
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 243-254.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00063
Qi Zhang1,2( ), Yonghong Su1(
), Yonghong Su1( ), Qi Feng1, Tengfei Yu1, Xiaohong Ma3
), Qi Feng1, Tengfei Yu1, Xiaohong Ma3
Received:2021-12-27
Revised:2022-04-12
Online:2022-11-20
Published:2023-01-09
Contact:
Yonghong Su
CLC Number:
Qi Zhang, Yonghong Su, Qi Feng, Tengfei Yu, Xiaohong Ma. Estimation of groundwater evapotranspiration of Populus euphratica forest ecosystem along desert river banks based on groundwater level dynamics[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 243-254.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00063
| 植被覆盖度 /% | 植株密度 /(株·hm-2) | 树高 /m | 胸径 /cm | 林龄 /a | 土壤质地 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—60 cm | 60—120 cm | 120—150 cm | |||||
| 75 | 350 | 10.1±1.7 | 22.9±4.8 | 30—60 | 沙壤土 | 沙土 | 沙、黏土混合 |
Table 1 Populus euphratica forest stand characteristics and soil texture
| 植被覆盖度 /% | 植株密度 /(株·hm-2) | 树高 /m | 胸径 /cm | 林龄 /a | 土壤质地 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—60 cm | 60—120 cm | 120—150 cm | |||||
| 75 | 350 | 10.1±1.7 | 22.9±4.8 | 30—60 | 沙壤土 | 沙土 | 沙、黏土混合 |
| 仪器 | 名 称 | 观测及采集对象 | 采样间隔及频率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 观测仪器 | 三维超声风速仪(CSAT3, Campbell Co, 美国) | 风速 | — |
| 开路式CO2/H2O分析仪(Li-7500A, LI-COR, 美国) | 水汽和CO2浓度 | ||
| 四分净辐射仪(CNR4, Kipp & Zonen, 荷兰) | 净辐射(Rn) | ||
| 相对温湿度传感器( HMP45C, Campbell,美国) | 气温(Ta)、湿度(RH) | ||
| 土壤热通量板( HFP, Hukse Flux Thermal Sensors B.V. , Delft, 荷兰。埋设在地下5 cm处,水平间隔0.5 m) | 土壤热通量(G) | ||
| 数据采集仪器 | CR3000数据采集器 | 通量观测数据、净辐射(Rn)、气温(Ta)、相对湿度(RH) | 采样间隔:30 min 采样频率:10 Hz |
Table 2 Eddy observation data and instruments
| 仪器 | 名 称 | 观测及采集对象 | 采样间隔及频率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 观测仪器 | 三维超声风速仪(CSAT3, Campbell Co, 美国) | 风速 | — |
| 开路式CO2/H2O分析仪(Li-7500A, LI-COR, 美国) | 水汽和CO2浓度 | ||
| 四分净辐射仪(CNR4, Kipp & Zonen, 荷兰) | 净辐射(Rn) | ||
| 相对温湿度传感器( HMP45C, Campbell,美国) | 气温(Ta)、湿度(RH) | ||
| 土壤热通量板( HFP, Hukse Flux Thermal Sensors B.V. , Delft, 荷兰。埋设在地下5 cm处,水平间隔0.5 m) | 土壤热通量(G) | ||
| 数据采集仪器 | CR3000数据采集器 | 通量观测数据、净辐射(Rn)、气温(Ta)、相对湿度(RH) | 采样间隔:30 min 采样频率:10 Hz |
| 年份 | 00:00—04:00 | 00:00—06:00 | 18:00—06:00 | 22:00—06:00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.33** | 0.29* | 0.30** | 0.27** |
| 2020 | 0.45** | 0.37** | 0.40** | 0.43* |
Table 3 Pearson correlation analysis of ecosystem ET with ETg estimated based on White′s method in different time windows in 2014 and 2020
| 年份 | 00:00—04:00 | 00:00—06:00 | 18:00—06:00 | 22:00—06:00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.33** | 0.29* | 0.30** | 0.27** |
| 2020 | 0.45** | 0.37** | 0.40** | 0.43* |
| 年份 | 1 d | 2 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.43** | 0.31** | 0.25* | 0.21 | 0.19 |
| 2020 | 0.41** | 0.29* | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.15 |
Table 4 Pearson correlation analysis of ecosystem ET with ETg estimated based on Soylu method in different moving windows in 2014 and 2020
| 年份 | 1 d | 2 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.43** | 0.31** | 0.25* | 0.21 | 0.19 |
| 2020 | 0.41** | 0.29* | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.15 |
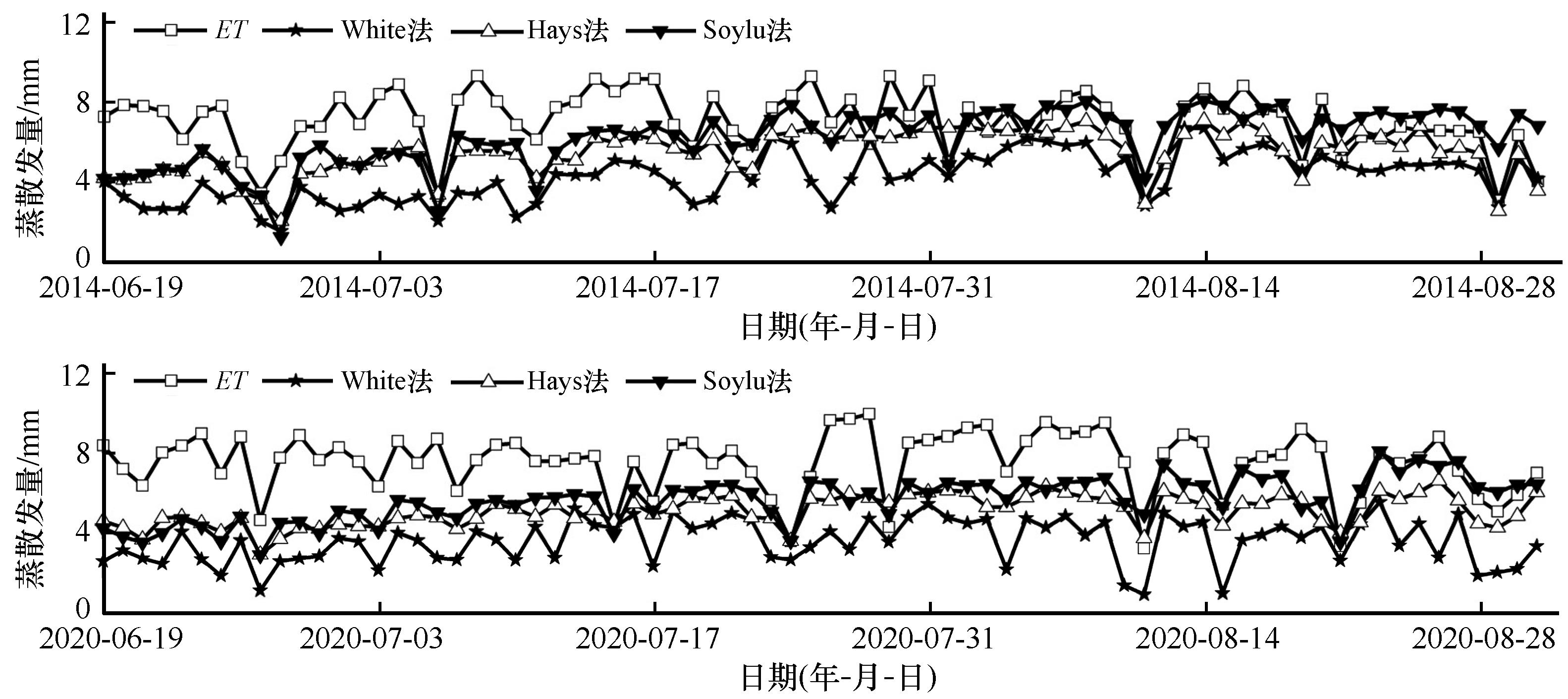
Fig.7 Ecosystem evapotranspiration (ET) and groundwater evapotranspiration (ETg) of Populus euphratica forest during the peak of the growing season in 2014 and 2020
| 年份 | White法 | Hays法 | Soylu法 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.33** | 0.64** | 0.43** |
| 2020 | 0.45** | 0.59** | 0.41* |
Table 5 Pearson correlation analysis of ecosystem ET with ETg estimated based on White, Hays and Soylu methods in 2014 and 2020
| 年份 | White法 | Hays法 | Soylu法 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.33** | 0.64** | 0.43** |
| 2020 | 0.45** | 0.59** | 0.41* |
| 年份 | 地下水位/m | 气温/℃ | 风速/(m·s-1) | 入射太阳辐射/(W·m-2) | VPD/hPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | -0.41** | 0.47** | 0.02 | 0.50** | 0.60** |
| 2020 | -0.54** | 0.19* | 0.04 | 0.36** | 0.54** |
Table 6 Pearson correlation analysis of ETg with groundwater level, temperature, wind speed, solar radiation or VPD in 2014 and 2020
| 年份 | 地下水位/m | 气温/℃ | 风速/(m·s-1) | 入射太阳辐射/(W·m-2) | VPD/hPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | -0.41** | 0.47** | 0.02 | 0.50** | 0.60** |
| 2020 | -0.54** | 0.19* | 0.04 | 0.36** | 0.54** |
| 年份 | 自变量 | 代表符号 | 系数 | R2 | 调整后R2 | 模型P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 地下水位/m | X1 | -2.276** | 0.685 | 0.672 | <0.01 |
| 太阳辐射/℃ | X2 | 0.008** | ||||
| 饱和水汽压差VPD/hPa | X3 | 0.081** | ||||
| 常量 | — | -2.388** | ||||
| 2020 | 地下水位/m | X1 | -2.609** | 0.706 | 0.693 | <0.01 |
| 太阳辐射/℃ | X2 | 0.006** | ||||
| 饱和水汽压差VPD/hPa | X3 | 0.021** | ||||
| 常量 | — | -2.118** |
Table 7 Groundwater level, solar radiation, VPD and ETg linear model coefficients and R2 in 2014 and 2020
| 年份 | 自变量 | 代表符号 | 系数 | R2 | 调整后R2 | 模型P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 地下水位/m | X1 | -2.276** | 0.685 | 0.672 | <0.01 |
| 太阳辐射/℃ | X2 | 0.008** | ||||
| 饱和水汽压差VPD/hPa | X3 | 0.081** | ||||
| 常量 | — | -2.388** | ||||
| 2020 | 地下水位/m | X1 | -2.609** | 0.706 | 0.693 | <0.01 |
| 太阳辐射/℃ | X2 | 0.006** | ||||
| 饱和水汽压差VPD/hPa | X3 | 0.021** | ||||
| 常量 | — | -2.118** |
| 1 | Feng S, Fu Q.Expansion of global drylands under a warming climate[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2013,13(19):10081-10094. |
| 2 | Yin L, Zhou Y, Ge S,et al.Comparison and modification of methods for estimating evapotranspiration using diurnal groundwater level fluctuations in arid and semiarid regions[J].Journal of Hydrology,2013,496:9-16. |
| 3 | 马小红,冯起.荒漠河岸胡杨林生态系统能量分配及蒸散发[J].生态学报,2020,40(23):8683-8693. |
| 4 | Xi H, Zhang J, Feng Q,et al.How changes of groundwater level affect the desert riparian forest ecosystem in the Ejina Oasis,Northwest China[J].Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions,2019,11(1):62-80. |
| 5 | Wang X, Huo Z, Shukla M K,et al.Energy fluxes and evapotranspiration over irrigated maize field in an arid area with shallow groundwater[J].Agricultural Water Management,2020,228:105922. |
| 6 | Yu T F, Feng Q, Si J H,et al.Evapotranspiration of a Populus euphratica Oliv.forest and its controlling factors in the lower Heihe River Basin,Northwest China[J].Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions,2017,9(2):175-182. |
| 7 | Chen H, Huo Z, Dai X,et al.Impact of agricultural water-saving practices on regional evapotranspiration:the role of groundwater in sustainable agriculture in arid and semi-arid areas[J].Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2018,263:156-168. |
| 8 | Soylu M E, Lenters J D, Istanbulluoglu E,et al.On evapotranspiration and shallow groundwater fluctuations:a Fourier-based improvement to the White method[J].Water Resources Research,2012,48(6):W06506. |
| 9 | Yue W, Wang T, Franz T E,et al.Spatiotemporal patterns of water table fluctuations and evapotranspiration induced by riparian vegetation in a semiarid area[J].Water Resources Research,2016,52(3):1948-1960. |
| 10 | Cheng D H, Li Y, Chen X,et al.Estimation of groundwater evaportranspiration using diurnal water table fluctuations in the Mu Us Desert,northern China[J].Journal of Hydrology,2013,490:106-113. |
| 11 | Wang P, Grinevsky S O, Pozdniakov S P,et al.Application of the water table fluctuation method for estimating evapotranspiration at two phreatophyte-dominated sites under hyper-arid environments[J].Journal of Hydrology,2014,519:2289-2300. |
| 12 | 袁国富,罗毅,邵明安,等.塔里木河下游荒漠河岸林蒸散规律及其关键控制机制[J].中国科学:地球科学,2015,45(5):695-706. |
| 13 | White W N.A Method of Estimating Ground-water Supplies based on Discharge by Plants and Evaporation from Soil:Results of Investigations in Escalante Valley,Utah[M].Washington DC,USA:US Government Printing Office,1932. |
| 14 | Hays K B.Water use by saltcedar (Tamarix sp.) and associated vegetation on the Canadian,Colorado and Pecos Rivers in Texas[D].College Station, Texas,USA:Texas A & M University,2003. |
| 15 | Loheide II S P.A method for estimating subdaily evapotranspiration of shallow groundwater using diurnal water table fluctuations[J].Ecohydrology,2008,1(1):59-66. |
| 16 | 王京晶,刘鹄,徐宗学,等.基于昼夜水位波动法估算地下水蒸散发量的研究:以河西走廊典型绿洲为例[J].干旱区研究,2021,38(1):59-67. |
| 17 | 吴立宗,王建华,年雁云.黑河流域边界数据集(1985、1995、2000、1995、2000)[DB].国家青藏高原科学数据中心,2013.DOI:10.11888/Geogra.tpdc.270587 . |
| 18 | Idso S B.An Introduction to environmental biophysics[J].Journal of Environmental Quality,1977,6(4):474. |
| 19 | Burba G, Schmidt A, Scott R L,et al.Calculating CO2 and H2O eddy covariance fluxes from an enclosed gas analyzer using an instantaneous mixing ratio[J].Global Change Biology,2012,18(1):385-399. |
| 20 | Foken T, Göockede M, Mauder M,et al.Post-field data quality control[M]//Beverly L,Shashi V.Handbook of Micrometeorology.Dordrecht,The Netherlands:Springer,2004:181-208. |
| 21 | Vickers D, Mahrt L.Quality Control and Flux Sampling Problems for Tower and Aircraft Data[J].Journal of Atmospheric & Oceanic Technology,1997,14(3):514-526. |
| 22 | Liu S M, Xu Z W, Wang W Z,et al.A comparison of eddy-covariance and large aperture scintillometer measurements with respect to the energy balance closure problem[J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2011,15(4):1291-1306. |
| 23 | Wilson K, Goldstein A, Falge E,et al.Energy balance closure at FLUXNET sites[J].Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2002,113(1):223-243. |
| 24 | Wutzler T, Lucas-Moffat A, Migliavacca M,et al.Basic and extensible post-processing of eddy covariance flux data with REddyProc[J].Biogeosciences,2018,15(16):5015-5030. |
| 25 | Wohlfahrt G, Haslwanter A, Hörtnagl L,et al.On the consequences of the energy imbalance for calculating surface conductance to water vapour[J].Agricultural & Forest Meteorology,2009,149(9):1556-1559. |
| 26 | 尹力,赵良菊,阮云峰,等.黑河下游典型生态系统水分补给源及优势植物水分来源研究[J].冰川冻土,2012,34(6):1478-1486. |
| 27 | Loheide S P, Butler J J, Gorelick S M.Estimation of groundwater consumption by phreatophytes using diurnal water table fluctuations:a saturated-unsaturated flow assessment[J].Water Resources Research,2005,41(7):372-380. |
| 28 | 鱼腾飞,冯起,司建华,等.黑河下游柽柳根系水力提升对林分蒸散的贡献[J].生态学报,2017,37(18):6029-6037. |
| 29 | Karl Pearson.Notes on the History of Correlation[J].Biometrika,1920,13(1):25-45. |
| 30 | Fan J, Ostergaard K T, Guyot A,et al.Estimating groundwater evapotranspiration by a subtropical pine plantation using diurnal water table fluctuations:implications from night-time water use[J].Journal of Hydrology,2016,542:679-685. |
| 31 | 孙海涛,陈亚鹏,陈亚宁,等.塔里木河下游荒漠河岸林地下水蒸散发[J].干旱区研究,2020,37(1):116-125. |
| 32 | Hou P, Beeton R J, Carter R W,et al.Response to environmental flows in the lower Tarim River,Xinjiang,China:ground water[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2007,83(4):371-382. |
| 33 | 张经天,席海洋,王春林,等.基于地下水位变化的荒漠河岸林蒸散估算[J].高原气象,2019,38(1):179-186. |
| 34 | Fahle M, Dietrich O.Estimation of evapotranspiration using diurnal groundwater level fluctuations:comparison of different approaches with groundwater lysimeter data[J].Water Resources Research,2014,50(1):273-286. |
| [1] | Qian Li, Long Ma, Tingxi Liu, Shuo Wang. Conversion of precipitation, surface water, groundwater and mine water affected by coal mining in the Hailiutu River Basin, Inner Mongolia, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 146-157. |
| [2] | Xueping Chen, Xueyong Zhao, Ruixiong Wang, Zhiying Ning, Jiannan Lu, Siteng Zhao. Research advances on the impact of climate change and LUCC for water resources in the northern agro-pastoral zone in China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(3): 170-177. |
| [3] | Shenghui Zhou, Tingxi Liu, Limin Duan, Ru Ji, Chunyu Zhang. Hydrogeological characteristics of underwater aquifer in the Hailiutu River Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(5): 103-110. |
| [4] | Yang Yufan, Cao Shengkui, Feng Qi, Cao Guangchao, Liu Ying, Lei Yizhen. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Composition of Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes of Shallow Groundwater in Shaliu River Basin of Qinghai Lake [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(5): 45-53. |
| [5] | Yue Ning, Wei Guoxiao, Sun Peng, Dong Jun, Dang Huihui, Wang Gang, Huang Shaowen. Rainfall Infiltration Recharge and Its Responses to Climate Change in the Ulan Buh Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2017, 37(5): 1016-1025. |
| [6] | Cao Le, Nie Zhenlong, Liu Xuequan, Wang Zhe, Meng Lingqun, Jiang Gaolei. Hydrochemical Cause of Lakes' Tufa in Badain Jaran Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2017, 37(5): 1026-1034. |
| [7] | Wei Shuilian, Liu Xinping, Zhao Xueyong, Zhang Tonghui, Yun Jianying, Zhang Jing, Zhang Jianpeng, Feng Jing, Su Na. Spatial and Temporal Variability Analysis of Groundwater Quality in Naiman Region of Horqin Sandy Land [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2017, 37(3): 571-579. |
| [8] | Yu Haijiao, Wen Xiaohu, Feng Qi, Yin Zhenliang, Chang Zongqiang, Yu Tengfei, Niu Xiaoyu. Prediction of Groundwater Depth in Arid Regions by Using Wavelet-Support Vector Machine (WA-SVM) [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(5): 1435-1442. |
| [9] | Wei Yaping, Fan Jinglong, Xu Xinwen, Jin Xiaojun, Zhou Hongwei. Hydrogeochemical Modelling of Groundwater Chemical Evolution fromSouthern Margin to Hinterland of the Taklamakan Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(3): 798-804. |
| [10] | Zhang Jing, Wang Xusheng, Hu Xiaonong, Lu Huiting, Gong Yanping, Wan Li. The Macro-characteristics of Groundwater Flow in the Badain Jaran Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2015, 35(3): 774-782. |
| [11] | An Shuai, Wang Naiang, Chen Huili, Zhao Liqiang. The Lakes’ Clustering of the Badain Jaran Desert Based on SOFM Network and Inferences of Their Sources of Groundwater Recharge [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2014, 34(2): 574-581. |
| [12] | SI Jian-hua, FENG Qi, XI Hai-yang, YU Teng-fei, LI Wei. Determination of Critical Period and Requirment of Ecological Water Demanded in the Ejina Oasis in Lower Reaches of the Heihe River [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2013, 33(2): 560-567. |
| [13] | LI Wen-zan;YAN Ping;LIU Yong-gang;DING Lian-gang;E You-hao. Phreatic Water Recharged Source on the Northeast of Kumtag Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2011, 31(6): 1617-1622. |
| [14] | HE Jian-hua;FU Su-jing;MA Jin-zhu;ZHANG Qing-huan. Groundwater Recharge and Geochemical Evolution in Quaternary Aquifer of Beidahe River Watershed [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2011, 31(6): 1630-1638. |
| [15] | WEI Guo-xiao;ZHU Xi-fen;MA Jin-zhu;XU Xiang;XU Tao. Hydrogeochemical Properties and Evolution of Groundwater from Helan Mountain to Jilantai Salt Lake [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2011, 31(5): 1330-1336. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech