
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 47-56.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00138
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yawei Fan1,2( ), Heqiang Du1(
), Heqiang Du1( ), Shanlong Lu3, Zhiwen Han1, Xiufan Liu1,2, Xinlei Liu1,2
), Shanlong Lu3, Zhiwen Han1, Xiufan Liu1,2, Xinlei Liu1,2
Received:2022-09-06
Revised:2022-10-16
Online:2023-05-20
Published:2023-05-31
Contact:
Heqiang Du
CLC Number:
Yawei Fan, Heqiang Du, Shanlong Lu, Zhiwen Han, Xiufan Liu, Xinlei Liu. Surface particle size composition and aeolian-sand flow structure of Zuo Lake Basin in the source of Yangtze River[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 47-56.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00138
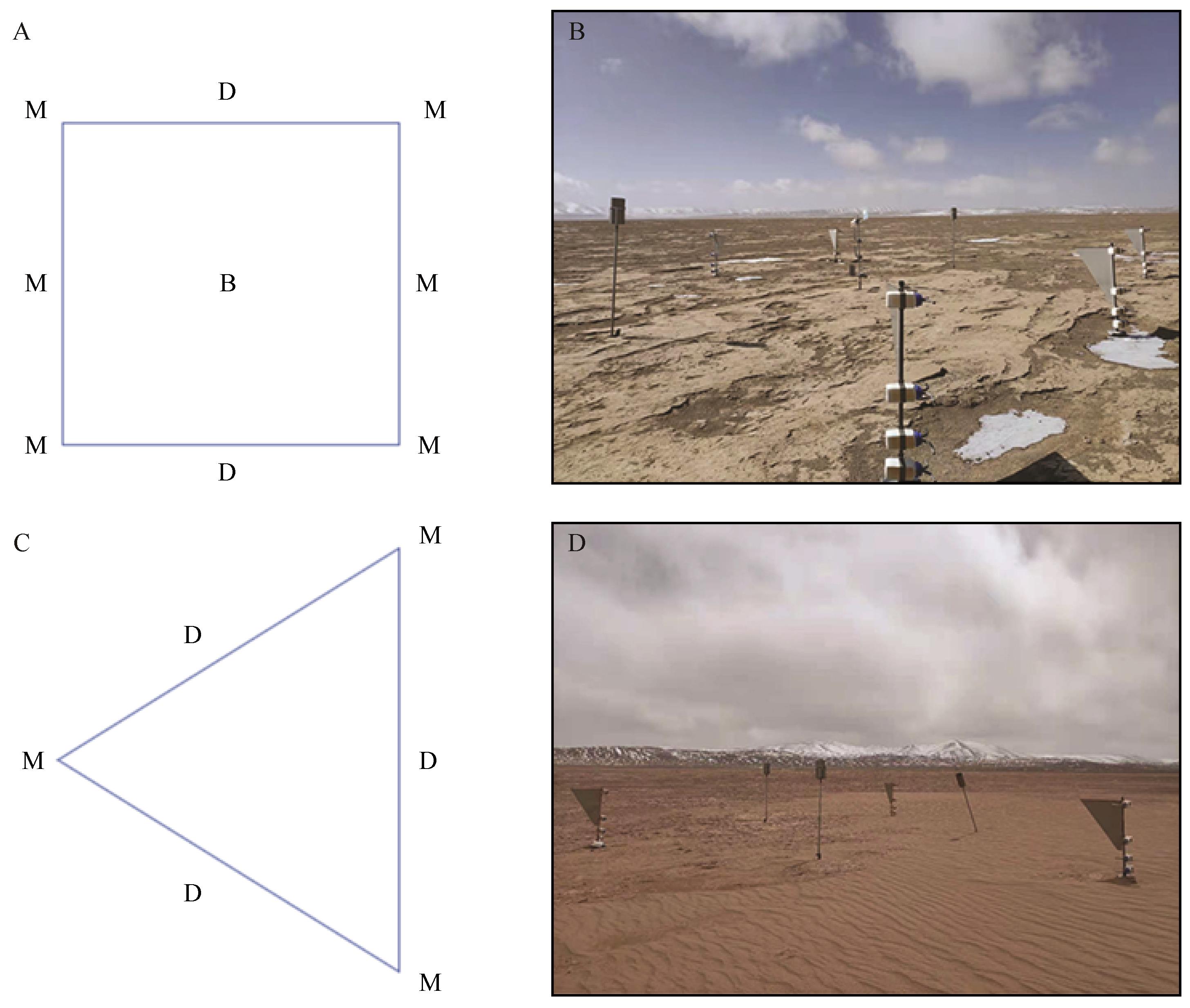
Fig.2 Schematic diagram of instrument group installation and erection point of aeolian sand observation field (A, The instrument installation schematic of W and S observation field. B, The sketch maps of S observation sites. C, The instruments installation schematic of E observation field. D, The sketch map of E observation field. B represents BSNE Sand Collector, M represents MWAC Sand Collector, D represents Dust Cylinder)
| 沉积物 | 粒径/Ф | 类别名称 | 沉积物 | 粒径/Ф | 类别名称 | 沉积物 | 粒径/Ф | 类别名称 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 砾石 | <-8 | 巨砾 | 砾石 | -1~-2 | 极细砾 | 粉砂 | 5~4 | 极粗粉砂 |
| -6~-8 | 卵石 | 砂 | 0~-1 | 极粗砂 | 6~5 | 粗粉砂 | ||
| -5~-6 | 极粗砾 | 1~0 | 粗砂 | 7~6 | 中粉砂 | |||
| -4~-5 | 粗砾 | 2~1 | 中砂 | 8~7 | 细粉砂 | |||
| -3~-4 | 中砾 | 3~2 | 细砂 | 8~9 | 极细粉砂 | |||
| -2~-3 | 细砾 | 4~3 | 极细砂 | 黏粒 | > 9 | 黏粒 |
Table 1 Sediment particle size range and category
| 沉积物 | 粒径/Ф | 类别名称 | 沉积物 | 粒径/Ф | 类别名称 | 沉积物 | 粒径/Ф | 类别名称 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 砾石 | <-8 | 巨砾 | 砾石 | -1~-2 | 极细砾 | 粉砂 | 5~4 | 极粗粉砂 |
| -6~-8 | 卵石 | 砂 | 0~-1 | 极粗砂 | 6~5 | 粗粉砂 | ||
| -5~-6 | 极粗砾 | 1~0 | 粗砂 | 7~6 | 中粉砂 | |||
| -4~-5 | 粗砾 | 2~1 | 中砂 | 8~7 | 细粉砂 | |||
| -3~-4 | 中砾 | 3~2 | 细砂 | 8~9 | 极细粉砂 | |||
| -2~-3 | 细砾 | 4~3 | 极细砂 | 黏粒 | > 9 | 黏粒 |
| 分选系数σ | 偏度SK | 峰度Kg | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围/Ф | 描述 | 范围 | 描述 | 范围 | 描述 | ||
| <0.35 | 分选极好 | -1.0~-0.3 | 极负偏 | <0.67 | 很宽 | ||
| 0.35~0.50 | 分选很好 | -0.3~-0.1 | 负偏 | 0.67~0.90 | 宽 | ||
| 0.50~0.71 | 分选较好 | -0.1~ 0.1 | 近对称 | 0.90~1.11 | 中等 | ||
| 0.71~1.00 | 分选中等 | 0.1~0.3 | 正偏 | 1.11~1.50 | 窄 | ||
| 1.00~2.00 | 分选较差 | 0.3~1.0 | 极正偏 | 1.50~3.00 | 很窄 | ||
| 2.00~4.00 | 分选很差 | >3.00 | 非常窄 | ||||
| >4.00 | 分选极差 | ||||||
Table 2 Classification standard of sorting coefficient, skewness and kurtosis
| 分选系数σ | 偏度SK | 峰度Kg | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围/Ф | 描述 | 范围 | 描述 | 范围 | 描述 | ||
| <0.35 | 分选极好 | -1.0~-0.3 | 极负偏 | <0.67 | 很宽 | ||
| 0.35~0.50 | 分选很好 | -0.3~-0.1 | 负偏 | 0.67~0.90 | 宽 | ||
| 0.50~0.71 | 分选较好 | -0.1~ 0.1 | 近对称 | 0.90~1.11 | 中等 | ||
| 0.71~1.00 | 分选中等 | 0.1~0.3 | 正偏 | 1.11~1.50 | 窄 | ||
| 1.00~2.00 | 分选较差 | 0.3~1.0 | 极正偏 | 1.50~3.00 | 很窄 | ||
| 2.00~4.00 | 分选很差 | >3.00 | 非常窄 | ||||
| >4.00 | 分选极差 | ||||||
| 土样采集部位 | 粒度参数 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均粒径Mz/Ф | 平均粒径标准差Sd | 分选系数σ/Ф | 偏度SK | 峰态Kg | |
| 西岸观测场 | 6.771 | 1.177 | 1.8433 | -0.0031 | 1.0796 |
| 南岸观测场 | 6.156 | 0.787 | 2.2729 | 0.0045 | 0.8975 |
| 东侧沉降区 | 5.103 | 1.107 | 1.9635 | 0.1024 | 1.3478 |
| 溃堤口与溃堤河道 | 5.879 | 0.577 | 2.0749 | 0.0111 | 0.9465 |
| 未溃堤地面 | 5.685 | 0.425 | 2.4684 | 0.0449 | 0.7716 |
Table 3 The particle size parameters of surface soil
| 土样采集部位 | 粒度参数 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均粒径Mz/Ф | 平均粒径标准差Sd | 分选系数σ/Ф | 偏度SK | 峰态Kg | |
| 西岸观测场 | 6.771 | 1.177 | 1.8433 | -0.0031 | 1.0796 |
| 南岸观测场 | 6.156 | 0.787 | 2.2729 | 0.0045 | 0.8975 |
| 东侧沉降区 | 5.103 | 1.107 | 1.9635 | 0.1024 | 1.3478 |
| 溃堤口与溃堤河道 | 5.879 | 0.577 | 2.0749 | 0.0111 | 0.9465 |
| 未溃堤地面 | 5.685 | 0.425 | 2.4684 | 0.0449 | 0.7716 |
| 沙粒采集部位 | 粒度参数 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均粒径Mz | 平均粒径标准差Sd | 分选系数σ | 偏度SK | 峰态Kg | |
| 西岸观测场 | 5.225 Ф | 0.996 | 1.9972 Ф | 0.0760 | 0.8388 |
| 南岸观测场 | 4.653 Ф | 0.339 | 2.0914 Ф | 0.1133 | 1.0685 |
| 东侧沉降区 | 3.595 Ф | 0.748 | 1.5590 Ф | 0.2148 | 1.6214 |
Table 4 The particle size parameters in aeolian-sand flow
| 沙粒采集部位 | 粒度参数 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 平均粒径Mz | 平均粒径标准差Sd | 分选系数σ | 偏度SK | 峰态Kg | |
| 西岸观测场 | 5.225 Ф | 0.996 | 1.9972 Ф | 0.0760 | 0.8388 |
| 南岸观测场 | 4.653 Ф | 0.339 | 2.0914 Ф | 0.1133 | 1.0685 |
| 东侧沉降区 | 3.595 Ф | 0.748 | 1.5590 Ф | 0.2148 | 1.6214 |
| 1 | 石广玉,赵思雄.沙尘暴研究中的若干科学问题[J].大气科学,2003,27(4):591-606. |
| 2 | Stulina G, Sektimenko V.The change in soil cover on the exposed bed of the Aral Sea[J].Journal of Marine Systems,2014,47(1/4):121-125. |
| 3 | Mees F, Singer A.Surface crusts on soils/sediments of the southern Aral Sea basin,Uzbekistan[J].Geoderma,2006,136(1/2):152-159. |
| 4 | Micklin P.The Aral Sea disaster[J].Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences,2007,35(1):47-72. |
| 5 | Cahill T A, Gill T E, Reid J S,et al.Saltating particles,playa crusts,and dust aerosols at Owens(dry) Lake,California[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,1996,21(7):625-639. |
| 6 | Gillette D, Fryrear D, Gill T,et al.Relation of vertical flux of particles smaller than 10μm to total aeolian horizontal mass flux at Owens Lake[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,1997,102(D22):26009-26015. |
| 7 | Gillette D, Ono D, Richmond K.A combined modeling and measurement technique for estimating windblown dust emissions at Owens(dry) Lake,California[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,2004,109(F01): F01003. |
| 8 | 王富葆,马春梅,夏训诚,等.罗布泊地区自然环境演变及其对全球变化的响应[J].第四纪研究,2008,28(1):150-153. |
| 9 | 郭树江,杨自辉,王强强,等.青土湖干涸湖底风沙流结构及输沙粒径特征[J].生态学杂志,2021,40(4):1166-1176. |
| 10 | 郭树江,杨自辉,王强强,等.青土湖干涸湖底风沙区植被特征与地表输沙量关系[J].水土保持研究,2021,28(1):19-24. |
| 11 | 马倩,武胜利,吴烨,等.艾比湖流域风沙强度特征及其空间差异[J].水土保持通报,2014,34(4):21-27. |
| 12 | Mu G J, Yan S, Abuduwai J,et al.Wind erosion at the dry-up bottom of Aiby Lake:a case study on the source of air dust[J]. Science in China(Series D),2002,45:157-164. |
| 13 | 吉力力·阿不都外力.风蚀作用对盐尘释放、输送过程的影响以新疆艾比湖地区为例[J].干旱区地理,2009,32(2):211-217. |
| 14 | 刘东伟,吉力力·阿不都外力,王立新.新疆艾比湖地区盐尘的沉积通量及其物质组成[J].冰川冻土,2014,36(2):352-359. |
| 15 | 荆耀栋.艾比湖干涸湖底沙尘暴形成与运行机制研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆师范大学,2007. |
| 16 | 李红军,杨青,何清.艾比湖地区的输沙势分析[J].干旱区研究,2003,20(4):322-325. |
| 17 | 张小曳.亚洲粉尘的源区分布、释放、输送、沉降与黄土堆积[J].第四纪研究,2001,21(1):29-40. |
| 18 | Du H Q, Xue X, Wang T,et al.Modeling dust emission in alpine regions with low air temperature and low air pressure-A case study on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau(QTP)[J].Geoderma,2022,422:115930. |
| 19 | Reynolds R L, Yount J C, Reheis M H,et al.Dust emission from wet and dry playas in the Mojave Desert,USA[J].Earth Surface Processes Landforms,2007,32(12):1811-1827. |
| 20 | Bucher E H, Stein A F.Large salt dust storms follow a 30-year rainfall cycle in the Mar Chiquita Lake(Córdoba,Argentina)[J].Plos One,2016,11(6):e0156672. |
| 21 | Wen J, Qin R, Zhang S,et al.Effects of long-term warming on the aboveground biomass and species diversity in an alpine meadow on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau of China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2020,12(2):252-266. |
| 22 | Liu B K, Du Y E, Li L,et al.Outburst flooding of the moraine-dammed Zhuonai Lake on Tibetan Plateau:causes and impacts[J].IEEE Geoscience & Remote Sensing Letters,2016,13(4):570-574. |
| 23 | Zhong L, Xu K P, Ma Y M,et al.Evapotranspiration estimation using surface energy balance system model:a case study in the Nagqu River Basin[J].Atmosphere,2019,10(5),268. |
| 24 | 谢昌卫,张钰鑫,刘文惠,等.可可西里卓乃湖溃决后湖区环境变化及盐湖可能的溃决方式[J].冰川冻土,2020,42(4):1344-1352. |
| 25 | Lu S L, Chen F, Zhou J F,et al.Cascading implications of a single climate change event for fragile ecosystems on the QTP[J].Ecosphere,2020,11(9),e03243. |
| 26 | Pye K.Eolian Dust and Dust Deposits[M].London,UK:Academic Press,1987. |
| 27 | Frank A, Kocurek G.Airflow up the stoss of sand dune:limitation of current understanding[J].Geomorphology,1996,17(1-3):47-54. |
| 28 | 韩致文,缑倩倩,杜鹤强,等.新月形沙丘表面100cm高度内风沙流输沙量垂直分布函数分段拟合[J].地理科学,2012,32(7):892-897. |
| 29 | Bagnold R.The transport of sand by wind[J].Geographical Journal,1937,89(5):409-438. |
| 30 | Bagnold R, Barndorff-Nielsen O.The pattern of natural size distributions[J].Sedimentology,1980,27(2):199-207. |
| 31 | 杜鹤强,韩致文,王涛,等.新月形沙丘表面风速廓线与风沙流结构变异研究[J].中国沙漠,2012,32(1):9-16. |
| 32 | 刘旭阳,宁文晓,王振亭.新月形沙丘脊线处的风沙流结构[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(6):76-82. |
| 33 | Selby M.Rates of denudation[J].Geology,1974,19(12):1169-1172. |
| 34 | Han Q J, Qu J J, Dong Z B,et al.Air density effects on aeolian sand movement:implications for sediment transport and sand control in regions with extreme altitudes or temperatures[J]. Sedimentology,2015,62:1024-1038. |
| 35 | Friedman G M, Sanders J E.Principles of Sedimentology[M].New York,USA:Wiley,1978. |
| 36 | Pye K.Properties of sediment particles[M]//Pye K.Sediment Transport and Depositional Processes. Oxford,UK:Blackwell Scientific,1994. |
| 37 | Folk R L, Ward W C.Brazos River Bar:a study in the significance of grain size parameters[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research,1957,27(1):3-26. |
| 38 | 吴正.风沙地貌学[M].北京:科学出版社,1987:59. |
| 39 | Shao Y P.Physics and Modelling Wind Erosion[M].Berlin,Germany:Springer Science & Business Media,2008. |
| 40 | Zhang J, Teng Z, Huang N,et al.Surface renewal as a significant mechanism for dust emission[J].Atmospheric Chemistry & Physics,2016,16:15517-15528. |
| 41 | Marticorena B, Bergametti G.Modeling the atmospheric dust cycle:1.design of soil-derived dust emission scheme[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,1995,100:16415-16430. |
| 42 | Zender C S, Bian H, Newman D. Mineral Dust Entrainment and Deposition(DEAD) model:description and 1990s dust climatology[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2003,108(D14):4416. |
| 43 | Shao Y P.A model for mineral dust emission[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,2001,106(20):239-254. |
| 44 | 哈斯.河北坝上高原土壤风蚀物垂直分布的初步研究[J].中国沙漠,1997,17(1):11-16. |
| 45 | 吴正.风沙地貌与治沙工程学[M].北京:科学出版社,2003:66-69. |
| [1] | Liyue Cao, Yulin Li, Jin Zhan, Lina Shi. Effects of tillage on distribution and stability of soil aggregates in Horqin Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 212-220. |
| [2] | Wenfan Wang, Rentao Liu, Zhixia Guo, Yonghong Feng, Jiayu Jiang. Physical and chemical properties and fractal dimension distribution of soil under shrubs in the southern area of Tengger Dseart [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 209-218. |
| [3] | Xiong Xin, Wang Haibin, Xiao Jianhua, Zuo Hejun. Particle Size Distribution Models of Gobi Sediments and Its Significance to the Effect of Sorting [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(2): 202-208. |
| [4] | Yang Huan, Li Yuqiang, Wang Xuyang, Niu Yayi, Gong Xiangwen, Yu Peidong. Characteristics of Aeolian Sediment Flux Structure over Different Underlying Surfaces in Semi-arid Area [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(6): 1144-1152. |
| [5] | Wang Zhongyuan, Luo Wanyin, Dong Zhibao, Lu Junfeng, Qian Guangqiang, Xu Guijiang. Grain Size Characteristics of the Blowout Surface Sediments and Its Aerodynamic Significance in the Alpine Meadow Region of the Gonghe Basin [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2017, 37(1): 7-16. |
| [6] | Wang Jinhua, Zhang Ronggang, Yao Wenyi, Li Zhanbin, Zheng Xiaomei. Sediment Particle Size Distribution Characteristics in a Desert Gully Influenced by Coupled Aeolian and Fluvial Processes [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(6): 1695-1700. |
| [7] | Zhao Guanghui, Su Fangli, Li Haifu, Li Yiming. Effects of Land Use on Fractal Dimension of Soil Particles in the Upper Reaches of the Liaohe River Watershed [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(6): 1622-1627. |
| [8] | Nan Ning, Mei Fanmin, Shao Tianjie, Wang Chunyang, Wang Nan. Effect of Sieving Duration and Samples Weight on Dry Sieving Analysis Results of Fine Sand Particles [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(5): 1260-1264. |
| [9] | Liu Fang, Hao Yuguang, Xin Zhiming, Chen Hailing, Xu Jun, Zhao Yingming. The Surface Aeolian-sand Flow Structure in the Northeastern Margin of the Ulanbuh Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2014, 34(5): 1200-1207. |
| [10] | Gao Zeyong, Wang Yibo, Wen Jing, Sheng Zhaohai. The Influence of Thermokarst Lake Formation on Soil Desertification Process in Permafrost Regions of the Source Region of the Yangtze River [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2014, 34(3): 758-764. |
| [11] | LI De-Lu, MAN Duo-qing, ZHU Guo-qing, WEI Lin-yuan, TANG Jin-nian. Aeolian-sand Flow Structure Characteristics at Different Positions in Inter-dune Lowland [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2012, 32(5): 1210-1215. |
| [12] | FAN Li;WU Sheng-zhi. Numerical Computation of Nonuniform Grains Saltation [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2011, 31(3): 583-587. |
| [13] | LI Wan-yuan;SHEN Zhi-bao;LU Shi-hua;LI Yao-hui. Sensitivity Tests of Factors Influencing Wind Erosion [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2007, 27(6): 984-993. |
| [14] | QUAN Jian-nong, XI Xiao-xia, WANG Xin, LI Jie, ZHANG Lei. Analysis on Aerosol Concentration in Lanzhou City from Sand-dust Storm in 2001 [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2005, 25(1): 93-97. |
| [15] | SANG Jian-ren, YANG You-ling. Characteristics of Aerosol Particle Size Distribution during Summer in Yinchuan City,Ningxi Province [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2003, 23(3): 328-330. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech