中国沙漠 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 20-31.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00088
梁依茹( ), 吕萍(
), 吕萍( ), 曹敏, 马芳, 夏子书, 余军林, 吴婧妍
), 曹敏, 马芳, 夏子书, 余军林, 吴婧妍
收稿日期:2024-04-23
修回日期:2024-07-07
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2025-01-13
通讯作者:
吕萍
作者简介:吕萍(E-mail: lvping@snnu.edu.cn)基金资助:
Yiru Liang( ), Ping Lv(
), Ping Lv( ), Min Cao, Fang Ma, Zishu Xia, Junlin Yu, Jingyan Wu
), Min Cao, Fang Ma, Zishu Xia, Junlin Yu, Jingyan Wu
Received:2024-04-23
Revised:2024-07-07
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-13
Contact:
Ping Lv
摘要:
风成沙波纹是风在沙质地表塑造的呈波状起伏的微地貌,其形态特征主要受风速和粒径的影响,然而很少有研究关注沙粒级配的作用,因此对于影响沙波纹形态因素的认知并不全面,数值模拟等研究方法的发展大大受限。基于风洞实验,设置了9组粒度配比下的沙波纹形态观测,并利用Matlab软件提取特征参数,再对沙波纹的发育过程、饱和形态进行了分析,期待对以往研究予以补充,并提供实验数据与对比参考。结果表明:(1)沙床颗粒中存在30%以上的相对细沙,可以有效促进沙波纹的形成;相对粗沙的存在,使得沙波纹波长和沙波纹指数的上限增大。(2)沙粒级配因素的介入,影响了沙波纹发育过程的复杂程度,使得到达稳定饱和阶段的时间并不随着风速的增加而线性减小。(3)当风速增加时,双粒径和三粒径混合沙形成的沙波纹形态的复杂性和不均匀性更加显著;细沙∶粗沙=1∶1的粒度配比可以更快地到达稳定,并更好地保持平衡;在等比双粒径的组别中,细沙∶中沙=1∶1的粒度配比有利于沙波纹的发育与发展;非等比双粒径条件下的沙波纹,表现出迎风坡波长小于背风坡波长的特点;非等比双粒径和等比三粒径的组别可以更好地在高风速条件下发展。
中图分类号:
梁依茹, 吕萍, 曹敏, 马芳, 夏子书, 余军林, 吴婧妍. 沙粒级配对沙波纹形态影响的风洞实验研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(1): 20-31.
Yiru Liang, Ping Lv, Min Cao, Fang Ma, Zishu Xia, Junlin Yu, Jingyan Wu. Wind tunnel research into the effect of particle size distribution on sand ripple morphology[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(1): 20-31.
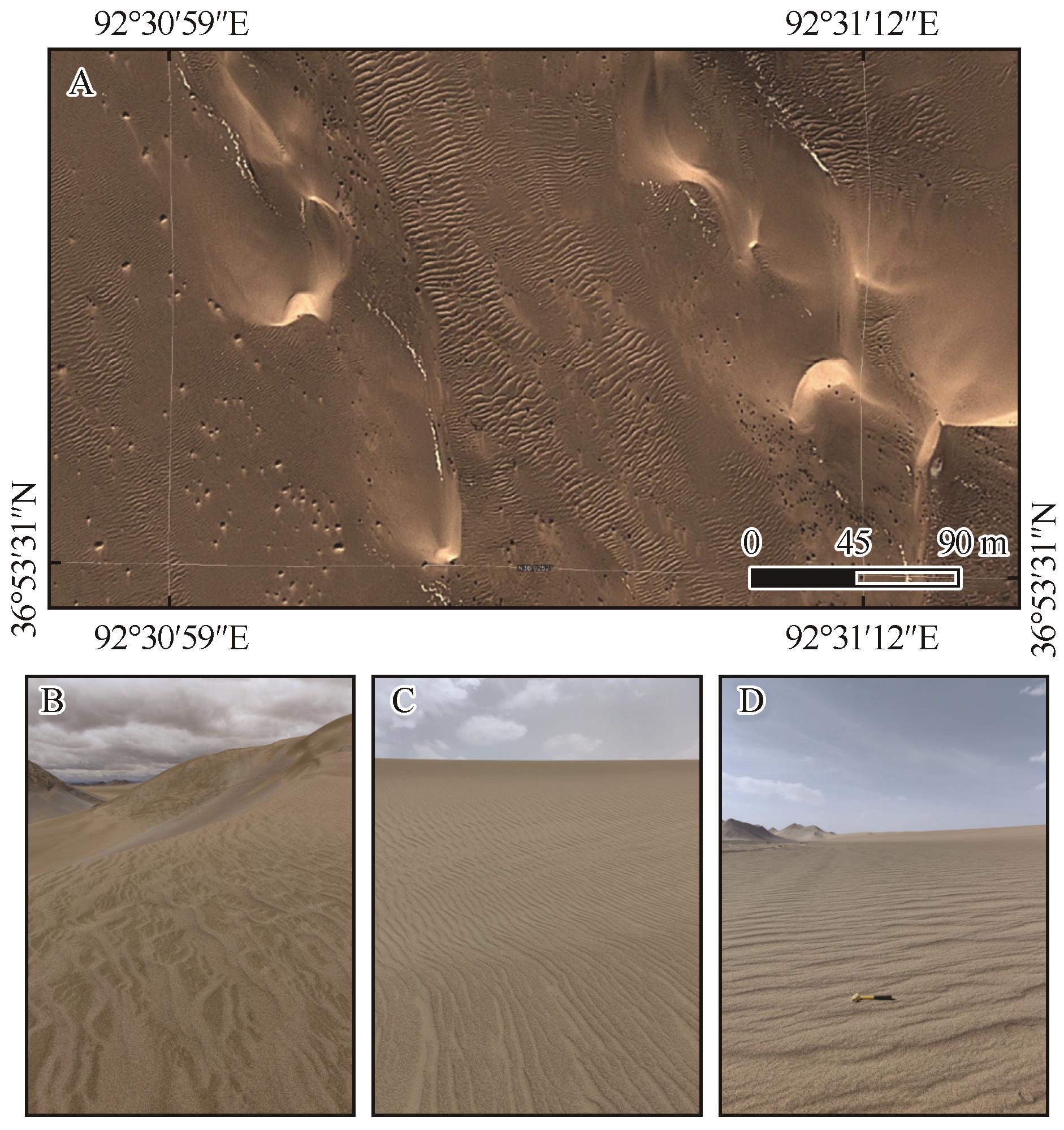
图2 柴达木盆地沙漠沙波纹卫星影像(A,资料来源于Google Earth)和实地照片(B~D)
Fig.2 Satellite aerial image (A, Image from Google Earth) and field photos (B-D) of sand ripples in the Qaidam Basin, China
| 组别 | 细沙 (<0.25 mm) | 中沙 (0.25~0.5 mm) | 粗沙 (0.5~1.0 mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| No.1 | 100 | ||
| No.2 | 100 | ||
| No.3 | 100 | ||
| No.4 | 50 | 50 | |
| No.5 | 50 | 50 | |
| No.6 | 50 | 50 | |
| No.7 | 70 | 30 | |
| No.8 | 30 | 70 | |
| No.9 | 33.3 | 33.3 | 33.3 |
表1 沙粒级配(%)设置
Table 1 Particle size distribution(%) of experiment
| 组别 | 细沙 (<0.25 mm) | 中沙 (0.25~0.5 mm) | 粗沙 (0.5~1.0 mm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| No.1 | 100 | ||
| No.2 | 100 | ||
| No.3 | 100 | ||
| No.4 | 50 | 50 | |
| No.5 | 50 | 50 | |
| No.6 | 50 | 50 | |
| No.7 | 70 | 30 | |
| No.8 | 30 | 70 | |
| No.9 | 33.3 | 33.3 | 33.3 |
| 分类 | 组别 | 沙粒级配 | 平均粒径Mz/μm | 分选 系数σ | 风速V1/(m?s-1) | 风速V2/(m?s-1) | 风速V3/(m?s-1) | 风速V4/(m?s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单粒径 | No.1 | 细沙(<0.25 mm)100% | 101.0 | 1.619 | 9.0 | 10.5 | 12.0 | 15.0 |
| No.2 | 中沙(0.25~0.5 mm)100% | 345.1 | 1.376 | \\ | \\ | \\ | \\ | |
| No.3 | 粗沙(0.5~1.0 mm)100% | 856.5 | 1.349 | \\ | \\ | \\ | \\ | |
| 等比双粒径 | No.4 | 细沙50%+粗沙50% | 176.0 | 2.266 | \\ | 10.5 | 12.0 | 15.0 |
| No.5 | 细沙50%+中沙50% | 193.5 | 1.993 | 9.0 | 10.5 | 12.0 | 15.0 | |
| No.6 | 中沙50%+粗沙50% | 440.7 | 1.536 | \\ | 10.5 | 12.0 | 15.0 | |
| 非等比双粒径 | No.7 | 细沙70%+粗沙30% | 135.3 | 2.000 | \\ | 10.5 | 12.0 | 15.0 |
| No.8 | 细沙30%+粗沙70% | 353.9 | 2.739 | \\ | \\ | \\ | \\ | |
| 等比三粒径 | No.9 | 细沙33.3%+中沙33.3%+粗沙33.3% | 283.2 | 2.247 | 9.0 | 10.5 | 12.0 | 15.0 |
表2 实验结果汇总
Table 2 Summary of experimental results
| 分类 | 组别 | 沙粒级配 | 平均粒径Mz/μm | 分选 系数σ | 风速V1/(m?s-1) | 风速V2/(m?s-1) | 风速V3/(m?s-1) | 风速V4/(m?s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 单粒径 | No.1 | 细沙(<0.25 mm)100% | 101.0 | 1.619 | 9.0 | 10.5 | 12.0 | 15.0 |
| No.2 | 中沙(0.25~0.5 mm)100% | 345.1 | 1.376 | \\ | \\ | \\ | \\ | |
| No.3 | 粗沙(0.5~1.0 mm)100% | 856.5 | 1.349 | \\ | \\ | \\ | \\ | |
| 等比双粒径 | No.4 | 细沙50%+粗沙50% | 176.0 | 2.266 | \\ | 10.5 | 12.0 | 15.0 |
| No.5 | 细沙50%+中沙50% | 193.5 | 1.993 | 9.0 | 10.5 | 12.0 | 15.0 | |
| No.6 | 中沙50%+粗沙50% | 440.7 | 1.536 | \\ | 10.5 | 12.0 | 15.0 | |
| 非等比双粒径 | No.7 | 细沙70%+粗沙30% | 135.3 | 2.000 | \\ | 10.5 | 12.0 | 15.0 |
| No.8 | 细沙30%+粗沙70% | 353.9 | 2.739 | \\ | \\ | \\ | \\ | |
| 等比三粒径 | No.9 | 细沙33.3%+中沙33.3%+粗沙33.3% | 283.2 | 2.247 | 9.0 | 10.5 | 12.0 | 15.0 |
| 1 | 董治宝,屈建军,钱广强,等.库姆塔格沙漠风沙地貌[M].北京:科学出版社,2011. |
| 2 | Bagnold R A.The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes[M].London,UK:Methuen,1942. |
| 3 | Lapotre M G A, Ewing R C, Lamb M P,et al.Large wind ripples on Mars:a record of atmospheric evolution[J].Science,2016,353(6294):55-58. |
| 4 | Hand E.Sandy ripples point to Mars's past[J].Science,2016,352(6281):16-17. |
| 5 | Rae J.Wind sand ripples[J].Nature,1884,29(746):357. |
| 6 | Sharp R P.Wind Ripples[J].The Journal of Geology,1963,71(5):617-636. |
| 7 | 刘贤万.实验风沙物理与风沙工程学[M].北京:科学出版社,1995. |
| 8 | Yizhaq H, Tholen K, Saban L,et al.Coevolving aerodynamic and impact ripples on Earth[J].Nature Geoscience,2024,17(1):66-72. |
| 9 | Wilson I G.Aeolian bedforms- their development and origins[J].Sedimentology,1972,19(3/4):173-210. |
| 10 | 吴正.风沙地貌与治沙工程学[M].北京:科学出版社,2003. |
| 11 | Walker J D.An experimental study of wind ripples[D].Cambridge,USA:Massachusetts Institute of Technology,1981. |
| 12 | Andreotti B, Claudin P, Pouliquen O.Aeolian sand ripples:experimental study of fully developed states[J].Physical Review Letters,2006,96(2):28001. |
| 13 | Cheng H, Liu C C, Li J F,et al.Experimental study of aeolian sand ripples in a wind tunnel[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2018,43(1):312-321. |
| 14 | Seppälä M, Lindé K.Wind tunnel studies of ripple formation[J].Geografiska Annaler.Series A,Physical Geography,1978,60(1/2):29-42. |
| 15 | Schmerler E, Katra I, Kok J F,et al.Experimental and numerical study of Sharp's shadow zone hypothesis on sand ripple wavelength[J].Aeolian Research,2016,22:37-46. |
| 16 | 凌裕泉,屈建军,李长治.应用近景摄影法研究沙纹的移动[J].中国沙漠,2003,23(2):118-120. |
| 17 | 凌裕泉,刘绍中,吴正.风成沙纹形成的风洞模拟研究[J].地理学报,1998,53(6):520. |
| 18 | 朱伟.风成沙波纹形成和发展过程研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2011. |
| 19 | Summers H J, Stone R O.Study of Subaqueous and Subaerial Sand Ripples[R].1968. |
| 20 | Calantoni J, Landry B J, Penko A M.Laboratory observations of sand ripple evolution using bimodal grain size distributions under asymmetric oscillatory flows[J].Journal of Coastal Research,2013,165:1497-1502. |
| 21 | Anderson R S.A theoretical model for aeolian impact ripples[J].Sedimentology,1987,34(5):943-956. |
| 22 | 李猛,董治宝,张正偲.风成沙波纹数学模型综述[J].中国沙漠,2013,33(5):1285-1292. |
| 23 | 罗昊,倪晋仁,李振山.风成沙纹数值模拟研究述评[J].中国沙漠,2004,24(6):783-790. |
| 24 | Wang P, Zhang J, Huang N.A theoretical model for aeolian polydisperse-sand ripples[J].Geomorphology,2019,335:28-36. |
| 25 | 常菊.风成沙波纹发育过程中形态特征分析[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2022. |
| 26 | 鲍锋,董治宝.察尔汗盐湖沙漠沙丘沉积物粒度特征分析[J].水土保持通报,2014,34(6):355-359. |
| 27 | Wentworth C K.A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments[J].The Journal of Geology,1922,30(5):377-392. |
| 28 | 常菊,肖锋军,董治宝,等.基于激光垂直照射沙床面的风成沙波纹二维形态特征分析[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(5):33-42. |
| 29 | Folk R L, Ward W C.Brazos River bar:a study in the significance of grain size parameters[J].Journal of Sedimentary Petrology,1957,27(1):3-26. |
| 30 | Zheng X J.Mechanics of Wind-blown Sand Movement[M].Berlin,Germany:Springer,2009. |
| 31 | Tanner W F.Ripple mark indices and their uses[J].Sedimentology,1967,9(2):89-104. |
| 32 | Hoyle R B, Woods A W.Analytical model of propagating sand ripples[J].Physical Review E,Statistical Physics,Plasmas,Fluids,and Related Interdisciplinary Topics,1997,56(6):6861-6868. |
| 33 | Forrest S B, Haff P K.Mechanics of wind ripple stratigraphy[J].Science,1992,255(5049):1240-1243. |
| 34 | 朱震达,吴正,刘恕,等.中国沙漠概论[M].北京:科学出版社,1980. |
| 35 | 郑晓静,薄天利,谢莉.风成沙波纹的离散粒子追踪法模拟[J].中国科学G辑,物理学 力学 天文学,2007,37(4):527-534. |
| 36 | Rumpel D A.Successive aeolian saltation:studies of idealized collisions[J].Sedimentology,1985,32(2):267-280. |
| 37 | Mitha S, Tran M Q, Werner B T,et al.The grain-bed impact process in aeolian saltation[J].Acta Mechanica,1986,63(1/4):267-278. |
| 38 | Willetts B B, Rice M A.Collisions in aeolian saltation[J].Acta Mechanica,1986,63(1/4):255-265. |
| 39 | Ungar J E, Haff P K.Steady state saltation in air[J].Sedimentology,1987,34(2):289-299. |
| 40 | Werner B T, Haff P K.The impact process in aeolian saltation two-dimensional simulations[J].Sedimentology,1988,35(2):186-196. |
| 41 | Werner B T.A steady state model of wind-blown sand transport[J].The Journal of Geology,1990,98(1):1-17. |
| 42 | 钱宁.泥沙运动力学[M].北京:科学出版社,1983. |
| 43 | Pye K, Tsoar H.Aeolian Sand and Sand Dunes[M].London,UK:Unwin Hyman,1990. |
| 44 | Ellwood J M, Evans P D, Wilson I G.Small scale aeolian bedforms[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research,1975,45:554-561. |
| 45 | Neuman C M, Bédard O.A wind tunnel investigation of particle segregation,ripple formation and armouring within sand beds of systematically varied texture[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2017,42(5):749-762. |
| 46 | Hong C, Huiru L, Yi F,et al.Particle size characteristics of aeolian ripple crests and troughs[J].Sedimentology,2018,65(6):1859-1874. |
| [1] | 杨奕颖, 苏思霖, 曹恩志, 李红有, 迟洪明, 蔺凯, 吴旭东, 何文强, 杨昊天. 沙漠大型光伏电站对固沙植物表型及生物量分配的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(1): 162-172. |
| [2] | 褚佳琦, 严平, 苏志珠, 袁文杰, 王晓旭, 张潇, 赵华刚. 雅鲁藏布江米林段爬坡沙丘形态演变及移动规律[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 220-230. |
| [3] | 蒋缠文, 董治宝, 罗万银, 钱广强, 张正偲, 逯军峰, 王晓艳. 基于原位风沙流观测的广冲击角的溅射函数构建[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 254-260. |
| [4] | 郭酉元, 钱广强, 杨转玲, 邢学刚. 库姆塔格沙漠三垄沙地区砾波纹形态、粒度及环境风况[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 37-45. |
| [5] | 万雨晨, 刘彦平, 吴永胜, 贾鸿飞, 张甜, 高艳红, 杨昊天, 尤万学, 杜军, 贾荣亮. 腾格里沙漠人工固沙植被区藓类植物形态演变特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 298-307. |
| [6] | 王录仓, 屈艳琦, 武潼. 城市群空间结构对城市群空间扩张模式与形态的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 63-74. |
| [7] | 韩敏, 高永, 贺明辉, 燕如, 白芳, 杨文源, 李小乐, 袁晓满, 杨娟. 藏锦鸡儿( Caragana tibetica )灌丛沙堆的形态与沉积物特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(2): 185-195. |
| [8] | 管超, 武子丰, 哈斯额尔敦. 库布齐沙漠西缘格状沙丘动态特征及其成因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(2): 239-253. |
| [9] | 王仁德, 蒋红军, 李庆, 付刚, 李玉强, 苑依笑, 常春平, 郭中领. 土壤粉尘释放能力与土壤性质关系的初步研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 43-49. |
| [10] | 张萌, 亢力强, 王晓美. 交错和矩形布置对树状植被地表剪应力和输沙率的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 50-60. |
| [11] | 许瑞聪, 董治宝, 南维鸽, 陈国祥, 杨馥宁, 孔玲玲. 柴达木盆地南缘死亡蛛丝蓬( Halogeton arachnoideus )风影沙丘形态和沉积特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 55-63. |
| [12] | 黄日辉, 张立婷, 冯淼彦, 刘铮瑶, 李健熙, 陈韵琪, 张志浩, 王璟. 广东省东海岛大岭剖面沉积物粒度、微形态特征与沉积环境[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 121-129. |
| [13] | 杨馥宁, 吕萍, 马芳, 曹敏, 肖南, 顾立霞, 杨迎. 腾格里沙漠南部格状沙丘的形态演变及移动特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 107-115. |
| [14] | 翟军团, 陈向向, 李秀, 张山河, 韩晓莉, 李志军. 胡杨( Populus euphratica )枝叶异速生长关系随发育阶段及冠层高度变化的性别差异[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 116-127. |
| [15] | 邹桐, 杨转玲, 韦锦芝, 廖应英, 邢学刚, 钱广强, 梁晓磊. 柴达木盆地西南缘新月形沙丘移动特征及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 212-221. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
