中国沙漠 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 253-265.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2025.00014
郭志霞1,2,3( ), 刘任涛1,2,3(
), 刘任涛1,2,3( ), 赵文智3,4
), 赵文智3,4
收稿日期:2024-07-14
修回日期:2025-02-18
出版日期:2025-09-20
发布日期:2025-09-27
通讯作者:
刘任涛
作者简介:郭志霞(1995—),女,山西吕梁人,博士研究生,主要从事草地生态研究。E-mail: 13753447471@163.com
基金资助:
Zhixia Guo1,2,3( ), Rentao Liu1,2,3(
), Rentao Liu1,2,3( ), Wenzhi Zhao3,4
), Wenzhi Zhao3,4
Received:2024-07-14
Revised:2025-02-18
Online:2025-09-20
Published:2025-09-27
Contact:
Rentao Liu
摘要:
为揭示降水梯度对灌丛微生境地面节肢动物群落的影响,根据年降水量选择干旱、半干旱和半湿润区草地,以共有的灌丛黑沙蒿(Artemisia ordosica)、柠条锦鸡儿(Caragana korshinskii)为对象,以灌丛间开阔地为对照(CK),连续3年利用陷阱杯法,研究了降水梯度下灌丛微生境下地面节肢动物的物种组成、多样性分布特征及影响因素。结果显示:干旱区微生境间地面节肢动物群落组成均存在显著差异;“虫岛效应”在半干旱区微生境间无显著性;在干旱和半湿润区,柠条锦鸡儿灌丛栽植有利于地面节肢动物个体数和类群数增加。dbRDA结果显示,土壤全碳、含水量和草本植物丰富度是影响降水梯度下微生境地面节肢动物群落结构的重要因素。随年降水减少,不同灌丛微生境下地面节肢动物群落组成差异增大,在干旱、半湿润区,栽植柠条锦鸡儿灌丛对地面节肢动物的保育效应要优于黑沙蒿灌丛。
中图分类号:
郭志霞, 刘任涛, 赵文智. 降水量对灌丛微生境地面节肢动物群落的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(5): 253-265.
Zhixia Guo, Rentao Liu, Wenzhi Zhao. Effect of different precipitation gradients on community characteristics of ground-active arthropods under shrub microhabitats[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(5): 253-265.
| 环境分区 | 年平均气温 /℃ | 年蒸散量/mm | 风速 /(m·s-1) | 土壤类型 | 地带性植被 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实际 | 潜在 | 地带性 | 非地带性 | ||||
| 干旱区 | 9.2 | 242 | 1 235 | 2.9 | 灰漠土与棕钙土 | 风砂土 | 草原化荒漠 |
| 半干旱区 | 8.5 | 287 | 1 120 | 2.8 | 黄绵土与灰钙土 | 风砂土 | 荒漠化草原 |
| 半湿润区 | 8.7 | 318 | 1 192 | 2.7 | 灰褐土 | 风砂土 | 荒漠化草原 |
表1 研究区概况
Table 1 General information about the research area
| 环境分区 | 年平均气温 /℃ | 年蒸散量/mm | 风速 /(m·s-1) | 土壤类型 | 地带性植被 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 实际 | 潜在 | 地带性 | 非地带性 | ||||
| 干旱区 | 9.2 | 242 | 1 235 | 2.9 | 灰漠土与棕钙土 | 风砂土 | 草原化荒漠 |
| 半干旱区 | 8.5 | 287 | 1 120 | 2.8 | 黄绵土与灰钙土 | 风砂土 | 荒漠化草原 |
| 半湿润区 | 8.7 | 318 | 1 192 | 2.7 | 灰褐土 | 风砂土 | 荒漠化草原 |
| 土壤理化性质 | 指标 | 测定方法 |
|---|---|---|
| 物理性质 | 含水量 | 烘干称重法[ |
| 电导率 | 1∶5土水比浸提后,使用便携式电导率仪(雷磁DDSJ-308F)测定[ | |
| 粒径组成 | 采用Mastersizer3000激光衍射粒度分析仪测[ 据国际制土壤质地分类划分土壤质地:砂粒(2~0.05 mm)、粉粒(0.05~0.002 mm)、黏粒(<0.02 mm)[ | |
| 化学性质 | pH | 1∶5土水比浸提后,使用PHS-3C酸度计测定[ |
| 全碳 | 采用元素分析仪(意大利 DK6,UDK140分析仪)测定[ | |
| 全氮 | 采用元素分析仪(意大利 DK6,UDK140分析仪)测定[ |
表2 土壤理化性质测定指标及测定方法
Table 2 Determination indicators and methods for soil physical and chemical properties
| 土壤理化性质 | 指标 | 测定方法 |
|---|---|---|
| 物理性质 | 含水量 | 烘干称重法[ |
| 电导率 | 1∶5土水比浸提后,使用便携式电导率仪(雷磁DDSJ-308F)测定[ | |
| 粒径组成 | 采用Mastersizer3000激光衍射粒度分析仪测[ 据国际制土壤质地分类划分土壤质地:砂粒(2~0.05 mm)、粉粒(0.05~0.002 mm)、黏粒(<0.02 mm)[ | |
| 化学性质 | pH | 1∶5土水比浸提后,使用PHS-3C酸度计测定[ |
| 全碳 | 采用元素分析仪(意大利 DK6,UDK140分析仪)测定[ | |
| 全氮 | 采用元素分析仪(意大利 DK6,UDK140分析仪)测定[ |
| 微生境 | 干旱区 | 半干旱区 | 半湿润区 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑沙蒿 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | CK | 黑沙蒿 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | CK | 黑沙蒿 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | CK | |
| pH | 0.28±0.000b | 0.28±0.001b | 0.29±0.000a | 0.29±0.000a | 0.29±0.001b | 0.29±0.000a | 0.28±0.001 | 0.28±0.001 | 0.28±0.001 |
| EC/% | 0.46±0.002a | 0.46±0.002a | 0.45±0.002b | 0.46±0.002b | 0.47±0.001a | 0.46±0.002b | 0.45±0.002 | 0.45±0.002 | 0.45±0.002 |
| SM/% | 0.07±0.005b | 0.07±0.007b | 0.09±0.005a | 0.15±0.006b | 0.17±0.007a | 0.15±0.004b | 0.20±0.011a | 0.16±0.009b | 0.18±0.006ab |
| Clay/% | 0.02±0.019 | 0.00±0.000 | 0.00±0.000 | 0.20±0.028 | 0.24±0.027 | 0.24±0.026 | 0.20±0.027 | 0.14±0.037 | 0.16±0.035 |
| Silt/% | 0.18±0.036 | 0.15±0.030 | 0.16±0.032 | 0.34±0.008b | 0.36±0.007ab | 0.36±0.009a | 0.34±0.006a | 0.31±0.005b | 0.32±0.005b |
| Sand/% | 0.47±0.001 | 0.48±0.000 | 0.48±0.001 | 0.46±0.002 | 0.46±0.004 | 0.45±0.004 | 0.46±0.001 | 0.47±0.001 | 0.47±0.002 |
| TC/(g·kg-1) | 0.09±0.00a | 0.07±0.01b | 0.05±0.01c | 0.14±0.025 | 0.17±0.027 | 0.15±0.026 | 0.15±0.026 | 0.14±0.021 | 0.13±0.021 |
| TN/(g·kg-1) | 0.01±0.003 | 0.01±0.003 | 0.01±0.002 | 0.02±0.005 | 0.03±0.010 | 0.02±0.006 | 0.04±0.011 | 0.03±0.007 | 0.03±0.007 |
| HD/(株·m-2) | 0.01±0.009b | 0.31±0.018a | 0.23±0.050a | 0.32±0.012b | 0.33±0.01b | 0.36±0.008a | 0.28±0.017 | 0.29±0.014 | 0.30±0.011 |
| HR | 0.00±0.003c | 0.15±0.008a | 0.09±0.021b | 0.20±0.006 | 0.21±0.012 | 0.23±0.008 | 0.16±0.011b | 0.17±0.012ab | 0.20±0.009a |
| HH/cm | 0.08±0.076a | 1.20±0.052a | 0.68±0.156b | 1.18±0.074 | 1.24±0.057 | 1.24±0.070 | 1.26±0.063 | 1.24±0.074 | 1.10±0.082 |
表3 不同降水梯度灌丛下环境因子变化特征
Table 3 Characterization of environmental factors under shrubs with different precipitation gradients
| 微生境 | 干旱区 | 半干旱区 | 半湿润区 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑沙蒿 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | CK | 黑沙蒿 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | CK | 黑沙蒿 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | CK | |
| pH | 0.28±0.000b | 0.28±0.001b | 0.29±0.000a | 0.29±0.000a | 0.29±0.001b | 0.29±0.000a | 0.28±0.001 | 0.28±0.001 | 0.28±0.001 |
| EC/% | 0.46±0.002a | 0.46±0.002a | 0.45±0.002b | 0.46±0.002b | 0.47±0.001a | 0.46±0.002b | 0.45±0.002 | 0.45±0.002 | 0.45±0.002 |
| SM/% | 0.07±0.005b | 0.07±0.007b | 0.09±0.005a | 0.15±0.006b | 0.17±0.007a | 0.15±0.004b | 0.20±0.011a | 0.16±0.009b | 0.18±0.006ab |
| Clay/% | 0.02±0.019 | 0.00±0.000 | 0.00±0.000 | 0.20±0.028 | 0.24±0.027 | 0.24±0.026 | 0.20±0.027 | 0.14±0.037 | 0.16±0.035 |
| Silt/% | 0.18±0.036 | 0.15±0.030 | 0.16±0.032 | 0.34±0.008b | 0.36±0.007ab | 0.36±0.009a | 0.34±0.006a | 0.31±0.005b | 0.32±0.005b |
| Sand/% | 0.47±0.001 | 0.48±0.000 | 0.48±0.001 | 0.46±0.002 | 0.46±0.004 | 0.45±0.004 | 0.46±0.001 | 0.47±0.001 | 0.47±0.002 |
| TC/(g·kg-1) | 0.09±0.00a | 0.07±0.01b | 0.05±0.01c | 0.14±0.025 | 0.17±0.027 | 0.15±0.026 | 0.15±0.026 | 0.14±0.021 | 0.13±0.021 |
| TN/(g·kg-1) | 0.01±0.003 | 0.01±0.003 | 0.01±0.002 | 0.02±0.005 | 0.03±0.010 | 0.02±0.006 | 0.04±0.011 | 0.03±0.007 | 0.03±0.007 |
| HD/(株·m-2) | 0.01±0.009b | 0.31±0.018a | 0.23±0.050a | 0.32±0.012b | 0.33±0.01b | 0.36±0.008a | 0.28±0.017 | 0.29±0.014 | 0.30±0.011 |
| HR | 0.00±0.003c | 0.15±0.008a | 0.09±0.021b | 0.20±0.006 | 0.21±0.012 | 0.23±0.008 | 0.16±0.011b | 0.17±0.012ab | 0.20±0.009a |
| HH/cm | 0.08±0.076a | 1.20±0.052a | 0.68±0.156b | 1.18±0.074 | 1.24±0.057 | 1.24±0.070 | 1.26±0.063 | 1.24±0.074 | 1.10±0.082 |
| 科 | 食性 | 干旱区 | 半干旱区 | 半湿润区 | 总计 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑沙蒿 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | CK | 黑沙蒿 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | CK | 黑沙蒿 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | CK | |||||||||||||
个 体数 | 相对 多度 | 个 体数 | 相 对 多度 | 个 体数 | 相 对 多 度 | 个 体 数 | 相 对 多 度 | 个 体 数 | 相 对 多 度 | 个 体 数 | 相 对 多 度 | 个 体 数 | 相 对 多 度 | 个 体 数 | 相 对 多 度 | 个 体 数 | 相 对 多 度 | 个 体 数 | 相 对 多 度 | ||
| 步甲科(Carabidae) | Pr | 7 | ++ | 16 | ++ | 11 | ++ | 26 | ++ | 18 | ++ | 29 | ++ | 43 | ++ | 33 | ++ | 29 | ++ | 212 | ++ |
| 蝽科(Pentatomidae) | He | 3 | ++ | 3 | + | 6 | ++ | 12 | + | ||||||||||||
| 盗蛛科(Pisauridae) | Pr | 3 | + | 3 | + | 3 | ++ | 6 | ++ | 3 | + | 6 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | + | 3 | + | 33 | ++ |
| 地蜈蚣科(Geophilidae) | Pr | 7 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 15 | + | ||||||||||||
| 盾蝽科(Scutelleridae) | He | 3 | + | 6 | ++ | 9 | + | ||||||||||||||
| 粪金龟科(Geotrupidae) | Sa | 6 | ++ | 3 | ++ | 3 | + | 5 | ++ | 3 | + | 20 | + | ||||||||
| 管巢蛛科(Clubionidae) | Pr | 3 | ++ | 3 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | + | 3 | + | 20 | + | ||||||
| 光盔蛛科(Liocranidae) | Pr | 3 | + | 4 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 7 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 3 | + | 4 | ++ | 5 | + | 40 | ++ |
| 虎甲科(Cicindelidae) | Pr | 3 | + | 3 | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 姬蝽科(Nabidae) | He | 3 | + | 63 | +++ | 66 | ++ | ||||||||||||||
| 角蝉科(Membracidae) | He | 3 | + | 3 | ++ | 3 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | + | 3 | + | 4 | ++ | 3 | + | 25 | + | ||
| 金龟子科(Scarabaeidae) | He | 6 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 23 | ++ | 35 | +++ | 54 | +++ | 8 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 10 | ++ | 150 | ++ |
| 近管蛛科(Anyphaonidaae) | Pr | 3 | + | 3 | + | 6 | ++ | 15 | ++ | 3 | + | 6 | ++ | 36 | ++ | ||||||
| 叩甲科(Elateridae) | Om | 3 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | + | 3 | + | 12 | + | ||||||||||
| 狼蛛科(Lycosidae) | Pr | 5 | ++ | 3 | + | 5 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 11 | ++ | 6 | ++ | 6 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 4 | + | 49 | ++ |
| 蝼蛄科(Gryllotalpidae) | Pr | 3 | ++ | 3 | + | 4 | ++ | 10 | + | ||||||||||||
| 盲蝽科(Miridae) | He | 3 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | + | 5 | ++ | 14 | + | ||||||||||
| 盲蛛科(Opilions) | Pr | 3 | + | 3 | + | 3 | + | 9 | + | ||||||||||||
| 虻科(Tabanidae) | Pr | 4 | ++ | 3 | + | 5 | ++ | 15 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | + | 8 | ++ | 5 | + | 46 | ++ | ||
| 拟步甲科(Tenebrionidae) | Om | 47 | +++ | 19 | ++ | 28 | +++ | 25 | ++ | 21 | ++ | 13 | ++ | 8 | ++ | 12 | ++ | 12 | ++ | 185 | ++ |
| 瓢甲科(Coccinellidae) | Om | 3 | + | 3 | + | 6 | + | ||||||||||||||
| 平腹蛛科(Gnaphosidae) | Pr | 4 | ++ | 3 | + | 5 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | + | 3 | + | 33 | ++ |
| 蜻科(Libellulidae) | Pr | 3 | ++ | 3 | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 球蚜科Adelgidae) | He | 3 | + | 3 | ++ | 46 | +++ | 31 | ++ | 26 | ++ | 36 | ++ | 29 | ++ | 24 | ++ | 198 | ++ | ||
| 蠼螋科(Labiduridae) | Om | 14 | ++ | 3 | + | 18 | ++ | 27 | ++ | 62 | ++ | ||||||||||
| 绒毛金龟科(Glaphyridae) | He | 3 | + | 14 | ++ | 81 | +++ | 3 | + | 101 | ++ | ||||||||||
| 鳃金龟科(Melolonthidae) | Om | 3 | + | 3 | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 食蚜蝇科(Syrphidae) | He | 3 | + | 15 | ++ | 3 | + | 4 | + | 25 | + | ||||||||||
| 跳蛛科(Salticidae) | Pr | 9 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 6 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | + | 36 | ++ | ||
| 网蝽科(Tingidae) | He | 9 | ++ | 9 | ++ | 6 | ++ | 9 | ++ | 6 | ++ | 188 | +++ | 17 | ++ | 203 | +++ | 447 | +++ | ||
| 蟋蟀科(Grylloidea) | He | 4 | ++ | 18 | ++ | 7 | ++ | 7 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 4 | + | 45 | ++ | ||||||
| 象甲科(Curculionidae) | He | 3 | + | 7 | ++ | 9 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 8 | ++ | 6 | ++ | 3 | + | 5 | ++ | 4 | + | 49 | ++ |
| 逍遥蛛科(Philodromidae) | Pr | 3 | + | 3 | + | 5 | ++ | 11 | + | ||||||||||||
| 蟹蛛科(Thomisidae) | Pr | 3 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 8 | ++ | 3 | + | 18 | + | ||||||||||
| 阎甲科(Histeridae) | Om | 5 | ++ | 27 | +++ | 9 | ++ | 9 | ++ | 50 | ++ | ||||||||||
| 蚁科(Formicidae) | Om | 261 | +++ | 197 | +++ | 121 | +++ | 19 | ++ | 54 | +++ | 33 | ++ | 144 | +++ | 140 | +++ | 64 | +++ | 1 033 | +++ |
| 异蝽科(Urostylidae) | He | 11 | ++ | 22 | ++ | 17 | ++ | 15 | ++ | 65 | ++ | ||||||||||
| 隐翅虫科(Stephylinidae) | Pr | 6 | ++ | 3 | + | 13 | ++ | 22 | + | ||||||||||||
| 蚰蜒科(Scutigeridae) | Pr | 3 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 12 | + | ||||||||||||
| 缘蝽科(Coreidae) | He | 14 | ++ | 3 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 27 | ++ | 11 | ++ | 74 | ++ | ||
| 螽斯科(Tettigoniidae) | Om | 3 | ++ | 3 | + | 6 | + | ||||||||||||||
表4 节肢动物群落个体数量
Table 4 The abundance of arthropods communities
| 科 | 食性 | 干旱区 | 半干旱区 | 半湿润区 | 总计 | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑沙蒿 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | CK | 黑沙蒿 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | CK | 黑沙蒿 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | CK | |||||||||||||
个 体数 | 相对 多度 | 个 体数 | 相 对 多度 | 个 体数 | 相 对 多 度 | 个 体 数 | 相 对 多 度 | 个 体 数 | 相 对 多 度 | 个 体 数 | 相 对 多 度 | 个 体 数 | 相 对 多 度 | 个 体 数 | 相 对 多 度 | 个 体 数 | 相 对 多 度 | 个 体 数 | 相 对 多 度 | ||
| 步甲科(Carabidae) | Pr | 7 | ++ | 16 | ++ | 11 | ++ | 26 | ++ | 18 | ++ | 29 | ++ | 43 | ++ | 33 | ++ | 29 | ++ | 212 | ++ |
| 蝽科(Pentatomidae) | He | 3 | ++ | 3 | + | 6 | ++ | 12 | + | ||||||||||||
| 盗蛛科(Pisauridae) | Pr | 3 | + | 3 | + | 3 | ++ | 6 | ++ | 3 | + | 6 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | + | 3 | + | 33 | ++ |
| 地蜈蚣科(Geophilidae) | Pr | 7 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 15 | + | ||||||||||||
| 盾蝽科(Scutelleridae) | He | 3 | + | 6 | ++ | 9 | + | ||||||||||||||
| 粪金龟科(Geotrupidae) | Sa | 6 | ++ | 3 | ++ | 3 | + | 5 | ++ | 3 | + | 20 | + | ||||||||
| 管巢蛛科(Clubionidae) | Pr | 3 | ++ | 3 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | + | 3 | + | 20 | + | ||||||
| 光盔蛛科(Liocranidae) | Pr | 3 | + | 4 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 7 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 3 | + | 4 | ++ | 5 | + | 40 | ++ |
| 虎甲科(Cicindelidae) | Pr | 3 | + | 3 | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 姬蝽科(Nabidae) | He | 3 | + | 63 | +++ | 66 | ++ | ||||||||||||||
| 角蝉科(Membracidae) | He | 3 | + | 3 | ++ | 3 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | + | 3 | + | 4 | ++ | 3 | + | 25 | + | ||
| 金龟子科(Scarabaeidae) | He | 6 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 23 | ++ | 35 | +++ | 54 | +++ | 8 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 10 | ++ | 150 | ++ |
| 近管蛛科(Anyphaonidaae) | Pr | 3 | + | 3 | + | 6 | ++ | 15 | ++ | 3 | + | 6 | ++ | 36 | ++ | ||||||
| 叩甲科(Elateridae) | Om | 3 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | + | 3 | + | 12 | + | ||||||||||
| 狼蛛科(Lycosidae) | Pr | 5 | ++ | 3 | + | 5 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 11 | ++ | 6 | ++ | 6 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 4 | + | 49 | ++ |
| 蝼蛄科(Gryllotalpidae) | Pr | 3 | ++ | 3 | + | 4 | ++ | 10 | + | ||||||||||||
| 盲蝽科(Miridae) | He | 3 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | + | 5 | ++ | 14 | + | ||||||||||
| 盲蛛科(Opilions) | Pr | 3 | + | 3 | + | 3 | + | 9 | + | ||||||||||||
| 虻科(Tabanidae) | Pr | 4 | ++ | 3 | + | 5 | ++ | 15 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | + | 8 | ++ | 5 | + | 46 | ++ | ||
| 拟步甲科(Tenebrionidae) | Om | 47 | +++ | 19 | ++ | 28 | +++ | 25 | ++ | 21 | ++ | 13 | ++ | 8 | ++ | 12 | ++ | 12 | ++ | 185 | ++ |
| 瓢甲科(Coccinellidae) | Om | 3 | + | 3 | + | 6 | + | ||||||||||||||
| 平腹蛛科(Gnaphosidae) | Pr | 4 | ++ | 3 | + | 5 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | + | 3 | + | 33 | ++ |
| 蜻科(Libellulidae) | Pr | 3 | ++ | 3 | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 球蚜科Adelgidae) | He | 3 | + | 3 | ++ | 46 | +++ | 31 | ++ | 26 | ++ | 36 | ++ | 29 | ++ | 24 | ++ | 198 | ++ | ||
| 蠼螋科(Labiduridae) | Om | 14 | ++ | 3 | + | 18 | ++ | 27 | ++ | 62 | ++ | ||||||||||
| 绒毛金龟科(Glaphyridae) | He | 3 | + | 14 | ++ | 81 | +++ | 3 | + | 101 | ++ | ||||||||||
| 鳃金龟科(Melolonthidae) | Om | 3 | + | 3 | + | ||||||||||||||||
| 食蚜蝇科(Syrphidae) | He | 3 | + | 15 | ++ | 3 | + | 4 | + | 25 | + | ||||||||||
| 跳蛛科(Salticidae) | Pr | 9 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 6 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 3 | + | 3 | + | 36 | ++ | ||
| 网蝽科(Tingidae) | He | 9 | ++ | 9 | ++ | 6 | ++ | 9 | ++ | 6 | ++ | 188 | +++ | 17 | ++ | 203 | +++ | 447 | +++ | ||
| 蟋蟀科(Grylloidea) | He | 4 | ++ | 18 | ++ | 7 | ++ | 7 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 4 | + | 45 | ++ | ||||||
| 象甲科(Curculionidae) | He | 3 | + | 7 | ++ | 9 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 8 | ++ | 6 | ++ | 3 | + | 5 | ++ | 4 | + | 49 | ++ |
| 逍遥蛛科(Philodromidae) | Pr | 3 | + | 3 | + | 5 | ++ | 11 | + | ||||||||||||
| 蟹蛛科(Thomisidae) | Pr | 3 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 8 | ++ | 3 | + | 18 | + | ||||||||||
| 阎甲科(Histeridae) | Om | 5 | ++ | 27 | +++ | 9 | ++ | 9 | ++ | 50 | ++ | ||||||||||
| 蚁科(Formicidae) | Om | 261 | +++ | 197 | +++ | 121 | +++ | 19 | ++ | 54 | +++ | 33 | ++ | 144 | +++ | 140 | +++ | 64 | +++ | 1 033 | +++ |
| 异蝽科(Urostylidae) | He | 11 | ++ | 22 | ++ | 17 | ++ | 15 | ++ | 65 | ++ | ||||||||||
| 隐翅虫科(Stephylinidae) | Pr | 6 | ++ | 3 | + | 13 | ++ | 22 | + | ||||||||||||
| 蚰蜒科(Scutigeridae) | Pr | 3 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 12 | + | ||||||||||||
| 缘蝽科(Coreidae) | He | 14 | ++ | 3 | ++ | 4 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 5 | ++ | 27 | ++ | 11 | ++ | 74 | ++ | ||
| 螽斯科(Tettigoniidae) | Om | 3 | ++ | 3 | + | 6 | + | ||||||||||||||
| 环境分区 | 类群 | 个体数 | 类群数 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑沙蒿 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | CK | 黑沙蒿 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | CK | |||
| 干旱区 | 优势 | 2.01±0.04a | 1.84±0.04b | 1.61±0.08c | 0.48±0.00a | 0.3.00±0.00b | 0.49±0.01a | |
| 常见 | 0.57±0.07b | 1.10±0.07a | 0.76±0.07b | 0.16±0.04b | 0.40±0.04a | 0.22±0.04b | ||
| 稀有 | 0.19±0.04 | 0.30±0.06 | 0.00±0.00 | 0.28±0.04 | 0.28±0.02 | 0.31±0.05 | ||
| 半干旱区 | 优势 | 0.50±0.15b | 1.30±0.11a | 0.81±0.17b | 0.39±0.04b | 0.61±0.03a | 0.43±0.05b | |
| 常见 | 1.56±0.05a | 1.32±0.11b | 1.62±0.04a | 1.00±0.04a | 0.84±0.07b | 1.00±0.03a | ||
| 稀有 | 0.00±0.00 | 0.31±0.05a | 0.20±0.05b | 0.00±0.00 | 0.80±0.03a | 0.57±0.05b | ||
| 半湿润区 | 优势 | 1.34±0.20 | 1.37±0.16 | 1.30±0.21 | 0.19±0.04 | 0.30±0.06 | 0.00±0.00 | |
| 常见 | 1.24±0.09 | 1.33±0.06 | 1.13±0.11 | 0.16±0.03b | 0.31±0.05a | 0.20±0.05b | ||
| 稀有 | 0.34±0.07b | 0.19±0.06b | 0.55±0.07a | 0.32±0.07ab | 0.19±0.06b | 0.48±0.06a | ||
表5 不同降水梯度灌丛微生境优势、常见和稀有类群的个体数和类群数变化特征(平均值±标准误)
Table 5 Changes in abundance and richness of dominant, common, and rare groups of arthropods(Mean±SE)
| 环境分区 | 类群 | 个体数 | 类群数 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黑沙蒿 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | CK | 黑沙蒿 | 柠条锦鸡儿 | CK | |||
| 干旱区 | 优势 | 2.01±0.04a | 1.84±0.04b | 1.61±0.08c | 0.48±0.00a | 0.3.00±0.00b | 0.49±0.01a | |
| 常见 | 0.57±0.07b | 1.10±0.07a | 0.76±0.07b | 0.16±0.04b | 0.40±0.04a | 0.22±0.04b | ||
| 稀有 | 0.19±0.04 | 0.30±0.06 | 0.00±0.00 | 0.28±0.04 | 0.28±0.02 | 0.31±0.05 | ||
| 半干旱区 | 优势 | 0.50±0.15b | 1.30±0.11a | 0.81±0.17b | 0.39±0.04b | 0.61±0.03a | 0.43±0.05b | |
| 常见 | 1.56±0.05a | 1.32±0.11b | 1.62±0.04a | 1.00±0.04a | 0.84±0.07b | 1.00±0.03a | ||
| 稀有 | 0.00±0.00 | 0.31±0.05a | 0.20±0.05b | 0.00±0.00 | 0.80±0.03a | 0.57±0.05b | ||
| 半湿润区 | 优势 | 1.34±0.20 | 1.37±0.16 | 1.30±0.21 | 0.19±0.04 | 0.30±0.06 | 0.00±0.00 | |
| 常见 | 1.24±0.09 | 1.33±0.06 | 1.13±0.11 | 0.16±0.03b | 0.31±0.05a | 0.20±0.05b | ||
| 稀有 | 0.34±0.07b | 0.19±0.06b | 0.55±0.07a | 0.32±0.07ab | 0.19±0.06b | 0.48±0.06a | ||
| 比较 | 干旱区 | 半干旱区 | 半湿润区 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | P | R2 | P | R2 | P | |||
| 黑沙蒿 vs 柠条锦鸡儿 | 0.12 | 0.030 | 0.14 | 0.003 | 0.02 | 0.759 | ||
| 黑沙蒿 vs 对照 | 0.18 | 0.011 | 0.05 | 0.128 | 0.04 | 0.440 | ||
| 柠条锦鸡儿 vs 对照 | 0.16 | 0.011 | 0.07 | 0.039 | 0.07 | 0.114 | ||
表6 不同降水梯度灌丛微生境间地面节肢动物群落结构的差异
Table 6 Differences in ground-dwelling arthropods community structure among scrub microhabitats with different precipitation gradients
| 比较 | 干旱区 | 半干旱区 | 半湿润区 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | P | R2 | P | R2 | P | |||
| 黑沙蒿 vs 柠条锦鸡儿 | 0.12 | 0.030 | 0.14 | 0.003 | 0.02 | 0.759 | ||
| 黑沙蒿 vs 对照 | 0.18 | 0.011 | 0.05 | 0.128 | 0.04 | 0.440 | ||
| 柠条锦鸡儿 vs 对照 | 0.16 | 0.011 | 0.07 | 0.039 | 0.07 | 0.114 | ||
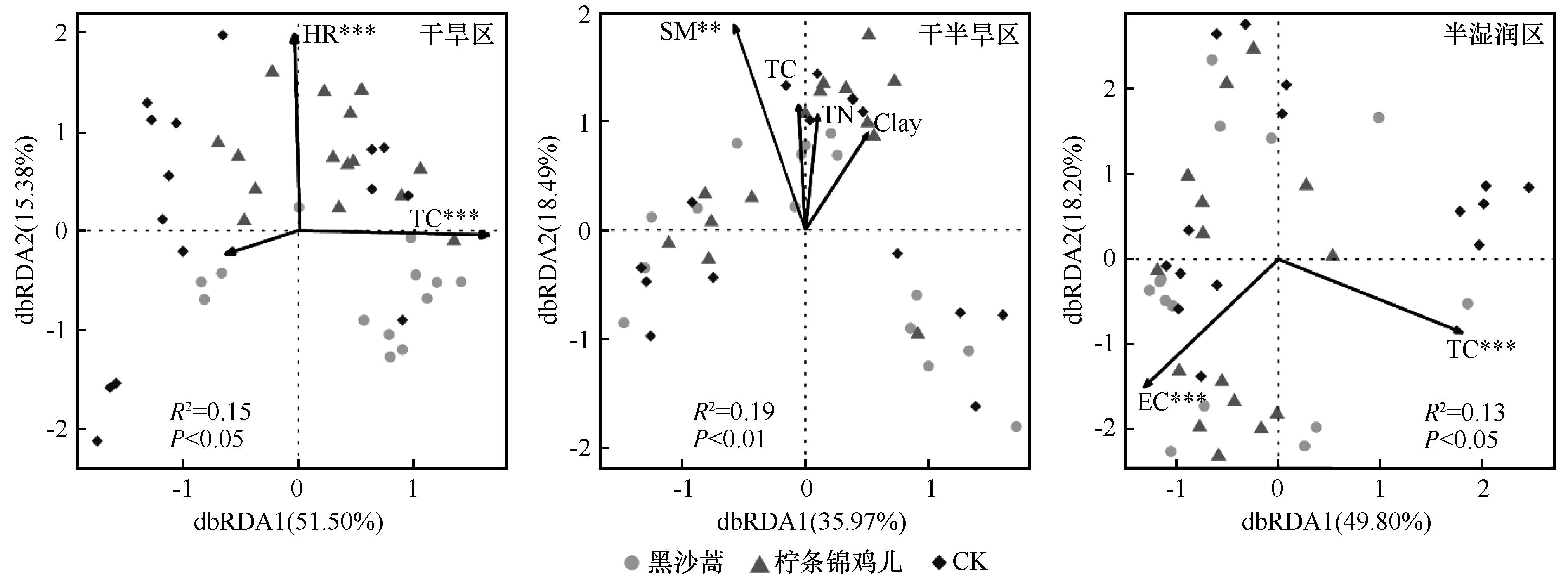
图4 环境因素对地面节肢动物群落影响的冗余分析(dbRDA)注:*代表相关性强度: *: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001; pH: 土壤酸碱度; EC: 土壤电导率; SM: 土壤含水量; Clay: 土壤黏粒; TC: 土壤全碳; TN: 土壤全氮; HR 草本植物丰富度
Fig.4 Redundancy analysis (dbRDA) of the effects of environmental factors on ground-dwelling arthropods communities
| 环境分区 | 类群 | 数量 | pH | EC | SM | Clay | Silt | Sand | TC | TN | HD | HR | HH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干旱区 | 优势 | I | 0.45** | -0.46** | 0.50** | ||||||||
| T | -0.36* | 0.32* | -0.54** | -0.62** | -0.65** | ||||||||
| 常见 | I | -0.34* | 0.35* | 0.36* | 0.44** | 0.39** | |||||||
| T | 0.31* | 0.35* | 0.41** | 0.40** | |||||||||
| 稀有 | I | 0.48** | -0.61** | ||||||||||
| T | 0.48** | -0.61** | |||||||||||
| 半干旱区 | 优势 | I | |||||||||||
| T | |||||||||||||
| 常见 | I | -0.30* | 0.33* | ||||||||||
| T | |||||||||||||
| 稀有 | I | -0.35* | -0.43** | ||||||||||
| T | -0.35* | -0.43** | |||||||||||
| 半湿润区 | 优势 | I | 0.40** | -0.34* | 0.45** | 0.46** | -0.38* | ||||||
| T | -0.36* | 0.38* | 0.46** | 0.46** | 0.30* | ||||||||
| 常见 | I | -0.39** | 0.34* | 0.43** | 0.41** | 0.33* | |||||||
| T | -0.33* | ||||||||||||
| 稀有 | I | ||||||||||||
| T |
表7 优势类群、常见类群和稀有类群的个体数和类群数与环境因子的相关性分析
Table 7 Correlation analysis on the abundance and richness of dominant, common and rare groups of arthropods with environment factors
| 环境分区 | 类群 | 数量 | pH | EC | SM | Clay | Silt | Sand | TC | TN | HD | HR | HH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干旱区 | 优势 | I | 0.45** | -0.46** | 0.50** | ||||||||
| T | -0.36* | 0.32* | -0.54** | -0.62** | -0.65** | ||||||||
| 常见 | I | -0.34* | 0.35* | 0.36* | 0.44** | 0.39** | |||||||
| T | 0.31* | 0.35* | 0.41** | 0.40** | |||||||||
| 稀有 | I | 0.48** | -0.61** | ||||||||||
| T | 0.48** | -0.61** | |||||||||||
| 半干旱区 | 优势 | I | |||||||||||
| T | |||||||||||||
| 常见 | I | -0.30* | 0.33* | ||||||||||
| T | |||||||||||||
| 稀有 | I | -0.35* | -0.43** | ||||||||||
| T | -0.35* | -0.43** | |||||||||||
| 半湿润区 | 优势 | I | 0.40** | -0.34* | 0.45** | 0.46** | -0.38* | ||||||
| T | -0.36* | 0.38* | 0.46** | 0.46** | 0.30* | ||||||||
| 常见 | I | -0.39** | 0.34* | 0.43** | 0.41** | 0.33* | |||||||
| T | -0.33* | ||||||||||||
| 稀有 | I | ||||||||||||
| T |
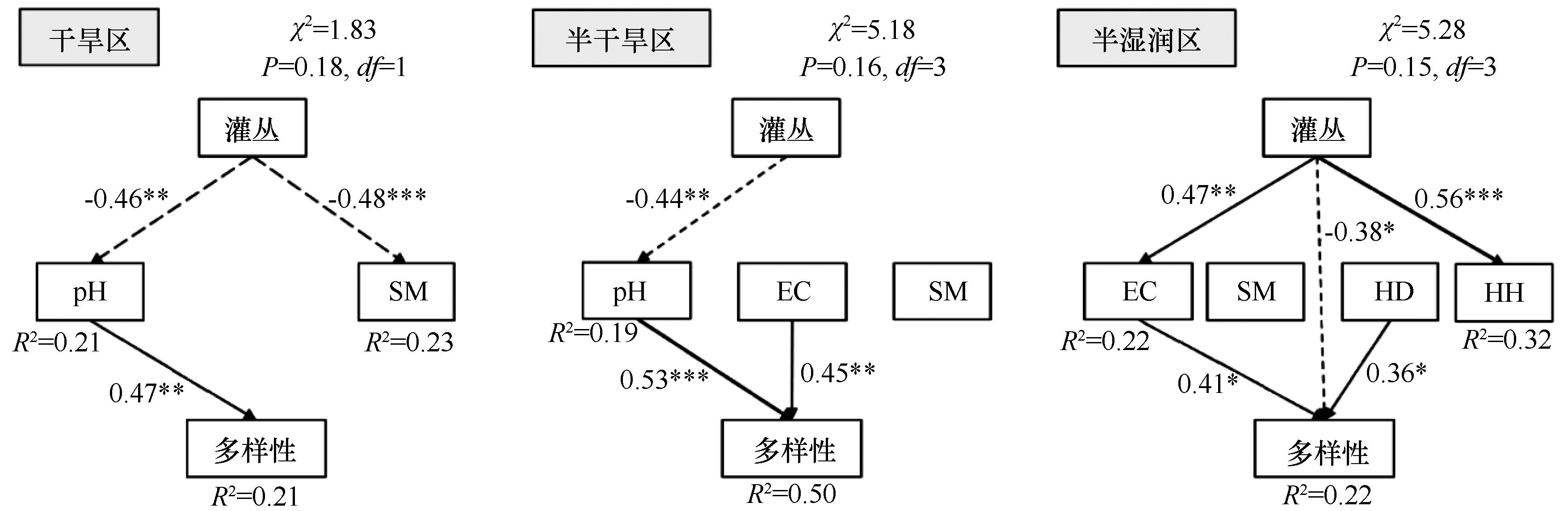
图5 不同降水梯度地面节肢动物多样性与环境因子的结构方程模型注:实线表示正向效应,虚线表示负向效应。*: P<0.05; **: P<0.01; ***: P<0.001。 pH: 土壤pH; SM: 土壤含水量; EC: 土壤电导率; HD: 草本植物密度; HH: 草本植物高度
Fig.5 Piecewise structural equation modelling (pSEM) of ground-dwelling arthropods diversity and environmental factors in different precipitation gradients
| [1] | 贺金生,王政权,方精云.全球变化下的地下生态学:问题与展望[J].科学通报,2004,49(13):1226-1233. |
| [2] | 赵哈林,郭轶瑞,周瑞莲.灌丛对沙质草地土壤结皮形成发育的影响及其作用机制[J].中国沙漠,2011,31(5):1105-1107. |
| [3] | Zhang A N, Chang H T, Liu R T,et al.Shrub facilitative effects on the plant litter arthropod community shifts with decreasing precipitation in desertified ecosystems in northwestern China[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2022,200:104724. |
| [4] | 郭志霞,刘任涛,赵文智.荒漠灌丛和土壤动物关系及对降水变化的响应研究进展[J].草业学报,2022,31:206-216. |
| [5] | 王永利,云文丽,王炜,等.气候变暖对典型草原区降水时空分布格局的影响[J].干旱区资源与环境,2009,23:82-85. |
| [6] | Convey P, Pugh P J A, Jackson C,et al.Response of Antarctic terrestrial microarthropods to long-term climate manipulations[J].Ecology,2002,83:3130-3140. |
| [7] | Berdugo M, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Soliveres S,et al.Global ecosystem thresholds driven by aridity[J].Science,2020,367:787-790. |
| [8] | Kardol P, Reynolds W N, Norby R J,et al.Climate change effects on soil microarthropod abundance and community structure[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2011,47:37-44. |
| [9] | 刘任涛,王少昆,周娟.科尔沁和毛乌素沙地灌丛"虫岛"效应比较[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(6):1599-1606. |
| [10] | Liu R T, Navon Y, Steinberger Y,et al.Effects of rainfall manipulations versus a natural aridity gradient on plant litter arthropods in desert and Mediterranean ecosystems[J].Applied Soil Ecology,2020,156:103716. |
| [11] | 郭志霞,刘任涛,冯永宏,等.不同降水对荒漠灌丛土壤理化性质和地表植被分布的影响[J].水土保持通报,2021,41(1):56-65. |
| [12] | 杨敏 刘任涛,曾飞越,等.腾格里沙漠东南缘人工固沙植被演替过程中地面节肢动物群落多样性分布特征[J].生态学报,2024,44(1):428-439. |
| [13] | 刘任涛,张安宁.固沙灌丛林营造初期地面节肢动物群落结构特征[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(5):190-199. |
| [14] | 王岳,丁国栋,刘梦婕,等.榆林沙区典型林地不同植被类型对土壤微生物群落结构的影响[J].土壤通报,2022,53(4):907-918. |
| [15] | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2005. |
| [16] | 常海涛,刘任涛,陈蔚,等.内蒙古乌拉特荒漠草原红砂灌丛林引入柠条后地面节肢动物群落结构分布特征[J].草业学报,2020,29(12):188-197. |
| [17] | 白燕娇,刘任涛,常海涛.干旱绿洲区不同生长年限枸杞林地面节肢动物群落分布特征[J].生态与农村环境学报,2021,37(9):1190-1199. |
| [18] | 尹文英.中国土壤动物检索图鉴[M].北京:科学出版社,1998. |
| [19] | 朱永恒,赵春雨,王宗英,等.我国土壤动物群落生态学研究综述[J].生态学杂志,2005,24(12):1477-1481. |
| [20] | 王新谱,杨贵军.宁夏贺兰山昆虫[M].银川:宁夏人民出版社,2010. |
| [21] | Spellerberg I F, Peter J F.A tribute to Claude Shannon (1916–2001) and a plea for more rigorous use of species richness,species diversity and the ‘Shannon-Wiener’ Index[J].Global Ecology and Biogeography,2003,12:177-179. |
| [22] | 赖江山,米湘成.基于Vegan软件包的生态学数据排序分析[Z].北京:国际生物多样性计划中国委员会,2010:332-343. |
| [23] | Borcard D, Gillet F, Legendre P,等.数量生态学:R语言的应用[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2019:20-22. |
| [24] | Wei T Y, Viliam S.R Package “corrplot”:Visualization of a Correlation Matrix (Version 0.84)[Z].2017:1-5. |
| [25] | 贾勃,王新杰.东北针阔混交林生物量动态过程及稳定性研究[J].林业科学研究,2023,36(5):41-49. |
| [26] | Lefcheck J S.piecewiseSEM:piecewise structural equation modelling in r for ecology,evolution,and systematics[J].Methods in Ecology and Evolution,2016,7(5):573-579. |
| [27] | 薛树媛,金海,李长青,等.荒漠地区主要饲用灌木类植物酚类物质含量及动态变化[J].饲料工业,2011,32(21):26-29. |
| [28] | 刘继亮,赵文智,王永珍,等.疏勒河源区高寒草甸中型土壤动物群落特征及对土壤水分变化的响应[J].冰川冻土,2023,45(6):1911-1922. |
| [29] | Li F R, Liu J L, Liu C A,et al.Shrubs and species identity effects on the distribution and diversity of ground-dwelling arthropods in a gobi desert[J].Journal of Insect Conservation,2013,17:319-331. |
| [30] | Lindberg N, Bengtsson J, Persson T.Effects of experimental irrigation and drought on the composition and diversity of soil fauna in a coniferous stand[J].Journal of Applied Ecology,2003,40:192. |
| [31] | Zhang A N, Chen S Y, Chen J W,et al.Shrub and precipitation interactions shape functional diversity of nematode communities on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J].Global Change Biology,2023,29:2746-2758. |
| [32] | Gao H, Li C, Jiao Y,et al.Shrubs alter alpha and beta diversity of soil fauna in a semiarid grassland[J].The Rangeland Journal,2023,44:213-220. |
| [33] | Allington, Ginger R H, Thomas J V.Islands of fertility:a byproduct of grazing?[J].Ecosystems,2014,17:127-141. |
| [34] | 刘学东,陈林,杨新国,等.荒漠草原2种柠条(Caragana korshinskii)和油蒿(Artemisia ordosica)灌丛土壤养分“肥岛”效应[J].西北林学院学报,2016,31(4):26-32. |
| [1] | 钟凌飞, 刘鹄, 张丽华. 河西走廊荒漠植被归一化指数(NDVI)与降水量的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(5): 318-327. |
| [2] | 刘伟春, 李玉霖, 程莉, 方海富. 科尔沁沙地南缘旱作农田保护性耕作对土壤风蚀的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 24-33. |
| [3] | 景家琪, 刘新平, 何玉惠, 丰洁, 胡鸿姣, 徐远志. 半干旱沙质草地植物群落构建对降水的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 314-323. |
| [4] | 赵鑫宇, 罗亚勇, 刘瑞香, 旭日, 王鹤松, 梁念来, 陈伊迪. 埋种深度及模拟降雨对少花蒺藜草( Cenchrus pauciflorus )幼苗生长的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 324-333. |
| [5] | 景家琪, 刘新平, 何玉惠, 丰洁, 胡鸿姣, 徐远志, 张尧. 降水量对半干旱沙质草地土壤胞外酶活性的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 368-377. |
| [6] | 刘新平, 胡鸿姣, 何玉惠, 徐远志, 景家琪, 张尧. 科尔沁沙质草地关键植物种群动态对降水变化的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(4): 43-56. |
| [7] | 马亚丽, 马莉, 杨丽萍, 王思晴, 赵长明, 陈宁. 生态水文视角下的旱区生物土壤结皮-维管植物共存模式[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(3): 121-130. |
| [8] | 王百竹, 白建华, 萨拉, 王丹雨, 杨晓晖, 朱媛君, 时忠杰. 呼伦贝尔沙化草地不同放牧潜力阶段群落特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(2): 205-216. |
| [9] | 何玉惠, 刘新平, 胡鸿姣, 徐远志. 降水和放牧对沙质草地优势植物出苗和存活的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(1): 103-111. |
| [10] | 郝芳唯, 宋兆斌, 李香云, 岳平, 张晓雪, 王怀海, 赵杏花, 左小安. 5年降水限制后荒漠草原植物多样性和生产力恢复特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(1): 112-120. |
| [11] | 张蕊, 赵学勇, 李刚, 武雅琳, 刘新平. 干旱半干旱区草地植物-土壤响应降水和管理措施的研究综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(1): 131-140. |
| [12] | 李军, 周发元, 焦亮, 李开明, 李超灿. 1960—2022年河西走廊主要气候要素特征及气候生产潜力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 14-25. |
| [13] | 张晶, 左小安, 吕朋. 生长季降水格局变化对科尔沁沙地典型生境植物群落结构、功能和地上生物量的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 1-13. |
| [14] | 卜凡蕊, 刘颖, 邹学勇, 张春来. 中国东部典型沙地植被稳定性与水资源关系特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 111-125. |
| [15] | 王帅, 马登科, 何志斌, 孙玮皓, 杜军, 李睿, 王文, 杨淑萍, 赵书玄. 宁夏河东沙地植被多样性与土壤的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 202-211. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
