
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 22-31.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00174
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xiaozhi Wang( ), Zhibao Dong(
), Zhibao Dong( ), Weige Nan, Chao Li, Chong Gao, Xin Zhang
), Weige Nan, Chao Li, Chong Gao, Xin Zhang
Received:2021-09-30
Revised:2021-11-17
Online:2022-07-20
Published:2022-08-29
Contact:
Zhibao Dong
CLC Number:
Xiaozhi Wang, Zhibao Dong, Weige Nan, Chao Li, Chong Gao, Xin Zhang. Sediment characteristics of climbing dunes in Lhasa River Valley, China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 22-31.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00174
| 采样点 | 粒度分级/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
黏土 <0.002 mm | 粉沙 0.002—0.063 mm | 极细沙 0.063—0.125 mm | 细沙 0.125—0.25 mm | 中沙 0.25—0.5 mm | 粗沙 >0.5 mm | |
| P1 | 0.00 | 1.45 | 4.72 | 56.89 | 36.59 | 0.34 |
| P2 | 0.00 | 3.69 | 8.26 | 49.68 | 37.02 | 1.35 |
| P3 | 0.05 | 8.00 | 14.04 | 44.55 | 31.91 | 1.44 |
| P4 | 0.67 | 10.79 | 23.94 | 47.70 | 16.90 | 0.00 |
| P5 | 0.18 | 21.27 | 24.74 | 29.31 | 20.78 | 3.72 |
| P6 | 0.32 | 3.73 | 25.75 | 56.77 | 13.43 | 0.00 |
| P7 | 0.04 | 13.99 | 36.64 | 39.47 | 9.86 | 0.00 |
Table 1 The surface sediment grain size composition of climbing dune
| 采样点 | 粒度分级/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
黏土 <0.002 mm | 粉沙 0.002—0.063 mm | 极细沙 0.063—0.125 mm | 细沙 0.125—0.25 mm | 中沙 0.25—0.5 mm | 粗沙 >0.5 mm | |
| P1 | 0.00 | 1.45 | 4.72 | 56.89 | 36.59 | 0.34 |
| P2 | 0.00 | 3.69 | 8.26 | 49.68 | 37.02 | 1.35 |
| P3 | 0.05 | 8.00 | 14.04 | 44.55 | 31.91 | 1.44 |
| P4 | 0.67 | 10.79 | 23.94 | 47.70 | 16.90 | 0.00 |
| P5 | 0.18 | 21.27 | 24.74 | 29.31 | 20.78 | 3.72 |
| P6 | 0.32 | 3.73 | 25.75 | 56.77 | 13.43 | 0.00 |
| P7 | 0.04 | 13.99 | 36.64 | 39.47 | 9.86 | 0.00 |
| 采样点 | 粒度分级/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
黏土 <0.004 mm | 粉沙 0.004—0.063 mm | 极细沙 0.063—0.125 mm | 细沙 0.125—0.25 mm | 中沙 0.25—0.5 mm | 粗沙 >0.5 mm | |
| 表层 | 0.18 | 8.99 | 19.73 | 46.34 | 23.78 | 0.98 |
| 4—10 cm | 1.18 | 13.39 | 20.63 | 42.58 | 21.88 | 0.33 |
| 10—40 cm | 0.75 | 12.89 | 21.09 | 43.76 | 21.26 | 0.28 |
| 40—60 cm | 1.03 | 14.83 | 21.66 | 42.06 | 20.07 | 0.36 |
Table 2 The sediment grain size composition of climbing dune at different depths
| 采样点 | 粒度分级/% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
黏土 <0.004 mm | 粉沙 0.004—0.063 mm | 极细沙 0.063—0.125 mm | 细沙 0.125—0.25 mm | 中沙 0.25—0.5 mm | 粗沙 >0.5 mm | |
| 表层 | 0.18 | 8.99 | 19.73 | 46.34 | 23.78 | 0.98 |
| 4—10 cm | 1.18 | 13.39 | 20.63 | 42.58 | 21.88 | 0.33 |
| 10—40 cm | 0.75 | 12.89 | 21.09 | 43.76 | 21.26 | 0.28 |
| 40—60 cm | 1.03 | 14.83 | 21.66 | 42.06 | 20.07 | 0.36 |
| 元素 | 变化范围 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 背景值* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 54.51—68.41 | 61.60 | 5.27 | 0.09 | 66.00 |
| Al2O3 | 8.69—14.03 | 11.02 | 1.47 | 0.13 | 15.20 |
| Na2O | 2.07—4.63 | 3.13 | 0.84 | 0.27 | 3.90 |
| Fe2O3 | 1.82—3.84 | 2.86 | 0.63 | 0.22 | 5.00 |
| K2O | 1.39—2.80 | 2.24 | 0.48 | 0.22 | 3.40 |
| CaO | 0.89—4.23 | 2.13 | 1.12 | 0.52 | 4.20 |
| MgO | 0.52—1.27 | 0.88 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 2.22 |
| TiO2 | 0.16—0.26 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.50 |
| P2O5 | 0.07—0.13 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.55 |
| MnO | 0.03—0.07 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 0.06 |
Table 3 Major elements composition of climbing dune surface deposition
| 元素 | 变化范围 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 背景值* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | 54.51—68.41 | 61.60 | 5.27 | 0.09 | 66.00 |
| Al2O3 | 8.69—14.03 | 11.02 | 1.47 | 0.13 | 15.20 |
| Na2O | 2.07—4.63 | 3.13 | 0.84 | 0.27 | 3.90 |
| Fe2O3 | 1.82—3.84 | 2.86 | 0.63 | 0.22 | 5.00 |
| K2O | 1.39—2.80 | 2.24 | 0.48 | 0.22 | 3.40 |
| CaO | 0.89—4.23 | 2.13 | 1.12 | 0.52 | 4.20 |
| MgO | 0.52—1.27 | 0.88 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 2.22 |
| TiO2 | 0.16—0.26 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 0.13 | 0.50 |
| P2O5 | 0.07—0.13 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.17 | 0.55 |
| MnO | 0.03—0.07 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.30 | 0.06 |
| 项目 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Na2O | Fe2O3 | K2O | CaO | MgO | TiO2 | P2O5 | MnO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常量元素含量 | 表层 | 61.93 | 11.18 | 3.10 | 3.02 | 2.24 | 2.18 | 0.97 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.05 |
| 4—10 cm | 67.11 | 10.06 | 2.32 | 2.38 | 2.74 | 1.14 | 0.70 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.04 | |
| 10—40 cm | 66.99 | 10.08 | 2.28 | 2.48 | 2.74 | 1.10 | 0.71 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.04 | |
| 40—60 cm | 67.14 | 9.9 | 2.32 | 2.53 | 2.69 | 1.11 | 0.67 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.03 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.38 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.20 | |
Table 4 Major elements composition of climbing dune at different depths
| 项目 | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Na2O | Fe2O3 | K2O | CaO | MgO | TiO2 | P2O5 | MnO | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 常量元素含量 | 表层 | 61.93 | 11.18 | 3.10 | 3.02 | 2.24 | 2.18 | 0.97 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.05 |
| 4—10 cm | 67.11 | 10.06 | 2.32 | 2.38 | 2.74 | 1.14 | 0.70 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.04 | |
| 10—40 cm | 66.99 | 10.08 | 2.28 | 2.48 | 2.74 | 1.10 | 0.71 | 0.21 | 0.09 | 0.04 | |
| 40—60 cm | 67.14 | 9.9 | 2.32 | 2.53 | 2.69 | 1.11 | 0.67 | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.03 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.38 | 0.18 | 0.02 | 0.09 | 0.20 | |
| 元素 | 变化范围 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 背景值* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba | 321.8—581.5 | 404.6 | 59.1 | 0.15 | 550.0 |
| Sr | 135.7—440.0 | 264.5 | 101.6 | 0.38 | 350.0 |
| Cr | 16.9—288.8 | 125.0 | 95.8 | 0.77 | 35.0 |
| Zr | 62.8—175.4 | 118.7 | 29.4 | 0.25 | 190.0 |
| Rb | 35.7—141.7 | 93.4 | 38.9 | 0.42 | 112.0 |
| V | 33.8—78.3 | 57.6 | 16.2 | 0.28 | 60.0 |
| Co | 1.9—489.9 | 83.3 | 120.4 | 1.44 | 10.0 |
| Zn | 12.2—44.0 | 32.9 | 7.5 | 0.23 | 71.0 |
| La | 10.5—31.8 | 21.1 | 5.4 | 0.26 | 30.0 |
| Pb | 12.1—25.1 | 19.5 | 3.9 | 0.20 | 15.0 |
| Cu | 8.2—46.9 | 17.5 | 10.9 | 0.63 | 25.0 |
| Y | 11.6—19.5 | 14.8 | 2.3 | 0.15 | 22.0 |
| Ga | 11.4—16.2 | 13.5 | 1.1 | 0.08 | 17.0 |
| Ni | 2.5—15.5 | 9.3 | 3.3 | 0.36 | 20.0 |
| Nb | 2.5—10.2 | 6.5 | 2.2 | 0.35 | 25.0 |
| Bi | 5.8—5.8 | 5.8 | 0.0 | 0.00 | 127.0 |
| Hf | 2.0—4.7 | 3.41 | 0.7 | 0.22 | 5.8 |
| Mo | 0.0—7.7 | 3.0 | 2.9 | 0.95 | 1.5 |
Table 5 Trace elements composition of climbing dune surface deposition
| 元素 | 变化范围 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 背景值* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ba | 321.8—581.5 | 404.6 | 59.1 | 0.15 | 550.0 |
| Sr | 135.7—440.0 | 264.5 | 101.6 | 0.38 | 350.0 |
| Cr | 16.9—288.8 | 125.0 | 95.8 | 0.77 | 35.0 |
| Zr | 62.8—175.4 | 118.7 | 29.4 | 0.25 | 190.0 |
| Rb | 35.7—141.7 | 93.4 | 38.9 | 0.42 | 112.0 |
| V | 33.8—78.3 | 57.6 | 16.2 | 0.28 | 60.0 |
| Co | 1.9—489.9 | 83.3 | 120.4 | 1.44 | 10.0 |
| Zn | 12.2—44.0 | 32.9 | 7.5 | 0.23 | 71.0 |
| La | 10.5—31.8 | 21.1 | 5.4 | 0.26 | 30.0 |
| Pb | 12.1—25.1 | 19.5 | 3.9 | 0.20 | 15.0 |
| Cu | 8.2—46.9 | 17.5 | 10.9 | 0.63 | 25.0 |
| Y | 11.6—19.5 | 14.8 | 2.3 | 0.15 | 22.0 |
| Ga | 11.4—16.2 | 13.5 | 1.1 | 0.08 | 17.0 |
| Ni | 2.5—15.5 | 9.3 | 3.3 | 0.36 | 20.0 |
| Nb | 2.5—10.2 | 6.5 | 2.2 | 0.35 | 25.0 |
| Bi | 5.8—5.8 | 5.8 | 0.0 | 0.00 | 127.0 |
| Hf | 2.0—4.7 | 3.41 | 0.7 | 0.22 | 5.8 |
| Mo | 0.0—7.7 | 3.0 | 2.9 | 0.95 | 1.5 |
| 项目 | Ba | Sr | Cr | Zr | Rb | V | Co | Zn | La | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微量元素含量 | 表层 | 396.7 | 259.7 | 136.7 | 127.9 | 96.7 | 59.5 | 52.5 | 36.2 | 21.6 |
| 4—10 cm | 384.2 | 172.8 | 70.6 | 142.5 | 132.5 | 42.5 | 97.6 | 31.2 | 22.4 | |
| 10—40 cm | 375.6 | 167.6 | 87.0 | 137.9 | 134.4 | 42.9 | 80.9 | 32.5 | 24.8 | |
| 40—60 cm | 380.3 | 170.2 | 199.4 | 136.05 | 131.8 | 44.5 | 4.1 | 34.7 | 25.5 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.47 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.70 | 0.07 | 0.08 | |
| 项目 | Pb | Cu | Y | Ga | Ni | Nb | Bi | Hf | Mo | |
| 微量元素含量 | 表层 | 19.8 | 19.2 | 15.5 | 13.9 | 10.5 | 7.2 | 5.8 | 3.7 | 3.5 |
| 4—10 cm | 23.0 | 10.6 | 17.0 | 13.3 | 11.1 | 8.4 | 5.8 | 3.9 | 1.2 | |
| 10—40 cm | 24.0 | 11.8 | 17.0 | 13.1 | 12.2 | 8.2 | 5.8 | 3.8 | 1.9 | |
| 40—60 cm | 22.5 | 12.2 | 16.7 | 12.9 | 13.5 | 8.3 | 5.8 | 3.8 | 5.2 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.60 | |
Table 6 Trace elements composition of climbing dune at different depths
| 项目 | Ba | Sr | Cr | Zr | Rb | V | Co | Zn | La | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 微量元素含量 | 表层 | 396.7 | 259.7 | 136.7 | 127.9 | 96.7 | 59.5 | 52.5 | 36.2 | 21.6 |
| 4—10 cm | 384.2 | 172.8 | 70.6 | 142.5 | 132.5 | 42.5 | 97.6 | 31.2 | 22.4 | |
| 10—40 cm | 375.6 | 167.6 | 87.0 | 137.9 | 134.4 | 42.9 | 80.9 | 32.5 | 24.8 | |
| 40—60 cm | 380.3 | 170.2 | 199.4 | 136.05 | 131.8 | 44.5 | 4.1 | 34.7 | 25.5 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.47 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.17 | 0.70 | 0.07 | 0.08 | |
| 项目 | Pb | Cu | Y | Ga | Ni | Nb | Bi | Hf | Mo | |
| 微量元素含量 | 表层 | 19.8 | 19.2 | 15.5 | 13.9 | 10.5 | 7.2 | 5.8 | 3.7 | 3.5 |
| 4—10 cm | 23.0 | 10.6 | 17.0 | 13.3 | 11.1 | 8.4 | 5.8 | 3.9 | 1.2 | |
| 10—40 cm | 24.0 | 11.8 | 17.0 | 13.1 | 12.2 | 8.2 | 5.8 | 3.8 | 1.9 | |
| 40—60 cm | 22.5 | 12.2 | 16.7 | 12.9 | 13.5 | 8.3 | 5.8 | 3.8 | 5.2 | |
| 变异系数 | 0.08 | 0.29 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.07 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.60 | |
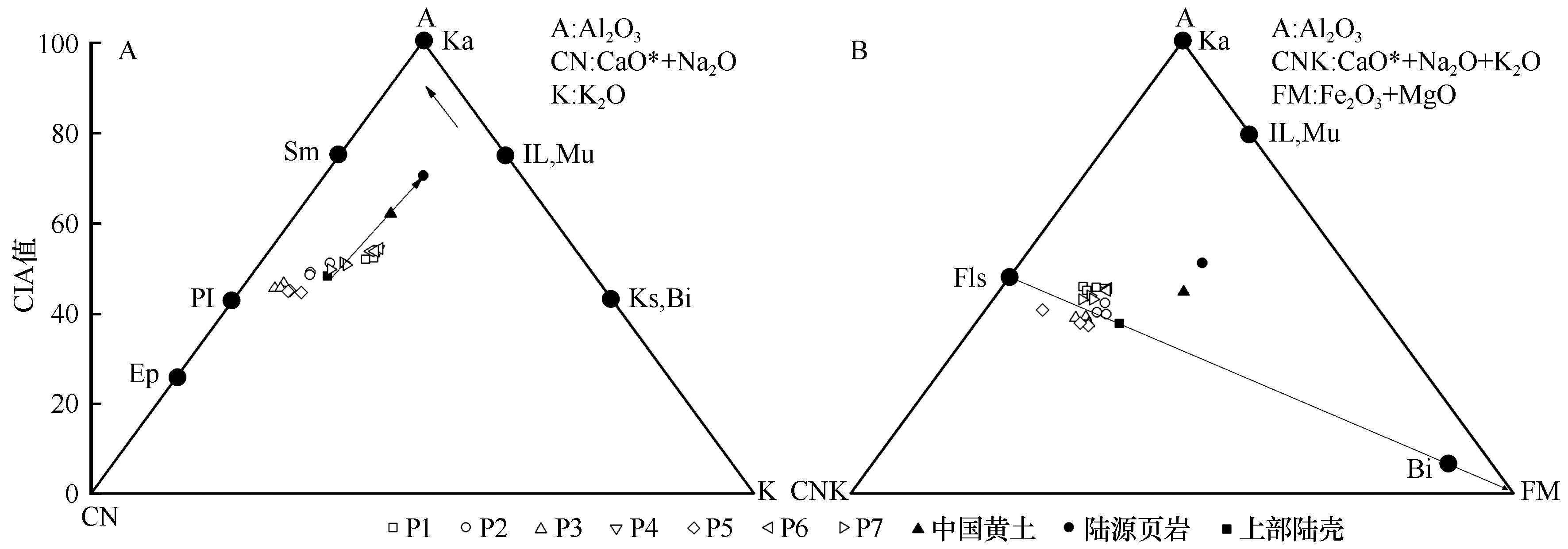
Fig.5 A-CN-K (A) and A-CNK-FM (B) ternary plots of climbing dune surface deposition (The long solid arrows represent the weathering direction of the continent; Ka=kaokin、Sm=smectites、PI=plagioclase、Ep=epidote、IL=illite、Mu=Muscovite、Bi=biotite、Ks=K—feldspar、Fls=feldspar)
| 1 | 董玉祥.青藏高原沙漠化研究的进展与问题[J].中国沙漠,1999,19(3):251-255. |
| 2 | Dong M, Yan P, Liu B L,et al.Distribution patterns and morphological classification of climbing dunes in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J].Aeolian Research,2018,35:58-68. |
| 3 | Dong Z B, Hu G Y, Qian G Q,et al.High-altitude aeolian research on the Tibetan Plateau[J].Reviews of Geophysics,2017,55(4):864. |
| 4 | 安庆,安萍,徐汝汝,等.青藏高原不同地区沉积物的粒度特征与沉积环境判别公式适用性对比研究[J].聊城大学学报(自然科学版),2017(4):1-11. |
| 5 | 钟诚,何宗宜,刘淑珍.西藏生态环境稳定性评价研究[J].地理科学,2005,25 (5):573-578. |
| 6 | 张佩民,张振德,李晓琴,等.青藏高原荒漠化遥感信息提取及演变分析[J].干旱区地理,2006,29(5):710-717. |
| 7 | 陈涛,宋友桂,李云.柴达木盆地末次盛冰期与全新世大暖期风沙活动的对比研究[J].干旱区研究,2016,33(4):877-883. |
| 8 | 董治宝,胡光印,颜长珍,等.江河源区沙漠化[M].北京:科学出版社,2012:126-138. |
| 9 | 张登山,高尚玉,石蒙沂,等.青海高原土地沙漠化及其防治[M].北京:科学出版社,2009:18-38. |
| 10 | 李栓科.我国海拔最高的沙漠:库木库里沙漠形成时代的初步探讨[J].中国沙漠,1991,11(3):29-35. |
| 11 | 李森,杨萍,董玉祥,等.西藏土地沙漠化及其防治[M].北京:科学出版社,2010:24-51. |
| 12 | Livingstone I.Grain-size variation on a 'complex' linear dune in the Namib Desert[J].Geological Society London Special Publications,1987,35(1):281-291. |
| 13 | Wang X M, Dong Z B, Zhang J W,et al.Grain size characteristics of dune sands in the central Taklimakan Sand Sea[J].Sedimentary Geology,2003,161:1-14. |
| 14 | Friedman G M.Distinction between dune,beach,and river sands from their textural characteristics[J].Journal of Sedimentary Petrology,1961,31(4):514-529. |
| 15 | Ahlbrandt T S.Textural parameters of eolian deposits[M]//McKee E.A Study of Global Sand Seas.Washington,USA:U.S.Government Printing Office,1979:21-51. |
| 16 | 龙黎,董玉祥,孙忠.海岸沙丘表面现代风成沙地球化学元素分异的典型研究:以河北昌黎黄金海岸横向沙脊为例[J].沉积学报,2012,30(4):724-730. |
| 17 | 郜学敏,屈欣,王萌,等.柴达木盆地西北部长垄状雅丹沉积物地球化学元素组成及指示意义[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(3):127-136. |
| 18 | 徐志伟,鹿化煜,赵存法,等.库姆塔格沙漠地表物质组成、来源和风化过程[J].地理学报,2010,65(1):53-64. |
| 19 | 崔徐甲,孙虎,董治宝,等.巴丹吉林沙漠高大沙山沉积物地球化学元素组成及其环境意义[J].中国沙漠,2017,37(1):17-25. |
| 20 | Hack J T.Dunes of the Western Navajo County[J].Geographical Review,1941,31(2):240-263. |
| 21 | Smith R S U.Eolian sand on desert mountains[C]//Geological Society of America Annual Meeting Abstract,1954:102-103. |
| 22 | Evans J R.Falling and climbing sand dunes in the Cronese (“cat”) Mountain area,San Bernardino County,California[J].Journal of Geology,1962,70(1):107-113. |
| 23 | 全国科学技术名词审定委员会.地理学名词[M].北京:科学出版社,2007:96. |
| 24 | 孟小楠,严平,董苗.爬坡沙丘的研究进展[J].北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2018(3):391-396. |
| 25 | Lancaster N, Tchakerian V P.Geomorphology and sediments of sand ramps in the Mojave desert[J].Geomorphology,1996,17(1/3):151-165. |
| 26 | Bateman M D, Bryant R G, Foster I,et al.On the formation of sand ramps:a case study from the Mojave Desert[J].Geomorphology,2012,161/162:93-109. |
| 27 | White B R, Tsoar H.Slope effect on saltation over a climbing sand dune[J].Geomorphology,1998,22(2):159-180. |
| 28 | 李森,董光荣,申建友,等.雅鲁藏布江河谷风沙地貌形成机制与发育模式[J].中国科学D辑,1999,29(1):88-96. |
| 29 | 李森,王跃,哈斯,等.雅鲁藏布江河谷风沙地貌分类与发育问题[J].中国沙漠,1997,17(4):342. |
| 30 | Li S, Liu X W, Li H C,et al.A wind tunnel simulation of the dynamic processes involved in sand dune formation on the western coast of Hainan Island[J].Journal of Geographical Sciences,2007,7:453-459. |
| 31 | 赵子允.东昆仑山区风沙地貌的特征[J].中国沙漠,1983,3(3):35. |
| 32 | Chojnacki M, Burr D M, Moersch J E.Valles Marineris dune fields as compared with other martian populations:diversity of dune compositions,morphologies,and thermophysical properties[J].Icarus,2014,230:96-142. |
| 33 | 杨逸畴,高登义,李渤生.雅鲁藏布江下游河谷水汽通道初探[J].中国科学B辑,1987,17(8):893-902. |
| 34 | 成都地质学院陕北队.沉积岩(物)粒度分析及其应用[M].北京:科学出版社,1978. |
| 35 | 任明达,王乃梁.现代沉积环境概论[M].北京:科学出版社,1981:8-15. |
| 36 | Visher G.Grain size distribution and depositional process[J].Journal of Sediment Research,1969,39(3):1074-1106. |
| 37 | 陈渭南.塔克拉玛干沙漠84°E沿线沙物质的粒度特征[J].地理学报,1993,48(1):33-46. |
| 38 | 周娜,尤源,雷加强,等.毛里塔尼亚努瓦克肖特沙丘粒度分布特征及其环境意义[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(2):252-261. |
| 39 | 邵天杰,赵景波,董治宝.巴丹吉林沙漠沙山粒度组成与沙山地貌分带[J].山地学报,2013,31(4):434-441. |
| 40 | Taylor S R, McLennan S M.The continenal crust:its composition and evolution[M].Boston,USA:Blackwell Scientific,1985. |
| 41 | 陈国祥.毛乌素沙地风成沉积物沉积学特征[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2019. |
| 42 | 李恩菊.巴丹吉林沙漠与腾格里沙漠沉积物特征的对比研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2011. |
| 43 | Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Early Proterozoric climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J].Nature,1982,229:715-717. |
| 44 | Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Formation and diagenesis of weathering profiles[J].The Journal of Geology,1989,97(2):129-147. |
| 45 | 董治宝.库姆塔格沙漠风沙地貌[M].北京:科学出版社,2011:116-117. |
| 46 | Cox R, Lowe D R, Cullers R L.The influence of sediment recycling and basement composition on evolution of mudrock chemistry in the southwestern United States[J].Geochimica Et Cosmochimica Acta,1995,59:2919-2940. |
| 47 | Cullers R L.The geochemistry of shales,siltstones,and sandstones of Pennsylvanian-Permian age,Colorado,USA:implications for provenance and metamorphic studies[J].Lithos,2000,51:181-203. |
| 48 | Cullers R L.The source and origin of terrigenous sedimentary rocks in the Mesoproterozoic Ui group,southeastern Russia[J].Precambrian Research,2002,117:157-183. |
| 49 | 罗万银,董治宝,钱广强,等.戈壁表层沉积物地球化学元素组成及其沉积意义[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(6):1441-1453. |
| 50 | 邵菁清,杨守业.化学蚀变指数(CIA)反映长江流域的硅酸盐岩化学风化与季风气候?[J].科学通报,2012,57(11):933-942. |
| 51 | 韩宗珠,张军强,邹昊,等.渤海湾北部底质沉积物中黏土矿物组成与物源研究[J].中国海洋大学学报,2011,41(11):95-102. |
| 52 | Horowitz A J.A Primer on Sediment-Trace Element Chemistry[M].Chelsea, Michigan,USA:Lewis Publishers,1991:136. |
| 53 | Jenne E A .Controls on Mn,Fe,Co,Ni,Cu,and Zn concentrations in soils and water:the significant role of hydrous Mn and Fe oxides[M]//Baker R.Trace Inorganic in Water.1968:337-387. |
| 54 | Jenne E A, Kennedy V, Burchard J,et al.Sediment collection and processing for selective extraction and for total metal analysis[M]//Baker R.Contaminants and Sediments.1980:169-189. |
| 55 | 陈静生,王飞越,宋吉杰,等.中国东部河流沉积物中重金属含量与沉积物主要性质的关系[J].环境化学,1996,15(1):8-14. |
| [1] | Yufeng Zheng, Xiaopeng Jia, Yuanzheng Wang. Selective deposition of coarse and fine sediments in the Ningxia-Inner Mongolia reach of the Yellow River [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(3): 233-240. |
| [2] | Hong Jia, Zhiyan Sun, Jinming Xie, Jie Chen, Yinghua Zheng, Mingrui Qiang. Environmental changes recorded by aeolian deposits in the coasts of China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(3): 51-62. |
| [3] | Xihao Xie, Zhizhong Li, Jianhui Jin, Rui Liu, Xiaojun Zou, Yunqiang Ma. Preliminary study on sedimentary structure and development model of vegetated linear dune in the southeastern Gurbantunggut Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(3): 74-84. |
| [4] | Chong Gao, Zhibao Dong, Weige Nan, Zhengyao Liu, Chunming Zhu, Xiaozhi Wang, Nan Xiao, Xin Zhang. Physicochemical characteristics and sedimentary environment of honeycomb dunes in Gurbantunggut Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(2): 14-24. |
| [5] | Miao Dong, Ping Yan, Xiaoxu Wang, Guoming Zhang, Xiaonan Meng, Xinran Ji, Yong Wang. Characteristics of surface sediments on the climbing dunes in Shannan wide valley section of Yarlung Tsangpo River, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(2): 153-163. |
| [6] | Baicheng Niu, Fenggui Liu, Qiang Zhou, Qiong Chen, Benli Liu. Comparative analysis of discriminant ability of quantitative discriminant models for reservoir sediment sources [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(2): 36-43. |
| [7] | Ming Yan, Yinghua Zhang, Li He, Weiming Cheng, Suiji Wang, Jiongxin Xu. Blocking effect of upper reaches of Wuding River on desertification [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(2): 62-68. |
| [8] | Yongchong Lin, Guijin Mu, Liling Chen, Chuna Wu, Lishuai Xu. Sorting characteristics and its implication of the grain size of modern atmospheric dust deposition near the surface of the Cele Oasis, Xinjiang, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 139-146. |
| [9] | Mengjun Hu, Dengyou Zheng, Tianqi Ji, Jing Zhuang, Wenli Sun. Geochemical characteristics of major element oxides and environmental evolution inferred from lacustrine sediments in Gonghe Basin, China during the early Late Pleistocene [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 147-157. |
| [10] | Jie Yin, Hasi Eerdun, Jing An, Yanguang Zhou, Rina Hu, Zifeng Wu. Geomorphologic significance of airflow and sand transport around an Artemisia ordosica nebkha in the Ordos Plateau, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 184-195. |
| [11] | Hui Zhao, Hongyu Yang, Xingfan Wang, Keqi Wang. Geochronology of the typical sediments in the Badain Jaran Desert: the progress and issues [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 57-65. |
| [12] | Ke Xie, Hui Yin. The characteristic of grain-size in Ejina Basin and associated sedimentary dynamic environmental analysis [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 111-119. |
| [13] | Meihui Pan, Zewen Hao, Yuhan Qi, Annan Yang, Yougui Chen, Chenlu Li. Grain size characteristics of moving dune in different geomorphological locations in Pengqu Basin, Tibet, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 138-147. |
| [14] | Qinni Huang, Zhibao Dong, Nan Xiao, Miaoyan Feng, Huanyu Shi, Guoxiang Chen, Ziyi Bai, Xin Zhang, Chong Gao, Xiaozhi Wang. Sediments and morphology of coastal Spinifex littoreus nebkhas on Jingxinjiao beach of Hainan Island, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 157-168. |
| [15] | Haiyun Yu, Zhengcai Zhang, Zhijun Wang. Sediment grain size characteristics at extinct lakes in the south Alxa, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(4): 177-184. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech