中国沙漠 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 60-72.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00034
苏靖茸1,2( ), 肖生春1(
), 肖生春1( ), 彭小梅1, 车存伟3, 赵鹏4
), 彭小梅1, 车存伟3, 赵鹏4
收稿日期:2023-10-20
修回日期:2024-02-17
出版日期:2024-09-20
发布日期:2024-10-15
通讯作者:
肖生春
作者简介:肖生春(E-mail: xiaosc@lzb.ac.cn)基金资助:
Jingrong Su1,2( ), Shengchun Xiao1(
), Shengchun Xiao1( ), Xiaomei Peng1, Cunwei Che3, Peng Zhao4
), Xiaomei Peng1, Cunwei Che3, Peng Zhao4
Received:2023-10-20
Revised:2024-02-17
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-10-15
Contact:
Shengchun Xiao
摘要:
油松(Pinus tabulaeformis)是中国特有且广泛分布的针叶树种,也是中国北方地区的主要造林树种。气候变化对油松生长的影响是种群生态学研究的热点。基于油松树木年轮学文献成果,系统梳理分析了不同降水、气温等因素影响下中国北方地区油松径向生长特征,试图明晰其区域分异特征,以期为油松天然林和人工林管理提供理论和决策依据。结果表明:(1)在年降水量低于400 mm的区域,限制油松径向生长的主要因素是生长季降水;在年降水量400~600 mm的区域,生长季的水热因素共同影响油松的径向生长;在年降水量高于600 mm区域,油松的径向生长主要受5月降水与平均气温及其共同作用的干旱胁迫影响。(2)上年降水对油松径向生长的“滞后效应”主要体现在年降水量低于600 mm和年均气温低于9 ℃的区域。(3)冬季气温对年降水量高于600 mm和年均气温高于9 ℃区域油松的生长起促进作用,对年降水量低于600 mm和年均气温低于9 ℃的区域起抑制作用。在全球气候变暖背景下,油松分布区将面临从干旱半干旱区向相对湿润区、从低海拔向高海拔移动的趋势。
中图分类号:
苏靖茸, 肖生春, 彭小梅, 车存伟, 赵鹏. 油松( Pinus tabulaeformis )径向生长对气候响应的区域分异特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 60-72.
Jingrong Su, Shengchun Xiao, Xiaomei Peng, Cunwei Che, Peng Zhao. Regional differentiation of radial growth to climate response of Chinese pine ( Pinus tabulaeformis )[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(5): 60-72.
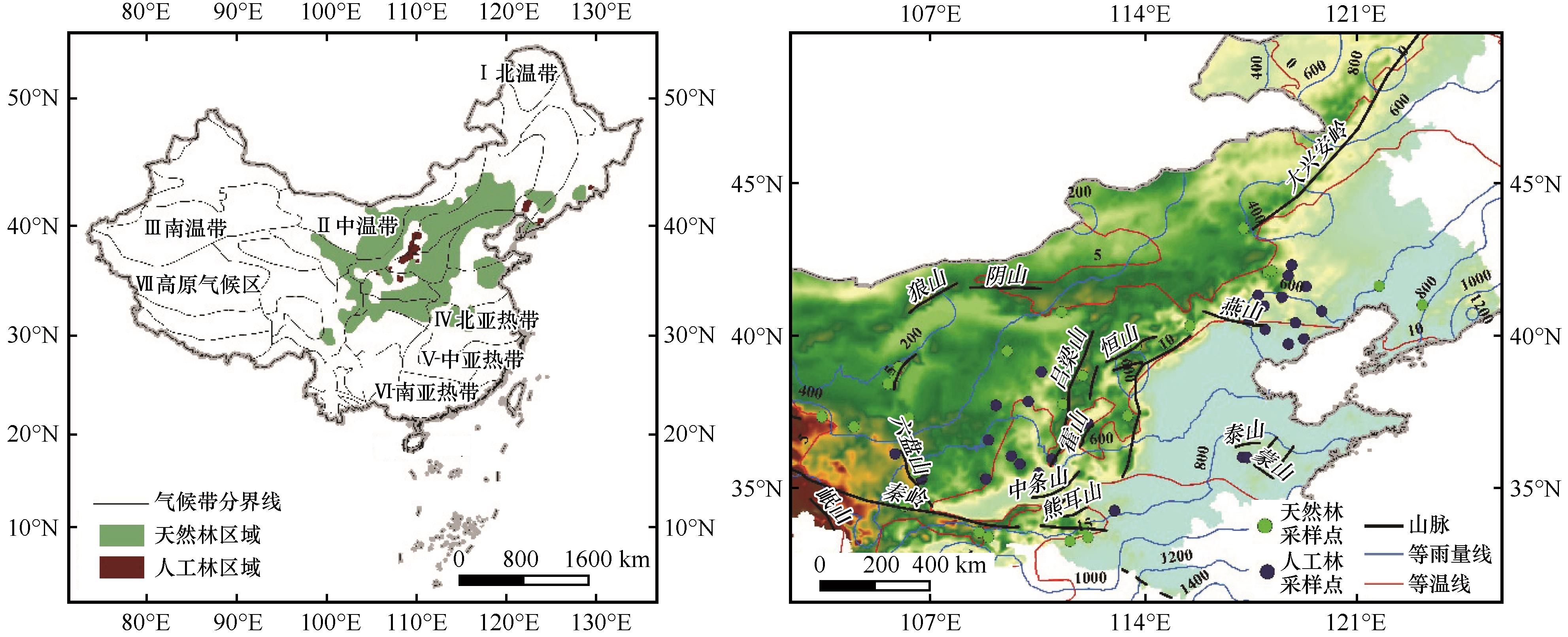
图1 研究区油松天然林与人工林采样点分布区注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:GS(2020)4619号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.1 Main distribution and tree-ring sampling points of the natural and planted Pinus tabulaeformis forests in China
| #1 | (Pinus tabuliformis [Title/Abstract]) OR (Chinese pine [Title/Abstract]) |
|---|---|
| #2 | (plantation[Title/Abstract]) OR (natural forests[Title/Abstract]) |
| #3 | (#1) AND (#2) |
| #4 | ((((Precipitation[Title/Abstract]) OR (Precipitation[Title/Abstract])) OR (PDSI[Title/Abstract])) OR (scPDSI[Title/Abstract])) OR (SPEI[Title/Abstract]) |
| #5 | (radial growth) OR (climate response) |
| #6 | (#4) AND (#5) |
| #7 | (#3) AND (#6) |
表1 PubMed搜索策略
Table 1 Search strategy on PubMed
| #1 | (Pinus tabuliformis [Title/Abstract]) OR (Chinese pine [Title/Abstract]) |
|---|---|
| #2 | (plantation[Title/Abstract]) OR (natural forests[Title/Abstract]) |
| #3 | (#1) AND (#2) |
| #4 | ((((Precipitation[Title/Abstract]) OR (Precipitation[Title/Abstract])) OR (PDSI[Title/Abstract])) OR (scPDSI[Title/Abstract])) OR (SPEI[Title/Abstract]) |
| #5 | (radial growth) OR (climate response) |
| #6 | (#4) AND (#5) |
| #7 | (#3) AND (#6) |
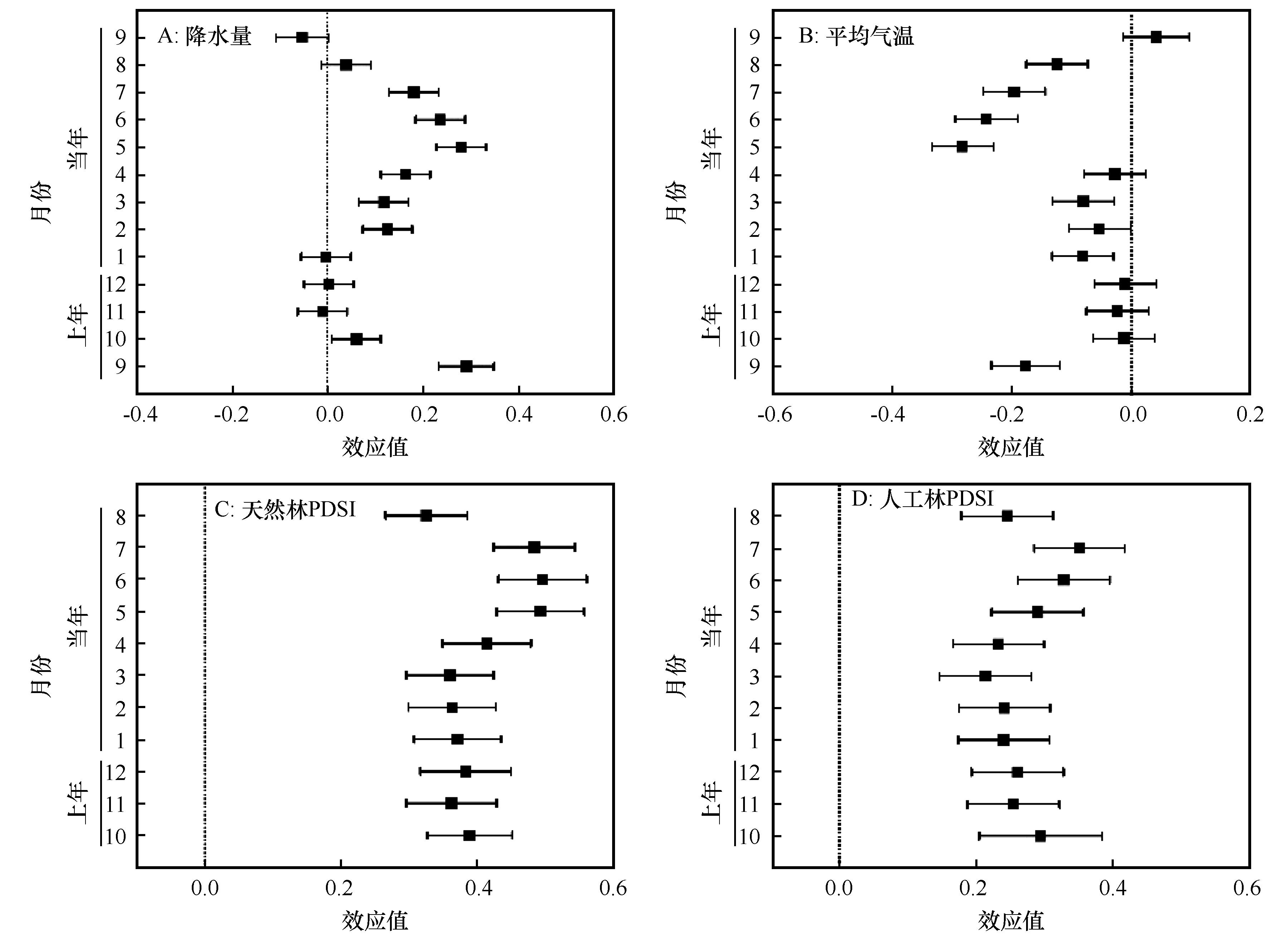
图2 油松天然林(A~C)与人工林(D)径向生长与气候因子的效应值注:误差线表示95%的置信区间,误差线与零线相交表明气候因子对油松生长影响的效应值未达到显著水平
Fig.2 Effect size (R) between the growth of Pinus tabulaeformis in natural (A-C) and plantation(D) forests and climate factors
| 气候因子 | 月份 | 效应值的系数 | 标准差 | t | P>|t| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降水 | 上年9月 | -0.0006 | 0.0002 | -2.93 | 0.009 |
| 当年3月 | -0.0003 | 0.0001 | -1.64 | 0.116 | |
| 当年5月 | -0.0001 | 0.0002 | -0.68 | 0.505 | |
| 当年6月 | -0.0003 | 0.0001 | -1.95 | 0.064 | |
| 当年7月 | -0.0003 | 0.0002 | -1.45 | 0.161 | |
| 气温 | 当年2月 | 0.0003 | 0.0002 | 1.21 | 0.240 |
| 当年5月 | 8.39×10-6 | 0.0002 | 0.04 | 0.965 | |
| 当年6月 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 1.06 | 0.300 | |
| 当年7月 | 0.0005 | 0.0950 | -4.33 | 0.000 |
表2 降水梯度下油松径向生长与气候因子效应值及统计参数
Table 2 Statistics of effect size ( R ) between radial growth of P. tabulaeformis and climatic factors under precipitation gradients
| 气候因子 | 月份 | 效应值的系数 | 标准差 | t | P>|t| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降水 | 上年9月 | -0.0006 | 0.0002 | -2.93 | 0.009 |
| 当年3月 | -0.0003 | 0.0001 | -1.64 | 0.116 | |
| 当年5月 | -0.0001 | 0.0002 | -0.68 | 0.505 | |
| 当年6月 | -0.0003 | 0.0001 | -1.95 | 0.064 | |
| 当年7月 | -0.0003 | 0.0002 | -1.45 | 0.161 | |
| 气温 | 当年2月 | 0.0003 | 0.0002 | 1.21 | 0.240 |
| 当年5月 | 8.39×10-6 | 0.0002 | 0.04 | 0.965 | |
| 当年6月 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 1.06 | 0.300 | |
| 当年7月 | 0.0005 | 0.0950 | -4.33 | 0.000 |
| 气候因子 | 月份 | 效应值的系数 | 标准差 | t | P>|t| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降水 | 上年9月 | -0.035 | 0.012 | -2.82 | 0.011 |
| 当年3月 | -0.025 | 0.010 | -0.29 | 0.032 | |
| 当年5月 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.03 | 0.315 | |
| 当年6月 | -0.015 | 0.01 | -1.50 | 0.147 | |
| 当年7月 | -0.028 | 0.01 | -2.54 | 0.018 | |
| 气温 | 当年2月 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 1.04 | 0.312 |
| 当年5月 | 0.009 | 0.012 | 0.72 | 0.478 | |
| 当年6月 | 0.037 | 0.012 | 2.97 | 0.007 | |
| 当年7月 | 0.039 | 0.01 | 3.73 | 0.001 |
表3 气温梯度下油松径向生长与气候因子之间的效应值及统计参数
Table 3 Statistics of effect size ( R ) between radial growth of Pinus tabulaeformis and climatic factors under temperature gradients
| 气候因子 | 月份 | 效应值的系数 | 标准差 | t | P>|t| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 降水 | 上年9月 | -0.035 | 0.012 | -2.82 | 0.011 |
| 当年3月 | -0.025 | 0.010 | -0.29 | 0.032 | |
| 当年5月 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 1.03 | 0.315 | |
| 当年6月 | -0.015 | 0.01 | -1.50 | 0.147 | |
| 当年7月 | -0.028 | 0.01 | -2.54 | 0.018 | |
| 气温 | 当年2月 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 1.04 | 0.312 |
| 当年5月 | 0.009 | 0.012 | 0.72 | 0.478 | |
| 当年6月 | 0.037 | 0.012 | 2.97 | 0.007 | |
| 当年7月 | 0.039 | 0.01 | 3.73 | 0.001 |

图5 降水(A)和气温(B)梯度下油松径向生长与降水之间的效应值
Fig.5 Effect size (R) between radial growth of Pinus tabulaeformis and precipitation under precipitation (A) and temperature (B) gradients
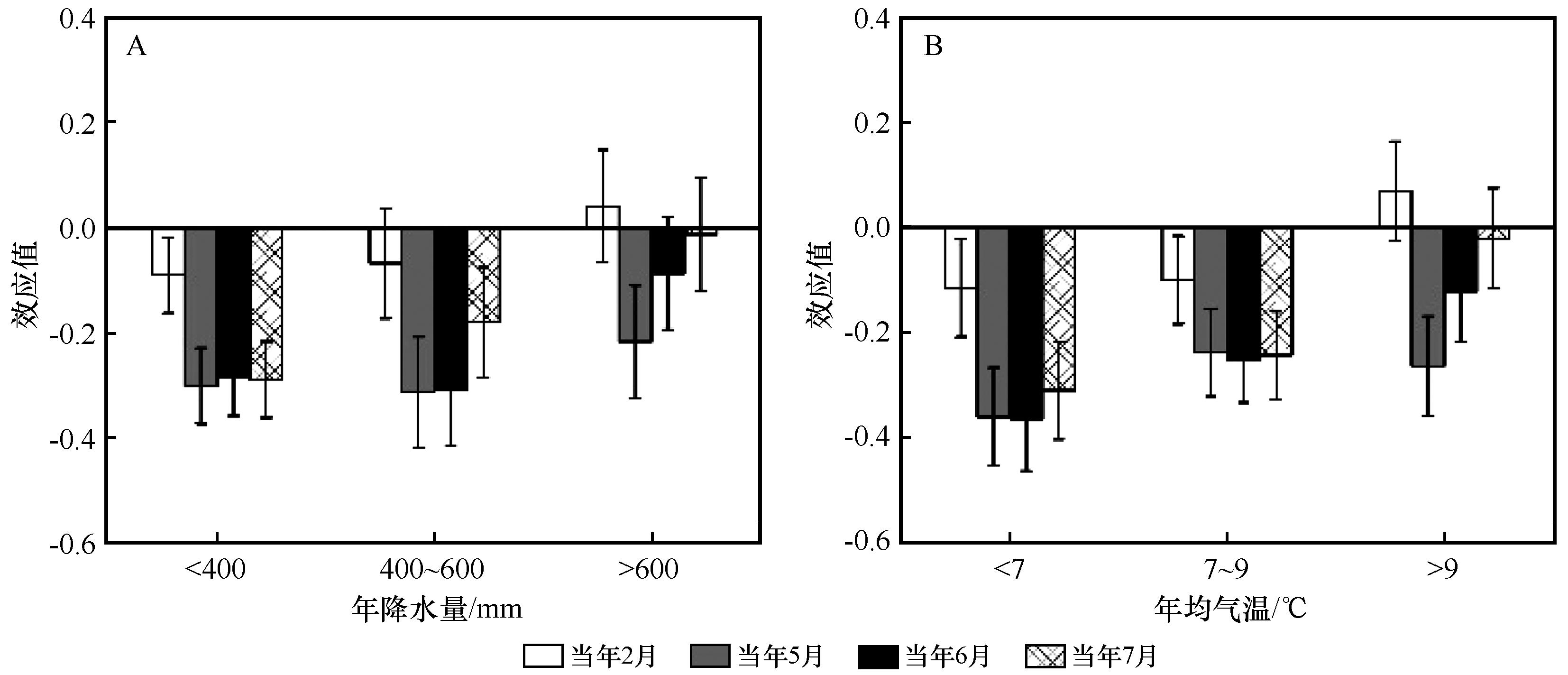
图6 降水(A)和气温(B)梯度下油松径向生长与气温之间的效应值
Fig.6 Effect size (R) between radial growth of Pinus tabulaeformis and temperature under precipitation (A) and temperature (B) gradients
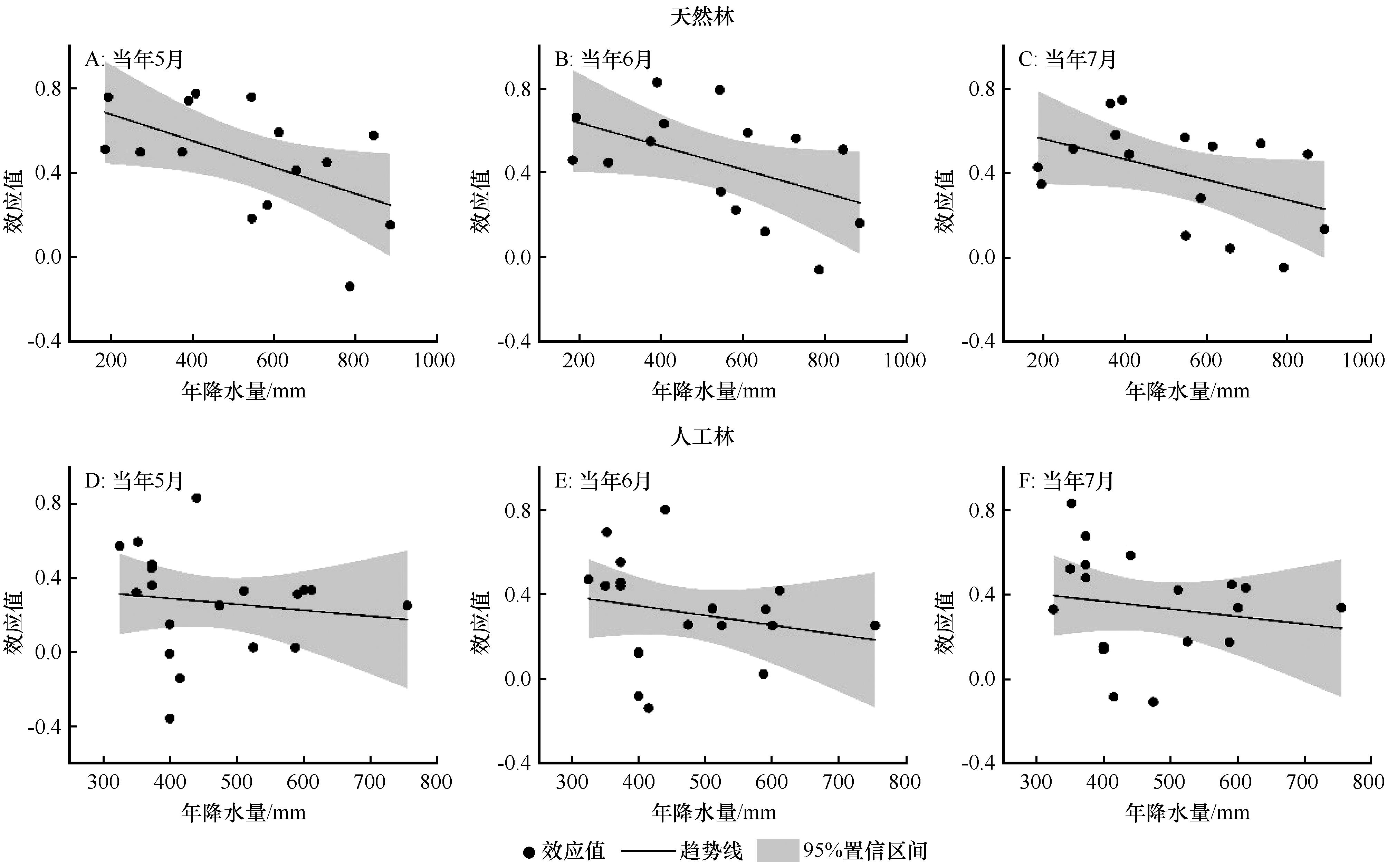
图7 降水梯度下油松天然林(A~C)和人工林(D~F)径向生长与PDSI的效应值
Fig.7 Effect size (R) between radial growth of Pinus tabulaeformis in natural (A-C) and plantation (D-F) forests and PDSI under precipitation gradients
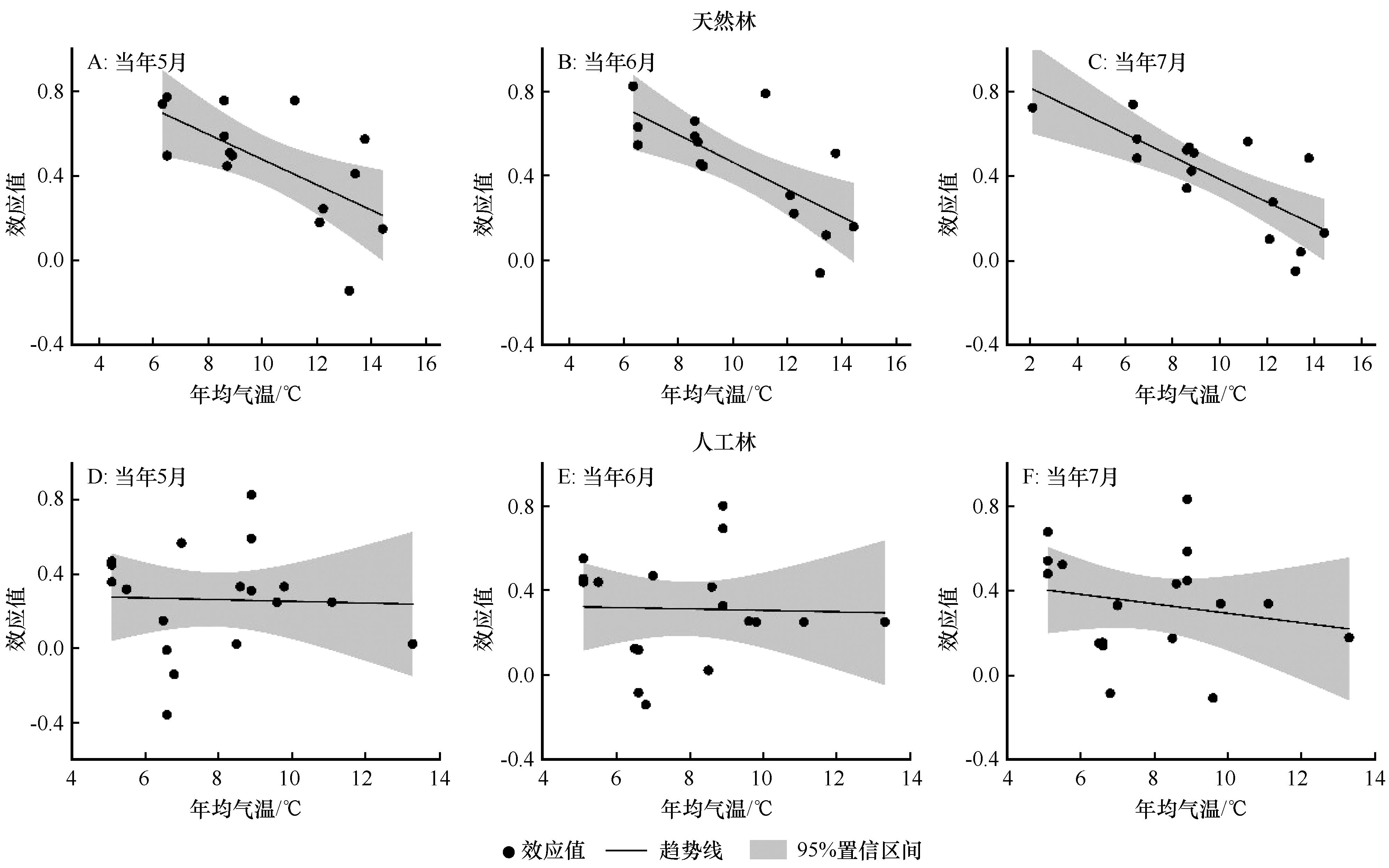
图8 气温梯度下油松天然林(A~C)和人工林(D~F)径向生长与PDSI的效应值
Fig.8 Effect size (R) between radial growth of Pinus tabulaeformis in natural (A-C) and plantation (D-F) forests and PDSI under temperature gradients
| 林分 来源 | 月份 | 效应值的 系数 | 标准差 | t | P>|t| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 天然林 | 当年5月 | -0.0006 | 0.0003 | -2.43 | 0.028 |
| 当年6月 | -0.0006 | 0.0003 | -2.18 | 0.046 | |
| 当年7月 | -0.0005 | 0.0003 | -1.54 | 0.145 | |
| 人工林 | 当年5月 | -0.0004 | 0.0005 | -0.69 | 0.500 |
| 当年6月 | -0.0005 | 0.0005 | -1.06 | 0.306 | |
| 当年7月 | -0.0004 | 0.0005 | -0.77 | 0.453 |
表4 降水梯度下油松径向生长与PDSI之间的效应值及统计参数
Table 4 Statistics of effect size ( R ) between radial growth of Pinus tabulaeformis and PDSI under precipitation gradients
| 林分 来源 | 月份 | 效应值的 系数 | 标准差 | t | P>|t| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 天然林 | 当年5月 | -0.0006 | 0.0003 | -2.43 | 0.028 |
| 当年6月 | -0.0006 | 0.0003 | -2.18 | 0.046 | |
| 当年7月 | -0.0005 | 0.0003 | -1.54 | 0.145 | |
| 人工林 | 当年5月 | -0.0004 | 0.0005 | -0.69 | 0.500 |
| 当年6月 | -0.0005 | 0.0005 | -1.06 | 0.306 | |
| 当年7月 | -0.0004 | 0.0005 | -0.77 | 0.453 |
| 林分 来源 | 月份 | 效应值的 系数 | 标准差 | t | P>|t| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 天然林 | 当年5月 | -0.06 | 0.020 | -3.03 | 0.008 |
| 当年6月 | -0.06 | 0.020 | -3.98 | 0.001 | |
| 当年7月 | -0.06 | 0.016 | -3.55 | 0.003 | |
| 人工林 | 当年5月 | -0.007 | 0.029 | -0.23 | 0.069 |
| 当年6月 | -0.005 | 0.026 | -0.20 | 0.845 | |
| 当年7月 | -0.023 | 0.026 | -0.86 | 0.403 |
表5 气温梯度下油松径向生长与PDSI之间的效应值及统计参数
Table 5 Statistics of effect size ( R ) between radial growth of Pinus tabulaeformis and PDSI under temperature gradients
| 林分 来源 | 月份 | 效应值的 系数 | 标准差 | t | P>|t| |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 天然林 | 当年5月 | -0.06 | 0.020 | -3.03 | 0.008 |
| 当年6月 | -0.06 | 0.020 | -3.98 | 0.001 | |
| 当年7月 | -0.06 | 0.016 | -3.55 | 0.003 | |
| 人工林 | 当年5月 | -0.007 | 0.029 | -0.23 | 0.069 |
| 当年6月 | -0.005 | 0.026 | -0.20 | 0.845 | |
| 当年7月 | -0.023 | 0.026 | -0.86 | 0.403 |
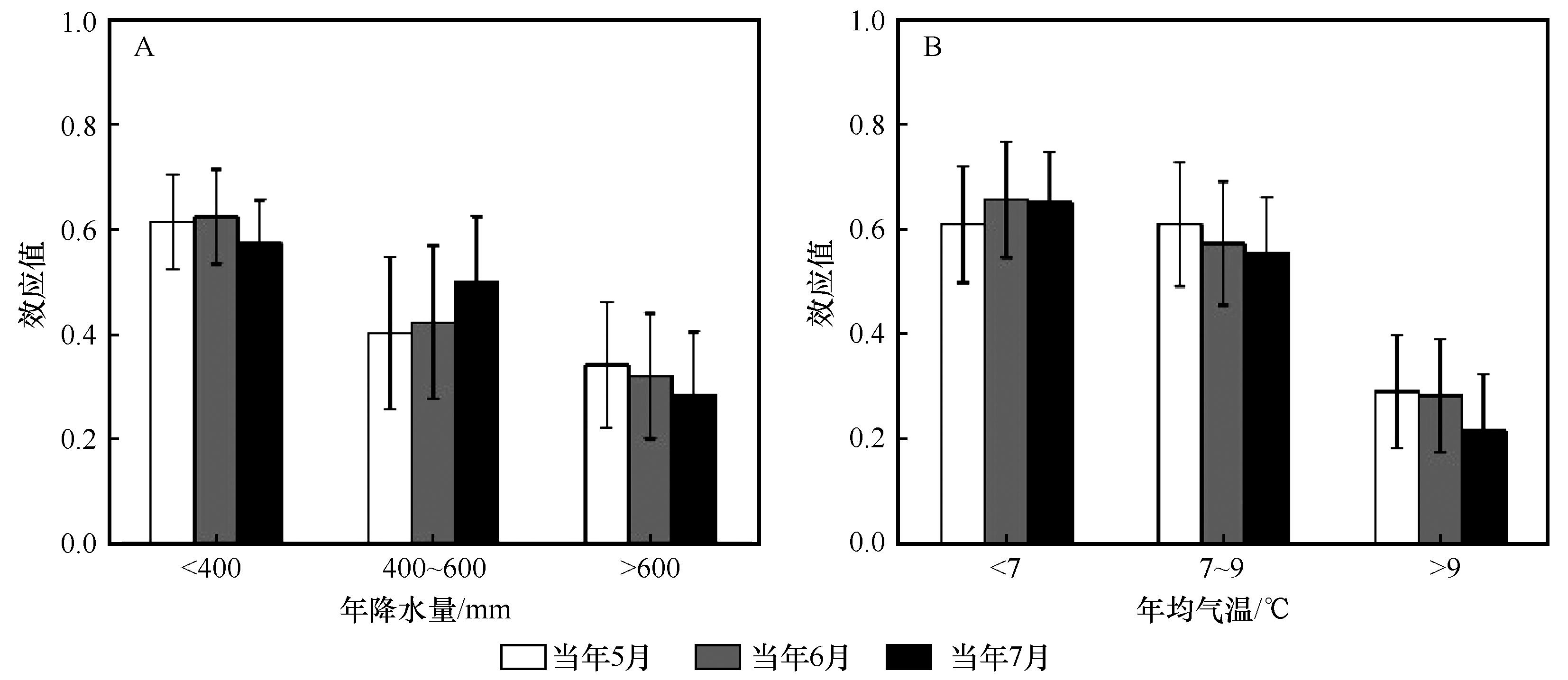
图9 降水(A)和气温(B)梯度下油松天然林径向生长与PDSI间的效应值
Fig.9 Effect size (R) between radial growth of natural Pinus tabulaeformis and PDSI under precipitation (A) and temperature (B) gradients

图10 降水(A)和气温(B)梯度下油松人工林径向生长与PDSI间的效应值
Fig.10 Effect size (R) between radial growth of planted Pinus tabulaeformis and PDSI under precipitation (A) and temperature (B) gradients
| 1 | Brubaker L B.Tree rings and climate[J].Ecology,1977,58(6):1400-1401. |
| 2 | 方克艳,勾晓华,陈发虎,等.树轮生态学研究进展[J].冰川冻土,2008,30(5):825-834. |
| 3 | Guo H, Wang B, Ma X Q,et al.Evaluation of ecosystem services of Chinese pine forests in China[J].Science in China Series C:Life Sciences,2008,51:662-670. |
| 4 | 王生军,韩丽华,李春红,等.樟子松、赤松、油松在形态结构及生态生物学特性的比较研究[J].干旱区资源与研究,2008,22(10):179-182. |
| 5 | 韩超,肖生春,丁爱军,等.腾格里沙漠南缘青海云杉(Picea crassifolia)和油松(Pinus tabulaeformis)年轮记录的气候变化[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(3):50-58. |
| 6 | Chen F, Yuan Y J, Chen F H,et al.Reconstruction of spring temperature on the southern edge of the Gobi Desert,Asia,reveals recent climatic warming[J].Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology,2014,409:145-52. |
| 7 | Fang K Y, Gou X H, Chen F,et al.Tree-ring based reconstruction of drought variability (1615-2009) in the Kongtong Mountain area,northern China[J].Global and Planetary Change,2012,80:190-197. |
| 8 | Sun J Y, Liu Y, Wang Y C,et al.Tree-ring based runoff reconstruction of the upper Fenhe River basin,North China,since 1799 AD[J].Quaternary International,2013,283:117-124. |
| 9 | Chen F, Yuan Y J, Wei W S,et al.Reconstructed precipitation for the north-central China over the past 380 years and its linkages to East Asian summer monsoon variability[J].Quaternary International,2013,283:36-45. |
| 10 | 陈智平,张涛,赵万奎,等.黄土高原子午岭林区油松林种子雨强度及时空动态特征[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(3):85-93. |
| 11 | 刘淑明,董立民.油松地理分布区质量等级的划分[J].西北林学院学报,1995,10(3):35-39. |
| 12 | 徐文铎,邹春静.中国沙地森林生态系统[M].北京:中国森林出版社,1998. |
| 13 | Li G Q, Xu G H, Guo K,et al.Geographical boundary and climatic analysis of Pinus tabulaeformis in China:insights on its afforestation[J].Ecological Engineering,2016,86:75-84. |
| 14 | Wang X F, Yang B.Divergent tree radial growth at alpine coniferous forest ecotone and corresponding responses to climate change in northwestern China[J].Ecological Indicators,2020,121:107052. |
| 15 | Chen K, Jiao L, Liu X P,et al.Evaluation of the response stability of two dominant conifer species to climate change in the southern margin of the Tengger Desert[J].Global Ecology and Conservation,2021,25:e01439. |
| 16 | 郭树杰,徐华,宋建昌,等.油松种质资源调查收集初报[J].陕西林业科技,2013(4):28-30. |
| 17 | 赵莹,蔡立新,靳雨婷,等.暖干化加剧东北半干旱地区油松人工林径向生长的水分限制[J].应用生态学报,2021,32(10):3459-3467. |
| 18 | Cai L X, Li J X, Bai X P,et al.Variations in the growth response of Pinus tabulaeformis to a warming climate at the northern limits of its natural range[J].Trees,2020,34:707-719. |
| 19 | 刘鸣.系统评价Meta分析与评价方法[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2011. |
| 20 | 郑景云,尹云鹤,李炳元.中国气候区划新方案[J].地理学报,2010,65(1):2-12. |
| 21 | 高艳红,许建伟,张萌.中国 400 mm 等降水量变迁与干湿变化研究进展[J].地球科学进展,2020,35(11):1101-1112. |
| 22 | Gong C, Tand Q U, Xua M X,et al.Mixed-species plantations can alleviate water stress on the Loess Plateau[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2020,458:117767. |
| 23 | Liu Y, Song H M, Sun C F,et al.The 600-mm precipitation isoline distinguishes tree-ring-width responses to climate in China[J].National Science Review,2019,6:359-368. |
| 24 | Van Mantgem P J, Stephenson N L, Byrne J C,et al.Widespread increase of tree mortality rates in the western United States[J].Science,2009,323:521-524. |
| 25 | 李颖辉,齐贵增,冯荣荣,等.秦岭北麓油松径向生长对气候变化的响应[J].应用生态学报,2022,33(8):2043-2050. |
| 26 | Liu Y, Linderholm H W, Song H M,et al.Temperature variations recorded in Pinus tabulaeformis tree rings from the southern and northern slopes of the central Qinling Mountains,central China[J].Journal of Quaternary Science,2008,38:285-291. |
| 27 | Van D, Barichivich J, Briffa K R,et al.A scPDSI-based global data set of dry and wet spells for 1901-2009[J].Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres,2013,118(10):4025-4048. |
| 28 | Gou X H, Chen F, Jacoby G,et al.Rapid tree growth with respect to the last 400 years in response to climate warming,northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J].International Journal of Climatology,2007,27(11):1497-1503. |
| 29 | Cai Q F, Liu Y.Climatic response of three tree species growing at different elevations in the Lüliang Mountains of northern China[J].Dendrochronologia,2013,31(4):311-317. |
| 30 | Zhang X, Liu Y, Song H,et al.Interannual variability of PDSI from tree-ring widths for the past 278 years in Baotou,China[J].Trees,2017,31:1531-1541. |
| 31 | Mäkinen H, Nöjd P, Kahle H P,et al.Large-scale climatic variability and radial increment variation of Picea abies (L.) in central and northern Europe[J].Trees,2003,17:173-184. |
| 32 | Camarero J J, Rubio-Cuadrado A.Relating climate,drought and radial growth in broadleaf mediterranean tree and shrub species:a new approach to quantify climate-growth relationships[J].Forest,2020,11(12):1250. |
| 33 | Bai M W, Dong Z P, Chen D,et al.Different responses of the radial growth of the planted and natural forests to climate change in humid subtropical China[J].Geografiska Annaler Series:A,Physical Geography,2020,102(1):1-12. |
| 34 | Domec J, King J S, Ward E,et al.Conversion of natural forests to managed forest plantations decreases tree resistance to prolonged droughts[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2015 355:58-71. |
| 35 | Che C W, Xiao S C, Ding A J,et al.Growth response of plantations Hippophae rhamnoides Linn.on different slope aspects and natural Caragana opulens Kom.to climate and implications for plantations management[J].Ecological Indicators,2022,138:108833. |
| 36 | Che C W, Xiao S C, Peng X M,et al.Radial growth of Korshinsk peashrub and its response to drought in different sub-arid climate regions of northwest China[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2023,326:116708. |
| 37 | IPCC.Climate Change 2021:the Physical Science Basis[M].Cambridge,UK:Cambridge University Press,2021. |
| 38 | Marcott S A, Shakun J, Clark P U,et al.A reconstruction of areasal and global temperature for the past 11,300 years[J].Science,2013,339(6124):1198-1201. |
| 39 | Liu H, Cui H, Yu P,et al.The origin of remnant forest stands of Pinus tabulaeformis in southeastern Inner Mongolia[J].Plant Ecology,2002,158:139-151. |
| 40 | 刘慎谔.东北木本植物图志[M].北京:科学出版社,1955 |
| 41 | 韦红红.北京松山不同地形条件下油松径向生长与气候的关系[D].北京:北京林业大学,2017. |
| 42 | Du H, Liu J, Li M H,et al.Warming-induced upward migration of the alpine treeline in the Changbai Mountains,northeast China[J].Global Change Biology,2018,24:1256-1266. |
| [1] | 吴倩倩, 张晓, 徐书兴, 杨晓晖, 刘艳书, 李瀚之, 时忠杰. 亚洲内陆干旱区NDVI与树木生长的气候响应及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 1-10. |
| [2] | 陈智平, 张涛, 赵万奎, 张晓庆, 王辉. 黄土高原子午岭林区油松林种子雨强度及时空动态特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(3): 85-93. |
| [3] | 韩超, 肖生春, 丁爱军, 滕泽宇. 腾格里沙漠南缘青海云杉(Picea crassifolia)和油松(Pinus tabulaeformis)年轮记录的气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 50-58. |
| [4] | 丁爱军, 肖生春, 彭小梅, 田全彦. 霸王(Sarcozygium xanthoxylon)灌木年轮记录的1902-2015年阿拉善荒漠中部气候干湿变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(2): 401-409. |
| [5] | 彭小梅, 肖生春, 程国栋, 肖洪浪, 田全彦. 胡杨(Populus euphratica)树轮记录的20世纪40年代前后黑河下游分水过程及其生态影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(1): 206-215. |
| [6] | 田全彦, 肖生春, 彭小梅, 肖洪浪. 胡杨(Populus euphratica)与柽柳(Tamarix ramosissima)径向生长特征对比[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(6): 1512-1519. |
| [7] | 贺敏慧, 杨保. 使用微树芯方法监测树木径向生长变化的研究综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(4): 1133-1142. |
| [8] | 徐海量1, 邓晓雅2, 赵新风1. 河道断流对胡杨(Populus euphratica)径向生长量的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(3): 731-736. |
| [9] | 安红燕;叶 茂;徐海量*;禹朴家;. 塔里木河下游胡杨径向生长量对生态输水的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(4): 957-962. |
| [10] | 王章勇;杨 保;秦 春;史 锋. 树木径向生长机制监测和模拟研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(3): 780-787. |
| [11] | 陈少勇;董安祥. 中国黄土高原土壤湿度的气候响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2008, 28(1): 66-72. |
| [12] | 鲁瑞洁;夏 虹*. 腾格里沙漠南缘油松树轮宽度变化及其对气候因子的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2006, 26(3): 399-402. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
