
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (3): 165-173.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00003
Yanli Tian( ), Peifang Chong(
), Peifang Chong( ), Wentao Lu, Xiangyang Jia
), Wentao Lu, Xiangyang Jia
Received:2020-07-04
Revised:2021-01-07
Online:2021-05-26
Published:2021-05-26
Contact:
Peifang Chong
CLC Number:
Yanli Tian, Peifang Chong, Wentao Lu, Xiangyang Jia. Effects of simulated nitrogen settlement and precipitation changes on physiological characteristics of Reaumuria soongorica and Salsola passerina[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(3): 165-173.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00003
| 处理 时间 | 每月平均 降水量 /mm | 每次灌水量/mL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W-(降水 减少30%) | W (对照) | W+(降水 增加30%) | ||
| 5月 | 11.2 | 13.05 | 18.64 | 24.23 |
| 6月 | 15.0 | 17.47 | 24.96 | 32.45 |
| 7月 | 23.0 | 26.80 | 38.28 | 49.76 |
| 8月 | 28.1 | 32.73 | 46.76 | 60.79 |
| 9月 | 18.2 | 21.20 | 30.29 | 39.38 |
Table 1 Average monthly precipitation during 1961-2008 (May-September) and the irrigation amount every time
| 处理 时间 | 每月平均 降水量 /mm | 每次灌水量/mL | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W-(降水 减少30%) | W (对照) | W+(降水 增加30%) | ||
| 5月 | 11.2 | 13.05 | 18.64 | 24.23 |
| 6月 | 15.0 | 17.47 | 24.96 | 32.45 |
| 7月 | 23.0 | 26.80 | 38.28 | 49.76 |
| 8月 | 28.1 | 32.73 | 46.76 | 60.79 |
| 9月 | 18.2 | 21.20 | 30.29 | 39.38 |
| 植物种 | 因素 | 丙二醛MDA | 过氧化氢酶CAT | 过氧化物酶POD | 超氧化物歧化酶SOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红砂 | 氮 | 113.877** | 2 977.441** | 627.185** | 59 320.919** |
| 水 | 310.148** | 8 779.43** | 1067.717** | 16 734.038** | |
| 生长方式 | 458.608** | 1519.006** | 1 651.706** | 25 127.108** | |
| 氮×水 | 2.556 | 387.83** | 13.831** | 499.512** | |
| 氮×生长方式 | 35.004** | 201.458** | 40.865** | 1 892.336** | |
| 水×生长方式 | 0.239 | 91.21** | 21.243** | 819.311** | |
| 氮×水×生长方式 | 1.206 | 40.52** | 24.863** | 218.649** | |
| 珍珠猪毛菜 | 氮 | 199.311** | 5 089.873** | 1 314.613** | 70 938.048** |
| 水 | 165.466** | 6 739.326** | 4 576.053** | 15 140.846** | |
| 生长方式 | 3 330.418** | 14 659.648** | 1 039.276** | 9 521.426** | |
| 氮×水 | 3.117* | 157.069** | 4.986** | 1 929.279** | |
| 氮×生长方式 | 3.856* | 1 230.202** | 11.71** | 1 200.972** | |
| 水×生长方式 | 0.405 | 428.483** | 88.045** | 173.447** | |
| 氮×水×生长方式 | 3.308* | 166.856** | 12.914** | 495.889** |
Table 2 Variance analysis results of the effects of nitrogen deposition, precipitation, growth mode and their interaction on malondialdehyde content and antioxidant enzyme activity in Reaumuria soongorica and Salsola passerina
| 植物种 | 因素 | 丙二醛MDA | 过氧化氢酶CAT | 过氧化物酶POD | 超氧化物歧化酶SOD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 红砂 | 氮 | 113.877** | 2 977.441** | 627.185** | 59 320.919** |
| 水 | 310.148** | 8 779.43** | 1067.717** | 16 734.038** | |
| 生长方式 | 458.608** | 1519.006** | 1 651.706** | 25 127.108** | |
| 氮×水 | 2.556 | 387.83** | 13.831** | 499.512** | |
| 氮×生长方式 | 35.004** | 201.458** | 40.865** | 1 892.336** | |
| 水×生长方式 | 0.239 | 91.21** | 21.243** | 819.311** | |
| 氮×水×生长方式 | 1.206 | 40.52** | 24.863** | 218.649** | |
| 珍珠猪毛菜 | 氮 | 199.311** | 5 089.873** | 1 314.613** | 70 938.048** |
| 水 | 165.466** | 6 739.326** | 4 576.053** | 15 140.846** | |
| 生长方式 | 3 330.418** | 14 659.648** | 1 039.276** | 9 521.426** | |
| 氮×水 | 3.117* | 157.069** | 4.986** | 1 929.279** | |
| 氮×生长方式 | 3.856* | 1 230.202** | 11.71** | 1 200.972** | |
| 水×生长方式 | 0.405 | 428.483** | 88.045** | 173.447** | |
| 氮×水×生长方式 | 3.308* | 166.856** | 12.914** | 495.889** |
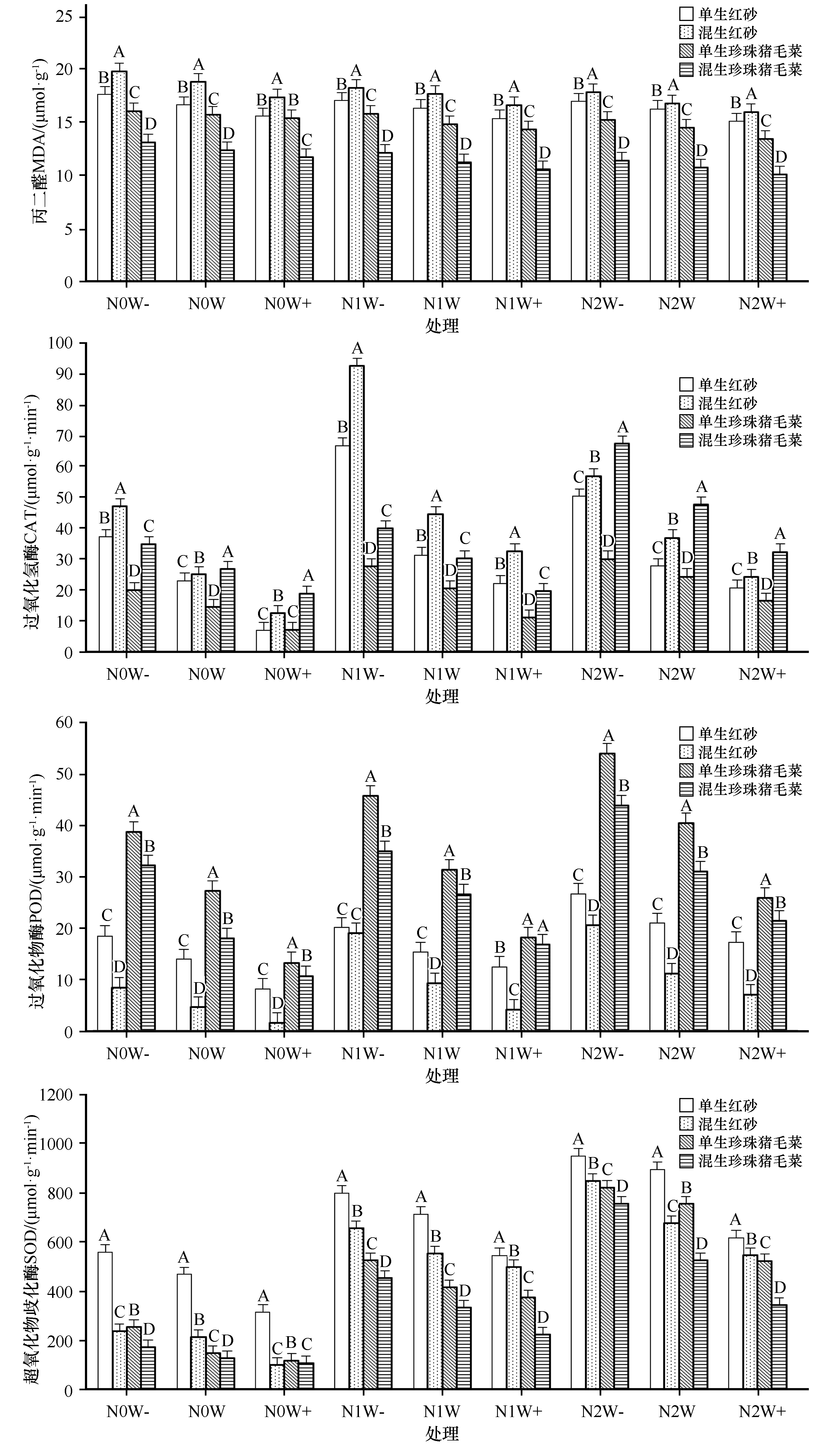
Fig.1 Effects of nitrogen deposition, precipitation, growth mode and their interaction on malondialdehyde content and antioxidant enzyme activity in Reaumuria soongorica and Salsola passerina
| 植物种 | 因素 | 可溶性蛋白SP | 脯氨酸Pro |
|---|---|---|---|
| 红砂 | 氮 | 1479.236** | 777.134** |
| 水 | 542.641** | 1315.021** | |
| 生长方式 | 110.267** | 1928.662** | |
| 氮×水 | 6.164** | 27.319** | |
| 氮×生长方式 | 1.068 | 59.441** | |
| 水×生长方式 | 5.308* | 120.339** | |
| 氮×水×生长方式 | 1.877 | 62.764** | |
| 珍珠猪毛菜 | 氮 | 4145.49** | 1843.819** |
| 水 | 1579.516** | 464.782** | |
| 生长方式 | 1614.298** | 10740.754** | |
| 氮×水 | 110.396** | 7.208** | |
| 氮×生长方式 | 50.814** | 1391.517** | |
| 水×生长方式 | 40.809** | 260.556** | |
| 氮×水×生长方式 | 18.191** | 6.376** |
Table 3 Variance analysis results of the effects of nitrogen deposition, precipitation, growth mode and their interaction on the contents of osmotic adjustment substances (SP, Pro) in Reaumuria soongorica and Salsola passerina
| 植物种 | 因素 | 可溶性蛋白SP | 脯氨酸Pro |
|---|---|---|---|
| 红砂 | 氮 | 1479.236** | 777.134** |
| 水 | 542.641** | 1315.021** | |
| 生长方式 | 110.267** | 1928.662** | |
| 氮×水 | 6.164** | 27.319** | |
| 氮×生长方式 | 1.068 | 59.441** | |
| 水×生长方式 | 5.308* | 120.339** | |
| 氮×水×生长方式 | 1.877 | 62.764** | |
| 珍珠猪毛菜 | 氮 | 4145.49** | 1843.819** |
| 水 | 1579.516** | 464.782** | |
| 生长方式 | 1614.298** | 10740.754** | |
| 氮×水 | 110.396** | 7.208** | |
| 氮×生长方式 | 50.814** | 1391.517** | |
| 水×生长方式 | 40.809** | 260.556** | |
| 氮×水×生长方式 | 18.191** | 6.376** |
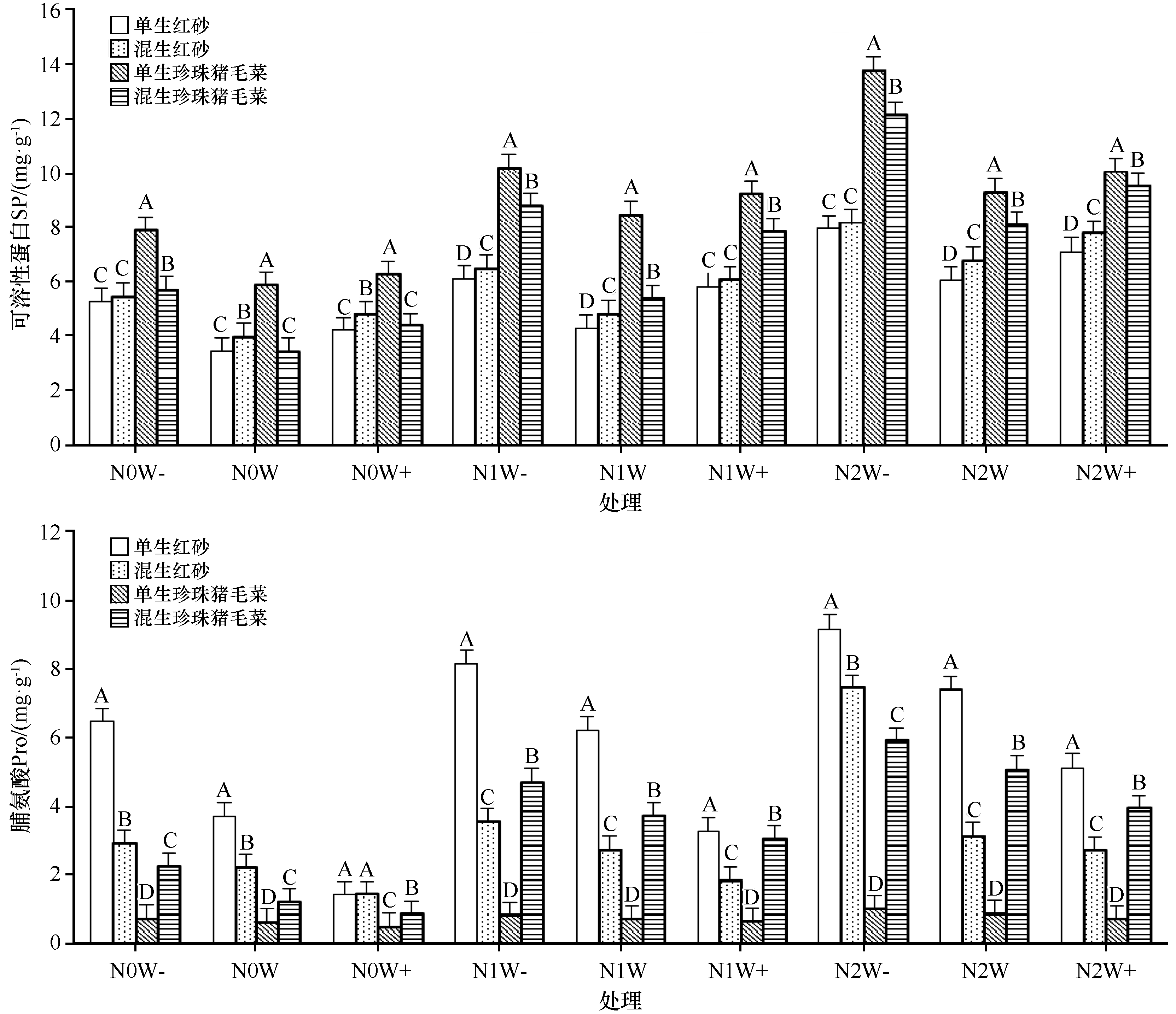
Fig.2 Effects of nitrogen deposition, precipitation, growth mode and their interaction on the contents of osmotic adjustment substances (SP, Pro) in Reaumuria soongorica and Salsola passerina(Different letters indicate significant differences)
| 1 | Galloway J N,Townsend A R,Erisman J W,et al.Transformation of the nitrogen cycle:recent trends,questions,and potential solutions[J].Science,2008,320(5878):889-892. |
| 2 | Liu X J,Zhang Y,Han W X,et al.Enhanced nitrogen deposition over China[J].Nature,2013,494:459-462. |
| 3 | Galloway J N,Cowling E B.Reactive nitrogen and the world:200 years of change[J].Ambio,2002,31(2):64-71. |
| 4 | 谢腾芳,薛立,王相娥.土壤-植物-大气连续体系中氮的研究进展[J].生态学杂志,2009,28(10): 2107-2116. |
| 5 | 段娜,李清河,多普增,等.植物响应大气氮沉降研究进展[J].世界林业研究,2019,32(4):6-11. |
| 6 | IPCC.Climate Change 2014:Mitigation of Climate Change[M].Cambridge,UK: Cambridge University Press,2014. |
| 7 | 张彬,朱建军,刘华民,等.极端降水和极端干旱事件对草原生态系统的影响[J].植物生态学报,2014,38(9):1008-1018. |
| 8 | Naumburg E,Housman D C,Huxman T E,et al.Photosynthetic responses of Mojave Desert shrubs to free air CO2 enrichment are greatest during wet years[J].Global Change Biology,2003,9:276-285. |
| 9 | 郑婧,佘维维,白宇轩,等.氮素和水分添加对毛乌素沙地油蒿群落优势植物叶片性状的影响[J].林业科学,2018,54(10):164-171. |
| 10 | Yin C Y,Pang X Y,Chen K,et al.The water adaptability of Jatrophacurcas is modulated by soil nitrogen availability[J].Biomass and Bioenergy,2012,47(12):71-81. |
| 11 | 李静静,陈雅君,张璐,等.水氮交互作用对草地早熟禾生理生化与坪用质量的影响[J].中国草地学报,2016,38(4):42-48. |
| 12 | 李香云,岳平,郭新新,等.荒漠草原植物群落光合速率对水氮添加的响应[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(1):116-124. |
| 13 | 马阔东,高丽,闫志坚,等.库布齐沙漠不同类型沙地上植物群落根系研究[J].草业科学,2010,27(5):1-9. |
| 14 | 刘玉冰,张腾国,李新荣,等.红砂(Reaumuria soongorica)忍耐极度干旱的保护机制: 叶片脱落和茎中蔗糖累积[J].中国科学C辑:生命科学,2006(4):328-333. |
| 15 | 赵昕,杨小菊,石勇,等.盐胁迫下荒漠共生植物红砂与珍珠的根茎叶中离子吸收与分配特征[J].生态学报,2014,34(4): 963-972. |
| 16 | Su P X,Yan Q D,Xie T T,et al.Associated growth of C3 and C4 desert plants helps the C3 species at the cost of the C4 species[J].Acta Physiologiae Plantarum,2012,34:2057-2068. |
| 17 | 苏铭,单立山,张正中,等.荒漠环境梯度下联生红砂(Reaumuria soongorica)、珍珠(Salsola passerina)荧光特性[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(6):1259-1266. |
| 18 | 金艳霞,王新平,张亚峰,等.红砂(Reaumuria soongorica)、珍珠(Salsola passerine)蒸腾耗水规律的尺度整合[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(2):286-293. |
| 19 | 种培芳,姬江丽,李毅,等.红砂(Reaumuria soongorica)对大气CO2浓度升高及降水变化的光合生理响应[J].中国沙漠,2017,37(4):714-723. |
| 20 | Jia Y L,Yu G R,He N P,et al.Spatial and decadal variations in inorganic nitrogen wet deposition in China induced by human activity[J].Scientific Reports,2014,4(1):1-7. |
| 21 | 常兆丰,韩福贵,仲生年.民勤荒漠区气候变化对全球变暖的响应[J].中国沙漠,2011,31(2):505-510. |
| 22 | 李合生.植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2000:134-263. |
| 23 | 王忠.植物生理学[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2000:65-66,128-133. |
| 24 | 李玲.植物生理学模块实验指导[M].北京:科学出版社,2009:37-38,95-100. |
| 25 | Mohammadi M,Karr A L.Membrane lipid peroxidation,nitrogen fixation andleghemoglobin content in soybean root nodules[J].Journal Plant Physiol,2001,158(1):9-19. |
| 26 | 肖凯,张荣铣,钱维朴.氮素营养调控小麦旗叶衰老和光合功能衰退的生理机制[J].植物营养与肥料学报,1998,4(4):371-378. |
| 27 | 姬江莉,种培芳,李毅,等.红砂对CO2浓度升高及降水变化的生理生长响应[J].西北植物学报,2017,37(5):923-932. |
| 28 | 邓世媛,陈建军.氮素营养对烤烟抗旱适应性的影响[J].干旱区研究,2007(4):499-503. |
| 29 | 李娜.落叶松幼苗对干旱胁迫及氮添加的生理生态响应[D].哈尔滨:东北林业大学,2014. |
| 30 | Mittal S,Kumari N,Sharma V.Differential response of salt stress on Brassica juncea:photosynthetic performance,pigment,proline,D1 and antioxidant enzymes[J].Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2012,54:17-26. |
| 31 | 王景燕,龚伟,李伦刚,等.水肥对汉源花椒幼苗抗逆生理的影响[J].西北植物学报,2015,35(3):530-539. |
| 32 | 杨晓清,周再知,梁坤南,等.氮素对模拟胁迫下土沉香幼苗抗旱生理的影响[J].热带作物学报,2013,34(6):1121-1127. |
| 33 | 曾化伟.土壤水分与施氮量对辣椒部分生理特性及产量品质的影响[D].贵阳:贵州大学,2007. |
| 34 | 褚建民,邓东周,王琼,等.降雨量变化对樟子松生理生态特性的影响[J].生态学杂志,2011,30(12):2672-2678. |
| 35 | 单立山,苏铭,张正中,等.不同生境下荒漠植物红砂-珍珠猪毛菜混生根系的垂直分布规律[J].植物生态学报,2018,42(4):475-486. |
| 36 | Callaway R M.Positive Interactions and Interdependence in Plant Communities[M].NetherlandsSpringer,2007. |
| 37 | 周海燕,谭会娟,张志山,等.红砂和珍珠对极端环境的生理响应与调节机制[J].中国沙漠,2012,32(1):24-32. |
| [1] | Shengxia Wang, Fei Wang. Response of oasis area to the surface runoff in Hexi inland river basin of China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 231-241. |
| [2] | Zheting Jia, Jiuyan Yang, Yanxia Sun, Qi Chen, Ruiling Yan. Spatial distribution pattern of Salsola passerina population in Alashan Plateau [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 119-128. |
| [3] | Xinxin Guo, Xiaoan Zuo, Ping Yue, Xiangyun Li, Shenglong Zhao, Peng Lv, Ya Hu. Responses of leaf morphological traits of three dominant plants to water and nitrogen in desert steppe of Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 137-144. |
| [4] | Yuanzheng He, Wenda Huang, Xin Zhao, Peng Lv, Huaihai Wang. Review on the impact of climate change on plant diversity [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 59-66. |
| [5] | Yimei Sun, Qing Tian, Aixia Guo, Xiaoan Zuo, Peng Lv, Senxi Zhang. Effects of water and nitrogen changes on vegetation characteristics and leaf traits in Horqin Sandy land, Northern China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(6): 223-232. |
| [6] | Xianzhi Yin, Yirong Wang, Han Luo, Yulong Ren, Tiantian Wang, Yanfeng Wang. The relationship between atmospheric water renewal and the spatial distribution of surface precipitation in Gansu Province from 1960 to 2019 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(6): 61-70. |
| [7] | Bingyao Wang, Xingchen Liu, Lichao Liu. Characteristics of precipitation in the surrounding area of Tengger Desert in 1957-2017 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 163-170. |
| [8] | Wu Lili, Liu Danyi, Yang Wenbin, Wang Tao, Li Wei, Feng Jinchao, Feng Wei. Relationship between precipitation and soil water storage and soil deep percolation in mobile sand land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(3): 210-218. |
| [9] | Li Xiangyun, Yue Ping, Guo Xinxin, Zhang Rui, Zhao Shenglong, Zhang Senxi, Wang Shaokun, Zuo Xiaoan. Response of photosynthetic rate of plant community to water and nitrogen addition in desert steppe of Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(1): 116-124. |
| [10] | Chen Juanli, Zhao Xueyong, Liu Xinping, Zhang Yaqiu, Luo Yongqing, Zhang Rui, Zhang Runxia, Yu Hailun. Effects of Precipitation on Growth and Physiology of Three Psammophytes in the Horqin Sandy Land, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(5): 163-173. |
| [11] | Bao Yongzhi, Duan Limin, Liu Tingxi, Wang Guanli, Tong Xin. Simulation of Evapotranspiration of Caragana microphylla Community [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(4): 177-186. |
| [12] | Tian Haijing, Sun Tao, Liu Xusheng, Kong Xiangji. Effect Evaluation of the Enclosure-Rehabilitation of Desertification Land in Cuogang Based on Time Series Remote Sensing Data [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(3): 155-162. |
| [13] | Zhang Rui, Zhao Xueyong, Zuo Xiaoan, Liu Xinping, Qu Hao, Ma Xujun, Liu Liangxu, Chen Juanli, Liu Liping. Responses of the Stipa glareosa Community Species Diversity and Above-ground Biomass to Precipitation in the Desert-steppe Region in Northern China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(2): 45-52. |
| [14] | Dong Xue, Xin Zhiming, Bao Fang, Bao Yanfeng, Li Xinle, Duan Ruibing, Liu Minghu. Phenotypic Variation of Nitraria tangutorum under Simulated Precipitation Patterns Change [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(1): 127-134. |
| [15] | Zhou Xueying, Jia Jian, Liu Guoqiang, Wang Fang, Qiu Huimin, Sun Huaiqin. Characteristics of Precipitation at Hinterland of Taklimakan Desert, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(1): 187-194. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech