
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 187-194.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00037
Previous Articles Next Articles
Xing Li1,2( ), Yuan Ma1,2, Xing Li1,2(
), Yuan Ma1,2, Xing Li1,2( ), Junliang Gao1,2, Zhiming Xin1,2(
), Junliang Gao1,2, Zhiming Xin1,2( ), Qi Lu1,3
), Qi Lu1,3
Received:2021-12-27
Revised:2022-03-11
Online:2022-09-20
Published:2022-09-22
Contact:
Zhiming Xin
CLC Number:
Xing Li, Yuan Ma, Xing Li, Junliang Gao, Zhiming Xin, Qi Lu. Plant community heterogeneity and its influencing factors in the Ulan Buh Desert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 187-194.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00037
| 环境因子 | 主成分 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 年均气温(MAT) | 0.358 | 0.143 | 0.222 | 0.16 |
| 最暖月最高气温 (MTWM) | 0.330 | 0.139 | 0.308 | <0.1 |
| 最冷月最低气温(MTCM) | 0.226 | <0.1 | -0.272 | 0.454 |
| 年降水量(MAP) | -0.413 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.114 |
| 最湿润月降水量 (PWM) | -0.406 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.109 |
| 最干旱月降水量 (PDM) | -0.151 | <0.1 | 0.586 | <0.1 |
| 最湿润季降水量(PWQ) | -0.412 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.123 |
| 最干旱季降水量(PDQ) | -0.181 | <0.1 | 0.584 | <0.1 |
| 全氮(STN) | <0.1 | -0.365 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| 全磷(STP) | 0.164 | -0.481 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| 全钾(STK) | 0.150 | -0.219 | <0.1 | -0.66 |
| 有机质(SOM) | <0.1 | -0.555 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| 速效磷(SAP) | 0.149 | -0.231 | <0.1 | 0.444 |
| 速效钾(SAK) | <0.1 | -0.399 | <0.1 | 0.244 |
| 海拔 | -0.263 | -0.149 | -0.277 | -0.152 |
| 特征值 | 5.37 | 2.60 | 2.19 | 1.17 |
| 贡献率/% | 35.8 | 17.3 | 14.6 | 7.8 |
| 累积贡献率/% | 35.8 | 53.1 | 66.7 | 75.5 |
Table 1 Principal component analysis of environmental factors in Ulan Buh Desert
| 环境因子 | 主成分 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| 年均气温(MAT) | 0.358 | 0.143 | 0.222 | 0.16 |
| 最暖月最高气温 (MTWM) | 0.330 | 0.139 | 0.308 | <0.1 |
| 最冷月最低气温(MTCM) | 0.226 | <0.1 | -0.272 | 0.454 |
| 年降水量(MAP) | -0.413 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.114 |
| 最湿润月降水量 (PWM) | -0.406 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.109 |
| 最干旱月降水量 (PDM) | -0.151 | <0.1 | 0.586 | <0.1 |
| 最湿润季降水量(PWQ) | -0.412 | <0.1 | <0.1 | 0.123 |
| 最干旱季降水量(PDQ) | -0.181 | <0.1 | 0.584 | <0.1 |
| 全氮(STN) | <0.1 | -0.365 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| 全磷(STP) | 0.164 | -0.481 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| 全钾(STK) | 0.150 | -0.219 | <0.1 | -0.66 |
| 有机质(SOM) | <0.1 | -0.555 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| 速效磷(SAP) | 0.149 | -0.231 | <0.1 | 0.444 |
| 速效钾(SAK) | <0.1 | -0.399 | <0.1 | 0.244 |
| 海拔 | -0.263 | -0.149 | -0.277 | -0.152 |
| 特征值 | 5.37 | 2.60 | 2.19 | 1.17 |
| 贡献率/% | 35.8 | 17.3 | 14.6 | 7.8 |
| 累积贡献率/% | 35.8 | 53.1 | 66.7 | 75.5 |
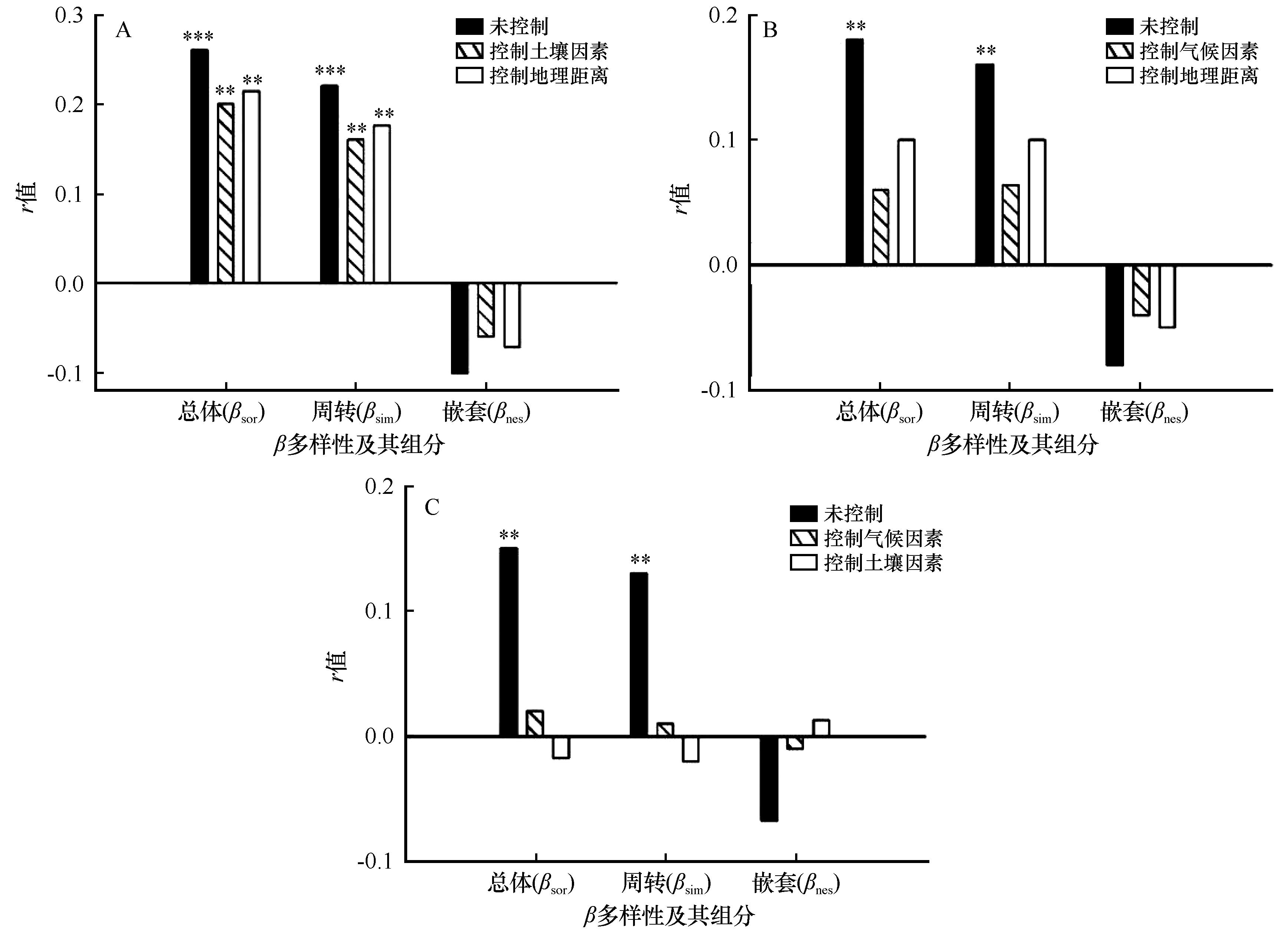
Fig.3 Mantel and Partial Mantel tests (*: P<0.05; ** : P<0.01;*** : P<0.001) showed that β diversity and its components were correlated with climatic factors (A), soil factors (B) and geographical distance (C)
| 1 | 秦洁,司建华,贾冰,等.巴丹吉林沙漠植被群落特征与土壤水分关系研究[J].干旱区研究,2021,38(1):207-222. |
| 2 | 朱军涛,于静洁,王平,等.额济纳荒漠绿洲植物群落的数量分类及其与地下水环境的关系分析[J].植物生态学报,2011,35(5):480-489. |
| 3 | Whittaker R H.Evolution and measurement of species diversity[J].TAXON,1972,21(2/3):213-251. |
| 4 | Condit R, Pitman N, Leigh E G,et al.Beta-diversity in tropical forest trees[J].Science,2009,90(3):663-674. |
| 5 | 彭思羿,胡广,于明坚.千岛湖岛屿维管植物β多样性及其影响因素[J].生态学报,2014,34(14):3866-3872. |
| 6 | Lennon J J, Koleff P, Greenwood J J D,et al.The geographical structure of British bird distributions:diversity,spatial turnover and scale[J].Journal of Animal Ecology,2001,70(6):966-979. |
| 7 | Baselga A.Partitioning the turnover and nestedness components of beta diversity[J].Global Ecology & Biogeography,2010,19(1):134-143. |
| 8 | James A, Pitchford J W, Plank M J.Disentangling nestedness from models of ecological complexity[J].Nature,2012,487(7046):227-230. |
| 9 | Soininen J, McDonald R, Hillebrand M.The distance decay of similarity in ecological communities[J].Ecography,2007,30(1):3-12. |
| 10 | Legendre P, Mi X, Ren H,et al.Partitioning beta diversity in a subtropical broadleaved forest of China[J].Ecology,2009,90(3):663-674. |
| 11 | Blundo C, González-Espinosa M, Malizia L R.Relative contribution of niche and neutral processes on tree species turnover across scales in seasonal forests of NW Argentina[J].Plant Ecology,2016,217(4):359-368. |
| 12 | 牛克昌,刘怿宁,沈泽昊,等.群落构建的中性理论和生态位理论[J].生物多样性,2009,17(6):579-593. |
| 13 | Qing Z, Xiangyang H, Yonghong L F,et al.Alpha,Beta and Gamma diversity differ in response to precipitation in the Inner Mongolia grassland[J].PLoS ONE,2014,9(3):e93518. |
| 14 | Peng Y, Feng J, Sang W,et al.Geographical divergence of species richness and local homogenization of plant assemblages due to climate change in grasslands[J].Biodiversity and Conservation,2022:136:1-14. |
| 15 | Miki T, Kondoh M.Feedbacks between nutrient cycling and vegetation predict plant species coexistence and invasion[J].Ecology Letters,2002,5(5):624-633. |
| 16 | Hubbell S P.The unified neutral theory of biodiversity and biogeography:reply[J].Ecology,2004,85(11):3175-3178. |
| 17 | Catano C P, Dickson T L, Myers J A,et al.Dispersal and neutral sampling mediate contingent effects of disturbance on plant beta‐diversity:a meta‐analysis[J].Ecology Letters,2017,20(3):347-356. |
| 18 | Whitford W G.Ecology of Desert Systems[M].San Diego,USA:Academic Press,2002. |
| 19 | Wang J, Chen C, Li J,et al.Different ecological processes determined the alpha and beta components of taxonomic,functional,and phylogenetic diversity for plant communities in dryland regions of Northwest China[J].PEER Journal,2019,6:e6220. |
| 20 | Li L, Wang Z, Zerbe S,et al.Species richness patterns and water-energy dynamics in the drylands of Northwest China[J].PLoS One,2013,8(6):e66450. |
| 21 | 靳虎甲,马全林,张德魁,等.乌兰布和沙漠典型灌木群落结构及数量特征[J].西北植物学报,2012,32(3):579-588. |
| 22 | 马全林,张德奎,袁宏波,等.乌兰布和沙漠植被数量分类及环境解释[J].干旱区资源与环境,2019,33(9):160-167. |
| 23 | 董雪,辛智鸣,段瑞兵,等.乌兰布和沙漠典型灌木群落多样性及其生态位[J].干旱区研究,2020,37(4):1009-1017. |
| 24 | 贾鹏,王乃昂,程弘毅,等.基于3S技术的乌兰布和沙漠范围和面积分析[J].干旱区资源与环境,2015,29(12):131-138. |
| 25 | 春喜,陈发虎,范育新,等.乌兰布和沙漠的形成与环境变化[J].中国沙漠,2007,27(6):927-931. |
| 26 | 马全林,袁宏波,张锦春,等.乌兰布和沙漠植被[M].兰州:甘肃科学技术出版社,2018. |
| 27 | 鲍士旦.土壤农化分析[M].北京:中国农业出版社,2000. |
| 28 | Baselga A, Cdl O.Betapart:an R package for the study of beta diversity[J].Methods in Ecology and Evolution,2012,3(5):808-812. |
| 29 | Legendre P, Borcard D, Peres-Nieto P R.Analyzing beta diversity: partitioning the spatial variation of community composition data[J].Ecological Monographs,2005,75(4):435-450. |
| 30 | 杨欢,王寅,王健铭,等.环境过滤和扩散限制对库姆塔格沙漠南缘植物群落β-多样性的影响[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(3):147-154. |
| 31 | Pueyo Y, Moret-Fernández D, Saiz H,et al.Relationships between plant spatial patterns,water infiltration capacity,and plant community composition in semi-arid Mediterranean ecosystems along atress gradients[J].Ecosystems,2013,16(3):452-466. |
| 32 | Jordan S E, Palmquist K A, Bradford J B,et al.Soil water availability shapes species richness in mid-latitude shrub steppe plant communities[J].Journal of Vegetation Science,2020,31(4):12874. |
| 33 | Jiang L, Lv G, Gong Y,et al.Characteristics and driving mechanisms of species beta diversity in desert plant communities[J].PLoS One,2021,16(1):e0245249. |
| 34 | 赵怀宝,刘彤,雷加强,等.古尔班通古特沙漠南部植物群落β多样性及其解释[J].草业学报,2010,19(3):29-37. |
| 35 | Harms K E, Condit R, Hubbell S P,et al.Habitat associations of trees and shrubs in a 50-ha Neotropical forest plots[J].Journal of Ecology,2001,89(6):947-959. |
| 36 | 翁昌露,张田田,巫东豪,等.古田山10种主要森林群落类型的α和β多样性格局及影响因素[J].生物多样性,2019,27(1):33-41. |
| 37 | Tuomisto H, Ruokolainen K, Yli-Halla M.Dispersal,environment and floristic variation of western Amazonian forests[J].Science,2003,5604(299):241-244. |
| 38 | Berdugo M, Delgadobaquerizo M, Soliveres S,et al.Global ecosystem thresholds driven by aridity[J].Science,2020,6479(347):787-790. |
| 39 | Poorter H, Niinemets Ü, Poorter L,et al.Causes and consequences of variation in leaf mass per area (LMA):a meta-analysis[J].New Phytologist,2010,182(3):565-588. |
| 40 | Schenk H J, Jackson R B.Rooting depths,lateral root spreads and below-ground/above-ground allometries of plants in water-limited ecosystems[J].Journal of Ecology,2002,90(3):480-494. |
| 41 | 霍佳璇,任梁,潘莹萍,等.柴达木盆地荒漠植物功能性状及其对环境因子的响应[J].生态学报,2022(11):1-10. |
| 42 | 张淼淼,秦浩,王烨,等.汾河中上游湿地植被β多样性[J].生态学报,2016,36(11):3292-3299. |
| 43 | 李新辉,刘延虹,刘晔,等.地理距离及环境差异对云南元江干热河谷植物群落beta多样性的影响[J].生物多样性,2016,24(4):399-406. |
| 44 | 谭珊珊,叶珍林,袁留斌,等.百山祖自然保护区植物群落beta多样性[J].生态学报,2013,33(21):6944-6956. |
| 45 | Jeannine C B, Adrienne K, Brianna M.Phylogenetic structure of floridian plant communities depends on taxonomic and spatial scale[J].Ecology,2006, 87(7):S109-S122. |
| 46 | Hong Q, Kissling W D.Spatial scale and cross-taxon congruence of terrestrial vertebrate and vascular plant species richness in China[J].Ecology,2010,91(4):1172-1183. |
| 47 | Zhang J L, Nathan G,Swenson,et al.Phylogenetic beta diversity in tropical forests:implications for the roles of geographical and environmental distance[J].Journal of Systematics and Evolution,2013,51(1):71-85. |
| [1] | Yali Liu, Jianhua Bai, Wei Xiong, Yuqing Han, Honglin Lian, Hao Guo, Zhiming Xin, Xiangjie Liu, Huaiyuan Liu. The characteristics of branch nocturnal sap flow and its environmental driving mechanism of Haloxylon ammodendron artificial shrub in the Ulan Buh Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 195-203. |
| [2] | Guangzhao Han, Guangchao Cao, Shengkui Cao, Wenqian Ye. Soil particle organic carbon isotope decomposition characteristics of ecological restoration grassland and woodland in alpine region [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 36-43. |
| [3] | Huan Yang, Yin Wang, Jianming Wang, Yanguo Xia, Jingwen Li, Xiaohong Jia, Bo Wu. Effects of environmental filtering and dispersal limitation on the β-diversity of plant communities in the south fringe of Kumtag Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(3): 147-154. |
| [4] | Ying Yang, Lü Ping, Fang Ma, Zhun Liang, Mingjing Xu. Characteristics of wind regime in the southwest edge of the Ulan Buh Desert and their influence on the formation of dome dune [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 19-26. |
| [5] | Liang Hairong, Li Jiatao, Li Yanli, Zhao Yingming, Feng Wei, Cheng Yiben, Yu Sijia, Yang Wenbin. Deep Leakage Characteristics and Water Balance of Irrigated Farmland in Ulan Buh Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(4): 187-194. |
| [6] | Luo Fengmin, Gao Junliang, Xin Zhiming, Hao Yuguang, Wang Lina, Li Shuai. Characteristics of Soil Temperature Variation and Influence Factors at Northeastern Margin Region of Ulan Buh Desert, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(1): 179-186. |
| [7] | Li Jinrong, Guo Jianying, Zhao Naqi, Zhang Zhijie, Liu Tiejun, Wu Qiang. The Spatial and Temporal Variability of Sand Erosion and Its Influences Factors across A Coastal Dune in Ulan Buh Desert, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(5): 928-935. |
| [8] | Yue Ning, Wei Guoxiao, Sun Peng, Dong Jun, Dang Huihui, Wang Gang, Huang Shaowen. Rainfall Infiltration Recharge and Its Responses to Climate Change in the Ulan Buh Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2017, 37(5): 1016-1025. |
| [9] | Li Yongshan, Peng Wenchang, Ren Liang, Li Yong. Evolution of Ulan Buh Desert Braided Channel of the Yellow River in Recent 50 Years [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(6): 1689-1694. |
| [10] | Chen Xinchuang, Guo Jianying, Dong Zhi, Li Hongli, Li Jinrong, Wang Heyun. Grain Size Characteristics of Dustfall in the Ulan Buh Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(2): 295-301. |
| [11] | Liu Fang, Zhang Yaoxiang, Ma Yingbin, Dong Lilong, Yu Xinchun, Huang Yaru. Growth Rhythm of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica in the Ulan Buh Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2015, 35(5): 1234-1238. |
| [12] | Gao Yong, Dang Xiaohong, Yu Yi, Wang Ji, Wang Shan, Yuan Weijie, Zhang Xiwei. Nabkha Morphological Characteristics and Sand Fixing Capacity of Artemisia sphaerocphala in the Southeastern Edge of the Ulan Buh Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2015, 35(1): 1-7. |
| [13] | DONG Zhi;LI Hong-li. Comprehensive Control Technology System of Sand Disasters in Artificial Oases in Ulan Buh Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2011, 31(2): 339-345. |
| [14] | LI Hong-li;DONG Zhi;ZUO He-jun;HAO Yu-guang. Farmland Wind-sand Disaster and Its Spatio-temporal Variation in Ulan Buh Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2011, 31(2): 346-351. |
| [15] | CHUN Xi;CHEN Fa-hu;FAN Yu-xin;XIA Dun-sheng;ZHAO Hui. Formation of Ulan Buh Desert and Its Environmental Evolution [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2007, 27(6): 927-931. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech