36.82 | 100.80 | <75 μm | 86.91 | 58.39 | 11.91 | 4.35 | 17.49 | 1.08 | 2.27 | 3.41 | 0.58 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 288.76 | 14.57 | 6.73 |
| HBB-1 | 古土壤 | 37.03 | 100.78 | <75 μm | 87.68 | 62.34 | 13.49 | 5.21 | 11.62 | 1.00 | 2.57 | 2.54 | 0.66 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 262.56 | 16.32 | 7.27 |
| HBB-2 | 黄土 | 37.03 | 100.78 | <75 μm | 88.83 | 62.59 | 13.00 | 4.68 | 11.28 | 1.49 | 2.36 | 3.42 | 0.64 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 299.48 | 14.99 | 7.29 |
| XH-2 | 古土壤 | 37.06 | 100.72 | <75 μm | 87.79 | 64.44 | 13.07 | 5.27 | 9.90 | 1.10 | 2.70 | 2.24 | 0.68 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 296.23 | 16.80 | 7.52 |
| GC-1 | 黄土 | 37.33 | 100.12 | <75 μm | 89.10 | 64.57 | 13.04 | 4.86 | 9.32 | 1.48 | 2.23 | 3.37 | 0.64 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 379.09 | 15.49 | 7.53 |
| SNH-1 | 黄土 | 36.98 | 99.60 | <75 μm | 86.41 | 60.51 | 12.36 | 4.48 | 15.53 | 0.96 | 2.50 | 2.56 | 0.60 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 258.41 | 15.48 | 6.99 |
| QHH-1 | 古土壤 | 36.84 | 99.71 | <75 μm | 89.03 | 65.43 | 13.79 | 4.93 | 8.27 | 1.36 | 2.53 | 2.50 | 0.67 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 268.61 | 15.80 | 7.65 |
| HMH | 古土壤 | 36.75 | 99.75 | <75 μm | 86.86 | 63.90 | 12.51 | 4.79 | 11.85 | 1.11 | 2.41 | 2.28 | 0.66 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 272.67 | 16.80 | 7.46 |
| HMH* | 古土壤 | 36.75 | 99.75 | <75 μm | 86.85 | 63.72 | 12.61 | 4.81 | 11.91 | 1.11 | 2.43 | 2.28 | 0.63 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 269.44 | 16.06 | 7.44 |
| JXG-1 | 古土壤 | 36.59 | 100.30 | <75 μm | 87.30 | 63.88 | 12.82 | 5.17 | 10.85 | 1.18 | 2.42 | 2.35 | 0.65 | 0.34 | 0.09 | 265.69 | 16.09 | 7.41 |
| JXG-2 | 黄土 | 36.59 | 100.30 | <75 μm | 88.69 | 62.80 | 13.05 | 4.66 | 11.17 | 1.35 | 2.40 | 3.38 | 0.64 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 284.27 | 15.89 | 7.34 |
| 151-1 | 古土壤 | 36.56 | 100.47 | <75 μm | 88.73 | 65.75 | 13.28 | 5.12 | 8.22 | 1.30 | 2.76 | 2.32 | 0.68 | 0.25 | 0.10 | 256.37 | 14.93 | 7.66 |
| 151-2 | 古土壤 | 36.56 | 100.47 | <75 μm | 89.17 | 65.18 | 13.81 | 5.34 | 8.02 | 1.21 | 2.74 | 2.48 | 0.67 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 265.48 | 16.06 | 7.52 |
| EH-1 | 黄土 | 36.55 | 100.72 | <75 μm | 87.49 | 60.84 | 11.85 | 4.57 | 14.42 | 1.60 | 2.33 | 3.28 | 0.59 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 248.76 | 15.41 | 7.08 |
| DTH-7 | 古土壤 | 36.43 | 101.07 | <75 μm | 87.96 | 61.20 | 13.06 | 5.16 | 12.74 | 0.92 | 2.60 | 3.13 | 0.65 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 238.89 | 15.90 | 7.11 |
| DTH-9 | 古土壤 | 36.51 | 100.91 | <75 μm | 88.16 | 65.25 | 13.44 | 5.54 | 8.67 | 1.10 | 2.63 | 2.11 | 0.70 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 259.77 | 16.97 | 7.60 |
| DTH-11 | 黄土 | 36.55 | 100.88 | <75 μm | 86.13 | 57.37 | 11.58 | 4.59 | 19.46 | 0.82 | 2.23 | 2.84 | 0.58 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 229.07 | 14.13 | 6.51 |
| RYS-1 | 古土壤 | 36.43 | 101.11 | <75 μm | 89.71 | 66.35 | 14.02 | 5.64 | 6.32 | 1.16 | 2.80 | 2.41 | 0.70 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 256.62 | 16.85 | 7.72 |
| RYS-2 | 古土壤 | 36.43 | 101.11 | <75 μm | 88.80 | 65.90 | 13.60 | 5.61 | 7.55 | 1.14 | 2.74 | 2.22 | 0.70 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 249.12 | 16.72 | 7.68 |
| RYS-3 | 黄土 | 36.43 | 101.11 | <75 μm | 89.18 | 64.64 | 13.70 | 5.14 | 8.75 | 1.30 | 2.60 | 2.68 | 0.67 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 263.10 | 15.33 | 7.54 |
| RYS-5 | 古土壤 | 36.43 | 101.07 | <75 μm | 88.40 | 63.67 | 13.17 | 4.98 | 10.20 | 1.72 | 2.47 | 2.58 | 0.68 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 285.92 | 14.15 | 7.45 |
| RYS-5 | 古土壤 | 36.43 | 101.07 | <75 μm | 88.31 | 63.55 | 13.16 | 4.97 | 10.37 | 1.70 | 2.49 | 2.57 | 0.66 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 279.93 | 14.92 | 7.44 |
| RYS-6 | 黄土 | 36.43 | 101.07 | <75 μm | 86.97 | 59.43 | 12.97 | 4.56 | 15.50 | 1.29 | 2.32 | 2.82 | 0.61 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 265.71 | 15.74 | 6.89 |
| LM-1 | 古土壤 | 36.24 | 101.08 | <75 μm | 87.77 | 64.10 | 12.92 | 4.93 | 10.61 | 1.15 | 2.57 | 2.55 | 0.66 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 284.48 | 16.03 | 7.45 |
| LM-2 | 黄土 | 36.24 | 101.08 | <75 μm | 87.77 | 60.41 | 12.05 | 4.30 | 14.74 | 1.52 | 2.30 | 3.61 | 0.59 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 247.95 | 13.66 | 7.01 |
| TJ-1 | 古土壤 | 37.29 | 99.04 | <75 μm | 88.11 | 63.95 | 13.21 | 4.89 | 10.46 | 1.36 | 2.49 | 2.44 | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 269.71 | 14.56 | 7.46 |
| TJ-2 | 黄土 | 37.29 | 99.04 | <75 μm | 87.42 | 64.79 | 12.26 | 4.31 | 11.28 | 1.53 | 2.29 | 2.32 | 0.69 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 311.47 | 14.23 | 7.55 |
| TJ-3 | 古土壤 | 37.20 | 98.89 | <75 μm | 88.03 | 65.09 | 13.04 | 5.16 | 9.26 | 1.10 | 2.58 | 2.57 | 0.66 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 253.91 | 15.45 | 7.62 |
| TJ-4 | 黄土 | 37.20 | 98.89 | <75 μm | 88.92 | 61.50 | 14.14 | 4.73 | 11.37 | 1.33 | 2.55 | 3.24 | 0.64 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 290.76 | 15.73 | 7.16 |
| WL | 黄土 | 36.94 | 98.40 | <75 μm | 91.38 | 59.05 | 15.04 | 5.55 | 10.89 | 1.63 | 2.92 | 3.62 | 0.71 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 189.26 | 17.35 | 6.75 |
| WL* | 黄土 | 36.94 | 98.40 | <75 μm | 91.38 | 59.16 | 14.97 | 5.55 | 10.84 | 1.64 | 2.91 | 3.63 | 0.71 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 192.38 | 14.45 | 6.82 |
| CK | 黄土 | 36.79 | 99.11 | <75 μm | 89.80 | 64.22 | 12.77 | 4.24 | 9.96 | 1.93 | 2.48 | 3.18 | 0.65 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 345.18 | 15.89 | 7.34 |
| LYX-1 | 黄土 | 36.15 | 100.95 | <75 μm | 85.78 | 56.84 | 10.56 | 3.99 | 21.45 | 1.14 | 2.10 | 2.90 | 0.55 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 243.90 | 14.06 | 6.52 |
| YJC-40a | 黄土 | 36.73 | 101.79 | <75 μm | 88.44 | 63.42 | 13.01 | 4.44 | 11.16 | 1.46 | 2.45 | 2.94 | 0.62 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 270.25 | 16.15 | 7.35 |
| LD-1a | 黄土 | 36.43 | 102.56 | <75 μm | 88.76 | 64.49 | 12.64 | 4.41 | 10.37 | 1.68 | 2.38 | 2.88 | 0.65 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 310.73 | 15.45 | 7.45 |
| HQSK-1 | 黄土 | 37.20 | 101.54 | <75 μm | 88.46 | 62.57 | 13.90 | 4.67 | 10.40 | 2.02 | 2.61 | 2.62 | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 281.45 | 14.68 | 7.49 |
| HQSK-2 | 古土壤 | 37.25 | 101.45 | <75 μm | 91.36 | 66.87 | 14.92 | 5.20 | 4.72 | 1.81 | 2.80 | 2.33 | 0.73 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 297.33 | 15.86 | 7.82 |
| QSZ-1 | 古土壤 | 37.63 | 101.36 | <75 μm | 90.83 | 66.49 | 16.27 | 6.31 | 2.30 | 1.52 | 3.30 | 2.39 | 0.77 | 0.23 | 0.13 | 274.72 | 17.47 | 8.22 |
| QSZ-2 | 黄土 | 37.63 | 101.36 | <75 μm | 83.18 | 59.40 | 14.86 | 5.27 | 12.47 | 1.43 | 2.79 | 2.56 | 0.66 | 0.20 | 0.11 | 254.95 | 15.54 | 7.86 |
| AR-1 | 古土壤 | 38.06 | 100.46 | <75 μm | 91.21 | 63.14 | 16.20 | 6.34 | 4.97 | 1.68 | 3.10 | 3.19 | 0.79 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 265.27 | 18.56 | 7.72 |
| WC-1 | 黄土 | 36.73 | 104.09 | <75 μm | 90.05 | 63.02 | 13.19 | 5.07 | 9.72 | 2.04 | 2.49 | 3.28 | 0.69 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 250.88 | 15.16 | 7.32 |
| WC-1* | 黄土 | 36.73 | 104.09 | <75 μm | 90.13 | 63.43 | 12.95 | 5.08 | 9.54 | 2.14 | 2.47 | 3.20 | 0.69 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 246.68 | 15.59 | 7.30 |
| WC-2 | 黄土 | 36.73 | 104.09 | <75 μm | 89.35 | 62.10 | 12.47 | 4.77 | 11.47 | 2.25 | 2.41 | 3.39 | 0.65 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 250.22 | 15.24 | 7.15 |
| JZT-1 | 黄土 | 36.10 | 103.78 | <75 μm | 88.50 | 65.57 | 12.45 | 4.43 | 9.82 | 1.39 | 2.35 | 2.89 | 0.62 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 260.28 | 14.06 | 7.57 |
| DXX-1 | 古土壤 | 35.65 | 103.40 | <75 μm | 87.03 | 63.97 | 12.93 | 4.64 | 11.52 | 1.11 | 2.42 | 2.23 | 0.65 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 279.23 | 14.51 | 7.53 |
| DXX-2 | 黄土 | 35.65 | 103.40 | <75 μm | 87.97 | 64.35 | 12.65 | 4.65 | 10.87 | 1.40 | 2.34 | 2.60 | 0.65 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 262.60 | 16.16 | 7.42 |
| HZ-1 | 古土壤 | 34.99 | 102.92 | <75 μm | 87.97 | 66.88 | 13.04 | 4.52 | 8.63 | 1.23 | 2.50 | 2.05 | 0.63 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 291.88 | 14.80 | 7.73 |
| HZ-2 | 黄土 | 34.99 | 102.92 | <75 μm | 88.20 | 66.72 | 12.41 | 4.25 | 9.29 | 1.44 | 2.41 | 2.43 | 0.59 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 258.40 | 14.98 | 7.70 |
| LMS-1 | 黄土 | 34.11 | 102.64 | <75 μm | 93.11 | 73.44 | 13.37 | 4.79 | 1.18 | 1.74 | 2.63 | 1.73 | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 274.01 | 17.82 | 8.10 |
| HR-1 | 古土壤 | 35.30 | 101.18 | <75 μm | 88.09 | 67.92 | 12.75 | 4.86 | 7.48 | 1.27 | 2.47 | 2.02 | 0.68 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 339.24 | 16.11 | 7.79 |
| MD-5 | 黄土 | 34.97 | 98.11 | <75 μm | 86.77 | 70.05 | 10.66 | 3.30 | 9.59 | 1.29 | 1.97 | 2.11 | 0.60 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 351.33 | 14.18 | 7.87 |
| MD-6 | 黄土 | 34.97 | 98.11 | <75 μm | 87.33 | 67.69 | 11.66 | 3.57 | 10.07 | 1.18 | 2.19 | 2.60 | 0.60 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 398.12 | 16.20 | 7.71 |
| HHX-1 | 黄土 | 34.67 | 98.15 | <75 μm | 87.11 | 70.29 | 11.80 | 3.72 | 7.91 | 1.21 | 2.27 | 1.68 | 0.63 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 481.64 | 15.23 | 7.92 |
| HHX-2 | 黄土 | 34.67 | 98.15 | <75 μm | 86.05 | 64.56 | 13.02 | 4.03 | 12.00 | 0.96 | 2.49 | 1.86 | 0.58 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 306.12 | 13.19 | 7.48 |
| 平均值b | 63.58 | 13.10 | 4.84 | 10.72 | 1.38 | 2.52 | 2.66 | 0.65 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 277.20 | 15.65 | 7.40 | |||||
| ZYC-57 | 风成砂 | 36.63 | 100.87 | <75 μm | 86.84 | 64.30 | 11.37 | 3.78 | 12.92 | 1.80 | 2.25 | 2.46 | 0.61 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 371.65 | 15.14 | 7.65 |
| ZYC-60 | 风成砂 | 36.63 | 100.87 | <75 μm | 87.26 | 63.68 | 11.79 | 3.93 | 12.80 | 1.72 | 2.33 | 2.62 | 0.61 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 345.19 | 14.58 | 7.51 |
| HD-A | 风成砂 | 36.76 | 100.77 | <75 μm | 86.55 | 63.87 | 11.23 | 4.21 | 13.17 | 1.62 | 1.93 | 2.39 | 0.89 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 1381.12 | 22.95 | 7.86 |
| HD-B | 风成砂 | 36.74 | 100.77 | <75 μm | 86.96 | 62.88 | 11.24 | 4.78 | 13.09 | 1.68 | 1.90 | 2.58 | 1.07 | 0.28 | 0.10 | 1842.33 | 29.68 | 7.91 |
| HD-C | 风成砂 | 36.73 | 100.78 | <75 μm | 86.87 | 61.44 | 11.20 | 5.27 | 13.91 | 1.61 | 1.85 | 2.62 | 1.23 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 2174.15 | 31.58 | 7.98 |
| SNH | 风成砂 | 36.98 | 99.60 | <75 μm | 88.05 | 64.57 | 12.17 | 3.90 | 11.45 | 1.82 | 2.39 | 2.63 | 0.59 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 270.32 | 13.69 | 7.51 |
| SNH-2 | 风成砂 | 36.98 | 99.60 | <75 μm | 87.11 | 64.67 | 11.62 | 3.95 | 12.20 | 1.58 | 2.17 | 2.67 | 0.63 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 388.50 | 14.68 | 7.54 |
| RYS-4 | 风成砂 | 36.43 | 101.11 | <75 μm | 87.53 | 69.38 | 12.11 | 3.53 | 8.16 | 1.47 | 2.27 | 2.17 | 0.49 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 272.27 | 13.70 | 7.95 |
| JXG-3 | 风成砂 | 36.59 | 100.30 | <75 μm | 87.51 | 64.22 | 11.85 | 4.06 | 12.17 | 1.58 | 2.09 | 2.80 | 0.66 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 585.17 | 16.48 | 7.55 |
| GC-2 | 风成砂 | 37.33 | 100.12 | <75 μm | 89.56 | 65.84 | 12.78 | 4.66 | 8.40 | 2.08 | 2.19 | 2.88 | 0.65 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 531.51 | 16.94 | 7.67 |
| LM-3 | 风成砂 | 36.24 | 101.08 | <75 μm | 89.22 | 62.55 | 13.42 | 4.38 | 10.92 | 1.88 | 2.50 | 3.26 | 0.59 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 293.54 | 14.29 | 7.29 |
| YQZ-1 | 风成砂 | 38.23 | 91.41 | <75 μm | 90.24 | 65.77 | 10.83 | 3.44 | 9.53 | 4.16 | 2.27 | 3.05 | 0.53 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 244.30 | 15.06 | 7.61 |
| YQZ-3 | 风成砂 | 38.23 | 91.38 | <75 μm | 90.61 | 60.70 | 15.47 | 6.31 | 9.19 | 1.08 | 2.90 | 3.12 | 0.70 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 152.19 | 15.00 | 7.16 |
| XT-3 | 风成砂 | 38.05 | 93.14 | <75 μm | 90.97 | 60.95 | 9.37 | 3.72 | 13.02 | 4.57 | 1.82 | 5.23 | 0.74 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 611.20 | 17.81 | 7.30 |
| HX-1 | 风成砂 | 37.28 | 97.45 | <75 μm | 84.99 | 58.44 | 11.33 | 4.15 | 19.20 | 1.33 | 2.00 | 2.34 | 0.71 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 464.20 | 17.74 | 7.25 |
| AM-1 | 风成砂 | 36.88 | 96.56 | <75 μm | 88.06 | 70.12 | 10.55 | 3.34 | 8.89 | 1.85 | 2.08 | 2.01 | 0.66 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 542.60 | 15.98 | 7.94 |
| AM-3 | 风成砂 | 36.97 | 96.26 | <75 μm | 88.49 | 67.35 | 10.88 | 3.49 | 9.59 | 2.38 | 2.03 | 3.18 | 0.57 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 451.25 | 15.48 | 7.74 |
| ZJN-2 | 风成砂 | 36.35 | 97.19 | <75 μm | 92.18 | 61.90 | 10.23 | 4.37 | 11.02 | 3.34 | 2.04 | 5.74 | 0.76 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 798.16 | 19.47 | 7.29 |
| NMHN-1 | 风成砂 | 36.76 | 96.51 | <75 μm | 89.33 | 62.50 | 12.90 | 4.14 | 11.09 | 1.76 | 2.42 | 4.03 | 0.54 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 261.10 | 11.25 | 7.22 |
| NMHN-2 | 风成砂 | 36.76 | 96.51 | <75 μm | 89.20 | 61.80 | 13.21 | 4.45 | 11.59 | 1.48 | 2.50 | 3.74 | 0.59 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 279.67 | 14.71 | 7.21 |
| NMHN-3 | 风成砂 | 36.77 | 96.52 | <75 μm | 88.94 | 61.49 | 12.78 | 4.16 | 12.22 | 2.28 | 2.43 | 3.51 | 0.54 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 235.20 | 10.40 | 7.16 |
| DGL-1 | 风成砂 | 36.39 | 95.75 | <75 μm | 87.63 | 67.13 | 10.32 | 3.71 | 11.11 | 1.78 | 1.93 | 2.82 | 0.66 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 511.67 | 17.03 | 7.66 |
| HHX-3 | 风成砂 | 34.67 | 98.15 | <75 μm | 83.98 | 57.97 | 12.32 | 3.45 | 20.47 | 1.05 | 1.98 | 1.73 | 0.54 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 219.75 | 10.31 | 6.91 |
| HHX-5 | 风成砂 | 34.74 | 98.12 | <75 μm | 86.28 | 71.44 | 10.06 | 3.07 | 9.62 | 1.41 | 1.76 | 1.55 | 0.64 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 457.43 | 14.39 | 7.97 |
| MD-2 | 风成砂 | 34.80 | 98.14 | <75 μm | 88.04 | 71.29 | 11.34 | 3.59 | 7.43 | 1.43 | 2.03 | 1.67 | 0.70 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 798.03 | 17.25 | 7.93 |
| HR-2 | 风成砂 | 35.30 | 101.18 | <75 μm | 87.92 | 66.63 | 12.03 | 4.06 | 9.90 | 1.44 | 2.27 | 2.54 | 0.63 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 403.15 | 16.08 | 7.65 |
| AR-2 | 风成砂 | 38.06 | 100.46 | <75 μm | 88.34 | 64.93 | 13.33 | 4.40 | 8.72 | 1.91 | 2.47 | 3.07 | 0.62 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 273.16 | 12.93 | 7.66 |
| 平均值 | 64.36 | 11.77 | 4.09 | 11.55 | 1.93 | 2.18 | 2.90 | 0.67 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 561.44 | 16.47 | 7.56 | |||||
| BHH-1 | 河流沉积 | 37.03 | 99.74 | <75 μm | 87.16 | 65.06 | 11.91 | 3.96 | 11.61 | 1.83 | 2.11 | 2.20 | 0.75 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 731.23 | 19.73 | 7.86 |
| BHH-2 | 河流沉积 | 37.03 | 99.74 | <75 μm | 87.77 | 62.37 | 13.18 | 4.33 | 12.43 | 1.60 | 2.39 | 2.53 | 0.65 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 292.80 | 16.78 | 7.30 |
| BHH-3 | 河流沉积 | 37.04 | 99.74 | <75 μm | 87.02 | 65.53 | 11.66 | 4.25 | 11.43 | 1.51 | 2.08 | 2.26 | 0.71 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 836.20 | 18.90 | 7.81 |
| DTHS-1 | 河流沉积 | 36.26 | 101.07 | <75 μm | 87.67 | 66.50 | 11.67 | 4.00 | 10.15 | 1.97 | 2.03 | 2.35 | 0.76 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 839.65 | 19.57 | 7.78 |
| DTHS-2 | 河流沉积 | 36.26 | 101.07 | <75 μm | 87.66 | 67.48 | 12.10 | 3.86 | 9.55 | 1.60 | 2.24 | 2.08 | 0.63 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 400.95 | 15.70 | 7.71 |
| JXG-R | 河流沉积 | 36.59 | 100.30 | <75 μm | 89.62 | 74.39 | 10.43 | 3.39 | 5.23 | 1.82 | 2.06 | 1.48 | 0.70 | 0.19 | 0.06 | 623.57 | 17.22 | 8.10 |
| RSC-1 | 河流沉积 | 37.16 | 100.54 | <75 μm | 87.91 | 67.79 | 12.14 | 4.21 | 8.90 | 1.41 | 2.32 | 2.07 | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 442.65 | 17.19 | 7.84 |
| SLH-1 | 河流沉积 | 37.33 | 100.12 | <75 μm | 89.53 | 68.90 | 12.49 | 5.22 | 6.08 | 1.62 | 2.19 | 2.21 | 0.70 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 763.06 | 18.34 | 7.92 |
| LM-4 | 河流沉积 | 36.24 | 101.08 | <75 μm | 87.20 | 65.00 | 11.55 | 4.58 | 11.25 | 1.66 | 2.08 | 2.39 | 0.84 | 0.22 | 0.09 | 1303.52 | 23.08 | 7.72 |
| KLKH-N | 洪积物 | 37.36 | 96.81 | <75 μm | 87.70 | 63.89 | 11.77 | 4.21 | 12.20 | 1.71 | 2.19 | 2.85 | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 407.88 | 16.45 | 7.42 |
| DCD-1 | 洪积物 | 37.73 | 95.44 | <75 μm | 91.22 | 64.43 | 14.76 | 4.39 | 7.50 | 1.67 | 2.94 | 3.31 | 0.57 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 300.47 | 13.67 | 7.51 |
| TSHW-1 | 河流沉积 | 37.17 | 96.66 | <75 μm | 87.25 | 64.62 | 11.38 | 4.17 | 12.16 | 1.60 | 2.19 | 2.56 | 0.74 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 852.00 | 17.80 | 7.64 |
| ZJN-1 | 河流沉积 | 36.35 | 97.02 | <75 μm | 89.00 | 68.38 | 10.72 | 4.08 | 8.82 | 1.97 | 2.17 | 2.72 | 0.64 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 281.70 | 15.29 | 7.73 |
| 平均值 | 66.49 | 11.98 | 4.20 | 9.79 | 1.69 | 2.23 | 2.39 | 0.70 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 621.21 | 17.67 | 7.72 | |||||
| ELJ-1 | 湖相沉积 | 36.65 | 100.43 | <75 μm | 89.80 | 65.68 | 12.77 | 4.37 | 8.84 | 2.16 | 2.51 | 2.47 | 0.69 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 491.58 | 16.51 | 7.66 |
| ELJ-2 | 湖相沉积 | 36.65 | 100.43 | <75 μm | 90.79 | 61.97 | 14.61 | 5.74 | 8.98 | 1.79 | 2.83 | 2.80 | 0.75 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 373.31 | 18.17 | 7.32 |
| HYW-3 | 湖相沉积 | 36.82 | 100.80 | <75 μm | 91.04 | 48.97 | 13.55 | 5.11 | 24.06 | 0.96 | 2.52 | 3.71 | 0.57 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 244.46 | 11.19 | 5.35 |
| GH-1 | 湖相沉积 | 37.02 | 100.59 | <75 μm | 87.57 | 67.61 | 10.81 | 4.42 | 9.60 | 1.48 | 2.06 | 2.39 | 0.94 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 1094.26 | 20.24 | 7.91 |
| GH-2 | 湖相沉积 | 37.02 | 100.59 | <75 μm | 88.47 | 69.38 | 11.01 | 4.35 | 7.91 | 1.51 | 2.24 | 2.33 | 0.68 | 0.28 | 0.07 | 513.34 | 17.58 | 7.95 |
| BQD-1 | 湖相沉积 | 36.52 | 96.20 | <75 μm | 86.95 | 67.82 | 10.64 | 4.03 | 10.35 | 1.91 | 2.09 | 2.01 | 0.63 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 379.71 | 15.02 | 7.84 |
| HTTL-1 | 湖相沉积 | 37.37 | 96.75 | <75 μm | 90.79 | 66.34 | 14.52 | 5.55 | 5.87 | 1.75 | 2.83 | 1.95 | 0.69 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 235.98 | 16.08 | 7.67 |
| NLZN | 湖相沉积 | 38.62 | 93.51 | <75 μm | 88.94 | 66.28 | 11.97 | 4.45 | 9.12 | 1.98 | 2.38 | 2.64 | 0.70 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 318.26 | 15.06 | 7.72 |
| XT-1 | 湖相沉积 | 38.05 | 93.14 | 全岩 | 91.62 | 58.12 | 10.73 | 3.91 | 14.88 | 2.05 | 2.10 | 7.11 | 0.58 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 341.49 | 14.84 | 6.79 |
| YQZ-2 | 湖相沉积 | 38.23 | 91.41 | 全岩 | 93.48 | 51.55 | 9.62 | 3.70 | 22.31 | 1.63 | 1.88 | 8.31 | 0.46 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 159.72 | 9.41 | 5.70 |
| YQZ-6 | 湖相沉积 | 38.38 | 91.31 | 全岩 | 95.13 | 58.85 | 15.74 | 6.24 | 7.31 | 1.98 | 3.36 | 5.39 | 0.65 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 129.52 | 14.43 | 6.82 |
| NMHN-4 | 湖相沉积 | 36.77 | 96.52 | 全岩 | 93.09 | 60.34 | 17.41 | 5.01 | 6.86 | 2.76 | 3.46 | 3.23 | 0.56 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 120.41 | 11.73 | 6.91 |
| NMHN-5 | 湖相沉积 | 36.77 | 96.52 | 全岩 | 93.38 | 67.50 | 14.32 | 7.11 | 2.18 | 2.47 | 2.87 | 2.38 | 0.66 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 240.79 | 15.83 | 7.95 |
| XT-2 | 湖相沉积 | 37.70 | 93.61 | 全岩 | 88.88 | 52.81 | 9.26 | 3.00 | 26.41 | 2.34 | 1.96 | 3.39 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 120.68 | 6.27 | 5.78 |
| LH2 | 湖相沉积 | 38.66 | 93.39 | 全岩 | 93.94 | 60.04 | 13.56 | 4.67 | 9.21 | 1.19 | 2.67 | 7.61 | 0.56 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 179.20 | 14.00 | 6.95 |
| YD-1 | 湖相沉积 | 38.66 | 93.27 | 全岩 | 91.21 | 55.99 | 12.70 | 4.79 | 15.77 | 1.26 | 2.52 | 5.92 | 0.52 | 0.18 | 0.10 | 152.91 | 12.40 | 6.30 |
| YD-2 | 湖相沉积 | 38.51 | 92.76 | 全岩 | 89.31 | 52.52 | 9.71 | 3.29 | 25.94 | 1.97 | 2.18 | 3.57 | 0.34 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 106.53 | 5.35 | 5.67 |
| YD-3 | 湖相沉积 | 38.30 | 92.23 | 全岩 | 90.63 | 55.63 | 11.88 | 4.42 | 17.36 | 1.21 | 2.44 | 5.99 | 0.55 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 183.28 | 11.83 | 6.37 |
| YD-3* | 湖相沉积 | 38.30 | 92.23 | 全岩 | 91.25 | 54.76 | 12.25 | 4.49 | 17.48 | 1.27 | 2.48 | 6.19 | 0.57 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 184.76 | 11.65 | 6.22 |
| YD-4 | 湖相沉积 | 38.03 | 91.85 | 全岩 | 88.70 | 57.96 | 10.37 | 2.38 | 18.32 | 3.48 | 2.12 | 4.74 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 107.53 | 7.19 | 6.97 |
| AM-2 | 湖相沉积 | 36.97 | 96.26 | 全岩 | 90.75 | 63.66 | 14.64 | 5.79 | 7.63 | 1.73 | 2.89 | 2.50 | 0.69 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 191.98 | 16.52 | 7.29 |
| TSHW-2 | 湖相沉积 | 37.17 | 96.66 | 全岩 | 91.30 | 64.69 | 14.61 | 6.11 | 6.19 | 1.73 | 2.63 | 2.79 | 0.77 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 231.82 | 17.28 | 7.56 |
| 平均值b | 60.65 | 12.59 | 4.69 | 12.62 | 1.87 | 2.50 | 3.96 | 0.60 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 281.75 | 13.66 | 6.98 | |||||
| UCC c | 66 | 15.2 | 5.0 | 4.2 | 3.9 | 3.4 | 2.2 | 0.68 | 0.16 | 0.08 |
表1 青藏高原东北部各类样品的岩性、经纬度和元素组成
Table 1 Lithology, latitude and longitude, and elemental compositions of different samples on the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
| 样品 编号 | 岩性 | 纬度 /(°) | 经度 /(°) | 测试 组分 | 原始 总浓 度/% | SiO2/% | Al2O3/% | Fe2O3/% | CaO /% | Na2O /% | K2O /% | MgO /% | TiO2/% | P2O5/% | MnO /% | Zr/ (mg·kg-1) | Nb/ (mg·kg-1) | Hf/ (mg·kg-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZYC-18 | 古土壤 | 36.63 | 100.87 | <75 μm | 89.25 | 62.96 | 13.94 | 5.60 | 9.54 | 1.35 | 2.94 | 2.32 | 0.73 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 255.04 | 17.80 | 7.46 |
| ZYC-25 | 古土壤 | 36.63 | 100.87 | <75 μm | 88.60 | 60.44 | 13.86 | 5.62 | 12.17 | 1.27 | 2.80 | 2.55 | 0.70 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 213.58 | 17.17 | 7.14 |
| ZYC-30 | 古土壤 | 36.63 | 100.87 | <75 μm | 88.81 | 58.50 | 13.74 | 5.40 | 14.06 | 1.51 | 2.68 | 2.87 | 0.65 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 195.11 | 16.47 | 6.78 |
| ZYC-43 | 黄土 | 36.63 | 100.87 | <75 μm | 87.89 | 58.60 | 12.64 | 4.89 | 15.69 | 1.60 | 2.50 | 2.84 | 0.65 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 234.78 | 15.47 | 6.77 |
| ZYC-46 | 黄土 | 36.63 | 100.87 | <75 μm | 87.71 | 59.35 | 12.60 | 4.77 | 15.17 | 1.58 | 2.46 | 2.85 | 0.63 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 257.75 | 14.86 | 6.85 |
| HYW-2 | 黄土 | 36.82 | 100.80 | <75 μm | 86.91 | 58.39 | 11.91 | 4.35 | 17.49 | 1.08 | 2.27 | 3.41 | 0.58 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 288.76 | 14.57 | 6.73 |
| HBB-1 | 古土壤 | 37.03 | 100.78 | <75 μm | 87.68 | 62.34 | 13.49 | 5.21 | 11.62 | 1.00 | 2.57 | 2.54 | 0.66 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 262.56 | 16.32 | 7.27 |
| HBB-2 | 黄土 | 37.03 | 100.78 | <75 μm | 88.83 | 62.59 | 13.00 | 4.68 | 11.28 | 1.49 | 2.36 | 3.42 | 0.64 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 299.48 | 14.99 | 7.29 |
| XH-2 | 古土壤 | 37.06 | 100.72 | <75 μm | 87.79 | 64.44 | 13.07 | 5.27 | 9.90 | 1.10 | 2.70 | 2.24 | 0.68 | 0.23 | 0.10 | 296.23 | 16.80 | 7.52 |
| GC-1 | 黄土 | 37.33 | 100.12 | <75 μm | 89.10 | 64.57 | 13.04 | 4.86 | 9.32 | 1.48 | 2.23 | 3.37 | 0.64 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 379.09 | 15.49 | 7.53 |
| SNH-1 | 黄土 | 36.98 | 99.60 | <75 μm | 86.41 | 60.51 | 12.36 | 4.48 | 15.53 | 0.96 | 2.50 | 2.56 | 0.60 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 258.41 | 15.48 | 6.99 |
| QHH-1 | 古土壤 | 36.84 | 99.71 | <75 μm | 89.03 | 65.43 | 13.79 | 4.93 | 8.27 | 1.36 | 2.53 | 2.50 | 0.67 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 268.61 | 15.80 | 7.65 |
| HMH | 古土壤 | 36.75 | 99.75 | <75 μm | 86.86 | 63.90 | 12.51 | 4.79 | 11.85 | 1.11 | 2.41 | 2.28 | 0.66 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 272.67 | 16.80 | 7.46 |
| HMH* | 古土壤 | 36.75 | 99.75 | <75 μm | 86.85 | 63.72 | 12.61 | 4.81 | 11.91 | 1.11 | 2.43 | 2.28 | 0.63 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 269.44 | 16.06 | 7.44 |
| JXG-1 | 古土壤 | 36.59 | 100.30 | <75 μm | 87.30 | 63.88 | 12.82 | 5.17 | 10.85 | 1.18 | 2.42 | 2.35 | 0.65 | 0.34 | 0.09 | 265.69 | 16.09 | 7.41 |
| JXG-2 | 黄土 | 36.59 | 100.30 | <75 μm | 88.69 | 62.80 | 13.05 | 4.66 | 11.17 | 1.35 | 2.40 | 3.38 | 0.64 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 284.27 | 15.89 | 7.34 |
| 151-1 | 古土壤 | 36.56 | 100.47 | <75 μm | 88.73 | 65.75 | 13.28 | 5.12 | 8.22 | 1.30 | 2.76 | 2.32 | 0.68 | 0.25 | 0.10 | 256.37 | 14.93 | 7.66 |
| 151-2 | 古土壤 | 36.56 | 100.47 | <75 μm | 89.17 | 65.18 | 13.81 | 5.34 | 8.02 | 1.21 | 2.74 | 2.48 | 0.67 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 265.48 | 16.06 | 7.52 |
| EH-1 | 黄土 | 36.55 | 100.72 | <75 μm | 87.49 | 60.84 | 11.85 | 4.57 | 14.42 | 1.60 | 2.33 | 3.28 | 0.59 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 248.76 | 15.41 | 7.08 |
| DTH-7 | 古土壤 | 36.43 | 101.07 | <75 μm | 87.96 | 61.20 | 13.06 | 5.16 | 12.74 | 0.92 | 2.60 | 3.13 | 0.65 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 238.89 | 15.90 | 7.11 |
| DTH-9 | 古土壤 | 36.51 | 100.91 | <75 μm | 88.16 | 65.25 | 13.44 | 5.54 | 8.67 | 1.10 | 2.63 | 2.11 | 0.70 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 259.77 | 16.97 | 7.60 |
| DTH-11 | 黄土 | 36.55 | 100.88 | <75 μm | 86.13 | 57.37 | 11.58 | 4.59 | 19.46 | 0.82 | 2.23 | 2.84 | 0.58 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 229.07 | 14.13 | 6.51 |
| RYS-1 | 古土壤 | 36.43 | 101.11 | <75 μm | 89.71 | 66.35 | 14.02 | 5.64 | 6.32 | 1.16 | 2.80 | 2.41 | 0.70 | 0.21 | 0.11 | 256.62 | 16.85 | 7.72 |
| RYS-2 | 古土壤 | 36.43 | 101.11 | <75 μm | 88.80 | 65.90 | 13.60 | 5.61 | 7.55 | 1.14 | 2.74 | 2.22 | 0.70 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 249.12 | 16.72 | 7.68 |
| RYS-3 | 黄土 | 36.43 | 101.11 | <75 μm | 89.18 | 64.64 | 13.70 | 5.14 | 8.75 | 1.30 | 2.60 | 2.68 | 0.67 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 263.10 | 15.33 | 7.54 |
| RYS-5 | 古土壤 | 36.43 | 101.07 | <75 μm | 88.40 | 63.67 | 13.17 | 4.98 | 10.20 | 1.72 | 2.47 | 2.58 | 0.68 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 285.92 | 14.15 | 7.45 |
| RYS-5 | 古土壤 | 36.43 | 101.07 | <75 μm | 88.31 | 63.55 | 13.16 | 4.97 | 10.37 | 1.70 | 2.49 | 2.57 | 0.66 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 279.93 | 14.92 | 7.44 |
| RYS-6 | 黄土 | 36.43 | 101.07 | <75 μm | 86.97 | 59.43 | 12.97 | 4.56 | 15.50 | 1.29 | 2.32 | 2.82 | 0.61 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 265.71 | 15.74 | 6.89 |
| LM-1 | 古土壤 | 36.24 | 101.08 | <75 μm | 87.77 | 64.10 | 12.92 | 4.93 | 10.61 | 1.15 | 2.57 | 2.55 | 0.66 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 284.48 | 16.03 | 7.45 |
| LM-2 | 黄土 | 36.24 | 101.08 | <75 μm | 87.77 | 60.41 | 12.05 | 4.30 | 14.74 | 1.52 | 2.30 | 3.61 | 0.59 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 247.95 | 13.66 | 7.01 |
| TJ-1 | 古土壤 | 37.29 | 99.04 | <75 μm | 88.11 | 63.95 | 13.21 | 4.89 | 10.46 | 1.36 | 2.49 | 2.44 | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 269.71 | 14.56 | 7.46 |
| TJ-2 | 黄土 | 37.29 | 99.04 | <75 μm | 87.42 | 64.79 | 12.26 | 4.31 | 11.28 | 1.53 | 2.29 | 2.32 | 0.69 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 311.47 | 14.23 | 7.55 |
| TJ-3 | 古土壤 | 37.20 | 98.89 | <75 μm | 88.03 | 65.09 | 13.04 | 5.16 | 9.26 | 1.10 | 2.58 | 2.57 | 0.66 | 0.19 | 0.10 | 253.91 | 15.45 | 7.62 |
| TJ-4 | 黄土 | 37.20 | 98.89 | <75 μm | 88.92 | 61.50 | 14.14 | 4.73 | 11.37 | 1.33 | 2.55 | 3.24 | 0.64 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 290.76 | 15.73 | 7.16 |
| WL | 黄土 | 36.94 | 98.40 | <75 μm | 91.38 | 59.05 | 15.04 | 5.55 | 10.89 | 1.63 | 2.92 | 3.62 | 0.71 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 189.26 | 17.35 | 6.75 |
| WL* | 黄土 | 36.94 | 98.40 | <75 μm | 91.38 | 59.16 | 14.97 | 5.55 | 10.84 | 1.64 | 2.91 | 3.63 | 0.71 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 192.38 | 14.45 | 6.82 |
| CK | 黄土 | 36.79 | 99.11 | <75 μm | 89.80 | 64.22 | 12.77 | 4.24 | 9.96 | 1.93 | 2.48 | 3.18 | 0.65 | 0.18 | 0.09 | 345.18 | 15.89 | 7.34 |
| LYX-1 | 黄土 | 36.15 | 100.95 | <75 μm | 85.78 | 56.84 | 10.56 | 3.99 | 21.45 | 1.14 | 2.10 | 2.90 | 0.55 | 0.17 | 0.07 | 243.90 | 14.06 | 6.52 |
| YJC-40a | 黄土 | 36.73 | 101.79 | <75 μm | 88.44 | 63.42 | 13.01 | 4.44 | 11.16 | 1.46 | 2.45 | 2.94 | 0.62 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 270.25 | 16.15 | 7.35 |
| LD-1a | 黄土 | 36.43 | 102.56 | <75 μm | 88.76 | 64.49 | 12.64 | 4.41 | 10.37 | 1.68 | 2.38 | 2.88 | 0.65 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 310.73 | 15.45 | 7.45 |
| HQSK-1 | 黄土 | 37.20 | 101.54 | <75 μm | 88.46 | 62.57 | 13.90 | 4.67 | 10.40 | 2.02 | 2.61 | 2.62 | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.10 | 281.45 | 14.68 | 7.49 |
| HQSK-2 | 古土壤 | 37.25 | 101.45 | <75 μm | 91.36 | 66.87 | 14.92 | 5.20 | 4.72 | 1.81 | 2.80 | 2.33 | 0.73 | 0.24 | 0.13 | 297.33 | 15.86 | 7.82 |
| QSZ-1 | 古土壤 | 37.63 | 101.36 | <75 μm | 90.83 | 66.49 | 16.27 | 6.31 | 2.30 | 1.52 | 3.30 | 2.39 | 0.77 | 0.23 | 0.13 | 274.72 | 17.47 | 8.22 |
| QSZ-2 | 黄土 | 37.63 | 101.36 | <75 μm | 83.18 | 59.40 | 14.86 | 5.27 | 12.47 | 1.43 | 2.79 | 2.56 | 0.66 | 0.20 | 0.11 | 254.95 | 15.54 | 7.86 |
| AR-1 | 古土壤 | 38.06 | 100.46 | <75 μm | 91.21 | 63.14 | 16.20 | 6.34 | 4.97 | 1.68 | 3.10 | 3.19 | 0.79 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 265.27 | 18.56 | 7.72 |
| WC-1 | 黄土 | 36.73 | 104.09 | <75 μm | 90.05 | 63.02 | 13.19 | 5.07 | 9.72 | 2.04 | 2.49 | 3.28 | 0.69 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 250.88 | 15.16 | 7.32 |
| WC-1* | 黄土 | 36.73 | 104.09 | <75 μm | 90.13 | 63.43 | 12.95 | 5.08 | 9.54 | 2.14 | 2.47 | 3.20 | 0.69 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 246.68 | 15.59 | 7.30 |
| WC-2 | 黄土 | 36.73 | 104.09 | <75 μm | 89.35 | 62.10 | 12.47 | 4.77 | 11.47 | 2.25 | 2.41 | 3.39 | 0.65 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 250.22 | 15.24 | 7.15 |
| JZT-1 | 黄土 | 36.10 | 103.78 | <75 μm | 88.50 | 65.57 | 12.45 | 4.43 | 9.82 | 1.39 | 2.35 | 2.89 | 0.62 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 260.28 | 14.06 | 7.57 |
| DXX-1 | 古土壤 | 35.65 | 103.40 | <75 μm | 87.03 | 63.97 | 12.93 | 4.64 | 11.52 | 1.11 | 2.42 | 2.23 | 0.65 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 279.23 | 14.51 | 7.53 |
| DXX-2 | 黄土 | 35.65 | 103.40 | <75 μm | 87.97 | 64.35 | 12.65 | 4.65 | 10.87 | 1.40 | 2.34 | 2.60 | 0.65 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 262.60 | 16.16 | 7.42 |
| HZ-1 | 古土壤 | 34.99 | 102.92 | <75 μm | 87.97 | 66.88 | 13.04 | 4.52 | 8.63 | 1.23 | 2.50 | 2.05 | 0.63 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 291.88 | 14.80 | 7.73 |
| HZ-2 | 黄土 | 34.99 | 102.92 | <75 μm | 88.20 | 66.72 | 12.41 | 4.25 | 9.29 | 1.44 | 2.41 | 2.43 | 0.59 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 258.40 | 14.98 | 7.70 |
| LMS-1 | 黄土 | 34.11 | 102.64 | <75 μm | 93.11 | 73.44 | 13.37 | 4.79 | 1.18 | 1.74 | 2.63 | 1.73 | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.06 | 274.01 | 17.82 | 8.10 |
| HR-1 | 古土壤 | 35.30 | 101.18 | <75 μm | 88.09 | 67.92 | 12.75 | 4.86 | 7.48 | 1.27 | 2.47 | 2.02 | 0.68 | 0.20 | 0.09 | 339.24 | 16.11 | 7.79 |
| MD-5 | 黄土 | 34.97 | 98.11 | <75 μm | 86.77 | 70.05 | 10.66 | 3.30 | 9.59 | 1.29 | 1.97 | 2.11 | 0.60 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 351.33 | 14.18 | 7.87 |
| MD-6 | 黄土 | 34.97 | 98.11 | <75 μm | 87.33 | 67.69 | 11.66 | 3.57 | 10.07 | 1.18 | 2.19 | 2.60 | 0.60 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 398.12 | 16.20 | 7.71 |
| HHX-1 | 黄土 | 34.67 | 98.15 | <75 μm | 87.11 | 70.29 | 11.80 | 3.72 | 7.91 | 1.21 | 2.27 | 1.68 | 0.63 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 481.64 | 15.23 | 7.92 |
| HHX-2 | 黄土 | 34.67 | 98.15 | <75 μm | 86.05 | 64.56 | 13.02 | 4.03 | 12.00 | 0.96 | 2.49 | 1.86 | 0.58 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 306.12 | 13.19 | 7.48 |
| 平均值b | 63.58 | 13.10 | 4.84 | 10.72 | 1.38 | 2.52 | 2.66 | 0.65 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 277.20 | 15.65 | 7.40 | |||||
| ZYC-57 | 风成砂 | 36.63 | 100.87 | <75 μm | 86.84 | 64.30 | 11.37 | 3.78 | 12.92 | 1.80 | 2.25 | 2.46 | 0.61 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 371.65 | 15.14 | 7.65 |
| ZYC-60 | 风成砂 | 36.63 | 100.87 | <75 μm | 87.26 | 63.68 | 11.79 | 3.93 | 12.80 | 1.72 | 2.33 | 2.62 | 0.61 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 345.19 | 14.58 | 7.51 |
| HD-A | 风成砂 | 36.76 | 100.77 | <75 μm | 86.55 | 63.87 | 11.23 | 4.21 | 13.17 | 1.62 | 1.93 | 2.39 | 0.89 | 0.24 | 0.09 | 1381.12 | 22.95 | 7.86 |
| HD-B | 风成砂 | 36.74 | 100.77 | <75 μm | 86.96 | 62.88 | 11.24 | 4.78 | 13.09 | 1.68 | 1.90 | 2.58 | 1.07 | 0.28 | 0.10 | 1842.33 | 29.68 | 7.91 |
| HD-C | 风成砂 | 36.73 | 100.78 | <75 μm | 86.87 | 61.44 | 11.20 | 5.27 | 13.91 | 1.61 | 1.85 | 2.62 | 1.23 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 2174.15 | 31.58 | 7.98 |
| SNH | 风成砂 | 36.98 | 99.60 | <75 μm | 88.05 | 64.57 | 12.17 | 3.90 | 11.45 | 1.82 | 2.39 | 2.63 | 0.59 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 270.32 | 13.69 | 7.51 |
| SNH-2 | 风成砂 | 36.98 | 99.60 | <75 μm | 87.11 | 64.67 | 11.62 | 3.95 | 12.20 | 1.58 | 2.17 | 2.67 | 0.63 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 388.50 | 14.68 | 7.54 |
| RYS-4 | 风成砂 | 36.43 | 101.11 | <75 μm | 87.53 | 69.38 | 12.11 | 3.53 | 8.16 | 1.47 | 2.27 | 2.17 | 0.49 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 272.27 | 13.70 | 7.95 |
| JXG-3 | 风成砂 | 36.59 | 100.30 | <75 μm | 87.51 | 64.22 | 11.85 | 4.06 | 12.17 | 1.58 | 2.09 | 2.80 | 0.66 | 0.23 | 0.08 | 585.17 | 16.48 | 7.55 |
| GC-2 | 风成砂 | 37.33 | 100.12 | <75 μm | 89.56 | 65.84 | 12.78 | 4.66 | 8.40 | 2.08 | 2.19 | 2.88 | 0.65 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 531.51 | 16.94 | 7.67 |
| LM-3 | 风成砂 | 36.24 | 101.08 | <75 μm | 89.22 | 62.55 | 13.42 | 4.38 | 10.92 | 1.88 | 2.50 | 3.26 | 0.59 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 293.54 | 14.29 | 7.29 |
| YQZ-1 | 风成砂 | 38.23 | 91.41 | <75 μm | 90.24 | 65.77 | 10.83 | 3.44 | 9.53 | 4.16 | 2.27 | 3.05 | 0.53 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 244.30 | 15.06 | 7.61 |
| YQZ-3 | 风成砂 | 38.23 | 91.38 | <75 μm | 90.61 | 60.70 | 15.47 | 6.31 | 9.19 | 1.08 | 2.90 | 3.12 | 0.70 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 152.19 | 15.00 | 7.16 |
| XT-3 | 风成砂 | 38.05 | 93.14 | <75 μm | 90.97 | 60.95 | 9.37 | 3.72 | 13.02 | 4.57 | 1.82 | 5.23 | 0.74 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 611.20 | 17.81 | 7.30 |
| HX-1 | 风成砂 | 37.28 | 97.45 | <75 μm | 84.99 | 58.44 | 11.33 | 4.15 | 19.20 | 1.33 | 2.00 | 2.34 | 0.71 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 464.20 | 17.74 | 7.25 |
| AM-1 | 风成砂 | 36.88 | 96.56 | <75 μm | 88.06 | 70.12 | 10.55 | 3.34 | 8.89 | 1.85 | 2.08 | 2.01 | 0.66 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 542.60 | 15.98 | 7.94 |
| AM-3 | 风成砂 | 36.97 | 96.26 | <75 μm | 88.49 | 67.35 | 10.88 | 3.49 | 9.59 | 2.38 | 2.03 | 3.18 | 0.57 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 451.25 | 15.48 | 7.74 |
| ZJN-2 | 风成砂 | 36.35 | 97.19 | <75 μm | 92.18 | 61.90 | 10.23 | 4.37 | 11.02 | 3.34 | 2.04 | 5.74 | 0.76 | 0.22 | 0.08 | 798.16 | 19.47 | 7.29 |
| NMHN-1 | 风成砂 | 36.76 | 96.51 | <75 μm | 89.33 | 62.50 | 12.90 | 4.14 | 11.09 | 1.76 | 2.42 | 4.03 | 0.54 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 261.10 | 11.25 | 7.22 |
| NMHN-2 | 风成砂 | 36.76 | 96.51 | <75 μm | 89.20 | 61.80 | 13.21 | 4.45 | 11.59 | 1.48 | 2.50 | 3.74 | 0.59 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 279.67 | 14.71 | 7.21 |
| NMHN-3 | 风成砂 | 36.77 | 96.52 | <75 μm | 88.94 | 61.49 | 12.78 | 4.16 | 12.22 | 2.28 | 2.43 | 3.51 | 0.54 | 0.15 | 0.07 | 235.20 | 10.40 | 7.16 |
| DGL-1 | 风成砂 | 36.39 | 95.75 | <75 μm | 87.63 | 67.13 | 10.32 | 3.71 | 11.11 | 1.78 | 1.93 | 2.82 | 0.66 | 0.22 | 0.07 | 511.67 | 17.03 | 7.66 |
| HHX-3 | 风成砂 | 34.67 | 98.15 | <75 μm | 83.98 | 57.97 | 12.32 | 3.45 | 20.47 | 1.05 | 1.98 | 1.73 | 0.54 | 0.13 | 0.10 | 219.75 | 10.31 | 6.91 |
| HHX-5 | 风成砂 | 34.74 | 98.12 | <75 μm | 86.28 | 71.44 | 10.06 | 3.07 | 9.62 | 1.41 | 1.76 | 1.55 | 0.64 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 457.43 | 14.39 | 7.97 |
| MD-2 | 风成砂 | 34.80 | 98.14 | <75 μm | 88.04 | 71.29 | 11.34 | 3.59 | 7.43 | 1.43 | 2.03 | 1.67 | 0.70 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 798.03 | 17.25 | 7.93 |
| HR-2 | 风成砂 | 35.30 | 101.18 | <75 μm | 87.92 | 66.63 | 12.03 | 4.06 | 9.90 | 1.44 | 2.27 | 2.54 | 0.63 | 0.18 | 0.08 | 403.15 | 16.08 | 7.65 |
| AR-2 | 风成砂 | 38.06 | 100.46 | <75 μm | 88.34 | 64.93 | 13.33 | 4.40 | 8.72 | 1.91 | 2.47 | 3.07 | 0.62 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 273.16 | 12.93 | 7.66 |
| 平均值 | 64.36 | 11.77 | 4.09 | 11.55 | 1.93 | 2.18 | 2.90 | 0.67 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 561.44 | 16.47 | 7.56 | |||||
| BHH-1 | 河流沉积 | 37.03 | 99.74 | <75 μm | 87.16 | 65.06 | 11.91 | 3.96 | 11.61 | 1.83 | 2.11 | 2.20 | 0.75 | 0.20 | 0.07 | 731.23 | 19.73 | 7.86 |
| BHH-2 | 河流沉积 | 37.03 | 99.74 | <75 μm | 87.77 | 62.37 | 13.18 | 4.33 | 12.43 | 1.60 | 2.39 | 2.53 | 0.65 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 292.80 | 16.78 | 7.30 |
| BHH-3 | 河流沉积 | 37.04 | 99.74 | <75 μm | 87.02 | 65.53 | 11.66 | 4.25 | 11.43 | 1.51 | 2.08 | 2.26 | 0.71 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 836.20 | 18.90 | 7.81 |
| DTHS-1 | 河流沉积 | 36.26 | 101.07 | <75 μm | 87.67 | 66.50 | 11.67 | 4.00 | 10.15 | 1.97 | 2.03 | 2.35 | 0.76 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 839.65 | 19.57 | 7.78 |
| DTHS-2 | 河流沉积 | 36.26 | 101.07 | <75 μm | 87.66 | 67.48 | 12.10 | 3.86 | 9.55 | 1.60 | 2.24 | 2.08 | 0.63 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 400.95 | 15.70 | 7.71 |
| JXG-R | 河流沉积 | 36.59 | 100.30 | <75 μm | 89.62 | 74.39 | 10.43 | 3.39 | 5.23 | 1.82 | 2.06 | 1.48 | 0.70 | 0.19 | 0.06 | 623.57 | 17.22 | 8.10 |
| RSC-1 | 河流沉积 | 37.16 | 100.54 | <75 μm | 87.91 | 67.79 | 12.14 | 4.21 | 8.90 | 1.41 | 2.32 | 2.07 | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 442.65 | 17.19 | 7.84 |
| SLH-1 | 河流沉积 | 37.33 | 100.12 | <75 μm | 89.53 | 68.90 | 12.49 | 5.22 | 6.08 | 1.62 | 2.19 | 2.21 | 0.70 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 763.06 | 18.34 | 7.92 |
| LM-4 | 河流沉积 | 36.24 | 101.08 | <75 μm | 87.20 | 65.00 | 11.55 | 4.58 | 11.25 | 1.66 | 2.08 | 2.39 | 0.84 | 0.22 | 0.09 | 1303.52 | 23.08 | 7.72 |
| KLKH-N | 洪积物 | 37.36 | 96.81 | <75 μm | 87.70 | 63.89 | 11.77 | 4.21 | 12.20 | 1.71 | 2.19 | 2.85 | 0.68 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 407.88 | 16.45 | 7.42 |
| DCD-1 | 洪积物 | 37.73 | 95.44 | <75 μm | 91.22 | 64.43 | 14.76 | 4.39 | 7.50 | 1.67 | 2.94 | 3.31 | 0.57 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 300.47 | 13.67 | 7.51 |
| TSHW-1 | 河流沉积 | 37.17 | 96.66 | <75 μm | 87.25 | 64.62 | 11.38 | 4.17 | 12.16 | 1.60 | 2.19 | 2.56 | 0.74 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 852.00 | 17.80 | 7.64 |
| ZJN-1 | 河流沉积 | 36.35 | 97.02 | <75 μm | 89.00 | 68.38 | 10.72 | 4.08 | 8.82 | 1.97 | 2.17 | 2.72 | 0.64 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 281.70 | 15.29 | 7.73 |
| 平均值 | 66.49 | 11.98 | 4.20 | 9.79 | 1.69 | 2.23 | 2.39 | 0.70 | 0.19 | 0.08 | 621.21 | 17.67 | 7.72 | |||||
| ELJ-1 | 湖相沉积 | 36.65 | 100.43 | <75 μm | 89.80 | 65.68 | 12.77 | 4.37 | 8.84 | 2.16 | 2.51 | 2.47 | 0.69 | 0.17 | 0.08 | 491.58 | 16.51 | 7.66 |
| ELJ-2 | 湖相沉积 | 36.65 | 100.43 | <75 μm | 90.79 | 61.97 | 14.61 | 5.74 | 8.98 | 1.79 | 2.83 | 2.80 | 0.75 | 0.17 | 0.09 | 373.31 | 18.17 | 7.32 |
| HYW-3 | 湖相沉积 | 36.82 | 100.80 | <75 μm | 91.04 | 48.97 | 13.55 | 5.11 | 24.06 | 0.96 | 2.52 | 3.71 | 0.57 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 244.46 | 11.19 | 5.35 |
| GH-1 | 湖相沉积 | 37.02 | 100.59 | <75 μm | 87.57 | 67.61 | 10.81 | 4.42 | 9.60 | 1.48 | 2.06 | 2.39 | 0.94 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 1094.26 | 20.24 | 7.91 |
| GH-2 | 湖相沉积 | 37.02 | 100.59 | <75 μm | 88.47 | 69.38 | 11.01 | 4.35 | 7.91 | 1.51 | 2.24 | 2.33 | 0.68 | 0.28 | 0.07 | 513.34 | 17.58 | 7.95 |
| BQD-1 | 湖相沉积 | 36.52 | 96.20 | <75 μm | 86.95 | 67.82 | 10.64 | 4.03 | 10.35 | 1.91 | 2.09 | 2.01 | 0.63 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 379.71 | 15.02 | 7.84 |
| HTTL-1 | 湖相沉积 | 37.37 | 96.75 | <75 μm | 90.79 | 66.34 | 14.52 | 5.55 | 5.87 | 1.75 | 2.83 | 1.95 | 0.69 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 235.98 | 16.08 | 7.67 |
| NLZN | 湖相沉积 | 38.62 | 93.51 | <75 μm | 88.94 | 66.28 | 11.97 | 4.45 | 9.12 | 1.98 | 2.38 | 2.64 | 0.70 | 0.19 | 0.07 | 318.26 | 15.06 | 7.72 |
| XT-1 | 湖相沉积 | 38.05 | 93.14 | 全岩 | 91.62 | 58.12 | 10.73 | 3.91 | 14.88 | 2.05 | 2.10 | 7.11 | 0.58 | 0.20 | 0.08 | 341.49 | 14.84 | 6.79 |
| YQZ-2 | 湖相沉积 | 38.23 | 91.41 | 全岩 | 93.48 | 51.55 | 9.62 | 3.70 | 22.31 | 1.63 | 1.88 | 8.31 | 0.46 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 159.72 | 9.41 | 5.70 |
| YQZ-6 | 湖相沉积 | 38.38 | 91.31 | 全岩 | 95.13 | 58.85 | 15.74 | 6.24 | 7.31 | 1.98 | 3.36 | 5.39 | 0.65 | 0.15 | 0.11 | 129.52 | 14.43 | 6.82 |
| NMHN-4 | 湖相沉积 | 36.77 | 96.52 | 全岩 | 93.09 | 60.34 | 17.41 | 5.01 | 6.86 | 2.76 | 3.46 | 3.23 | 0.56 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 120.41 | 11.73 | 6.91 |
| NMHN-5 | 湖相沉积 | 36.77 | 96.52 | 全岩 | 93.38 | 67.50 | 14.32 | 7.11 | 2.18 | 2.47 | 2.87 | 2.38 | 0.66 | 0.15 | 0.04 | 240.79 | 15.83 | 7.95 |
| XT-2 | 湖相沉积 | 37.70 | 93.61 | 全岩 | 88.88 | 52.81 | 9.26 | 3.00 | 26.41 | 2.34 | 1.96 | 3.39 | 0.34 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 120.68 | 6.27 | 5.78 |
| LH2 | 湖相沉积 | 38.66 | 93.39 | 全岩 | 93.94 | 60.04 | 13.56 | 4.67 | 9.21 | 1.19 | 2.67 | 7.61 | 0.56 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 179.20 | 14.00 | 6.95 |
| YD-1 | 湖相沉积 | 38.66 | 93.27 | 全岩 | 91.21 | 55.99 | 12.70 | 4.79 | 15.77 | 1.26 | 2.52 | 5.92 | 0.52 | 0.18 | 0.10 | 152.91 | 12.40 | 6.30 |
| YD-2 | 湖相沉积 | 38.51 | 92.76 | 全岩 | 89.31 | 52.52 | 9.71 | 3.29 | 25.94 | 1.97 | 2.18 | 3.57 | 0.34 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 106.53 | 5.35 | 5.67 |
| YD-3 | 湖相沉积 | 38.30 | 92.23 | 全岩 | 90.63 | 55.63 | 11.88 | 4.42 | 17.36 | 1.21 | 2.44 | 5.99 | 0.55 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 183.28 | 11.83 | 6.37 |
| YD-3* | 湖相沉积 | 38.30 | 92.23 | 全岩 | 91.25 | 54.76 | 12.25 | 4.49 | 17.48 | 1.27 | 2.48 | 6.19 | 0.57 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 184.76 | 11.65 | 6.22 |
| YD-4 | 湖相沉积 | 38.03 | 91.85 | 全岩 | 88.70 | 57.96 | 10.37 | 2.38 | 18.32 | 3.48 | 2.12 | 4.74 | 0.32 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 107.53 | 7.19 | 6.97 |
| AM-2 | 湖相沉积 | 36.97 | 96.26 | 全岩 | 90.75 | 63.66 | 14.64 | 5.79 | 7.63 | 1.73 | 2.89 | 2.50 | 0.69 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 191.98 | 16.52 | 7.29 |
| TSHW-2 | 湖相沉积 | 37.17 | 96.66 | 全岩 | 91.30 | 64.69 | 14.61 | 6.11 | 6.19 | 1.73 | 2.63 | 2.79 | 0.77 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 231.82 | 17.28 | 7.56 |
| 平均值b | 60.65 | 12.59 | 4.69 | 12.62 | 1.87 | 2.50 | 3.96 | 0.60 | 0.16 | 0.08 | 281.75 | 13.66 | 6.98 | |||||
| UCC c | 66 | 15.2 | 5.0 | 4.2 | 3.9 | 3.4 | 2.2 | 0.68 | 0.16 | 0.08 |
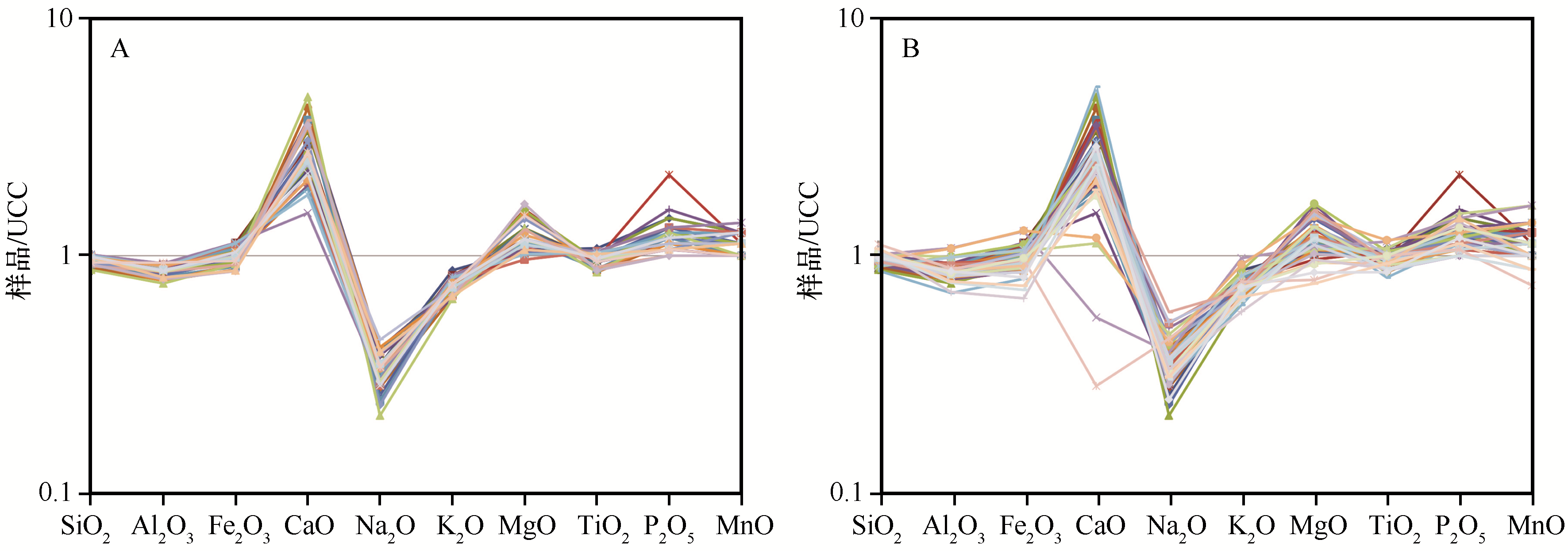
图2 晚第四纪黄土-古土壤常量元素含量UCC标准化图(A,青海湖地区;B,青藏高原东北部)
Fig.2 UCC-normalized abundances of major elements for the loess and paleosol samples from Qinghai Lake area (A), and northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau (B)
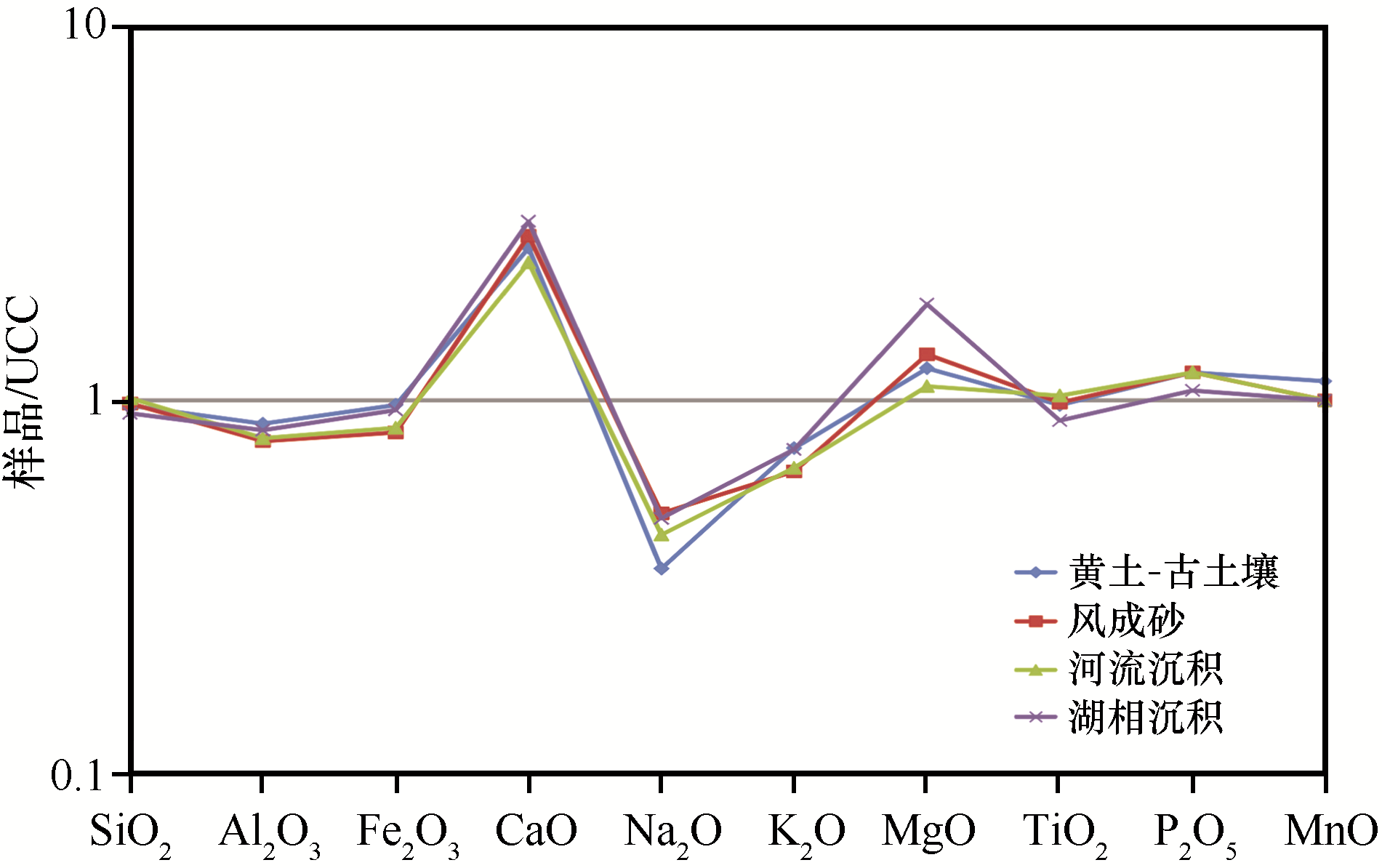
图3 青藏高原东北部各类样品常量元素含量平均值UCC标准化图
Fig.3 UCC-normalized abundances of major elements (average value) for different samples from the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
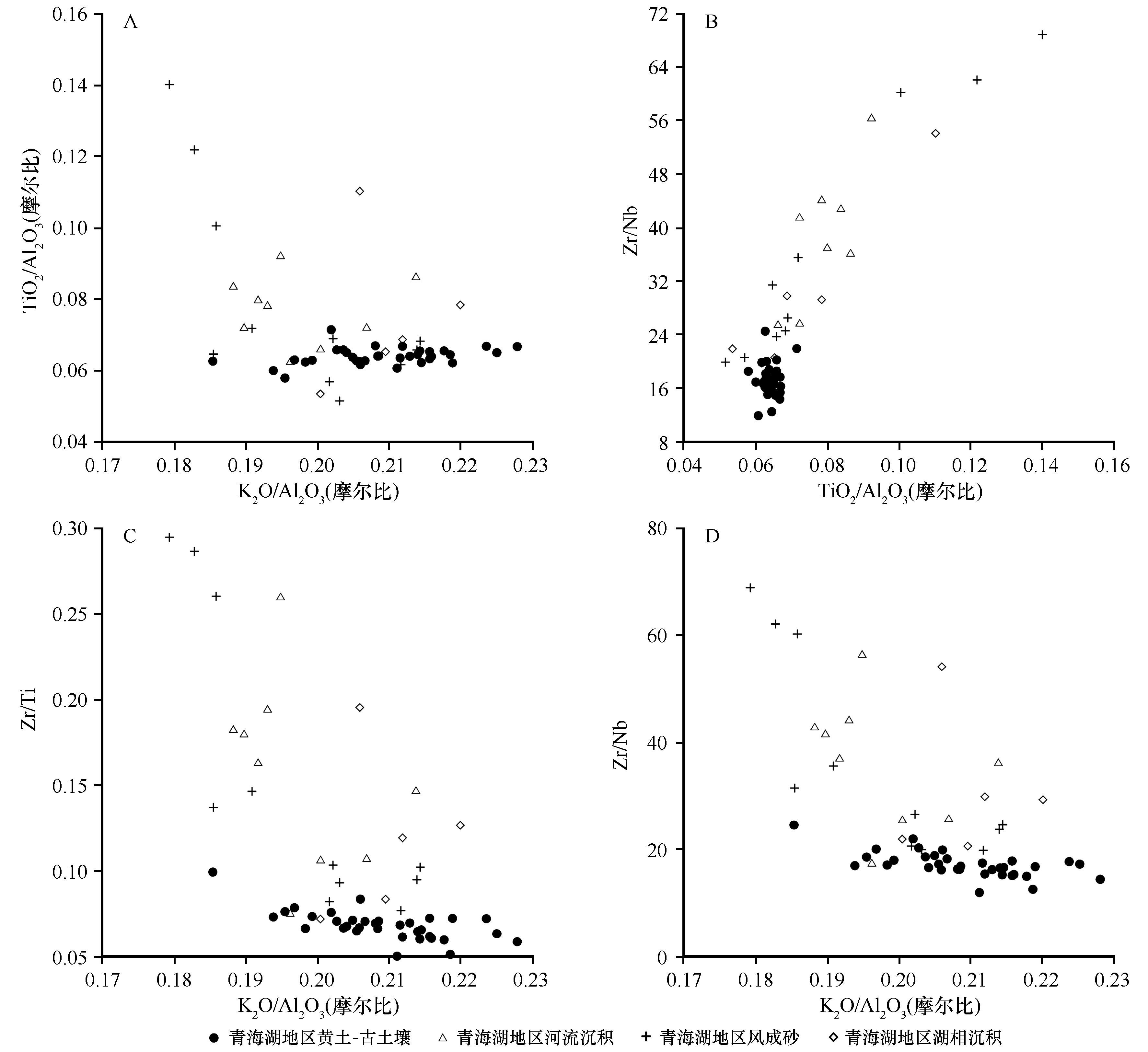
图5 青海湖地区各类样品的K2O/Al2O3-TiO2/Al2O3、TiO2/Al2O3-Zr/Nb、K2O/Al2O3-Zr/Ti、K2O3/Al2O3-Zr/Nb图解
Fig.5 Plots of K2O/Al2O3 vs. TiO2/Al2O3, TiO2/Al2O3 vs. Zr/Nb, K2O/Al2O3 vs. Zr/Ti, and K2O3/Al2O3 vs. Zr/Nb for samples from the Qinghai Lake area
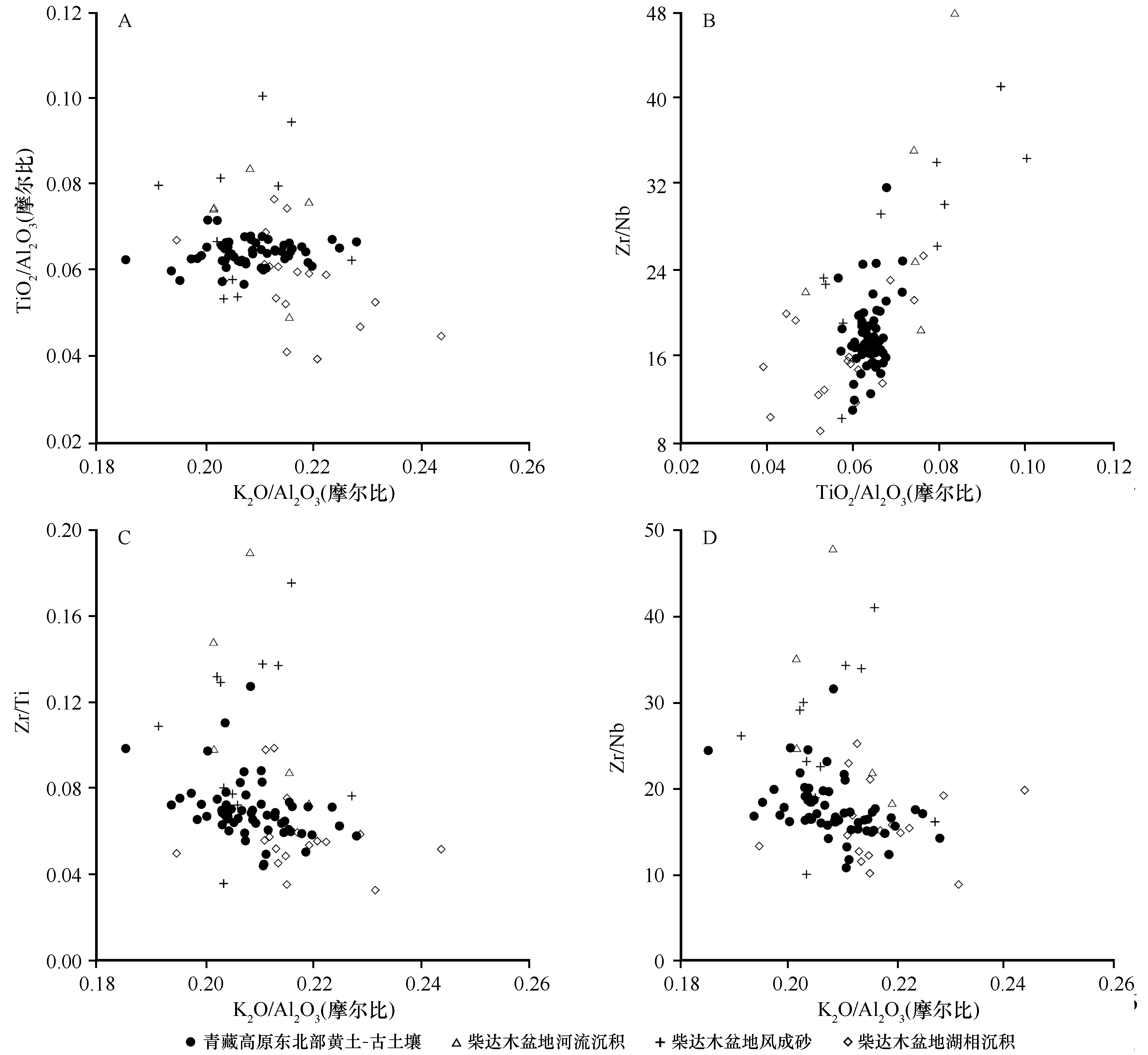
图6 青藏高原东北部各类样品的K2O/Al2O3-TiO2/Al2O3、TiO2/Al2O3-Zr/Nb、K2O/Al2O3-Zr/Ti、K2O3/Al2O3-Zr/Nb图解
Fig.6 Plots of K2O/Al2O3 vs. TiO2/Al2O3, TiO2/Al2O3 vs. Zr/Nb, K2O/Al2O3 vs. Zr/Ti, and K2O3/Al2O3 vs. Zr/Nb for samples from the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
| 1 | 刘东生等.黄土与环境[M].北京:科学出版社,1985. |
| 2 | Ding Z L,Derbyshire E,Yang S L,et al.Stacked 2.6-Ma grain size record from the Chinese loess based on five sections and correlation with the deep-sea δ18O record[J].Paleoceanography,2002,17(3):1003-1023. |
| 3 | Gao L,Nie J S,Clemens S,et al.The importance of solar insolation on the temperature variations for the past 110 kyr on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2012,317/318:128-133. |
| 4 | Liu X M,Rolph T,Bloemendal J,et al.Quantitative estimates of palaeoprecipitation at Xifeng,in the Loess Plateau of China[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,1995,113(2):243-248. |
| 5 | Liu T S,Ding Z L.Chinese loess and the paleomonsoon[J].Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences,1998,26:111-145. |
| 6 | An Z S,Kukla G J,Porter S C,et al.Magnetic susceptibility evidence of monsoon variation on the Loess Plateau of Central China during the last 130,000 years[J].Quaternary Research,1991,36(1):29-36. |
| 7 | Kang S,Du J,Wang N,et al.Early Holocene weakening and mid- to late Holocene strengthening of the East Asian winter monsoon[J].Geology,2020.Doi:10.1130/G47621.1. |
| 8 | Jiang W,Cheng Y,Yang X,et al.Chinese Loess Plateau vegetation since the Last Glacial Maximum and its implications for vegetation restoration[J].Journal of Applied Ecology,2013,50:440-448. |
| 9 | Zhu Z Y,Dennell R,Huang W W,et al.Hominin occupation of the Chinese Loess Plateau since about 2.1 million years ago[J].Nature,2018,559(7715):608-612. |
| 10 | Hao Q Z,Wang L,Oldfield F,et al.Delayed build-up of Arctic ice sheets during 400,000-year minima in insolation variability[J].Nature,2012,490(7420):393-396. |
| 11 | Ding Z L,Sun J M,Yang S L,et al.Geochemistry of the Pliocene red clay formation in the Chinese Loess Plateau and implications for its origin,source provenance and paleoclimate change[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2001,65(6):901-913. |
| 12 | Guo Z T,Peng S Z,Hao Q Z,et al.Origin of the Miocene-Pliocene Red-Earth formation at Xifeng in northern China and implications for paleoenvironments[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2001,170(1/2):11-26. |
| 13 | Guo Z T,Ruddiman W F,Hao Q Z,et al.Onset of Asian desertification by 22 Myr ago inferred from loess deposits in China[J].Nature,2002,416(6877):159-163. |
| 14 | Heller F,Liu T S.Magnetostratigraphical dating of loess deposits in China[J].Nature,1982,300(5891):431-433. |
| 15 | Sun Y B,Clemens S C,Morrill C,et al.Influence of Atlantic meridional overturning circulation on the East Asian winter monsoon[J].Nature Geoscience,2012,5(1):46-49. |
| 16 | Zeng F M,Liu X J,Li X Z,et al.Aquatic species dominate organic matter in Qinghai Lake during the Holocene:evidence from eolian deposits around the lake[J].Journal of Earth Science,2017,28(3):484-491. |
| 17 | Lu R J,Jia F F,Gao S Y,et al.Holocene aeolian activity and climatic change in Qinghai Lake basin,northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2015,430:1-10. |
| 18 | Liu X J,Lai Z P,Yu L P,et al.Luminescence chronology of aeolian deposits from the Qinghai Lake area in the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and its palaeoenvironmental implications[J].Quaternary Geochronology,2012,10:37-43. |
| 19 | Stauch G,Ijmker J,Pötsch S,et al.Aeolian sediments on the north-eastern Tibetan Plateau[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2012,57:71-84. |
| 20 | Liu X J,Xiao G Q,E C Y,et al.Accumulation and erosion of aeolian sediments in the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and implications for provenance to the Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2017,135:166-174. |
| 21 | Ding Z Y,Lu R J,Lyu Z Q,et al.Geochemical characteristics of Holocene aeolian deposits east of Qinghai Lake,China,and their paleoclimatic implications[J].Science of the Total Environment,2019,692:917-929. |
| 22 | 鹿化煜,王先彦,孙雪峰,等.钻探揭示的青藏高原东北部黄土地层与第四纪气候变化[J].第四纪研究,2007,27(2):230-241. |
| 23 | 曾方明.西宁地区新近纪风尘堆积的元素组成特征及物源指示意义[J].第四纪研究,2017,37(6):1309-1319. |
| 24 | 曾方明.青海湖地区晚第四纪黄土的物质来源[J].地球科学,2016,41(1):131-138. |
| 25 | Che X D,Li G J.Binary sources of loess on the Chinese Loess Plateau revealed by U-Pb ages of zircon[J].Quaternary Research,2013,80(3):545-551. |
| 26 | Kapp P,Pelletier J D,Rohrmann A,et al.Wind erosion in the Qaidam basin,central Asia:implications for tectonics,paleoclimate,and the source of the Loess Plateau[J].GSA Today,2011,21:4-10. |
| 27 | Pullen A,Kapp P,McCallister A T,et al.Qaidam Basin and northern Tibetan Plateau as dust sources for the Chinese Loess Plateau and paleoclimatic implications[J].Geology,2011,39(11):1031-1034. |
| 28 | 李继彦,赵二丹,柳文龙,等.察尔汗盐湖线形沙丘沙物质来源及输移路径[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(5):909-918. |
| 29 | 凌智永,王建萍,陈亮,等.柴达木盆地灌丛沙丘稀土元素地球化学特征与物源[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(5):963-971. |
| 30 | 毛晓长,刘祥,董颖,等.柴达木盆地鸭湖地区水上雅丹地貌成因研究[J].地质论评,2018,64(6):193-206. |
| 31 | Chen J,Li G J,Yang J D,et al.Nd and Sr isotopic characteristics of Chinese deserts:implications for the provenances of Asian dust[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,2007,71(15):3904-3914. |
| 32 | Zeng F M,Liang M Y,Peng S Z,et al.Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of the Neogene eolian deposits in the Xining basin and implication for their dust sources[J].Journal of Earth Science,2015,26(5):669-676. |
| 33 | Taylor S R,McLennan S M.The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution[M].Oxford,UK:Blackwell Scientific Publications,1985:46. |
| 34 | Mclennan S M.Relationships between the trace element composition of sedimentary rocks and upper continental crust[J].Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems,2001,2(4):GC000109. |
| 35 | Gallet S,Jahn B,Van Vliet Lano B,et al.Loess geochemistry and its implications for particle origin and composition of the upper continental crust[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1998,156(3/4):157-172. |
| 36 | Taylor S R,McLennan S M,McCulloch M T.Geochemistry of loess,continental crustal composition and crustal model ages[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1983,47(11):1897-1905. |
| 37 | Nesbitt H W,Young G M.Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J].Nature,1982,299(5885):715-717. |
| 38 | 曾方明.九江下蜀黄土和红土的化学风化特征[J].盐湖研究,2018,26(1):27-33. |
| 39 | McLennan S M.Weathering and global denudation[J].The Journal of Geology,1993,101:295-303. |
| 40 | 冯连君,储雪蕾,张启锐,等.化学蚀变指数(CIA)及其在新元古代碎屑岩中的应用[J].地学前缘,2003,10(4):539-544. |
| 41 | Nesbitt H W,Markovics G,Price R C.Chemical processes affecting alkalis and alkaline earths during continental weathering[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta,1980,44(11):1659-1666. |
| 42 | Hao Q Z,Guo Z T,Qiao Y S,et al.Geochemical evidence for the provenance of middle Pleistocene loess deposits in southern China[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2010,29(23/24):3317-3326. |
| 43 | Chen J,Ji J F,Qiu G,et al.Geochemical studies on the intensity of chemical weathering in Luochuan loess-paleosol sequence,China[J].Science in China (Series D),1998,41(3):235-241. |
| 44 | 顾兆炎.中国北方风成堆积的风化作用与环境变迁:U-Th、10Be及元素地球化学的研究[D].北京:中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所,1999. |
| 45 | 郝青振.陇西盆地晚第三纪风尘沉积的地层学研究[D].北京:中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所,2001. |
| 46 | Bhatia M R,Crook K A W.Trace element characteristics of graywackes and tectonic setting discrimination of sedimentary basins[J].Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology,1986,92(2):181-193. |
| 47 | Han W,Ma Z,Lai Z,et al.Wind erosion on the north-eastern Tibetan Plateau:constraints from OSL and U-Th dating of playa salt crust in the Qaidam Basin[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2014,39(6):779-789. |
| 48 | Sun J M.Provenance of loess material and formation of loess deposits on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2002,203:845-859. |
| [1] | 王子婷, 杨磊, 李广, 柴春山, 张洋东, 刘冬皓. 黄土丘陵区坡面柠条(Caragana korshinskii)林地草本植物分布特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 120-128. |
| [2] | 梁爱民, 屈建军, 董治宝, 苏志珠, 吴波, 张正偲, 钱广强, 高君亮, 庞营军, 张彩霞. 库姆塔格沙漠沉积物粒度端元特征及其物源启示[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 33-42. |
| [3] | 杜慧荣, 谢远云, 康春国, 迟云平, 王嘉新, 孙磊. 哈尔滨黄土的粒度与地球化学特征及其对粉尘物源的指示[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(1): 64-76. |
| [4] | 王子婷, 李广, 蔡国军, 柴春山, 张洋东, 戚建莉. 陇中黄土丘陵区农户收入对退耕还林(草)政策的响应——以龙滩小流域为例[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(1): 223-232. |
| [5] | 雷晨, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 查小春, 周亚利, 温瑞艳, 炊郁达. 渭河上游地区樊家城黄土-古土壤剖面Rb、Sr、Ba存留特征及意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(6): 90-98. |
| [6] | 李继彦, 周玲, 刘益, 张倩, 蔡莹莹, 张宝贵. 晋西北地区表层土壤粒度与地球化学元素组成[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(5): 155-162. |
| [7] | 文海燕, 吴淑娟, 傅华. 氮添加对黄土高原草原生态系统净碳交换的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(3): 34-40. |
| [8] | 李继彦, 赵二丹, 柳文龙, 闫加亮, 周玲. 察尔汗盐湖线形沙丘沙物质来源及输移路径[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(5): 909-918. |
| [9] | 凌智永, 王建萍, 陈亮, 芦宝良. 柴达木盆地灌丛沙丘稀土元素地球化学特征与物源[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(5): 963-971. |
| [10] | 孙立凡, 史兴民, 王露. 农户对气候变化适应行为的有效性评价[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(2): 428-436. |
| [11] | 丁之勇, 马龙, 吉力力·阿不都外力, 刘文, 葛拥晓. 新疆艾比湖湖泊沉积物元素地球化学记录及其生态环境意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(1): 101-110. |
| [12] | 张文桐, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 周亚利, 查小春, 崔天宇, 王海燕, 杨丹. 汉江上游郧县庹家湾剖面光释光测年及意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(5): 885-892. |
| [13] | 郎丽丽, 王训明, 朱秉启, 王向东, 花婷, 王广涛, 李晖, 张彩霞. 河西走廊西端灌丛沙丘发育过程及其对沙漠化的指示意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(4): 611-620. |
| [14] | 王友郡, 贾佳, 高福元, 陆浩, 刘浩, 夏敦胜. 阿拉善地区古水下沉积物与风沙沉积物磁学特征及意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(4): 626-634. |
| [15] | 吕安琪, 鹿化煜, 曾琳, 弋双文, 卓海昕, 徐志伟, 张文超. 1.08 Ma以来中国东北赤峰地区黄土粒度变化及其揭示的沙地扩张事件[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(4): 659-665. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
