
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 195-206.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00075
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yue Wang1( ), Nana Yi2(
), Nana Yi2( ), Xuegong Jiang3, Guicai Ning1, Lian Su1, Haiyun Xia1(
), Xuegong Jiang3, Guicai Ning1, Lian Su1, Haiyun Xia1( )
)
Received:2024-04-26
Revised:2024-08-28
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-12-06
Contact:
Nana Yi,Haiyun Xia
CLC Number:
Yue Wang, Nana Yi, Xuegong Jiang, Guicai Ning, Lian Su, Haiyun Xia. Diagnosis of severe dust weather process based on multi-source observational data[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(6): 195-206.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00075
| 参数 | 值 |
|---|---|
| 波长 | 1.5 μm |
| 脉冲能量 | 150 μJ |
| 望远镜口径 | 70 mm |
| 脉冲重复频率 | 10 kHz |
| 时间分辨率 | 1 s |
| 空间分辨率 | 30 m |
| 最大探测距离 | 15 km |
| 方位角 | 0°~360° |
| 俯仰角 | 0°~90° |
Table 1 Key parameters of the CDWL
| 参数 | 值 |
|---|---|
| 波长 | 1.5 μm |
| 脉冲能量 | 150 μJ |
| 望远镜口径 | 70 mm |
| 脉冲重复频率 | 10 kHz |
| 时间分辨率 | 1 s |
| 空间分辨率 | 30 m |
| 最大探测距离 | 15 km |
| 方位角 | 0°~360° |
| 俯仰角 | 0°~90° |
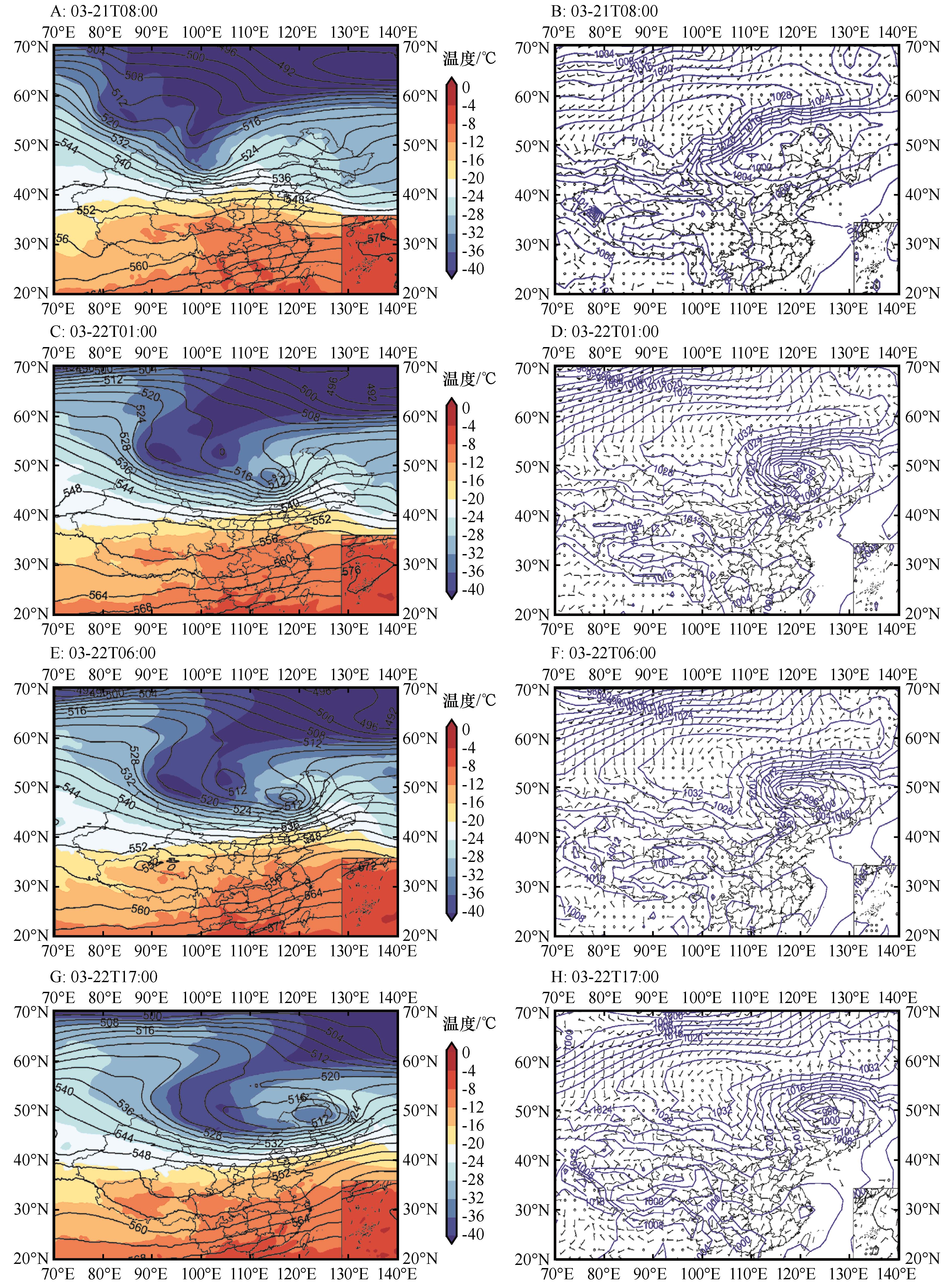
Fig.1 500 hPa temperature (shading; units: ℃;A,C,E,G), 500 hPa geopotential height (contours; units: gpm;A,C,E,G), sea level pressure (contours;B,D,F,H), 10 m gust wind plume (B,D,F,H;unit:m·s-1) at 08:00 BJT on 21(A,B), 01:00 BJT on 22(C,D), 06:00 BJT on 22 (E,F) and 17:00 BJT on 22(G,H), March 2023
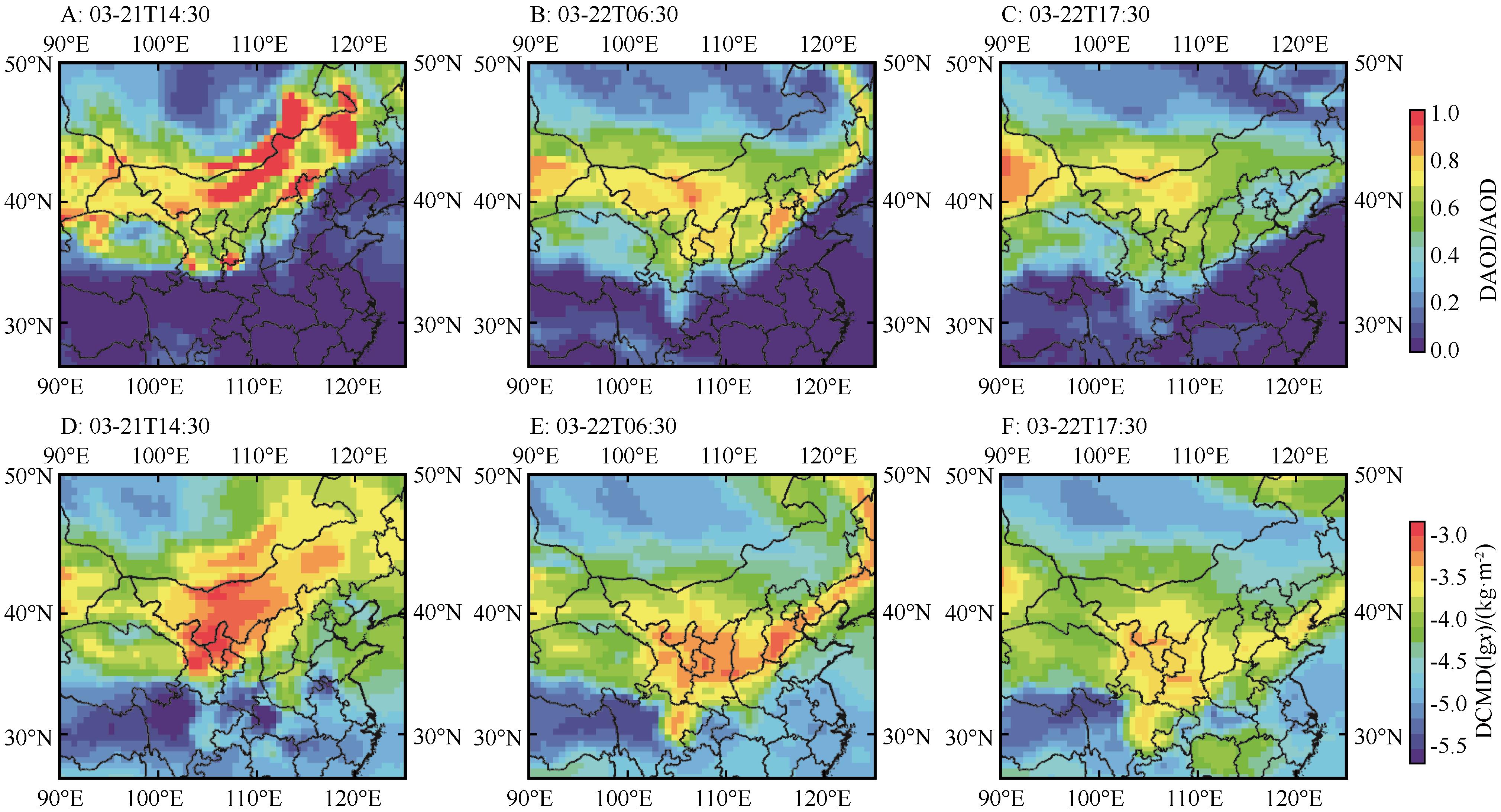
Fig.2 Spatial distribution of the typical dust storm occurred for multi-source datasets (DAOD/AOD, DCMD) at (A, D) 14:30 BJT on 21 March, (B, E) 06:30 BJT and (C, F) 17:30 BJT on 22, March 2023

Fig.3 Spatial distribution of the typical dust storm occurred for PM10 concentration at (A) 15:00 BJT on 21 March, (B) 06:00 BJT and (C) 18:00 BJT on 22, March 2023
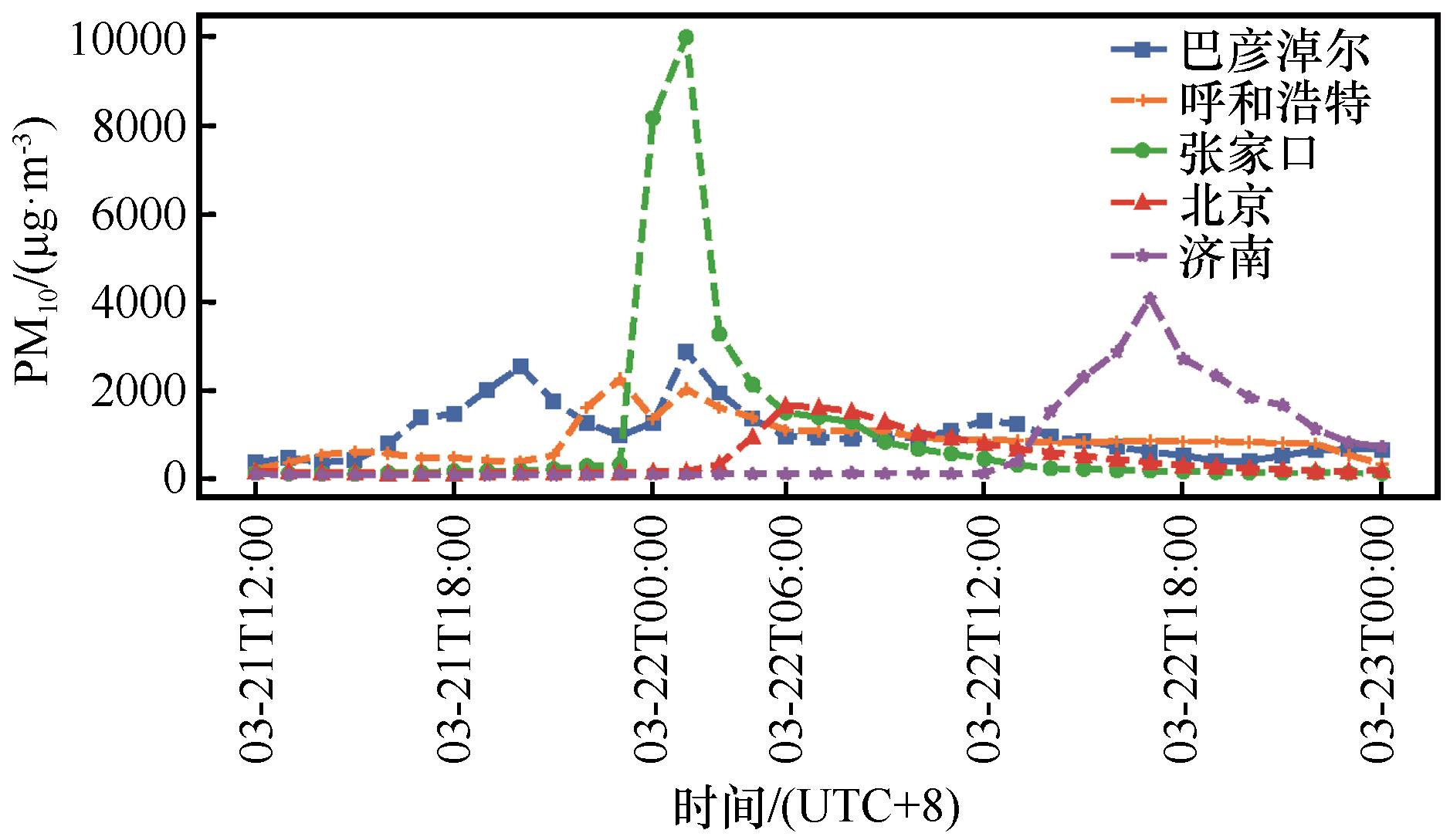
Fig.4 Hourly variation characteristics of PM10 concentration during sand and dust pollution weather events in cities along the route of dust pollution weather event from 12:00 BJT 21 to 00:00 BJT 23, March 2023 (Missing values at 02:00 and 05:00 on March 22)
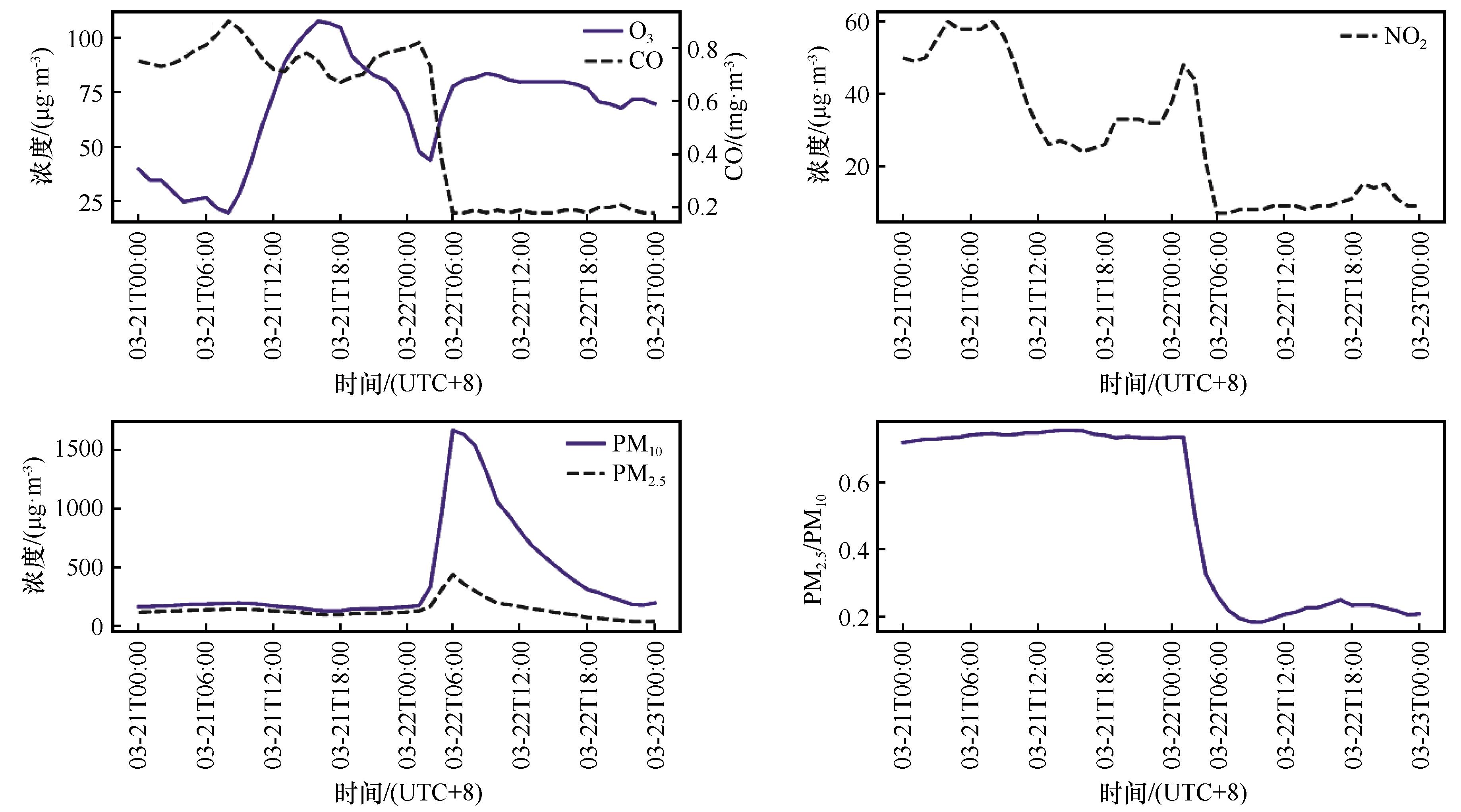
Fig.6 Time series of particle concentration, proportion and gaseous pollutant concentration in Beijing City before and after the impact of dust (Missing values at 02:00 and 05:00 on March 22)
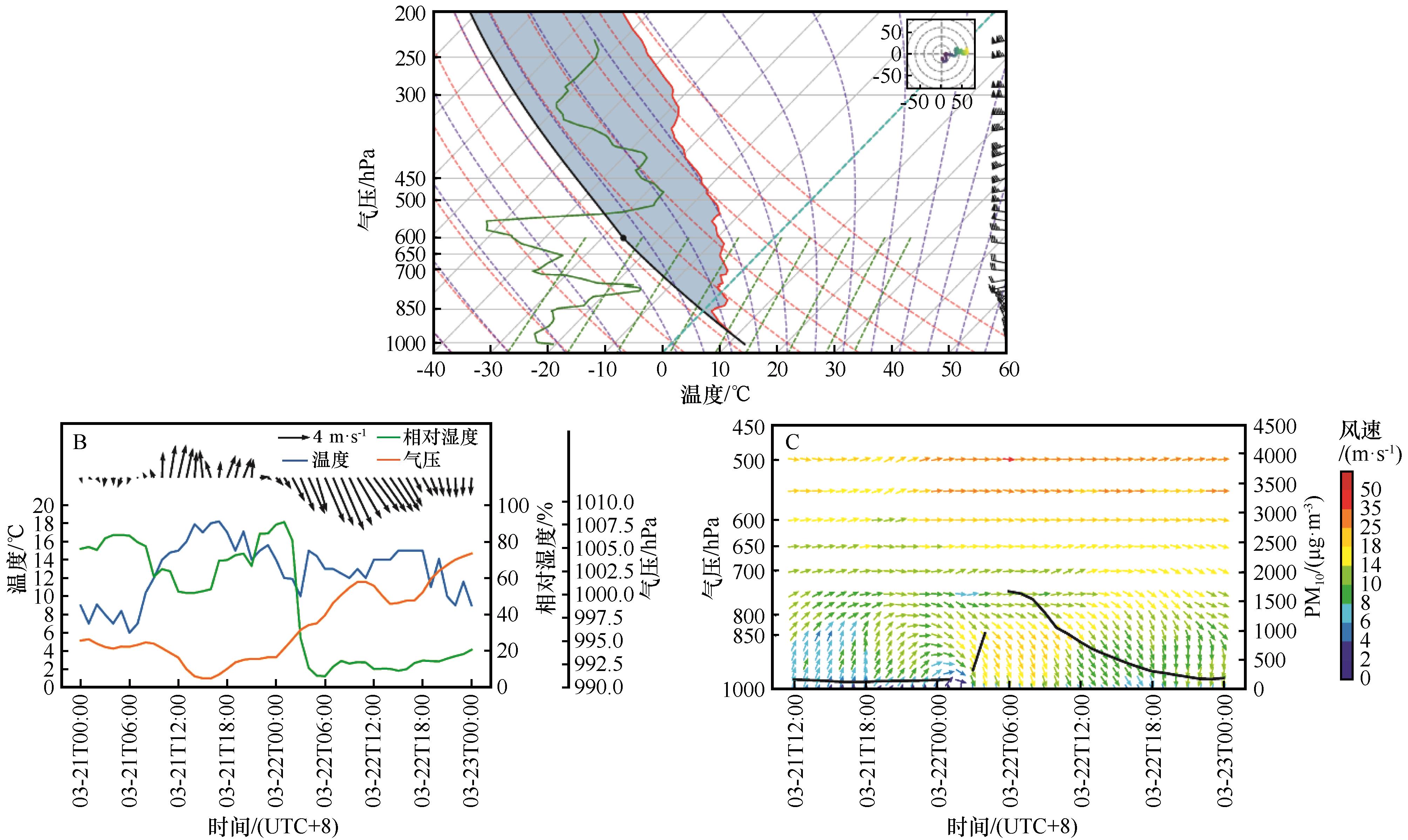
Fig.8 (A) The Skew T-lnP diagram of Beijing Sounding Station at 08:00 BJT on 22, March 2023, (B) Time series of wind speed, wind direction, temperature, relative humidity, ground pressure in Beijing City from 00:00 BJT 21 to 00:00 BJT 23, March 2023, (C) The temporal changes of PM10 and wind field (u,v) during sand and dust pollution weather events in cities along the route of dust pollution weather event from 12:00 BJT 21 to 00:00 BJT 23, March 2023 (Missing PM10 values at 02:00 and 05:00 on March 22)
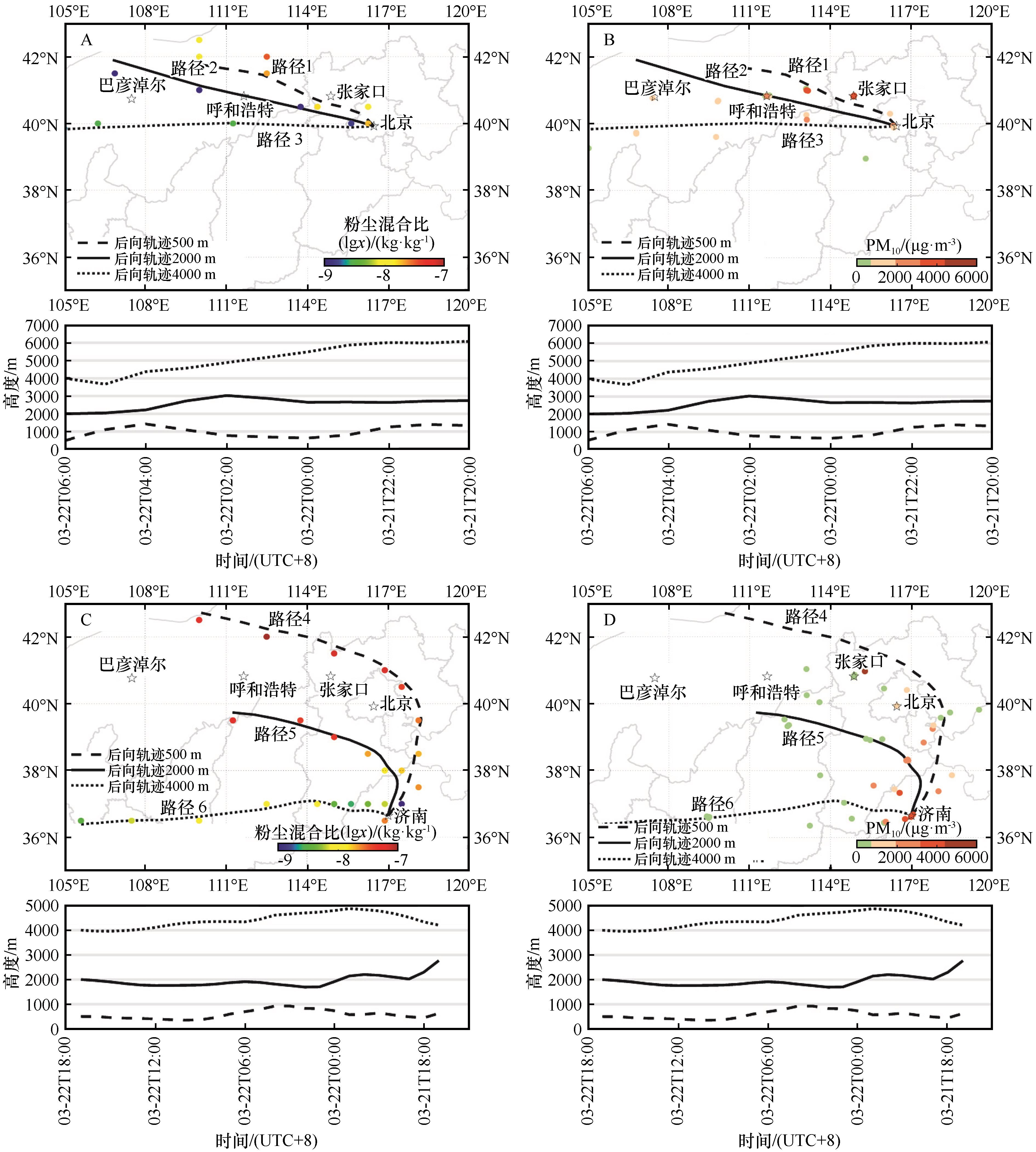
Fig.9 Backward trajectory during dust pollution weather events. (A, C) spatial distribution of MERRA-2 Dust Mixing Ratio; (B, D) spatial distribution of ground PM10 concentration along the route of dust pollution weather event, respectively. The dashed line is the 500 m air mass path, the dashed line is the 2 000 m air mass path, and the dash dot line is the 4 000 m air mass path
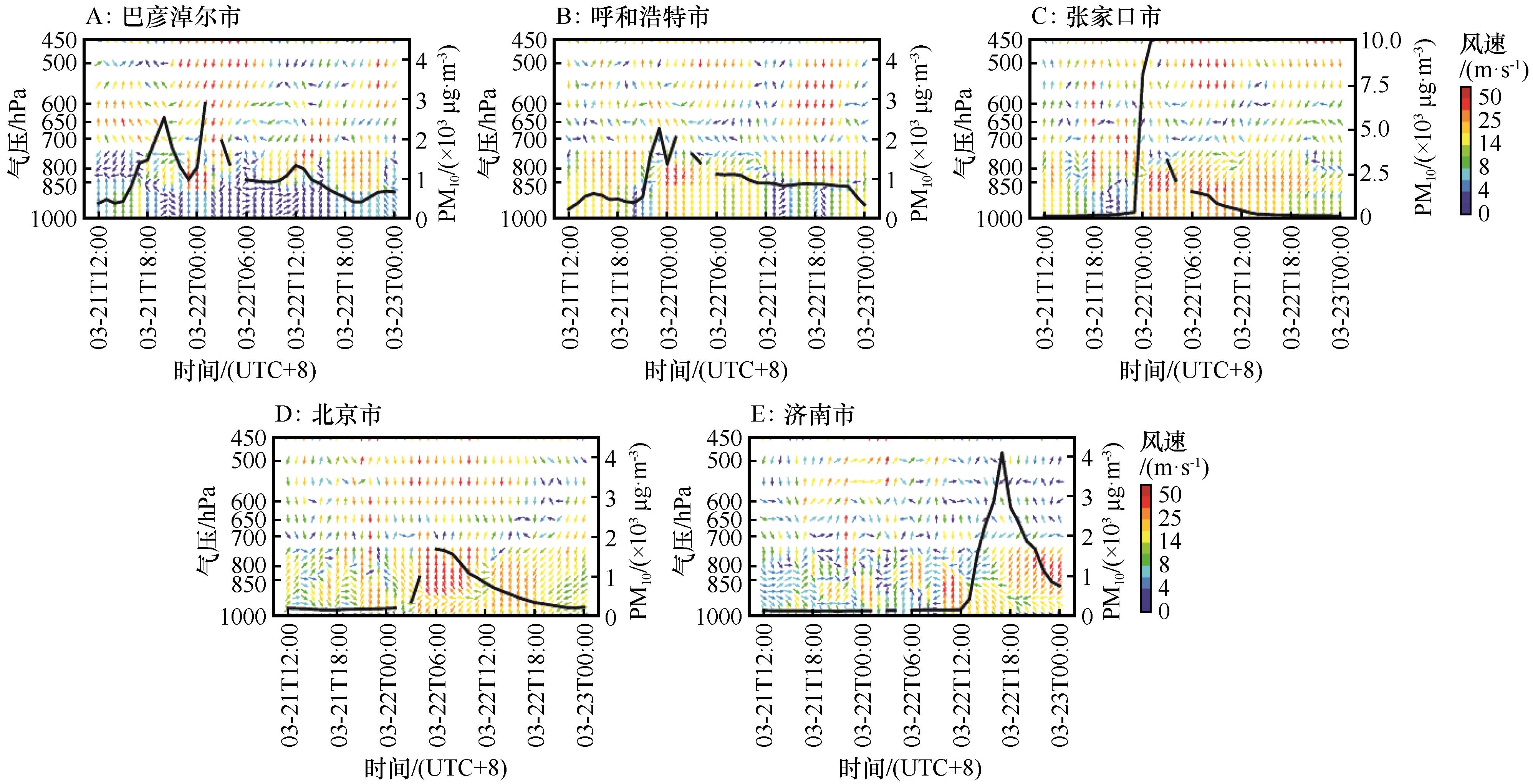
Fig.10 The temporal changes of PM10 and wind field (v, w×(-50)) during sand and dust pollution weather events in cities along the route of dust pollution weather event from 12:00 BJT 21 to 00:00 BJT 23, March 2023 (Missing PM10 values at 02:00 and 05:00 on March 22)
| 1 | 魏巍,孙萌,王明丽.沙尘天气对青岛市空气质量的影响分析[J].科学技术创新,2019(17):54-55. |
| 2 | 邱海杰,周佺,周辉,等.2018年沙尘天气对随州空气质量的影响分析[J].环境科学与技术,2019,42():159-162. |
| 3 | 廖乾邑,罗彬,杜云松,等.北方沙尘对四川盆地环境空气质量影响和特征分析[J].中国环境监测,2016,32(5):51-55. |
| 4 | 马雁军,刘宁微,洪也,等.2011年春季辽宁一次沙尘天气过程及其对不同粒径颗粒物和空气质量的影响[J].环境科学学报,2012,32(5):1160-1167. |
| 5 | Wang J Y, Su S X, Yin Z L,et al.Quantitatively assessing the contributions of dust aerosols to direct radiative forcing based on remote sensing and numerical simulation[J].Remote Sensing,2022,14(3):660-668. |
| 6 | 陈洪武,王旭,马禹.塔里木盆地局地和区域性强沙尘暴天气过程研究[J].中国沙漠,2003,23(5):533-538. |
| 7 | Lu X, Mao F Y, Pan Z X,et al.Three-dimensional physical and optical characteristics of aerosols over central China from long-term CALIPSO and HYSPLIT data[J].Remote Sensing,2018,10(2):314-321. |
| 8 | Attiya A A, Jones B G.An extensive dust storm impact on air quality on 22 November 2018 in Sydney,Australia,using satellite remote sensing and ground data[J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment,2022,194(6):432-439. |
| 9 | Peng Z R, Wang D S, Wang Z Y,et al.A study of vertical distribution patterns of PM2.5 concentrations based on ambient monitoring with unmanned aerial vehicles:a case in Hangzhou,China[J].Atmospheric Environment,2015,123:357-369. |
| 10 | Zhang S, Huang Z W, Li M S,et al.Vertical structure of dust aerosols observed by a ground-based Raman Lidar with polarization capabilities in the center of the Taklimakan Desert[J].Remote Sensing,2022,14(10):2461-2470. |
| 11 | Song M Q, Wang Y, Mamtimin A,et al.Applicability assessment of coherent Doppler Wind LiDAR for monitoring during dusty weather at the northern edge of the Tibetan Plateau[J].Remote Sensing,2022,14(20):5264-5273. |
| 12 | Wei T W, Xia H Y, Hu J J,et al.Simultaneous wind and rainfall detection by power spectrum analysis using a VAD scanning coherent Doppler lidar[J].Optics Express,2019,27(22):31235-31245. |
| 13 | Xia H Y, Chen Y X, Yuan J L,et al.Windshear detection in rain using a 30 km Radius Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar at mega airport in plateau[J].Remote Sensing,2024,16(5):924-935. |
| 14 | Wang L, Qiang W, Xia H Y,et al.Robust solution for boundary layer height detections with coherent Doppler wind lidar[J].Advances in Atmospheric Sciences,2021,38(11):1920-1928. |
| 15 | Yu S F, Zhang Z, Xia H Y,et al.Photon-counting distributed free-space spectroscopy[J].Light:Science Applications,2021,10:212-220. |
| 16 | Zhai X C, Wu S H, Liu B Y.Doppler lidar investigation of wind turbine wake characteristics and atmospheric turbulence under different surface roughness[J].Optics Express,2017,25(12):A515-A529. |
| 17 | Yuan J L, Wu Y B, Xia H Y,et al.Real‐time synchronous 3‐D detection of air pollution and wind using a Solo Coherent Doppler Wind Lidar[J].Remote Sensing,2022,14(12):2809-2817. |
| 18 | 吴占华,任国玉.我国北方区域沙尘天气的时间特征分析[J].气象科技,2007,35(1):96-100. |
| 19 | 唐杨,徐志方,韩贵琳.北京及其北部地区大气降尘时空分布特征[J].环境科学与技术,2011,34(2):115-119. |
| 20 | 马俊.北方今春为何风沙有点多[N/OL].环球时报,2023-03-24(3). |
| 21 | 徐文帅,张大伟,李云婷,等.北京两次沙尘污染过程中PM2.5浓度变化特征[J].气候与环境研究,2016,21(1):78-86. |
| 22 | Filonchyk M.Characteristics of the severe March 2021 gobi desert dust storm and its impact on air pollution in China[J].Chemosphere,2022,287:132219. |
| 23 | Hammer M S, Martin R V, Li C,et al.Insight into global trends in aerosol composition from 2005 to 2015 inferred from the OMI ultraviolet aerosol index[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2018,18(11):8097-8112. |
| 24 | Farooqui M, West J, Shankar U,et al.Assessment of dust emissions model and PM10 in the United Arab Emirates during dust storms using the CMAQ-WRF Modeling System[C]//American Geophysical Union,Fall Meeting,2013,abstract id.A41G-0138. |
| 25 | 霍文,智协飞,杨莲梅,等.沙漠气象若干问题研究进展[J].大气科学学报,2019,42(3):469-480. |
| 26 | Rizza U, Barnaba F, Miglietta M,et al.WRF-Chem model simulations of a dust outbreak over the central Mediterranean and comparison with multi-sensor desert dust observations[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2017,17(1):93-115. |
| 27 | Chen S Y, Zhao D, Huang J P,et al.Mongolia contributed more than 42% of the dust concentrations in northern China in March and April 2023[J].Advances in Atmospheric Sciences,2023,40:1549-1557. |
| 28 | 陈思宇,黄建平,李景鑫,等.塔克拉玛干沙漠和戈壁沙尘起沙、传输和沉降的对比研究[J].中国科学:地球科学,2017,47(8):939-957. |
| 29 | 顿耀权,罗万银,邵梅,等.干旱区内陆湖盆沙尘水平通量及粒度特征[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(6):166-175. |
| 30 | 秦豪君,杨晓军,马莉,等.2000-2020年中国西北地区区域性沙尘暴特征及成因[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(6):53-64. |
| 31 | Sun E W, Xu X F, Che H Z,et al.Variation in MERRA-2 aerosol optical depth and absorption aerosol optical depth over China from 1980 to 2017[J].Journal of Atmospheric and Solar-Terrestrial Physics,2019,186:8-19. |
| 32 | Gueymard C A, Yang D Z.Worldwide validation of CAMS and MERRA-2 reanalysis aerosol optical depth products using 15 years of AERONET observations[J].Atmospheric Environment,2020,225:117216. |
| 33 | Yao W R, Che H Z, Gui K,et al.Can MERRA-2 reanalysis data reproduce the three-dimensional evolution characteristics of a typical dust process in East Asia?a case study of the dust event in May 2017[J].Remote Sensing,2020,12(6):902-911. |
| 34 | Rui W Y, Ke G, Q Wang Ya,et al.Identifying the dominant local factors of 2000-2019 changes in dust loading over East Asia[J].Science of The Total Environment,2021,777:146064. |
| 35 | Fang G C, Chang C N, Wu Y S,et al.Concentration of atmospheric particulates during a dust storm period in central Taiwan,Taichung[J].Science of The Total Environment,2002,287(1/2):141-145. |
| 36 | 林葳.你不可不知的2500条地理常识[M],内蒙古呼伦贝尔:内蒙古文化出版社,2011:306. |
| 37 | Lyu Y L, Qu Z Q, Liu L Y,et al.Characterization of dustfall in rural and urban sites during three dust storms in northern China,2010[J].Aeolian Research,2017,28:29-37. |
| 38 | 王式功,董光荣,陈惠忠,等.沙尘暴研究的进展[J].中国沙漠,2000,20(4):349-356. |
| 39 | Chan Y C, Mctainsh G, Leys J,et al.Influence of the 23 October 2002 dust storm on the air quality of four Australian cities[J].Water Air Soil Pollution,2005,164:329-348. |
| 40 | Liu C M, Young C Y, Lee Y C.Influence of Asian dust storms on air quality in Taiwan[J].Science of the Total Environment,2006,368(2/3):884-897. |
| 41 | 陈跃浩,高庆先,高文康,等.沙尘天气对大气环境质量影响的量化研究[J].环境科学研究,2013,26(4):364-369. |
| 42 | 杨青,杨莲梅,张广兴,等.能见度与空气质量的关系研究[J].中国沙漠,2006,26(2):278-282. |
| 43 | 孙兆彬,安兴琴,崔甍甍,等.北京地区颗粒物健康效应研究:沙尘天气、非沙尘天气下颗粒物(PM2.5、PM10)对心血管疾病入院人次的影响[J].中国环境科学,2016,36(8):2536-2544. |
| 44 | 袁瑞瑞,王建英,张卫红,等.不同路径冷空气导致的宁夏沙尘重污染天气特征及传输规律[J].中国沙漠,2024,44(1):209-217. |
| 45 | 盛慧,颜为军,孟鑫鑫,等.一次典型沙尘过程对我国热带地区空气质量影响分析[J].环境科学学报,2024,44(2):310-319. |
| 46 | Xie S, Qi Y Z L, Tang X.Characteristics of air pollution in Beijing during sand-dust storm periods[J].Water Air Soil Pollution:Focus,2005,5(3):217-229. |
| 47 | 魏巍,皮冬勤,晏平仲,等.2017年春季华北地区一次典型沙尘重污染天气过程研究[J].环境科学学报,2018,38(5):1699-1707. |
| 48 | 陈辉,赵琳娜,赵鲁强,等.沙尘天气过程对北京空气质量的影响[J].环境科学研究,2012,25(6):609-614. |
| [1] | Lang Zhang, Guofeng Dang, Tengfei Yu, Tuo Han, Yidan Yin, Yong Chen. Monitoring and change analysis of vegetation coverage in Ejin Oasis based on UAV-LiDAR [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(5): 170-181. |
| [2] | Ming Zhao, Chunxiao Zhou, Chong Li, Shuo Liu, Hujia Zhao. Temporal-spatial distribution of sand dust intensity during 1960-2020 in Liaoning [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(2): 113-120. |
| [3] | Xiaopeng Jia, Qimin Ma, Yinping Long, Haibing Wang. Soil evaporation monitored with medium-lysimeter in an artificial forest in the Hobq Desert, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 211-222. |
| [4] | Jiaoyue Wang, Shugao Qin, Yuqing Zhang. Spatial-temporal patterns of vegetation water use efficiency in the Mu Us Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(5): 120-129. |
| [5] | Yang Yanping, Wang Lina, Yang Lili, Tao Huijie, Jiang Lin. Air pollution characteristics and potential sources in Lanzhou during dust weather [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(3): 60-66. |
| [6] | Li Xia, Liu Tingxi, Duan Limin, Wang Guanli, Tong Xin, Zhou Yajun, Yang Xiaojun. Simulation of reference crop evapotranspiration and analysis of the factor effect in Horqin wet meadow [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(2): 134-143. |
| [7] | Wang Juan, Li Xingcai. Exploration of the atmospheric electricity at 5-7 000 m height in sandstorm and its effect on the electrification of sands [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(1): 23-28. |
| [8] | Yue Xiyuan, Zuo Xiaoan, Chang Xueli, Xu Chong, Lv Peng, Zhang Jing, Zhao Shenglong, Cheng Qingping. NDVI of Typical Steppe and Desert Steppe in Inner Mongolia in Response to Meteorological Factors [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(3): 25-33. |
| [9] | Li Fan, Xiao Jianshe, Qi Donglin, Li Lin. Impact Factors of Dust Storms in Qaidam Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(2): 144-150. |
| [10] | Luo Fengmin, Gao Junliang, Xin Zhiming, Hao Yuguang, Wang Lina, Li Shuai. Characteristics of Soil Temperature Variation and Influence Factors at Northeastern Margin Region of Ulan Buh Desert, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(1): 179-186. |
| [11] | Su Yang, Qi Yuan, Wang Jianhua, Xu Feinan, Zhang Jinlong. Vegetation Coverage Classification and Vegetation Structure Parameters Extraction of Populus euphratica Forest in Ejina Oasis by LiDAR Data [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2017, 37(4): 689-697. |
| [12] | Wang Shaokun, Zhao Xueyong, Jia Kunfeng, Gao Baolan, Qu Hao, Mao Wei, Lian Jie, Chen Min, Zhu Yangchun. Soil Bacterial Diversity and Its Vertical Distribution in Stipa klemenzii Community of Urad Desert Steppe [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(6): 1564-1570. |
| [13] | Gao Chanchan, Zhao Chuanyan, Li Wenjuan, Bie Qiang, Peng Shouzhang, Wang Qingtao. Modeling Spatial Distribution of Rainfall Interception by Qinghai Spruce Forest Based on Airborne LiDAR Data [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(2): 515-521. |
| [14] | Huang Haitao, Chang Xueli, Yue Xiyuan, Lv Deyan. Responses of NDVI Changes to Air Temperature and Precipitation of Different Sandy Landscape Areas in the Horqin Sandy Land [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(1): 40-49. |
| [15] | Fang Jing, Ding Yongjian. An Experimental Observation of the Relationship between Sandy Soil Condensation Water and Micrometeorological Factors in the Arid Desert Region [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2015, 35(5): 1200-1205. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech