中国沙漠 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 213-221.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00105
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2023-09-26
修回日期:2023-12-04
出版日期:2024-05-20
发布日期:2024-06-11
作者简介:刘任涛(1980—),男,河南南阳人,研究员,主要从事荒漠化与生态恢复相关研究。E-mail: nxuliu2012@126.com
基金资助:Received:2023-09-26
Revised:2023-12-04
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-06-11
摘要:
生物多样性与生态系统多功能性的关系是国际生态学领域新兴的热点研究方向。蚂蚁是全球陆地生态系统中分布最广、数量最大的社会性昆虫,具有多种重要的生态系统功能。但是,在干旱荒漠生态系统中,前人在研究中往往忽略蚂蚁多样性是土壤生态系统功能维持的关键基础。针对干旱区生态系统中蚂蚁多样性与生态系统功能关系,首先分析蚂蚁作为生态系统“工程师”的生态作用,系统梳理了蚂蚁筑巢活动对土壤结构、物理化学性质和土壤养分及能量流动的影响,然后从蚂蚁与土壤生物间的作用关系分析了蚂蚁筑巢活动对土壤微生物、土壤动物分布的影响规律,并总结了蚂蚁和非蚁土壤动物间的营养级作用关系,其次总结了蚂蚁本身作为土壤动物的优势类群对土壤功能的直接影响作用。综合分析表明,蚂蚁具有重要的生态系统“工程师”作用,深刻影响土壤物理化学性质与土壤功能;通过上行效应或下行效应,蚂蚁与土壤生物间的营养级作用关系是土壤生物多样性形成与维持的关键,在土壤生态系统功能中具有重要的基础性作用。在干旱、半旱区,蚂蚁活动形成蚁丘影响土壤环境及其土壤生物多样性,进而影响土壤生态系统功能及其生态系统多功能性,关系到脆弱生态系统功能恢复与稳定性维持,可以为未来干旱、半旱生态系统服务能力提升及多服务性奠定重要基础。
中图分类号:
刘任涛. 干旱半干旱区蚂蚁的生态功能综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 213-221.
Rentao Liu. Ecological function of ants and its implication for ecological restoration of semiarid and arid ecosystems[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(3): 213-221.
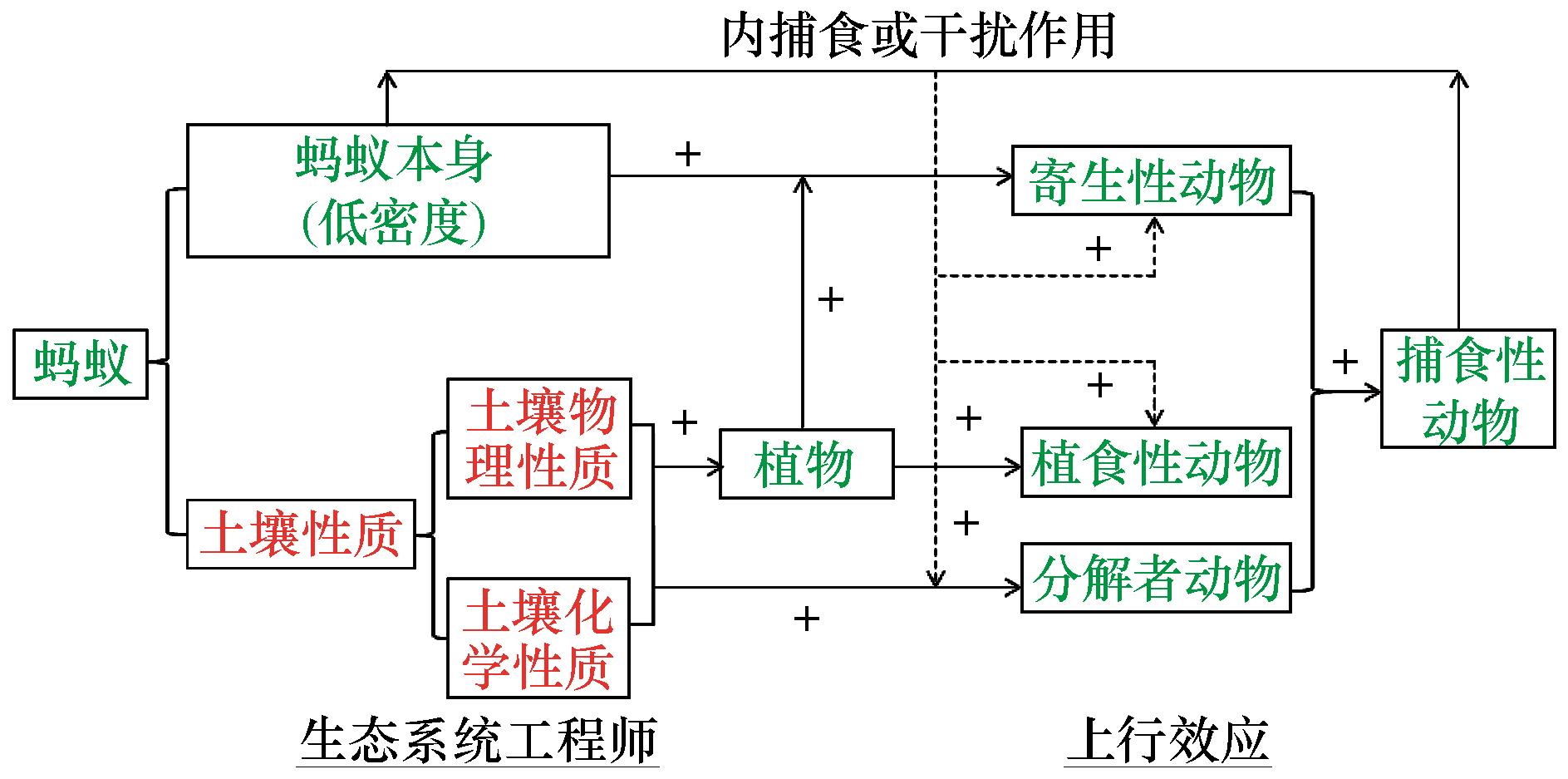
图3 蚂蚁生态系统工程师作用(通过上行效应)对土壤动物营养级结构的影响[17]注:+表示正效应
Fig.3 Effect of ecological engineering acted by ants (i.e., bottom-up effect) on trophic structure of soil faunal communities[17]
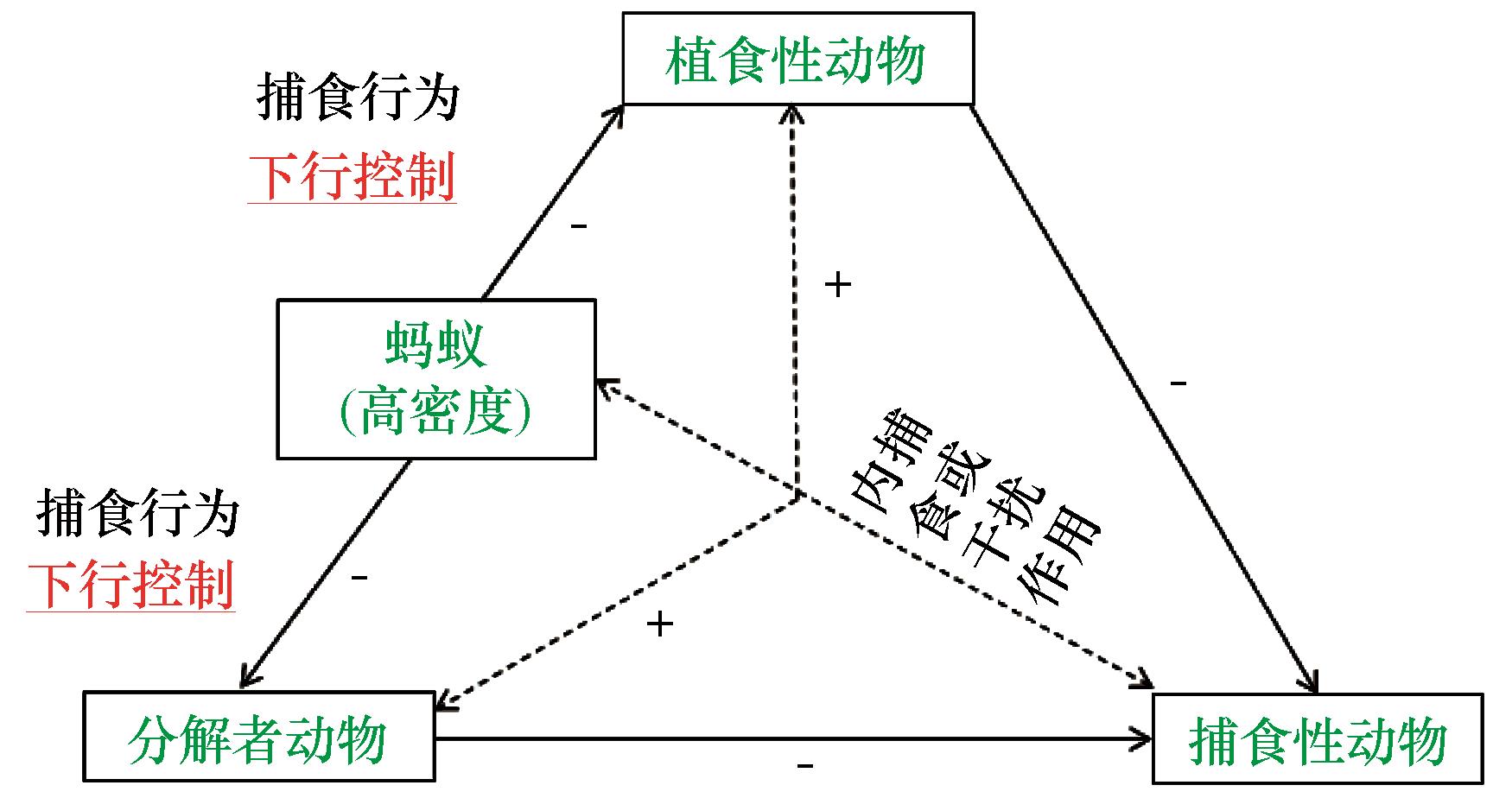
图4 蚂蚁捕食行为(通过下行效应)对土壤动物营养级结构的影响[17]注:+表示正效应,-表示负效应
Fig.4 Effect of predation acted by ants (i.e., top-down effect) on trophic structure of soil faunal communities[17]
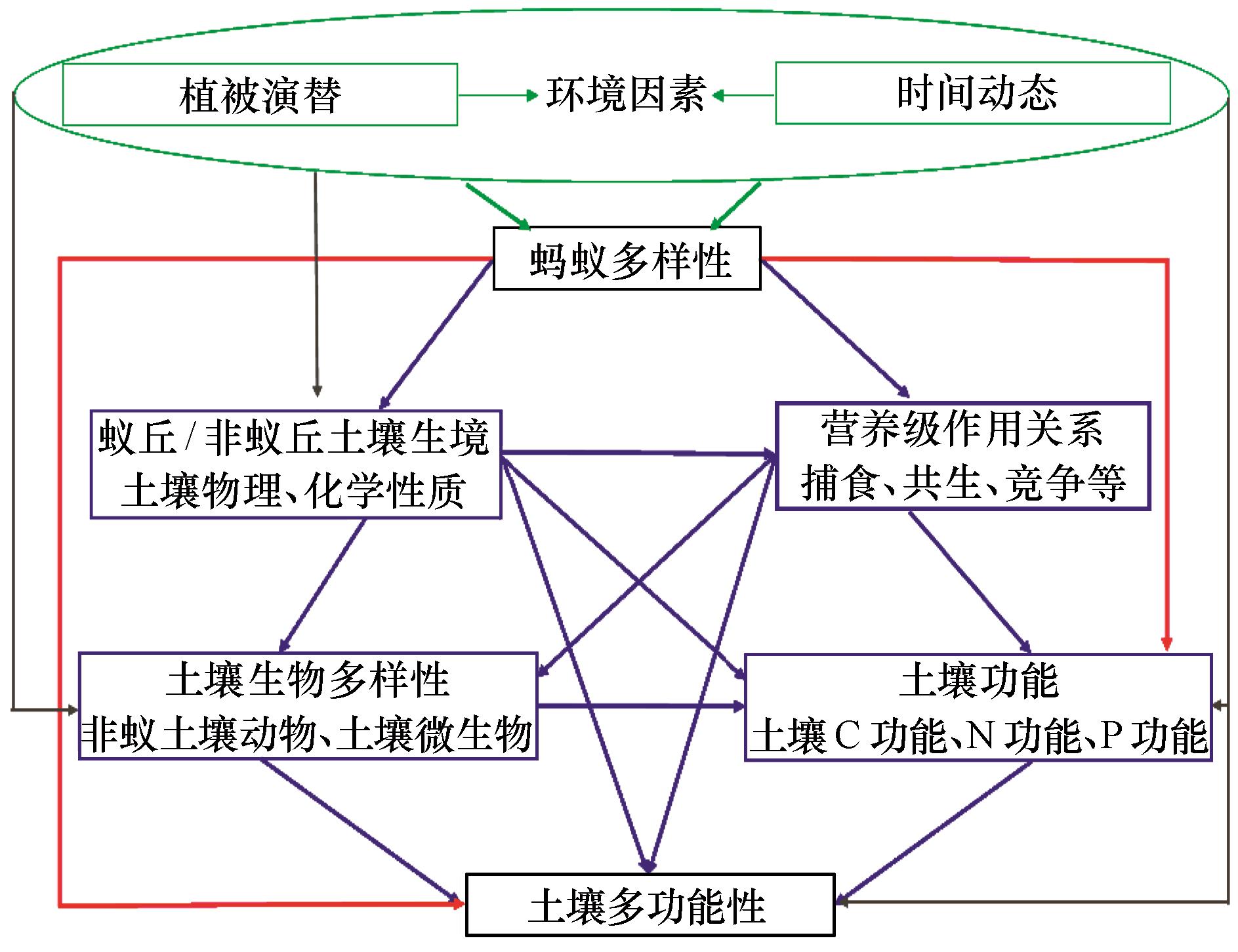
图5 固沙植被区蚂蚁多样性与土壤多功能性关系的框架概念注:红线代表蚂蚁多样性直接影响;蓝线代表蚂蚁多样性间接影响;灰线代表环境因素的可能影响
Fig.5 Conceptual framework of the relationship between ant diversity and soil multifunctionality in revegetated areas
| 1 | Creamer R E, Barel J M, Bongiorno G,et al.The life of soils:integrating the who and how of multifunctionality[J].Oil Biology and Biochemistry,2022,166:108561. |
| 2 | Wagg C, Bender S F, Widmer F,et al.Soil biodiversity and soil community composition determine ecosystem multifunctionality[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences-PNAS,2014,111(14):5266-5270. |
| 3 | 井新,贺金生.生物多样性与生态系统多功能性和多服务性的关系:回顾与展望[J].植物生态学报,2021,45(10):1094-1111. |
| 4 | 王凯,王聪,冯晓明,等. 生物多样性与生态系统多功能性的关系研究进展[J].生态学报,2022,42(1):11-23. |
| 5 | 朱永官,陈保冬,付伟.土壤生态学研究前沿[J].科技导报,2022,40(3):25-31. |
| 6 | Cheng B, Liu H, Bai J,et al.Soil fungal composition drives ecosystem multifunctionality after long-term field nitrogen and phosphorus addition in alpine meadows on the Tibetan Plateau[J].Plants-Basel,2022,11(21):2893. |
| 7 | Delgado-Baquerizo M, Maestre F T, Reich P B,et al. Microbial diversity drives multifunctionality in terrestrial ecosystems[J].Nature Communications,2016,7:10541. |
| 8 | 傅声雷,刘满强,张卫信,等.土壤动物多样性的地理分布及其生态功能研究进展[J].生物多样性,2022,30(10):146-163. |
| 9 | 冯怡琳,王永珍,林永一,等.河西走廊中部荒漠收获蚁(Messor desertus)蚁穴对秋季地表节肢动物群落结构的影响[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(6):121-130. |
| 10 | 崔文夏,房华,徐正会,等.文山国家级自然保护区蚂蚁多样性与分布格局[J].森林与环境学报,2023,43(1):103-112. |
| 11 | 蒋富国,郭宗林,王亚璐,等.中国东南部农区蚂蚁物种多样性研究[J].环境昆虫学报,2023,23(4):1-15. |
| 12 | Folgarait P J.Ant biodiversity and its relationship to ecosystem functioning:a review[J].Biodiversity Conservation,1998,7(9):1221-1244. |
| 13 | Whitford W G, Eldridge D J.Effects of ants and termites on soil and geomorphological processes[M]//Shroder J,Butler D R,Hupp C R.Treatise on Geomorphology.San Diego,USA:Academic Press,2013:281-292. |
| 14 | Balzani P, Masoni A, Venturi S,et al.CO2 biogeochemical investigation and microbial characterization of red wood ant mounds in a Southern Europe montane forest[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2022,166:108536. |
| 15 | Wang S, Li J, Zhang Z,et al.The contributions of underground-nesting ants to CO2 emission from tropical forest soils vary with species[J].Science of the Total Environments,2018,630:1095-1102. |
| 16 | Wu H, Lu X, Wu D,et al.Ant mounds alter spatial and temporal patterns of CO2,CH4 and N2O emissions from a marsh soil[J].Soil Biology and Biochemistry,2013,57:884-891. |
| 17 | Sanders D, van Veen F J F.Ecosystem engineering and predation:the multi-trophic impact of two ant species[J].Journal of Animal Ecology,2011,80(3):569-576. |
| 18 | Almeida F S, Elizalde L, Silva L M S,et al.The effects of two abundant ant species on soil nutrients and seedling recruitment in Brazilian Atlantic Forest[J].Revista Brasileira De Entomologia,2019,63(4):296-301. |
| 19 | Farji-Brener A G, Werenkraut V.The effects of ant nests on soil fertility and plant performance:a meta-analysis[J].Journal of Animal Ecology,2017,86(4):866-877. |
| 20 | Wu H, Lu X, Tong S,et al.Soil engineering ants increase CO2 and N2O emissions by affecting mound soil physicochemical characteristics from a marsh soil:a laboratory study[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2015,87:19-26. |
| 21 | Wu H, Batzer D P, Yan X,et al.Contributions of ant mounds to soil carbon and nitrogen pools in a marsh wetland of Northeastern China[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2013,70:9-15. |
| 22 | Soliveres S, van der Plas F, Manning P,et al.Biodiversity at multiple trophic levels is needed for ecosystem multifunctionality[J].Nature,2016,536(7617):456-459. |
| 23 | Schuldt A, Assmann T, Brezzi M,et al.Biodiversity across trophic levels drives multifunctionality in highly diverse forests[J].Nature Communications,2018,9(1):2989. |
| 24 | Viles H A, Goudie A S, Goudie A M.Ants as geomorphological agents:a global assessment[J].Earth-Science Review,2021,213:103469. |
| 25 | 赵一军,赵敏,毛文娅,等.蚂蚁对草地动植物及土壤作用的研究进展[J].云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2019,34(5):889-895. |
| 26 | Wang C, Wang G, Wu P,et al.Effects of ant mounds on the plant and soil microbial community in an alpine meadow of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J].Land Degradation and Development,2017,28(5):1538-1548. |
| 27 | 冯怡琳,王永珍,林永一,等.戈壁生态系统蚁穴微生境对大型土壤动物多样性的影响[J].生物多样性,2022,30(12):88-98. |
| 28 | 薛娟,魏雪,何先进,等.高寒草甸生态系统中蚁丘对小型土壤节肢动物群落的影响[J].生态学报,2021,41(4):1-12. |
| 29 | Mehring A S, Martin R M, Delavaux C S,et al.Leaf-cutting ant (Atta cephalotes) nests may be hotspots of methane and carbon dioxide emissions in tropical forests[J].Pedobiologia,2021,87/88:150754. |
| 30 | 刘任涛,赵哈林,赵学勇.沙地生态系统中蚂蚁活动与地表植被及土壤环境间的互作关系[J].干旱区资源与环境,2011,25(12):166-170. |
| 31 | Eschenbrenner V.The influence of fungus-cultivating ants (Hymenoptera,Formicidae,Attini) on the morphology of andosols in Martinique[M]//Ringrose-Voase A J,Humphreys G S.Soil Micromorphology:Studies in Management and Genesis.Amsterdam,Netherlands:Elsevier,1993:405-410. |
| 32 | Humphreys G S, Ringrose-Voase A J, Humphreys G S.Bioturbation,biofabrics and the biomantle:an example from the Sydney Basin[J].Developments in Soil Science,1994,22:421-436. |
| 33 | Drager K I, Hirmas D R, Hasiotis S T.Effects of ant (Formica subsericea) nests on physical and hydrological properties of a fine-textured soil[J].Soil Science Society of America Journal,2016,80(2):364-375. |
| 34 | 陈应武,李新荣,苏延桂,等.腾格里沙漠人工植被区掘穴蚁(Formica cunicularia)的生态功能[J].生态学报,2007,27(4):1508-1514. |
| 35 | McGinley M A, Dhillion S S, Neumann J C.Environmental heterogeneity and seedling establishment:ant-plant-microbe interactions[J].Functional Ecology,1994,8(5):607-615. |
| 36 | Lobry De Bruyn L A.Ants as bioindicators of soil function in rural environments[J].Agriculture,Ecosystems & Environment,1999,74(1):425-441. |
| 37 | Mandel R D, Sorenson C J.The role of the western harvester ant (Pogonomyrmex occidentalis) in soil formation[J].Soil Science Society of America Journal,1982,46(4):785. |
| 38 | Paton T R, Humphreys G S, Mitchell P B.Soils.A New Global View[M].London,UK:UCL Press,1995. |
| 39 | Levan M A, Stone E L.Soil modification by colonies of black meadow ants in a new york old field[J].Soil Science Society of America Journal,1983,47:1192-1195. |
| 40 | Lavelle P, Chauvel A, Fragoso C.Faunal activity in acid soils[M]//DateR A,GrundonN J,RaymentG E,alet.Plant-Soil Interactions at Low pH:Principles and Management[M].The Netherlands:Kluwer Academic Publishers,1995:201-211. |
| 41 | Petal J, Kusinska A.Fractional composition of organic matter in the soil of anthills and the environment of meadows[J].Pedobiologia,1994,38:493-501. |
| 42 | Haines B L.Element and energy flows through colonies of the leaf-cutting ant,Atta colombica,in Panama[J].Biotropica,1978,10(4):270-277. |
| 43 | Lugo A E, Farnworth E G, Pool D,et al.Impact of the leaf cutter ant atta colombica on the energy flow of a tropical west forest[J].Ecology,1973,54(6):1292-1301. |
| 44 | Hidalgo F J, Canepuccia A D, Arcusa J,et al.Black fire ant mounds modify soil properties and enhanced plant growth in a salt marsh in Argentina[J].Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,2021,261:107534. |
| 45 | Potapov A M, Beaulieu F, Birkhofer K,et al.Feeding habits and multifunctional classification of soil-associated consumers from protists to vertebrates[J].Biological Reviews,2022,97(3):1057-1117. |
| 46 | Petal J.The role of ants in nutrient cycling in forest ecosystems[M]//Billen J.Biology and Evolution of Social Insects.Leuven,Belgium:Leuven University Press,1992:167-170. |
| 47 | Gabet E J, Reichman O J, Seabloom E W.The effects of bioturbation on soil processes and sediment transport[J].Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences,2003,31(1):249-273. |
| 48 | Taylor A R, Lenoir L, Vegerfors B,et al.Ant and earthworm bioturbation in cold-temperate ecosystems[J].Ecosystems,2019,22(5):981-994. |
| 49 | Jones C G, Lawton J H, Shachak M.Positive and negative effects of organisms as physical ecosystem engineers[J].Ecology,1997,78(7):1946-1957. |
| 50 | 井新,蒋胜竞,刘慧颖,等.气候变化与生物多样性之间的复杂关系和反馈机制[J].生物多样性,2022,30(10):289-307. |
| 51 | Vander M R.Ant interactions with soil organisms and associated semiochemicals[J].Journal of Chemical Ecology,2012,38(6):728-745. |
| 52 | Ginzburg O, Whitford W G, Steinberger Y.Effects of harvester ant (Messor spp.) activity on soil properties and microbial communities in a Negev Desert ecosystem[J].Biology and Fertility of Soils,2008,45(2):165-173. |
| 53 | 陈闽昆,王邵军,陈武强,等.蚂蚁筑巢对西双版纳热带森林土壤微生物生物量碳及熵的影响[J].应用生态学报,2019,30(9):2973-2982. |
| 54 | 曹乾斌,王邵军,任玉连,等.蚂蚁筑巢对西双版纳热带森林土壤碳矿化动态的影响[J].应用生态学报,2019,30(12):4231-4239. |
| 55 | 李少辉,王邵军,张哲,等.蚂蚁筑巢对西双版纳热带森林土壤易氧化有机碳时空动态的影响[J].应用生态学报,2019,30(2):413-419. |
| 56 | Janson L, Mallott L, Mcginty L.Soil temperature and arthropod abundance are lower near ant mounds near ant mounds[J].Tillers,2012,3:15-19. |
| 57 | Tschinkel W R, Seal J N.Bioturbation by the fungus-gardening ant,Trachymyrmex septentrionalis [J].PLoS One,2016,11(7):e158920. |
| 58 | Vidal M C, Murphy S M.Bottom-up vs.top-down effects on terrestrial insect herbivores:a meta-analysis[J].Ecology Letters,2018,21(1):138-150. |
| 59 | Moya-Laraño J, Wise D H.Direct and indirect effects of ants on a forest-floor food web[J].Ecology,2007,88(6):1454-1465. |
| 60 | Piñol J, Espadaler X, Cañellas N,et al.Ant versus bird exclusion effects on the arthropod assemblage of an organic citrus grove[J].Ecological Entomology,2010,35(3):367-376. |
| 61 | Leite P A M, Carvalho M C, Wilcox B P.Good ant,bad ant? Soil engineering by ants in the Brazilian Caatinga differs by species[J].Geoderma,2018,323:65-73. |
| 62 | Sanders D, Platner C.Intraguild interactions between spiders and ants and top-down control in a grassland food web[J].Oecologia,2006,150(4):611-624. |
| 63 | Lenoir L, Bengtsson J, Persson T.Effects of Formica ants on soil fauna-results from a short-term exclusion and a long-term natural experiment[J].Oecologia,2003,134(3):423-430. |
| 64 | Lenoir L, Persson T, Bengtsson J,et al.Bottom-up or top-down control in forest soil microcosms?Effects of soil fauna on fungal biomass and C/N mineralisation[J].Biology and Fertility of Soils,2006,43(3):281-294. |
| 65 | Dibner R R, Doak D F, Lombardi E M.An ecological engineer maintains consistent spatial patterning,with implications for community-wide effects[J].Ecosphere,2015,6(9):1-17. |
| 66 | Wills B D, Landis D A.The role of ants in north temperate grasslands:a review[J].Oecologia,2018,186(2):323-338. |
| 67 | Jones C G, Lawton J H, Shachak M.Organisms as ecosystem engineers[J].Oikos,1994,69(3):373-386. |
| 68 | 郑洲.不同食性蚂蚁消化道细菌群落组成及多样性研究[D].陕西杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2022. |
| 69 | Eisner T, Happ G.The infrabuccal pocket of a formicine ant:a social filtration device[J].Psyche,1962,69:107-116. |
| 70 | Sudhaus W.The guild of saprobiontic nematodes associated with ants (Formicoidea)[J].Ecologica Montenegrina,2016,7:600-613. |
| 71 | Lützow M V, Kögel-Knabner I, Ekschmitt K,et al.Stabilization of organic matter in temperate soils:mechanisms and their relevance under different soil conditions-a review[J].European Journal of Soil Science,2006,57:426-445. |
| 72 | Vidkjær N H, Wollenweber B, Gislum R,et al.Are ant feces nutrients for plants?A metabolomics approach to elucidate the nutritional effects on plants hosting weaver ants[J].Metabolomics,2015,11(4):1013-1028. |
| 73 | Christianini A V, Mayhé-nunes A J, Oliveira P S.The role of ants in the removal of non-myrmecochorous diaspores and seed germination in a neotropical savanna[J].Journal of Tropical Ecology,2007,23(3):343. |
| 74 | Rabeling C, Bacci M.A new workerless inquiline in the Lower Attini (Hymenoptera:Formicidae),with a discussion of social parasitism in fungus‐growing ants[J].Systematic Entomology,2010,35(3):379-392. |
| 75 | 鱼小军,蒲小鹏,黄世杰,等.蚂蚁对东祁连山高寒草地生态系统的影响[J].草业学报,2010,19(2):140. |
| [1] | 李丹丹, 李佳文, 高广磊, 张英, 任悦, 柳叶, 赵珮杉. 科尔沁沙地樟子松( Pinus sylvestris var. mongolia )人工林土壤真菌群落结构和功能特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 241-251. |
| [2] | 许文文, 赵燕翘, 王楠, 赵洋. 人工生物土壤结皮对草本植物群落组成与多样性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 204-211. |
| [3] | 尤南山, 蒙吉军. 基于生态敏感性和生态系统服务的黑河中游生态功能区划与生态系统管理[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(1): 186-197. |
| [4] | 吴玉环, 程国栋, 高谦. 苔藓植物的生态功能及在植被恢复与重建中的作用[J]. 中国沙漠, 2003, 23(3): 215-220. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn

