


Aeolian sand transport and its potential amount into Longyangxia Reservoir in 1987-2019 based on COSI-Corr
Received date: 2021-10-09
Revised date: 2021-11-04
Online published: 2021-12-17
Aeolian sand invasion has negative effect on the Yellow River and Longyangxia reservoirs. It is of great significance to sort out the provenance and the potential amount of sand transported into the reservoir to reduce the aeolian sandy hazards. In this study, the dune migrating trends were monitored and the potential amount of sand transported into the Longyangxia reservoir was evaluated using the Co-registration of Optically Sensed Images and Correlation (COSI-Corr) technique based on the Landsat images in 1987, 1995, 2003, 2013 and 2019. The results revealed that: (1) The mean annual dune migration rates upwind the study area was 5.81 m·a-1, with a trend of increasing from 1987 to 2003, then decreasing from 2003-2013 and increasing finally from 2013 to 2019. The dune migration directions were ranged from 132.81° to 165.82° during the 32 years, consisting well with the local prevailing wind. (2) The total potential amount of sand transported into the Longyangxia Reservoir from 1987 to 2019 was 7.82×107 m3(1.20×108 t). The upwind Talatan sandy land contributed 7.38×107 m3 (1.14×108 t) sand into the reservoir, while the downwind Mugetan sandy land only contributed 0.44×107 m3 (0.68×107 t). (3) The factors that affect the sand into the reservoir include the wind, climate and vegetation cover. With the future global warming on the Tibet Plateau, the intensity of aeolian activity will increase, therefore the long-term sand cumulative damage will seriously threaten the security of the reservoir area according to our evaluation, which must be paid enough attention and take some necessary actions to control it.
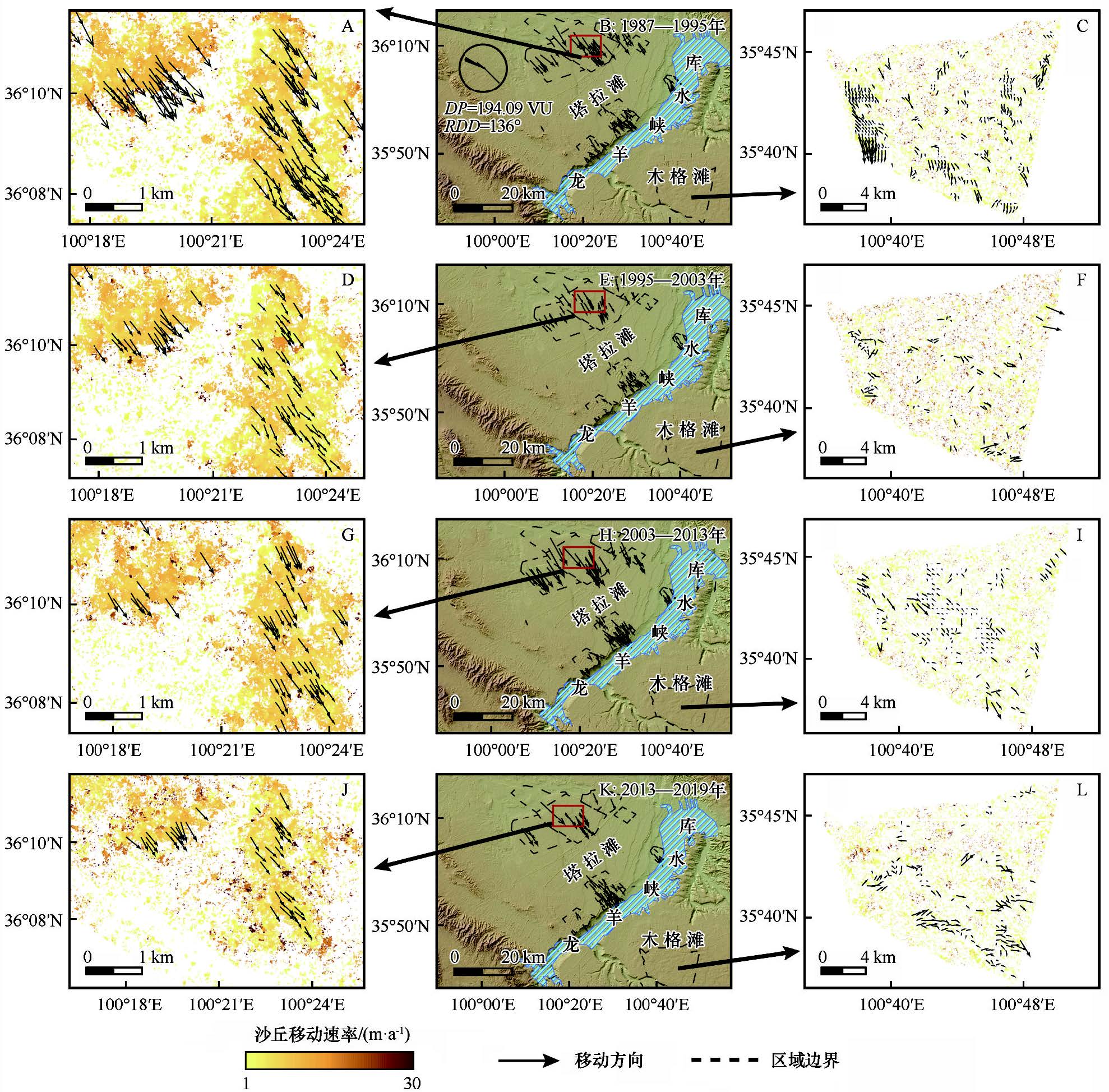
Mei Shao , Wanyin Luo , Xuehua Che , Fang Wang , Junfeng Lu , Songbing Zou . Aeolian sand transport and its potential amount into Longyangxia Reservoir in 1987-2019 based on COSI-Corr[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021 , 41(6) : 249 -261 . DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00154
| 1 | 徐勇,王传胜.黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展:框架、路径与对策[J].中国科学院院刊,2020,35(7):875-883. |
| 2 | 马柱国,符淙斌,周天军,等.黄河流域气候与水文变化的现状及思考[J].中国科学院院刊,2020,35(1):52-60. |
| 3 | 郑子彦,吕美霞,马柱国.黄河源区气候水文和植被覆盖变化及面临问题的对策建议[J].中国科学院院刊,2020,35(1):61-72. |
| 4 | Bullard J E,Livingstone I.Interactions between aeolian and fluvial systems in dryland environments[J].Area,2002,34(1):8-16. |
| 5 | 宋阳,严平,杜建会,等.巴图湾水库风沙入库量的估算[J].干旱区资源与环境,2008,22(5):68-73. |
| 6 | Belnap J,Munson S M,Field J P.Aeolian and fluvial processes in dryland regions:the need for integrated studies[J].Ecohydrology,2011,4(5):615-622. |
| 7 | Moustafa W M,Hussien R A,Nassar N.Evaluation of potential hazards associated with qattara depression as a national hydropower project in Egypt[J].Arab Journal of Nuclear Sciences and Applications,2018,51(2):58-67. |
| 8 | 段庆光,石蒙沂,王斌,等.龙羊峡库区风沙现状及其对库区的影响[J].干旱区研究,1990,8:22-29. |
| 9 | 姚檀栋,朱立平.青藏高原环境变化对全球变化的响应及其适应对策[J].地球科学进展,2006,21(5):459-464. |
| 10 | 杨根生,刘阳宜,史培军.黄河沿岸风成沙入黄沙量估算[J].科学通报,1988,13:1017-1021. |
| 11 | 方学敏.黄河干流宁蒙河段风沙入黄量计算[J].人民黄河,1993,4:1-4. |
| 12 | 高宏智,邹桂香.龙羊峡水库周围风沙流观测、计算及对库区的影响[J].干旱区资源与环境,1989,3(1):59-69. |
| 13 | 杨东亮,王雪芹,胡永锋,等.风沙流输沙通量垂向分布研究:以塔克拉玛干沙漠南缘流沙地表风沙流观测为例[J].中国沙漠,2012,32(3):631-639. |
| 14 | 韩致文,缑倩倩,杜鹤强,等.新月形沙丘表面100 cm高度内风沙流输沙量垂直分布函数分段拟合[J].地理科学,2012,32(7):892-897. |
| 15 | 毛东雷,蔡富艳,雷加强,等.新疆策勒河下游塔克拉玛干沙漠南缘风沙活动特征[J].干旱区资源与环境,2016,30(7):169-174. |
| 16 | 刘芳,郝玉光,徐军,等.乌兰布和沙区风沙运移特征分析[J].干旱区地理,2014,37(6):1163-1169. |
| 17 | 张正偲,董治宝.腾格里沙漠东南部野外风沙流观测[J].中国沙漠,2013,33(4):973-980. |
| 18 | Eryrear D W,Saleh A,Bilbro J D,et al.Revised Wind Erosion Equation[R].Lubbork,USA:ARS,1998. |
| 19 | Shao Y P.A model for mineral dust emission[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,2001,106(20):236-254. |
| 20 | 李振全.黄河石嘴山至巴彦高勒河段风沙入黄量研究[D].西安:西安理工大学,2019. |
| 21 | 董治宝,吕萍.深空探测时代的风沙地貌学[J].地球科学进展,2019,34(10):1001-1014. |
| 22 | 董治宝,吕萍.70年来中国风沙地貌学的发展[J].地理学报,2020,75(3):509-528. |
| 23 | 何京丽,张三红,崔巍,等.黄河内蒙古段乌兰布和沙漠入黄风积沙监测研究[J].水土保持,2011,10:46-48. |
| 24 | Ayoub F,Sébastien L,Avouac J P.Co-registration and correlation of aerial photographs for ground deformation measurements[J].Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing,2009,64(6):551-560. |
| 25 | Leprince S,Ayoub F,Klinger Y,et al.Co-Registration of optically sensed images and Correlation (Cosi-Corr):an operational methodology for ground deformation measurements[J].IEEE,2007:1943-1946. |
| 26 | Turk T.Determination of mass movements in slow-motion landslides by the COSI-Corr method[J].Geomatics,Natural Hazards and Risk,2018,9(1):325-336. |
| 27 | Michele M D,Sébastien L,Jérme T,et al.Direct measurement of ocean waves velocity field from a single SPOT-5 dataset[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2012,119:266-271. |
| 28 | Al-Mutiry M,Hermas E A,Al-Ghamdi K A,et al.Estimation of dune migration rates north Riyadh City,KSA,using SPOT 4 panchromatic images[J].Journal of African Earth Sciences,2016,124:258-269. |
| 29 | Vermeesch P.A 45-year time series of Saharan dune mobility from remote sensing[J].EGU General Assembly,2012,39:1-5. |
| 30 | Vermeesch P,Drake N.Remotely sensed dune celerity and sand flux measurements of the world's fastest barchans (Bodele,Chad) [J].Geophysical Research Letters,2008,35:1-6. |
| 31 | Scheidt S P,Lancaster N.The application of COSI-Corr to determine dune system dynamics in the southern Namib Desert using ASTER data[J].Earth Surface Process and Landforms,2013,38:1004-1019. |
| 32 | 邵梅,罗万银,车雪华.COSI-Corr技术在风沙地貌研究中的初步应用及精度检验[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(3):151-158. |
| 33 | 李森,颜长珍,宋翔,等.近30 a龙羊峡水库周边地区沙漠化遥感监测[J].中国沙漠,2011,31(4):836-841. |
| 34 | 沙占江,马海州,李玲琴,等.共和盆地龙羊峡库区1987—1999年间土地覆被变化过程[J].中国沙漠,2005,25(1):22-28. |
| 35 | 黄华兵,马海州,沙占江,等.基于RS的龙羊峡库区悬浮泥沙分布研究[J].盐湖研究,2004,4:34-37. |
| 36 | 董治宝.中国风沙物理研究五十年(I)[J].中国沙漠,2005,25(3):293-305. |
| 37 | Necsoiu M,Sébastien L,Hooper D M,et al.Monitoring migration rates of an active subarctic dune field using optical imagery[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2009,113(11):2441-2447. |
| 38 | Baird T,Bristow C S,Vermeesch P.Measuring sand dune migration rates with COSI-Corr and Landsat:opportunities and challenges[J].Remote Sensing,2019,11(20):2423. |
| 39 | 邵梅.沙源限制条件下沙丘的移动和变形研究:以共和盆地二塔拉地区为例[D].兰州:中国科学院西北生态环境资源研究院,2021. |
| 40 | 王翠,李生宇,雷加强,等.不同下垫面沙通量估算:以策勒绿洲-沙漠过渡带为例[J].干旱区地理,2017,40(3):533-540. |
| 41 | Luo W Y,Wang Z Y,Shao M,et al.Historical evolution and controls on mega-blowouts in northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau,China[J].Geomorphology,2019,329:17-31. |
| 42 | Michele M D,Leprince S,Thiébota J,et al.Direct measurement of ocean waves velocity field from a single SPOT-5 dataset[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2012,119:266-271. |
| 43 | Wolfe S A,David P.Parabolic dunes:examples from the great sand hills,southwestern saskatchewan[J].The Canadian geographer,1997,41(2):207-214. |
| 44 | Hesp P.The formation of shadow dunes[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research,1981,51(1):101-112. |
| 45 | 余沛东,陈银萍,李玉强,等.植被盖度对沙丘风沙流结构及风蚀量的影响[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(5):29-36. |
| 46 | 高艳红,刘伟,冉有华,等.黑河流域植被覆盖度计算及其影响的中尺度模拟[J].高原气象,2007(2):270-277. |
| 47 | Vandijk P M,Arens S M,Boxel J H V.Aeolian processes across transverse dunes.II:modelling the sediment transport and profile development[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,1999,24:319-333. |
| 48 | 王中原,罗万银,董治宝,等.共和盆地高寒草原风蚀坑表层沉积物粒度特征及动力学意义[J].中国沙漠,2017,37(1):7-16. |
| 49 | Mckenna W.An evolutionary model of parabolic dune development:from blowout to mature parabolic,padre island national seashore,Texas[D].Manoa,USA:University of Hawai’I at Manoa,2007. |
| 50 | 孙建光,李保国,卢琦.青海共和盆地气温的时空动态及其效应分析[J].地理科学进展,2004,23(3):100-106. |
| 51 | 郭连云,熊联胜,王万满.近50年气候变化对塔拉滩草地荒漠化的影响[J].水土保持研究,2008,15(6):57-63. |
| 52 | Dong Z B,Hu G Y,Qian G Q,et al.High-altitude aeolian research on the Tibetan Plateau[J].Reviews of Geophysics,2017,55(6):1-38. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |