中国沙漠 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 33-42.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00064
彭小梅1( ), 车存伟1,2, 苏靖茸1,2, 肖生春1(
), 车存伟1,2, 苏靖茸1,2, 肖生春1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-04-21
修回日期:2023-05-15
出版日期:2024-01-20
发布日期:2023-12-26
通讯作者:
肖生春
作者简介:肖生春(E-mail: xiaosc@lzb.ac.cn )基金资助:
Xiaomei Peng1( ), Cunwei Che1,2, Jingrong Su1,2, Shengchun Xiao1(
), Cunwei Che1,2, Jingrong Su1,2, Shengchun Xiao1( )
)
Received:2023-04-21
Revised:2023-05-15
Online:2024-01-20
Published:2023-12-26
Contact:
Shengchun Xiao
摘要:
中国北方干旱区生态系统结构改善及生态功能稳定维持和调控,是目前该区域生态建设的重要研究内容。开展干旱区人工林稳定性和适宜性评价,并提出气候变化背景下人工林稳定性维持的管理对策,对区域生态恢复和可持续发展具有重要实践意义。基于国内外相关研究进展,针对乔灌木人工林主体,初步构建了以树轮学方法为主的稳定性与适宜性评价体系。该评价体系突出树木径向生长过程和气候-环境限制因素分析,辅以林分生长表观、林相特征、立地条件和土壤水分状况等指标对比,基于对人工林稳定性和适宜性的综合评价,提出人工林稳定维持的针对性抚育管理对策。同时展示了黄土高原区不同降雨梯度、林分类型、立地条件和管理方式下多个树种的应用实例,并提出了进一步拓展的领域。
中图分类号:
彭小梅, 车存伟, 苏靖茸, 肖生春. 干旱区人工林稳定性与适宜性的树轮学评价体系构建与应用[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 33-42.
Xiaomei Peng, Cunwei Che, Jingrong Su, Shengchun Xiao. Construction and application of a dendrochronological evaluation method for the stability and suitability of artificial forests in arid areas[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(1): 33-42.
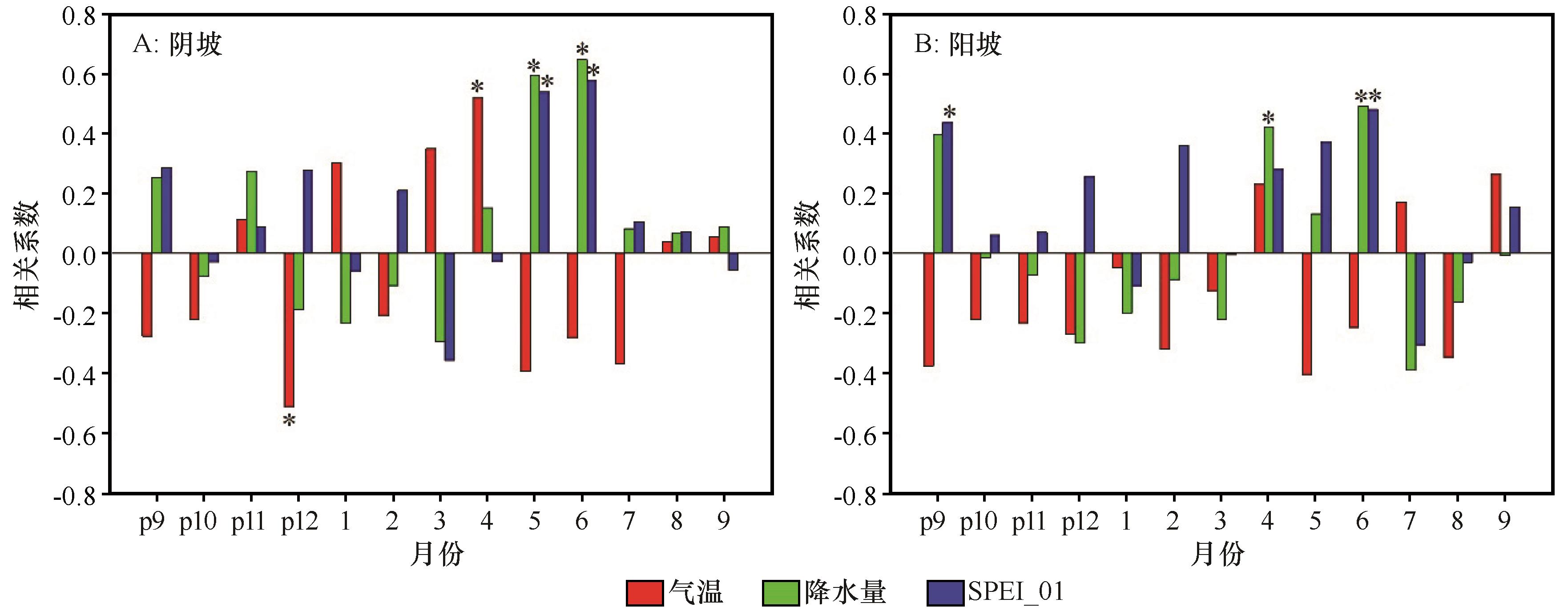
图4 不同坡向沙棘轮宽年表与月平均气温、月降水量和SPEI_01间的相关性分析注:p代表前一年;*代表95%的显著性水平
Fig.4 Correlation coefficient between Hippophae rhamnoides ring-width chronologies and month mean temperature, month precipitation and SPEI_01 (prepresents previous year; Significance: *P<0.05)
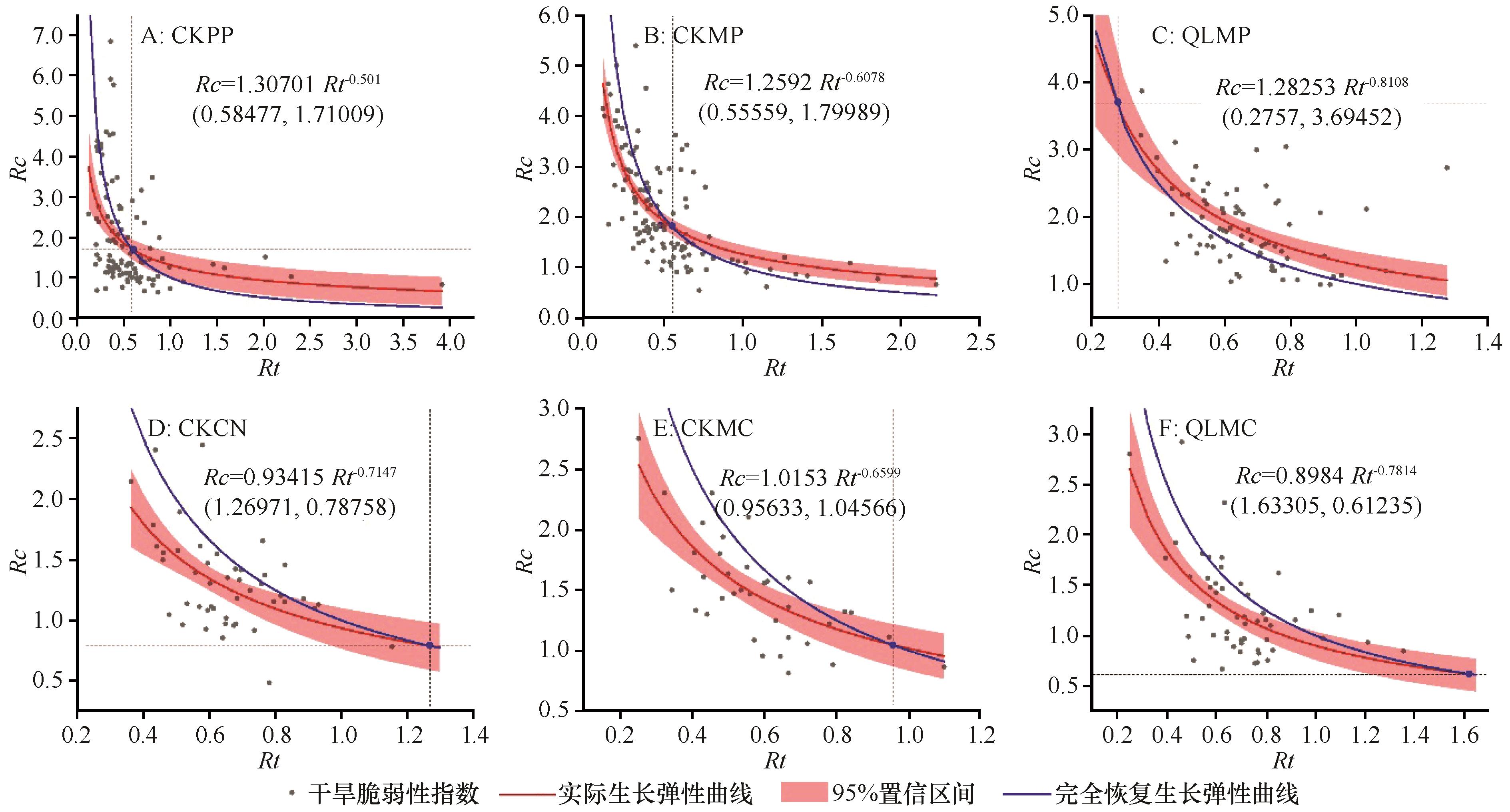
图5 乔灌混交树种“完全恢复生长弹性曲线”与“实际生长弹性曲线”间的差异注LCKPP、CKCN:侧柏和柠条纯林;CKMP、CKMC和QLMP、QLMC:侧柏-柠条混交林;Rc和Rt为恢复力和抵抗力
Fig.5 Comparisons of the “Line of full resilience” and “Line of actual resilience” under different tree species and stand structures(CKPP、CKCN:Pure Platycladus orientalis and Caragana korshinskii,CKMP, CKMC and QLMP, QLMC:Mixed Platycladus orientalis and Caragana korshinskii in two sampling sites;Rc and Rt: recovery and resistance)
| 1 | Fu B J, Liu Y, Lü Y H,et al.Assessing the soil erosion control service of ecosystems change in the Loess Plateau of China[J].Ecological Complexity,2011,8(4):284-293. |
| 2 | Cheng X R, Huang M B, Si B C,et al.The differences of water balance components of Caragana korshinkii grown in homogeneous and layered soils in the desert:Loess Plateau transition zone[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2013,98:10-19. |
| 3 | Yang X P, Liu T, Yuan B Y.The Loess Plateau of China:aeolian sedimentation and fluvial erosion,both with superlative rates[M]//Migon P.Geomorphological Landscapes of the World.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer,2010:275-282. |
| 4 | 傅伯杰,陈利顶,马克明.黄土丘陵区小流域土地利用变化对生态环境的影响:以延安市羊圈沟流域为例[J].地理学报,1999,54(3):51-56. |
| 5 | Chen H S, Shao M A, Li Y Y.Soil desiccation in the Loess Plateau of China[J].Geoderma,2008,143(1/2):91-100. |
| 6 | 杨永胜,卜崇峰,高国雄.平茬措施对柠条生理特征及土壤水分的影响[J].生态学报,2012,32(4):323-332. |
| 7 | Jiang W Y, Yang S L, Yang X X,et al.Negative impacts of afforestation and economic forestry on the Chinese Loess Plateau and proposed solutions[J].Quaternary International,2016,399:165-173. |
| 8 | Liu B X, Shao M A.Modeling soil-water dynamics and soil-water carrying capacity for vegetation on the Loess Plateau,China[J].Agricultural Water Management,2015,159:176-184. |
| 9 | Guo Z S, Shao M A.Soil water carrying capacity of vegetation and soil desiccation in artificial forestry and grassland in semi-arid regions of the Loess Plateau[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica,2003,23(8):1460-1647. |
| 10 | Chen L D, Huang Z L, Gong J,et al.The effect of land cover/vegetation on soil water dynamic in the hilly area of the loess plateau,China[J].Catena,2007,70(2):200-208. |
| 11 | Wang Z Q, Liu B Y, Zhang Y.Soil moisture of different vegetation types on the Loess Plateau[J].Journal of Geographical Sciences,2009,19:707-718. |
| 12 | Wang Z J, Jiao J Y, Su Y,et al.The efficiency of large-scale afforestation with fish-scale pits for revegetation and soil erosion control in the steppe zone on the hill-gully Loess Plateau[J].Catena,2014,115:159-167. |
| 13 | 李小芳,李军,王学春,等.半干旱黄土丘陵区柠条林水分生产力和土壤干燥化效应模拟研究[J].干旱地区农业研究,2007,3:113-119. |
| 14 | Jia Y H, Shao M A.Temporal stability of soil water storage under four types of revegetation on the northern Loess Plateau of China[J].Agricultural Water Management,2013,117:33-42. |
| 15 | Hou J Y, Yin R S, Wu W G.Intensifying forest management in China:what does it mean,why,and how?[J].Forest Policy and Economics,2019,98:82-89. |
| 16 | 梁非凡,朱清科,王露露,等.陕北黄土区油松径向生长对气候因子的响应[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2015,43(5):33-41. |
| 17 | Li G Q, Zhang X Q, Huang J H,et al.Afforestation and climatic niche dynamics of black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia)[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2018,407:184-190. |
| 18 | 曾德慧,姜凤岐,范志平,等.樟子松人工固沙林稳定性的研究[J].应用生态学报,1996,7(4):337-343. |
| 19 | 冯耀宗.人工生态系统稳定性概念及其指标[J].生态学杂志,2002,21(5):58-60. |
| 20 | 林考焕,叶功富.人工林生态系统稳定性研究综述[J].西南林学院学报,2010,30(5):88-94. |
| 21 | 李旭光,于法稳.大头茶种群动态模型及稳定性分析[J].植物生态学报,1997,21(1):29-34. |
| 22 | 吴明作,刘玉萃.栓皮栎种群数量动态的谱分析与稳定性[J].生态学杂志,2000,19(4):23-26. |
| 23 | 郑元润.森林群落稳定性研究方法初探[J].林业科学,2000,36(5):28-32. |
| 24 | 王露露.陕北黄土区主要人工乔木林群落稳定性研究[D].北京:北京林业大学,2013. |
| 25 | Jiao L, Lu N, Fu B J,et al.Comparison of transpiration between different aged black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia) trees on the semi-arid Loess Plateau,China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2016,8:604-617. |
| 26 | 陈洪松,邵明安.黄土区深层土壤干燥化程度的评价标准[J].水土保持学报,2004,18(3):164-166. |
| 27 | 李军,陈兵,李小芳,等.黄土高原不同干旱类型区苜蓿草地深层土壤干燥化效应[J].生态学报,2007,27(1):75-89. |
| 28 | 李军,陈兵,李小芳,等.黄土高原不同植被类型区人工林地深层土壤干燥化效应[J].生态学报,2008,28(4):1429-1445. |
| 29 | 段建军,王小利,张彩霞,等.黄土高原土壤干层评定指标的改进及分级标准[J].水土保持学报,2007,21(6):151-154. |
| 30 | 王力,邵明安,侯庆春.土壤干层量化指标初探[J].水土保持学报,2000,14(4):87-90. |
| 31 | 刘淑明,陈海滨,孙长忠,等.黄土高原主要造林树种的抗旱性研究[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2003,31(4):149-153. |
| 32 | 蒋志荣,杨占彪,汪君,等.兰州九州台四种绿化树种抗旱性机理比较研究[J].中国沙漠,2006,26(4):553-558. |
| 33 | 夏永秋,邵明安.黄土高原半干旱区柠条(Caragana korshinskii)树干液流动态及其影响因子[J].生态学报,2008,28(4):1376-1382. |
| 34 | 宋耀选,肖洪浪,段争虎,等.黄土高原西部植物耗水实验研究[J].中国沙漠,2006,26(4):543-547. |
| 35 | 于占辉,陈云明,杜盛.黄土高原半干旱区侧柏(Platycladus orientalis)树干液流动态[J].生态学报,2009,29(7):3970-3976. |
| 36 | 徐炳成,山仑.半干旱黄土丘陵区沙棘和柠条水分利用与适应性特征比较[J].应用生态学报,2004,15(11):2025-2028. |
| 37 | 王志强,刘宝元,王晓兰.黄土高原半干旱区天然锦鸡儿灌丛对土壤水分的影响[J].地理研究,2005,24(1):113-120. |
| 38 | 张益望,程积民,贺学礼.半干旱区人工林生长与水分生态研究[J].水土保持通报,2006,26(3):18-22. |
| 39 | 李蒙蒙,丁国栋,高广磊,等.樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var.mongholica)在中国北方10省(区)引种的适宜性[J].中国沙漠,2016,36(4):1021-1028. |
| 40 | 程积民,万惠娥,王静,等,半干旱区柠条生长与土壤水分消耗过程研究 [J].林业科学,2005,41(2):37-41. |
| 41 | 徐荣,张玉发,潘占兵,等.不同柠条密度在退化草地恢复过程中对土壤水分的影响[J].干旱地区农业研究,2004,22(1):172-175. |
| 42 | 赵艳云,程积民,王延平,等.半干旱区环境因子对柠条灌木林结构的影响[J].水土保持通报,2005,25(3):10-14. |
| 43 | 莫保儒,蔡国军,杨磊,等.半干旱黄土区成熟柠条林地土壤水分利用及平衡特征[J].生态学报,2013,33(13):4011-4020. |
| 44 | 陈云明,刘国彬,杨勤科.黄土高原人工林土壤水分效应的地带性特征[J].自然资源学报,2004,19(2):195-200. |
| 45 | 陈小红,段争虎,宋耀选,等.兰州市南北两山人工灌木林地土壤水分动态[J].中国沙漠,2006,26(4):532-535. |
| 46 | 段争虎,肖洪浪,宋耀选,等.黄土高原西部兰州市郊地貌驱动的土壤水分变化及对植物的影响分析[J].中国沙漠,2006,26(4):522-526. |
| 47 | 黄海霞,张玉珍.兰州北山“三水”造林区柠条的生长适宜性[J].中国水土保持科学,2013,11(2):72-76. |
| 48 | Schweingruber F H.Tree Rings and Environment:Dendroecology[M].Berne,Germany:Paul Haupt Publishers,1996:1-609. |
| 49 | Downes G M, Wimmer R, Evans R.Understanding wood formation:gains to commercial forestry through tree-ring research[J].Dendrochronologia,2002,20(1/2):37-51. |
| 50 | Fritts H C, Shatz D J.Selecting and characterizing tree-ring chronologies for dendroclimatic analysis[J].Tree-Ring Bulletin,1975,35:31-40. |
| 51 | Måren I E, Karki S, Prajapati C,et al.Facing north or south:does slope aspect impact forest stand characteristics and soil properties in a semiarid trans-Himalayan valley?[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2015,121:112-123. |
| 52 | Toigo M, Vallet P, Tuilleras V,et al.Species mixture increases the effect of drought on tree ring density,but not on ring width,in Quercus petraea-Pinus sylvestris stands[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2015,345:73-82. |
| 53 | Xiao S C, Xiao H L, Peng X M,et al.Dendroecological assessment of Korshinsk peashrub (Caragana korshinskii Kom.) from the perspective of interactions among growth,climate,and topography in the western Loess Plateau,China[J].Dendrochronologia,2015,33:61-68. |
| 54 | Spiecker H.Tree rings and forest management in Europe[J].Dendrochronologia,2002,20(1/2):191-202. |
| 55 | Antos J A, Parish R, Nigh G D.Growth patterns prior to mortality of mature Abies lasiocarpa in old-growth subalpine forests of southern British Columbia[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2008,255(5/6):1568-1574. |
| 56 | 李露露,李丽光,陈振举,等.辽宁省人工林樟子松径向生长对水热梯度变化的响应[J].生态学报,2015,35(13):4508-4517. |
| 57 | 王利娜.黄土高原油松人工林干旱风险评价[D].北京:北京林业大学,2016. |
| 58 | Costa M S, Ferreira K E, Botosso P C,et al.Growth analysis of five Leguminosae native tree species from a seasonal semidecidual lowland forest in Brazil[J].Dendrochronologia,2015,36:23-32. |
| 59 | Rodríguez-Catón M, Villalba R, Srur A M,et al.Long-term trends in radial growth associated with Nothofagus pumilio forest decline in Patagonia:integrating local-into regional-scale patterns[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2015,339:44-56. |
| 60 | Pommerening A, Muszta A.Relative plant growth revisited:towards a mathematical standardisation of separate approaches[J].Ecological Modelling,2016,320:383-392. |
| 61 | Lloret F, Keeling E G, Sala A.Components of tree resilience:effects of successive low‐growth episodes in old ponderosa pine forests[J].Oikos,2011,120(12):1909-1920. |
| 62 | Fang O Y, Zhang Q B.Tree resilience to drought increases in the Tibetan Plateau[J].Global Change Biology,2019,25(1):245-253. |
| 63 | Bigler C, Gričar J, Bugmann H,et al.Growth patterns as indicators of impending tree death in silver fir[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2004,199(2/3):183-190. |
| 64 | Schöngart J, Wittmann F, Worbes M,et al.Management criteria for Ficus insipida Willd.(Moraceae) in Amazonian white-water floodplain forests defined by tree-ring analysis[J].Annals of Forest Science,2007,64(6):657-664. |
| 65 | 刘荣.间伐抚育对刺槐人工林林分结构和林分健康的影响[D].杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2016. |
| 66 | Cabon A, Mouillot F, Lempereur M,et al.Thinning increases tree growth by delaying drought-induced growth cessation in a Mediterranean evergreen oak coppice[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2018,409:333-342. |
| 67 | Bär A, Pape R, Bräuning A,et al.Growth-ring variations of dwarf shrubs reflect regional climate signals in alpine environments rather than topoclimatic differences[J].Journal of Biogeography,2008,35(4):625-636. |
| 68 | Liang E Y, Shao X M, Eckstein D,et al.Topography-and species-dependent growth responses of Sabina przewalskii and Picea crassifolia to climate on the northeast Tibetan Plateau[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2006,236(2/3):268-277. |
| 69 | Kirchhefer A J.The influence of slope aspect on tree-ring growth of Pinus sylvestris L.in northern Norway and its implications for climate reconstruction[J].Dendrochronologia,2000,18:27-40. |
| 70 | Fekedulegn D, Hicks Jr R R, Colbert J.Influence of topographic aspect,precipitation and drought on radial growth of four major tree species in an Appalachian watershed[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2003,177(1/3):409-425. |
| 71 | Young A B, Watts D A, Taylor A H,et al.Species and site differences influence climate-shrub growth responses in West Greenland[J].Dendrochronologia,2016,37:69-78. |
| 72 | Graumlich L J.Response of tree growth to climatic variation in the mixed conifer and deciduous forests of the upper Great Lakes region[J].Canadian Journal of Forest Research,1993,23(2):133-143. |
| 73 | 赵西平,郭明辉,关鑫.人工林落叶松生长轮宽度年表的建立[J].东北林业大学学报,2007,35(3):7-9. |
| 74 | 刘芳,章尧想,马迎宾,等.乌兰布和沙漠绿洲樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var.mongolica)生长规律初探[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(5):1234-1238. |
| 75 | Bailey L D, Van De Pol M.Climwin:an R toolbox for climate window analysis[J].PloS One,2016,11(12):e0167980. |
| 76 | Van De Pol M, Bailey L D, Mclean N,et al.Identifying the best climatic predictors in ecology and evolution[J].Methods in Ecology and Evolution,2016,7(10):1246-1257. |
| 77 | Camarero J J, Rubio-Cuadrado I.Relating climate,drought and radial growth in broadleaf mediterranean tree and shrub species:a new approach to quantify climate-growth relationships[J].Forests,2020,11(12):1250. |
| 78 | Schwarz J, Skiadaresis G, Kohler M,et al.Quantifying growth responses of trees to drought:acritique of commonly used resilience indices and recommendations for future studies[J].Current Forestry Reports,2020,6:185-200. |
| 79 | Che C W, Xiao S C, Ding A J,et al.The characteristics of radial growth and ecological response of Caragana korshinskii Kom.under different precipitation gradient in the western Loess Plateau,China[J].Frontiers in Plant Science,2022,13:862529. |
| 80 | Che C W, Xiao S C, Ding A J,et al.Growth response of plantations Hippophae rhamnoides Linn.on different slope aspects and natural Caragana opulens Kom.to climate and implications for plantations management[J].Ecological Indicators,2022,138:108833. |
| 81 | Che C W, Xiao S C, Peng X M,et al.Radial growth ofKorshinsk peashrub and its response to drought in different sub-arid climate regions of northwest China[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2023,326:116708. |
| 82 | Xiao S C, Peng X M, Tian Q Y,et al.Stem radial growth indicate the options of species,topography and stand management for artificial forests in the western Loess Plateau,China[J].Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions,2019,11(3):226-238. |
| [1] | 马启民, 王海兵, 贾晓鹏. 库布齐沙漠人工柠条(Caragana korshinskii)林地表辐射特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 43-50. |
| [2] | 杨军怀, 董治宝, 南维鸽, 宋绍鹏, 肖南, 刘生权, 孟小强. 毛乌素沙地东南缘樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica)人工林土壤粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(4): 815-822. |
| [3] | 彭小梅, 肖生春, 程国栋, 肖洪浪, 田全彦. 胡杨(Populus euphratica)树轮记录的20世纪40年代前后黑河下游分水过程及其生态影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(1): 206-215. |
| [4] | 任小玢, 胡光印, 董治宝. 沙漠化脆弱性的概念与评价[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(1): 40-50. |
| [5] | 肖生春, 肖洪浪, 彭小梅. 梭梭(Haloxylon ammodendron)不宜用于树木年轮学研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(6): 1692-1698. |
| [6] | 李玉强;赵学勇;刘新平;尚 雯;冯 静;苏 娜. 樟子松固沙林土壤碳截存及土壤呼吸对干湿变化的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(2): 282-287. |
| [7] | 崔秀萍;刘果厚*;张存厚. 浑善达克沙地黄柳人工林根系分布及生物量研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(2): 447-450. |
| [8] | 肖生春;肖洪浪;宋耀选;段争虎;陆明峰. 荒漠植被红砂(Reaumurta soongorica)水热响应的年轮学研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2006, 26(4): 548-552. |
| [9] | 王万鹏;李正平;钟 芳. 兰州市郊人工林群落结构及稳定性初探[J]. 中国沙漠, 2006, 26(4): 569-573. |
| [10] | 李艳花;赵景波;. 西安南郊丰水年秋季土壤水分研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2006, 26(1): 113-116. |
| [11] | 赵文智. 河北坝上半干旱/半湿润过渡带华北落叶松人工林研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 1997, 17(3): 243-249. |
| [12] | 康向阳. 甘肃胡杨恢复发展的限制因子及对策[J]. 中国沙漠, 1997, 17(1): 53-57. |
| [13] | 赵文智, 宝音. 河北坝上疏缓丘陵华北落叶松人工林生长特性研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 1994, 14(4): 66-71. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
