中国沙漠 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 29-40.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00028
池静姚1,2( ), 潘磊磊3, SeMyung Kwon3, 张晓1,2, 李雨衡1,2, 杨晓晖1,2, 时忠杰1,2(
), 潘磊磊3, SeMyung Kwon3, 张晓1,2, 李雨衡1,2, 杨晓晖1,2, 时忠杰1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-01-04
修回日期:2024-02-08
出版日期:2024-09-20
发布日期:2024-10-15
通讯作者:
时忠杰
作者简介:时忠杰(E-mail: shizj@caf.ac.cn)基金资助:
Jingyao Chi1,2( ), Leilei Pan3, Kwon SeMyung3, Xiao Zhang1,2, Yuheng Li1,2, Xiaohui Yang1,2, Zhongjie Shi1,2(
), Leilei Pan3, Kwon SeMyung3, Xiao Zhang1,2, Yuheng Li1,2, Xiaohui Yang1,2, Zhongjie Shi1,2( )
)
Received:2024-01-04
Revised:2024-02-08
Online:2024-09-20
Published:2024-10-15
Contact:
Zhongjie Shi
摘要:
沙地樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica)天然林在中国呼伦贝尔沙地发挥着重要的生态服务功能,但林分结构和竞争作用对沙地樟子松树木生长的影响仍不明确。采用全样地调查法和树木年轮取样法,估算了9种林分结构多样性指数和46种竞争指数,利用相关分析、多元线性回归模型等方法分析林分结构多样性与竞争对沙地樟子松天然林树木生长的影响,确定竞争和林分结构多样性在决定树木生长中的作用。结果表明:(1) 树木大小比数、大小分异指数和Clark-Evans聚集指数显著影响着树木的生长;(2) 竞争也是影响树木生长的重要因素,树木生长随竞争强度的增加而降低;(3) 竞争、林分结构指数(大小分异指数)和树木自身属性(高径比和冠幅)共同影响了沙地樟子松树木的生长。其中竞争的影响最大,解释了树木生长约三分之一的变异性。森林管理者应多重视林分结构多样性和竞争的作用,优化林分结构与密度,提高林分生产力。
中图分类号:
池静姚, 潘磊磊, SeMyung Kwon, 张晓, 李雨衡, 杨晓晖, 时忠杰. 呼伦贝尔沙地樟子松天然林结构多样性和竞争对树木生长的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 29-40.
Jingyao Chi, Leilei Pan, Kwon SeMyung, Xiao Zhang, Yuheng Li, Xiaohui Yang, Zhongjie Shi. Influence of stand structure diversity and competition on tree growth of natural Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica forest in Hulun Buir Sandy Land[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(5): 29-40.
| 纬度(N) | 经度(E) | 密度/(株·hm-2) | 林下植被盖度/% | 海拔/m | 坡度/(°) | 坡向 | 胸径/cm | 树高/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 49°04′46.30″ | 120°28′12.79″ | 2 440 | 40 | 680 | 10 | ES | 12.77±6.15 | 9.93±2.56 |
表1 试验样地基本概况
Table 1 Basic information of the sample plots
| 纬度(N) | 经度(E) | 密度/(株·hm-2) | 林下植被盖度/% | 海拔/m | 坡度/(°) | 坡向 | 胸径/cm | 树高/m |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 49°04′46.30″ | 120°28′12.79″ | 2 440 | 40 | 680 | 10 | ES | 12.77±6.15 | 9.93±2.56 |
| 竞争指数 | 文献 | 竞争指数 | 文献 | 竞争指数 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | ||||
| [ | [ |
表2 单木竞争指数
Table 2 Individual tree competition index
| 竞争指数 | 文献 | 竞争指数 | 文献 | 竞争指数 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | [ | |||
| [ | [ | ||||
| [ | [ |
| 名称 | 公式 | 意义 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 香农-威纳指数 | SW越大,树木大小差异越大 | [ | |
| 辛普森指数 | S数大,代表树木大小分化程度高 | [ | |
| 大小比数 | NCI越大,表示相邻木相比于目标木优势越大 | [ | |
| 大小分异指数 | DFI越大,代表树木大小差异越大 | [ | |
| 基尼系数 | GC越大,代表树木大小分布越不平衡 | [ | |
| 变异系数 | CV越小,代表林木大小差异越小 | [ | |
| 偏度 | SK越大,代表树木大小分布偏态程度越高 | [ | |
| 峰度 | Kg越大,树木胸径最大值越大,分布越陡峭 | [ | |
| Clark-Evans指数 | 判断林木种群空间分布格局(聚集、随机、均匀)的指数 | [ |
表3 林分结构多样性指数
Table 3 Stand structure diversity indices
| 名称 | 公式 | 意义 | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 香农-威纳指数 | SW越大,树木大小差异越大 | [ | |
| 辛普森指数 | S数大,代表树木大小分化程度高 | [ | |
| 大小比数 | NCI越大,表示相邻木相比于目标木优势越大 | [ | |
| 大小分异指数 | DFI越大,代表树木大小差异越大 | [ | |
| 基尼系数 | GC越大,代表树木大小分布越不平衡 | [ | |
| 变异系数 | CV越小,代表林木大小差异越小 | [ | |
| 偏度 | SK越大,代表树木大小分布偏态程度越高 | [ | |
| 峰度 | Kg越大,树木胸径最大值越大,分布越陡峭 | [ | |
| Clark-Evans指数 | 判断林木种群空间分布格局(聚集、随机、均匀)的指数 | [ |
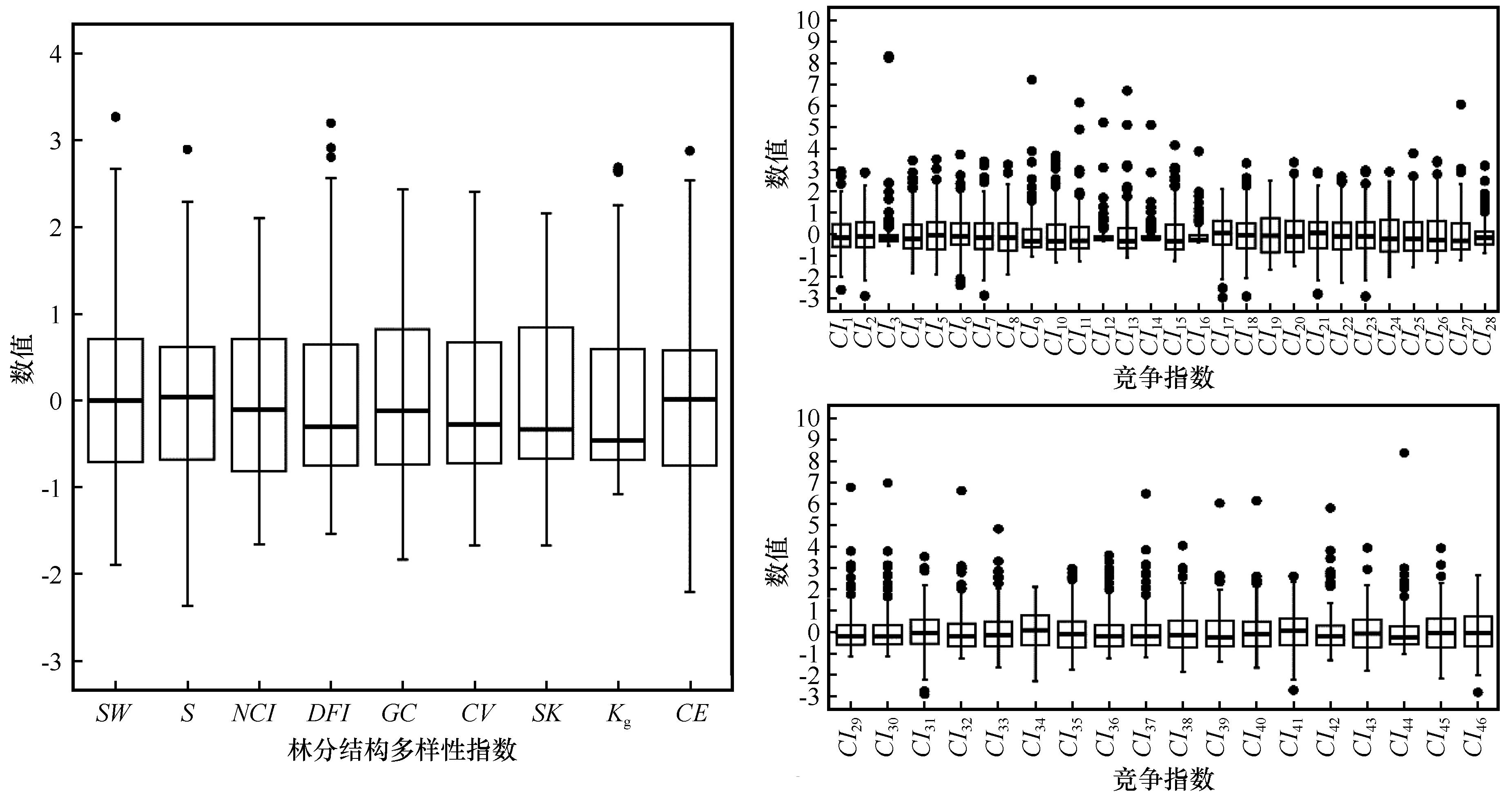
图2 标准化的林分结构多样性指数和竞争指数箱线图注:SW为香农-威纳指数,S为辛普森指数,NCI为大小比数,DFI为大小分异指数,GC为基尼系数,CV为变异系数,SK为偏度,Kg为峰度,CE为林木聚集指数,CI1~CI28为基于距离的竞争指数,CI29~CI46为与距离无关的竞争指数
Fig.2 Boxplot of standardized indices in stand structure and competition characteristic
| 指标 | 香农-威纳 指数SW | 辛普森 指数S | 大小比数NCI | 大小分异 指数DFI | 基尼系数 GC | 变异系数 CV | 偏度 SK | 峰度 Kg | Clark-Evans 指数CE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 胸高断面积生长量BAI | 0.012 | 0.026 | -0.812** | -0.606** | -0.002 | -0.000 | -0.006 | -0.021 | -0.15* |
表4 林分结构多样性指数与胸高断面积生长量的相关系数
Table 4 Correlation coefficient between stand structure and basal area growth at tree breast height
| 指标 | 香农-威纳 指数SW | 辛普森 指数S | 大小比数NCI | 大小分异 指数DFI | 基尼系数 GC | 变异系数 CV | 偏度 SK | 峰度 Kg | Clark-Evans 指数CE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 胸高断面积生长量BAI | 0.012 | 0.026 | -0.812** | -0.606** | -0.002 | -0.000 | -0.006 | -0.021 | -0.15* |
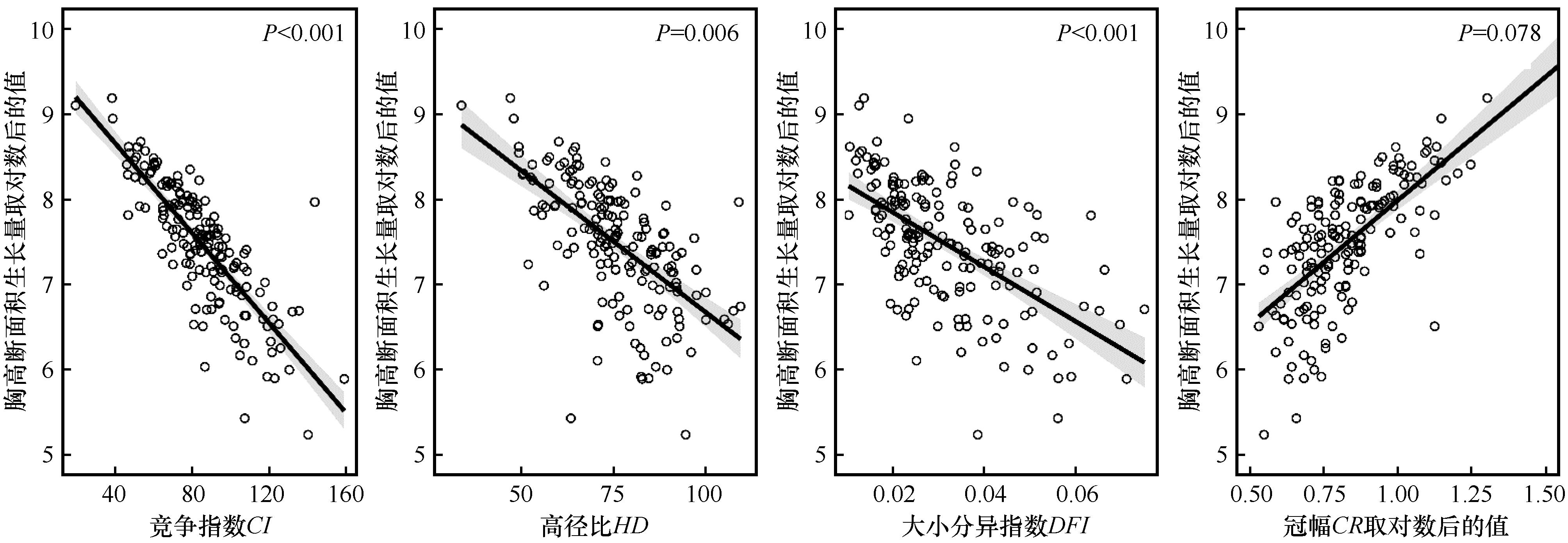
图4 基于多元回归模型的林分结构、竞争和树木自身特性对胸高断面积生长量的影响
Fig.4 Stand structure and competition influence on basal area at breast height independently based on multiple regression ananysis
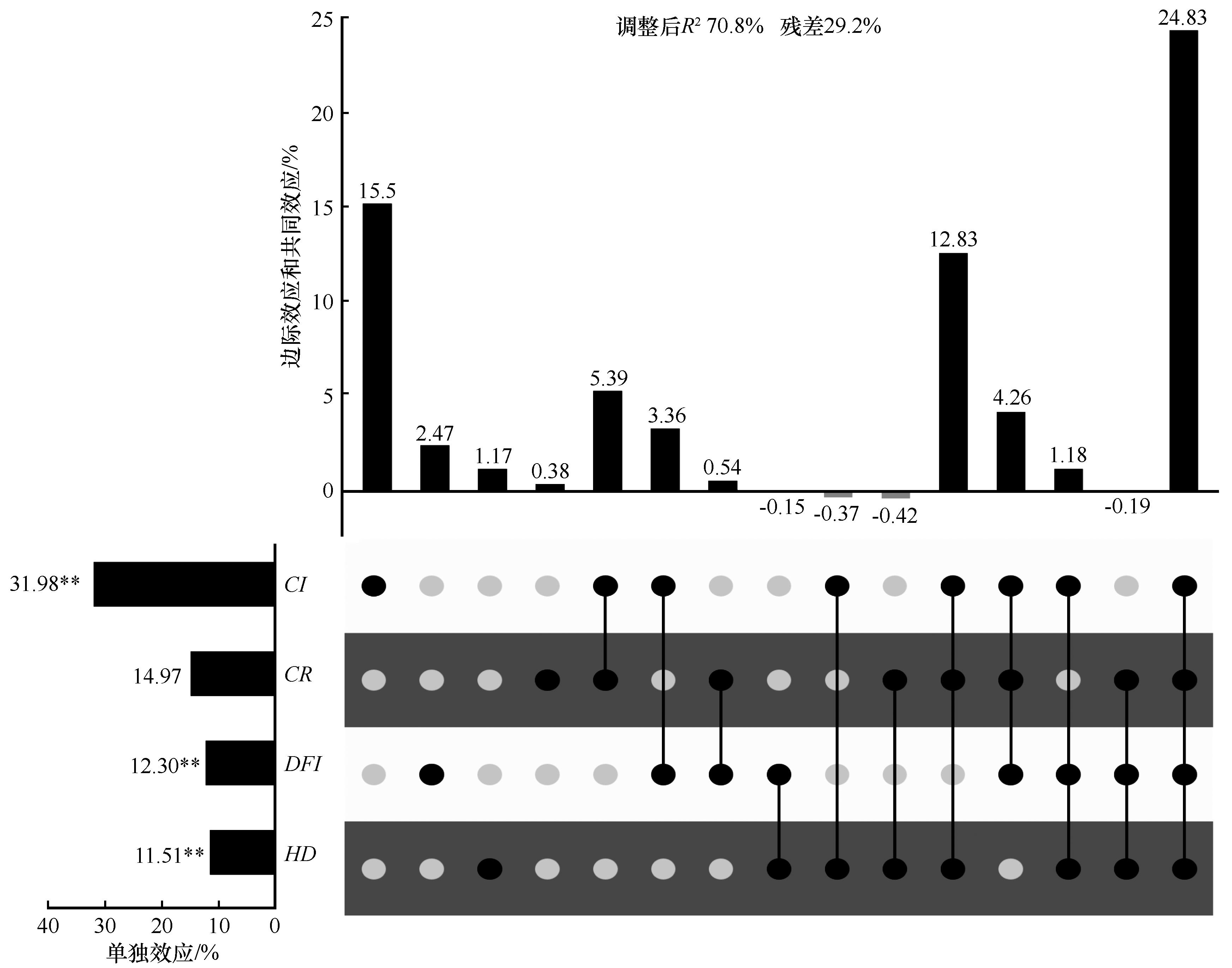
图5 单木竞争、林分结构、树木本身特性对樟子松胸高断面积生长量的相对重要性注:用UpSet图展示变差分解和层次分割分析的结果。右侧下方的点阵图中,每行对应因子的不同指标,每列单独的黑点代表该指标的边际效应,多点间连线表明这些因子间的共同效应。各组分解释的变差百分比(来自变差分解)展示在上方柱形图中,左侧柱形图为因子不同指标的单独效应(来自层次分割),其值等同于该环境因子的边际效应加上与其他环境因子的共同效应的平均分配值。CI为竞争指数,HD为高径比,DFI为大小分异指数,CR为冠幅。*P<0.05; **P<0.01。
Fig.5 Upset plot with the variation partitioning and hierarchical partitioning result show the relative importance of factors influence on basal area growth of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, including individual tree competition indices, stand structure and trees' own property.
| 1 | 李凤日,孙玉军,胥辉,等.测树学[M].北京:中国林业出版社,2019:100,231-232. |
| 2 | Gourlet-Fleury S, Rossi V, Forni E,et al.Competition and site weakly explain tree growth variability in undisturbed Central African moist forests[J].Journal of Ecology,2023,111:1950-1967. |
| 3 | 臧颢,刘洪生,黄锦程,等.竞争和气候及其交互作用对杉木人工林胸径生长的影响[J].林业科学,2021,57(3):39-50. |
| 4 | 康剑,梁寒雪,蒋少伟,等.竞争和气候对新疆阿尔泰山西伯利亚五针松树木径向生长的影响[J].植物生态学报,2020,44(12):1195-1202. |
| 5 | 哈雪梅.基于综合竞争指数和数量化理论模型的红松人工林立地质量评价[D].哈尔滨:东北林业大学,2021. |
| 6 | Kahriman A, Şahin A, Sönmez T,et al.A novel approach to selecting a competition index:the effect of competition on individual-tree diameter growth of Calabrian pine[J].Canadian Journal of Forest Research,2018,48(10):1217-1226. |
| 7 | Ledermann T.Evaluating the performance of semi-distance-independent competition indices in predicting the basal area growth of individual trees[J].Canadian Journal of Forest Research,2010,40(4):796-805. |
| 8 | Contreras A M, Affleck D, Chung W.Evaluating tree competition indices as predictors of basal area increment in western Montana forests[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2011,262(11):1939-1949. |
| 9 | 龙俊松,汤孟平.天目山常绿阔叶林空间结构与地形因子的关系[J].浙江农林大学学报,2021,38(1):47-57. |
| 10 | 赵中华,惠刚盈.林分结构多样性研究进展[J].林业科学,2020,56(9):143-152. |
| 11 | 李新建,杨子铎,何海梅,等.湖南栎类天然林林分结构对林分生长的影响研究[J].林业资源管理,2022(4):164-171. |
| 12 | Lin S L, Chen Y, Li M F,et al.Effects of local neighbourhood structure on radial growth of Picea crassifolia Kom.and Betula platyphylla Suk.plantations in the loess alpine region,China[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2021,491:119195. |
| 13 | 时忠杰,喻泓,杨晓晖,等.沙地樟子松天然林对火干扰及气候变化的响应[M].北京:科学出版社,2018. |
| 14 | 曹恭祥,郭中,王云霓,等.呼伦贝尔沙地樟子松人工林乔木层固碳速率及其对气象因子的响应[J].生态学杂志,2020,39(4):1082-1090. |
| 15 | 张立志,孙亚娟,宋银平,等.不同强度林火干扰对红花尔基樟子松天然林更新的影响[J].防护林科技,2015(5):16-19. |
| 16 | 喻泓,杨晓晖,慈龙骏,等.地表火干扰下呼伦贝尔沙地樟子松林乔木层不同组分空间格局的变化[J].干旱区资源与环境,2009,23(2):130-136. |
| 17 | 潘磊磊.沙地樟子松天然林树木竞争对其生长及气候敏感性影响[D].北京:中国林业科学研究院,2019. |
| 18 | Kwon S.沙地樟子松天然林林分结构及气候对其生长的影响[D].北京:北京林业大学,2019. |
| 19 | Wen S, Shi Z, Zhang X,et al.Effect of climate and competition on radial growth of Pinus sylvestris var.mongolica forest in Hulunbuir Sandy Land of Inner Mongolia,China[J].Plants,2023,12:2584. |
| 20 | 牛进松,刘小粉, Kwon S,等.呼伦贝尔沙地樟子松生产力及其对气候因子的响应[J].林业科学研究,2022,35(3):141-150. |
| 21 | 刘灵,胡艳波,王千雪,等.沙地樟子松天然纯林的结构特征[J].林业科学研究,2016,29(5):623-629. |
| 22 | 赵兴梁,李万英.樟子松[M].北京:农业出版社,1963. |
| 23 | 郑元润.红花尔基沙地樟子松种群优势度增长动态及自疏规律的研究[J].武汉植物学研究,1999(4):339-344. |
| 24 | 朱教君,曾德慧,康宏樟,等.沙地樟子松人工林衰退机制[M].北京:中国林业出版社,2005. |
| 25 | 姚慧芳,王超,卢杰.单木竞争的研究概述[J].广西农学报,2021,36(4):77-81. |
| 26 | 潘磊磊, Kwon S,刘艳书,等.沙地樟子松天然林南缘分布区林木竞争、空间格局及其更新特征[J].生态学报,2019,39(10):3687-3699. |
| 27 | Hegyi F.A simulation model for managing jack-pine stands[C]//Fries J.Growth Models for Tree and Stand Simulation.Stockholm,Sweden:Royal College of Forest,1974:74-90. |
| 28 | Martin G L, Ek A R.A comparison of competition measures and growth models for predicting plantation red pine diameter and height growth[J].Forest Science,1984,30(3):731-743. |
| 29 | Rouvinen S, Kuuluvainen T.Structure and asymmetry of tree crowns in relation to local competition in a natural mature Scots pine forest[J].Canadian Journal of Forest Research,1997,27(6):890-902. |
| 30 | Moore J A, Budelsky C A, Schlesinger R C.A new index representing individual tree competitive status[J].Canadian Journal of Forest Research,1973,3:495-505. |
| 31 | Pukkala T, Kolström T.Competition indices and the prediction of radial growth in Scots pine[J].Silva Fennica,1987,21(1):55-67. |
| 32 | 窦啸文,汤孟平.基于引力模型的林木竞争分析[J].应用生态学报,2022,33(10):2695-2704. |
| 33 | Staebler G R.Growth and spacing in an even-aged stand of Douglas fir[D].Ann Arbor,Michigan,USA:University of Michigan,1951. |
| 34 | Álvarez Taboada M F, Anta M B, Varela J G,et al.Influencia de la competencia en el crecimiento en sección en Pinus radiata D.Don[J].Investigación agraria.Sistemasy Recursos Forestales,2003,12(2):25-35. |
| 35 | Castagneri D, Vacchiano G, Lingua E,et al.Analysis of intraspecific competition in two subalpine Norway spruce(Picea abies(L.) Karst.) stands in Paneveggio(Trento,Italy)[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2008,255(3/4):651-659. |
| 36 | Arnoni E C, Guimarães A C F, Felipe A H.Competition indices and their relationship with Basal Area Increment of Araucaria[J].Journal of Agricultural Science,2018,10(5):198-210. |
| 37 | Gerrard D I.Competition quotient:a new measure for the competition affecting individual forest trees[J].Michigan State University.Agriculture Research Station Research Bulliten,1969,20:1-32. |
| 38 | Bella I E.A new competition model for individual trees[J].Forest Science,1971,17(3):364-372. |
| 39 | Sun O.Growth model for simulation of a Calabrian pine(Pinus brutia Ten.) tree[R].Ankara,Turkey:Forestry Research Institute,1977. |
| 40 | Ek A R, Monserud R A.Trials with program FOREST:growth and reproduction simulation for mixed species even and or uneven-aged forest stands[C]//Fries J.Growth models for tree and stand simulation.Stockholm,Sweden:Royal College of Forestry,1974:56-73. |
| 41 | Alemdag I S.Evaluation of some competition indexes for the prediction of diameter increment in planted white spruce[R].1978. |
| 42 | Glover G R, Hool J N.A basal area ratio predictor of loblolly pine plantation mortality[J].Forest Science,1979,25(2):275-282. |
| 43 | Daniels R F, Burkhart H E, Clason T R.A comparison of competition measures for predicting growth of loblolly pine trees[J].Canadian Journal of Forest Research,1986,16(6):1230-1237. |
| 44 | Stage A R.Prognosis model for stand development[R]//Research Paper INT-137.Washington,USA:USDA Forest Service,1973. |
| 45 | Wykoff W R, Crookston N L, Stage A R.User's guide to the stand prognosis model[R]//Technical Report INT-133.Washington,USA:USDA Forest Service,1982:119. |
| 46 | Tomé M, Burkhart H E.Distance-dependent competition measures for predicting growth of individual trees[J].Forest Science,1989,35(3):816-831. |
| 47 | Corona P, Ferrara A.Individual competition indices for conifer plantations[J].Agriculture,Ecosystems & Environment,1989,27:429-437. |
| 48 | 曹小玉,李际平.林分空间结构指标研究进展[J].林业资源管理,2016(4):65-73. |
| 49 | 马履一,王希群.生长空间竞争指数及其在油松、侧柏种内竞争中的应用研究[J].生态科学,2006,25(5):385-389. |
| 50 | 向钦,郭秋菊,艾训儒,等.湖北木林子自然保护区天然林不同恢复阶段林分结构特征[J].东北林业大学学报,2023,51(11):21-26. |
| 51 | 黄小男.六盘山华北落叶松人工林生物量对立地条件和林分结构的响应与模拟[D].北京:北京林业大学,2020. |
| 52 | 李远发.林分空间结构参数二元分布的研究[D].北京:中国林业科学研究院,2014. |
| 53 | Shannon C E.A mathematical theory of communication[J].Bell System Technical Journal,1948,27(3):379-423. |
| 54 | Simpson E H.Measurement of diversity[J].Nature,1949,163:688. |
| 55 | 惠刚盈, Klaus von G, Matthias A.一个新的林分空间结构参数-大小比数[J].林业科学研究,1999,12(1):4-9. |
| 56 | Pommerening A.Approaches to quantifying forest structures[J].Forestry,2002,75(3):305-324. |
| 57 | 谭凌照,范春雨,范秀华.吉林蛟河阔叶红松林木本植物物种多样性及群落结构与生产力的关系[J].植物生态学报,2017,41(11):1149-1156. |
| 58 | 峁诗松,程依明,濮晓龙,等.概率论与数理统计教程[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2019:237-238. |
| 59 | Clark P J, Evans F C.Distance to nearest neighbor as measure of spatial relationships in populations[J].Ecology,1954,35(4):445-453. |
| 60 | McBride J R.Analysis of tree rings and fire scars to establish fire history[J].Tree-Ring Bulletin,1983,43:69-78. |
| 61 | Bunn A G.A dendrochronology program library in R(dplR)[J].Dendrochronologia,2008,26(2):115-124. |
| 62 | Lai J, Zou Y, Zhang J,et al.Generalizing hierarchical and variation partitioning in multiple regression and canonical analyses using the rdacca.hp R package[J].Methods in Ecology and Evolution,2022,13(4):782-788. |
| 63 | Liu Y.UpSetVP:An Alternative Visualization of VPA and HP in Canonical Analysis.R package version 1.0.0[CP].. |
| 64 | 刘尧,于馨,于洋,等.R程序包“rdacca.hp”在生态学数据分析中的应用:案例与进展[J].植物生态学报,2023,47(1):134-144. |
| 65 | Hui G, Zhang G, Zhao Z,et al.Methods of forest structure research:a review[J].Current Forestry Reports,2019,5:142-154. |
| 66 | Peter D, Olga F, Yuanyuan H,et al.Tree diversity effects on productivity depend on mycorrhizae and life strategies in a temperate forest experiment[J].Ecology,2022,104(2):1-16. |
| 67 | Elizabeth A, Jonathan A, Grant M,et al.Structural diversity as a reliable and novel predictor for ecosystem productivity[J].Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment,2023,21(1):33-39. |
| 68 | Giovanni I, Federico S, Filippo B,et al.Tree diversity and identity modulate the growth response of thermophilous deciduous forests to climate warming[J].Oikos,2022(3):1-14. |
| 69 | Zeller L, Pretzsch H.Effect of forest structure on stand productivity in Central European forests depends on developmental stage and tree species diversity[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2019,434:193-204. |
| 70 | Kwon S,潘磊磊,时忠杰,等.不同竞争强度下的沙地樟子松天然林树木径向生长及其气候响应[J].生态学杂志,2019,38(7):1962-1972. |
| 71 | 刘耀凤,董利虎,郝元朔,等.竞争对天然针阔混交林树木直径生长的影响[J].东北林业大学学报,2023,51(9):1-7. |
| 72 | Sánchez-Salguero R, Linares C J, Camarero J J,et al.Disentangling the effects of competition and climate on individual tree growth:a retrospective and dynamic approach in Scots pine[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2015,358:12-25. |
| 73 | Liang H, Huang J, Ma Q,et al.Contributions of competition and climate on radial growth of Pinus massoniana in subtropics of China[J].Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2019,274:7-17. |
| 74 | 窦啸文,吴登瑜,张笑菁,等.天目山常绿阔叶林胸高断面积生长量影响因子研究[J].浙江农林大学学报,2023,40(5):1063-1072. |
| 75 | Britton G T, Richards A S, Hovenden J M.Quantifying neighbour effects on tree growth:Are common 'competition' indices biased?[J].Journal of Ecology,2023,111(6):1270-1280. |
| 76 | 韩大校,金光泽.地形和竞争对典型阔叶红松林不同生长阶段树木胸径生长的影响[J].北京林业大学学报,2017,39(1):9-19. |
| 77 | 刘轩,赵珮杉,高广磊,等.沙地樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var.mongolica)物候特征及其对气候的响应[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(2):25-35. |
| 78 | 惠刚盈,胡艳波,赵中华.结构化森林经营研究进展[J].林业科学研究,2018,31(1):85-93. |
| 79 | 徐欢,李美丽,梁海斌,等.退化森林生态系统评价指标体系研究进展[J].生态学报,2018,38(24):9034-9042. |
| [1] | 李丹丹, 李佳文, 高广磊, 张英, 任悦, 柳叶, 赵珮杉. 科尔沁沙地樟子松( Pinus sylvestris var. mongolia )人工林土壤真菌群落结构和功能特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 241-251. |
| [2] | 刘轩, 赵珮杉, 高广磊, 赵媛媛, 丁国栋, 糜万林. 沙地樟子松( Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica )物候特征及其对气候的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 25-35. |
| [3] | 杨军怀, 董治宝, 南维鸽, 宋绍鹏, 肖南, 刘生权, 孟小强. 毛乌素沙地东南缘樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica)人工林土壤粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(4): 815-822. |
| [4] | 罗维成, 赵文智, 孙程鹏, 闫加亮. 科尔沁沙地樟子松(Pinus sylvestris)人工固沙林演变过程中物种多样性和土壤水分特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(1): 126-132. |
| [5] | 赵哈林, 李瑾, 周瑞莲, 云建英, 冯静, 苏娜. 风沙流短暂吹袭对樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica)幼苗光合蒸腾特性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(2): 254-260. |
| [6] | 李蒙蒙, 丁国栋, 高广磊, 赵媛媛, 于明含, 王德英. 樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var.mongholica)在中国北方10省(区)引种的适宜性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(4): 1021-1028. |
| [7] | 刘新平, 何玉惠, 魏水莲, 赵学勇, 张铜会, 岳祥飞. 科尔沁沙地樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica)生长对降水和温度的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(1): 57-63. |
| [8] | 毛新安, 赵哈林, 李瑾, 周瑞莲, 云建英, 曲浩, 潘成臣. 樟子松(Pinus sylvestnis var. mongolica)幼苗对持续风吹的光合生理响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(1): 64-70. |
| [9] | 赵哈林, 李瑾, 周瑞莲, 曲浩, 云建英, 潘成臣. 沙埋对樟子松(Pinus sylvestnis var. mongolica)幼树生长特性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(1): 60-65. |
| [10] | 王少昆, 赵学勇, 张铜会, 李玉强, 连 杰, 黄文达, 云建英. 造林对沙地土壤微生物的数量、生物量碳及酶活性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(2): 529-535. |
| [11] | 李玉强;赵学勇;刘新平;尚 雯;冯 静;苏 娜. 樟子松固沙林土壤碳截存及土壤呼吸对干湿变化的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(2): 282-287. |
| [12] | 李得禄;廖空太;严子柱;等. 不同类型防护林中樟子松的构型特征分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2008, 28(1): 113-118. |
| [13] | 郭轶瑞;赵哈林;赵学勇;左小安;罗亚勇. 科尔沁沙地人工林下结皮发育对表土特性影响的研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2007, 27(6): 1000-1006. |
| [14] | 荔克让, 孙宏义, 张华. 干旱荒漠地区沙地樟子松育苗试验研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2000, 20(1): 98-101. |
| [15] | 韩广, 张桂芳. 呼伦贝尔草原沙漠化土地的综合整治区划[J]. 中国沙漠, 2000, 20(1): 25-29. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
