
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 41-54.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00168
Previous Articles Next Articles
Linyan Luo1,2( ), Xin Gao1,2(
), Xin Gao1,2( ), Yongcheng Zhao1,2
), Yongcheng Zhao1,2
Received:2022-11-27
Revised:2022-12-15
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-08-14
Contact:
Xin Gao
CLC Number:
Linyan Luo, Xin Gao, Yongcheng Zhao. The surface flow pattern characteristics of barchan dunes[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 41-54.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00168
| 网格 | 第一层网格高度/m | 网格数 |
|---|---|---|
| 网格1 | 0.05 | 401 813 |
| 网格2 | 0.025 | 436 577 |
| 网格3 | 0.0125 | 614 183 |
| 网格4 | 0.00625 | 825 661 |
| 网格5 | 0.003125 | 1 213 342 |
Table 1 Mesh details at five different scales
| 网格 | 第一层网格高度/m | 网格数 |
|---|---|---|
| 网格1 | 0.05 | 401 813 |
| 网格2 | 0.025 | 436 577 |
| 网格3 | 0.0125 | 614 183 |
| 网格4 | 0.00625 | 825 661 |
| 网格5 | 0.003125 | 1 213 342 |
| 不同沙丘高度 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高度/m | 迎风坡坡度/(°) | 迎风坡长度/m | 背风坡坡度/(°) | 背风坡长度/m | 翼长/m | 沙丘宽度/m | 摩阻风速/(m·s-1) |
| 1.20 | 15.00 | 6.81 | 34.00 | 1.78 | 4.80 | 12.00 | 0.50 |
| 1.60 | 15.00 | 9.07 | 34.00 | 2.37 | 6.40 | 16.00 | 0.50 |
| 2.00 | 15.00 | 11.34 | 34.00 | 2.97 | 8.00 | 20.00 | 0.50 |
| 2.40 | 15.00 | 13.61 | 34.00 | 3.56 | 9.60 | 24.00 | 0.50 |
| 2.80 | 15.00 | 15.88 | 34.00 | 4.15 | 11.20 | 28.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.60 | 15.00 | 20.42 | 34.00 | 5.34 | 14.40 | 36.00 | 0.50 |
| 4.00 | 15.00 | 22.69 | 34.00 | 5.93 | 16.00 | 40.00 | 0.50 |
| 4.40 | 15.00 | 24.95 | 34.00 | 6.52 | 17.60 | 44.00 | 0.50 |
| 4.80 | 15.00 | 27.22 | 34.00 | 7.12 | 19.20 | 48.00 | 0.50 |
| 不同迎风坡坡度 | |||||||
| 高度/m | 迎风坡坡度/(°) | 迎风坡长度/m | 背风坡坡度/(°) | 背风坡长度/m | 翼长/m | 沙丘宽度/m | 摩阻风速/(m·s-1) |
| 3.20 | 8.00 | 22.77 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.20 | 10.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.20 | 12.00 | 15.05 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.20 | 14.00 | 12.83 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.20 | 16.00 | 11.16 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.20 | 18.00 | 9.85 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.20 | 20.00 | 8.79 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 不同来流风速 | |||||||
| 高度/m | 迎风坡坡度/(°) | 迎风坡长度/m | 背风坡坡度/(°) | 背风坡长度/m | 翼长/m | 沙丘宽度/m | 摩阻风速/(m·s-1) |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.30 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.35 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.40 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.45 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.60 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.70 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.80 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.90 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 1.00 |
Table 2 Parameters of the CFD simulation experiments
| 不同沙丘高度 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高度/m | 迎风坡坡度/(°) | 迎风坡长度/m | 背风坡坡度/(°) | 背风坡长度/m | 翼长/m | 沙丘宽度/m | 摩阻风速/(m·s-1) |
| 1.20 | 15.00 | 6.81 | 34.00 | 1.78 | 4.80 | 12.00 | 0.50 |
| 1.60 | 15.00 | 9.07 | 34.00 | 2.37 | 6.40 | 16.00 | 0.50 |
| 2.00 | 15.00 | 11.34 | 34.00 | 2.97 | 8.00 | 20.00 | 0.50 |
| 2.40 | 15.00 | 13.61 | 34.00 | 3.56 | 9.60 | 24.00 | 0.50 |
| 2.80 | 15.00 | 15.88 | 34.00 | 4.15 | 11.20 | 28.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.60 | 15.00 | 20.42 | 34.00 | 5.34 | 14.40 | 36.00 | 0.50 |
| 4.00 | 15.00 | 22.69 | 34.00 | 5.93 | 16.00 | 40.00 | 0.50 |
| 4.40 | 15.00 | 24.95 | 34.00 | 6.52 | 17.60 | 44.00 | 0.50 |
| 4.80 | 15.00 | 27.22 | 34.00 | 7.12 | 19.20 | 48.00 | 0.50 |
| 不同迎风坡坡度 | |||||||
| 高度/m | 迎风坡坡度/(°) | 迎风坡长度/m | 背风坡坡度/(°) | 背风坡长度/m | 翼长/m | 沙丘宽度/m | 摩阻风速/(m·s-1) |
| 3.20 | 8.00 | 22.77 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.20 | 10.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.20 | 12.00 | 15.05 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.20 | 14.00 | 12.83 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.20 | 16.00 | 11.16 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.20 | 18.00 | 9.85 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.20 | 20.00 | 8.79 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 不同来流风速 | |||||||
| 高度/m | 迎风坡坡度/(°) | 迎风坡长度/m | 背风坡坡度/(°) | 背风坡长度/m | 翼长/m | 沙丘宽度/m | 摩阻风速/(m·s-1) |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.30 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.35 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.40 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.45 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.50 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.60 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.70 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.80 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 0.90 |
| 3.20 | 15.00 | 18.15 | 34.00 | 4.74 | 12.80 | 32.00 | 1.00 |
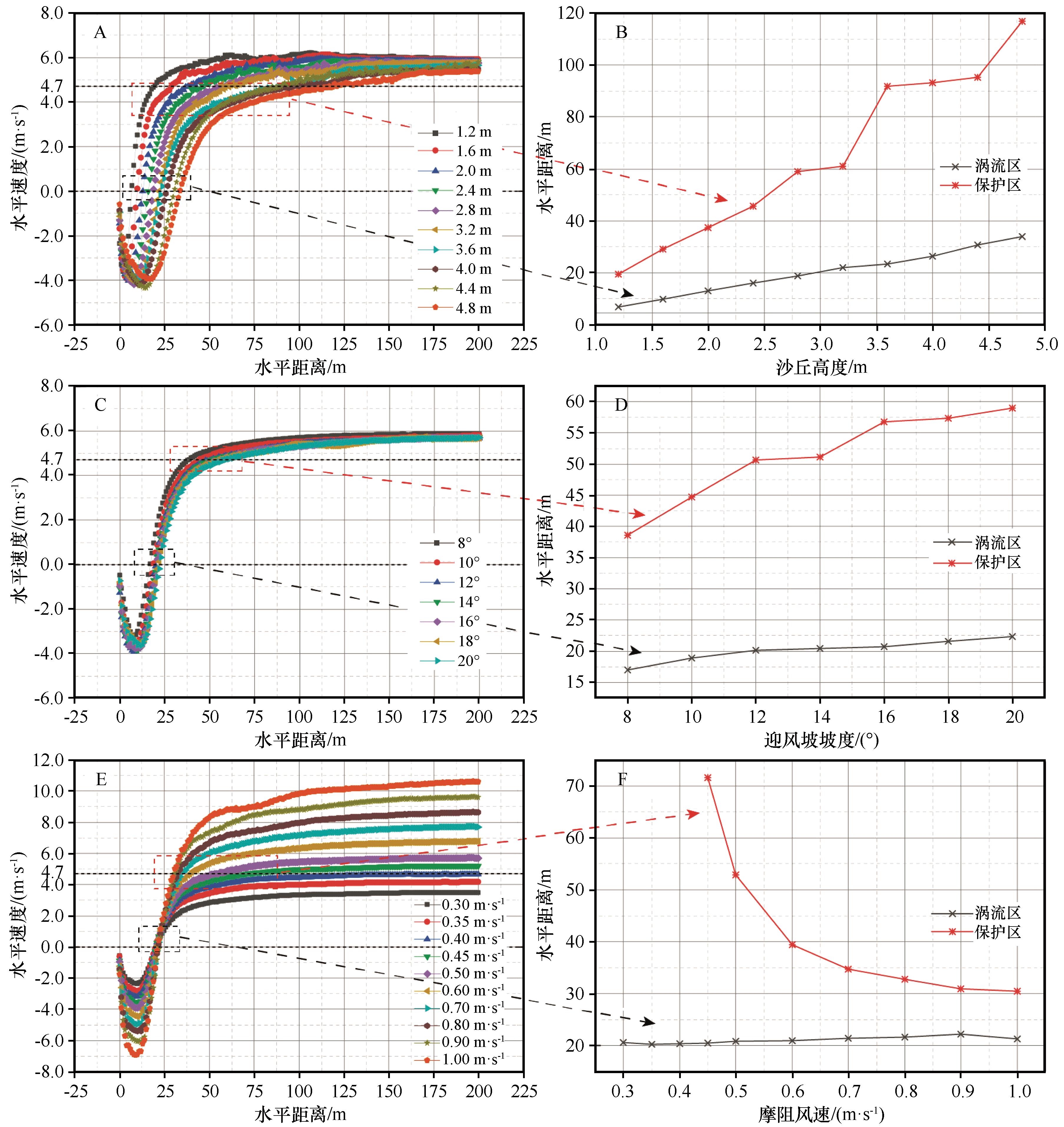
Fig. 3 The horizontal wind velocity distribution of the axis of the calculation domain at 0.1 m from the barchan dune surface under different working conditions (The zero point of the x-axis coordinates is located in the leeward slope toe of the dune). A: Different dune heights. C: Different windward slope gradients. E: Different inlet velocities. B, D and F are the relationship between vortex zone and protected zone and dune heights, windward slope gradients and inlet shear velocities, respectively
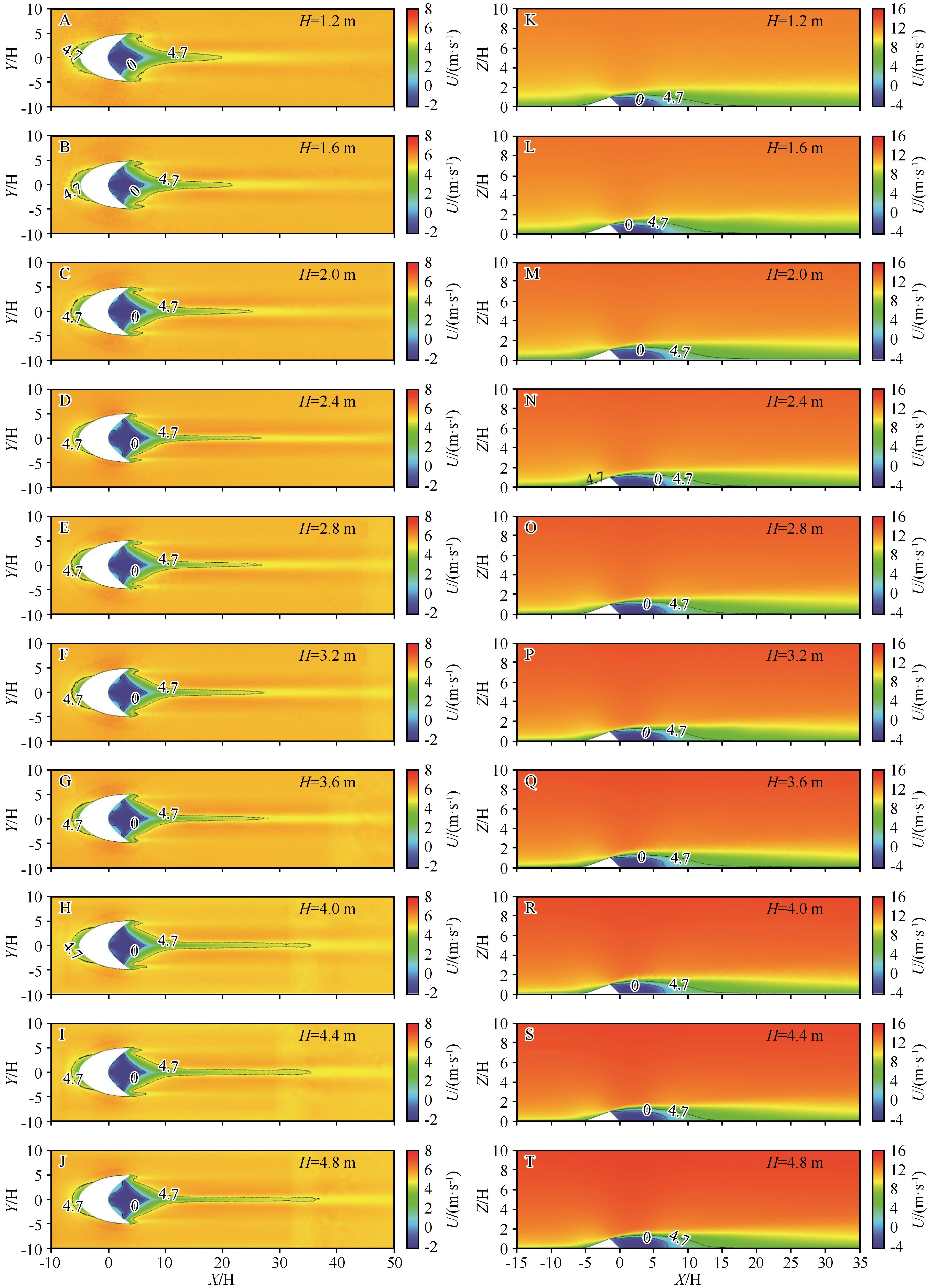
Fig. 4 Cloud map of horizontal velocity distribution of barchan dunes with different heights. A-J are horizontal velocity distribution cloud map at 0.1 m from the surface; K-T are horizontal velocity distribution cloud map at the longitudinal profile of the central axis of the dunes
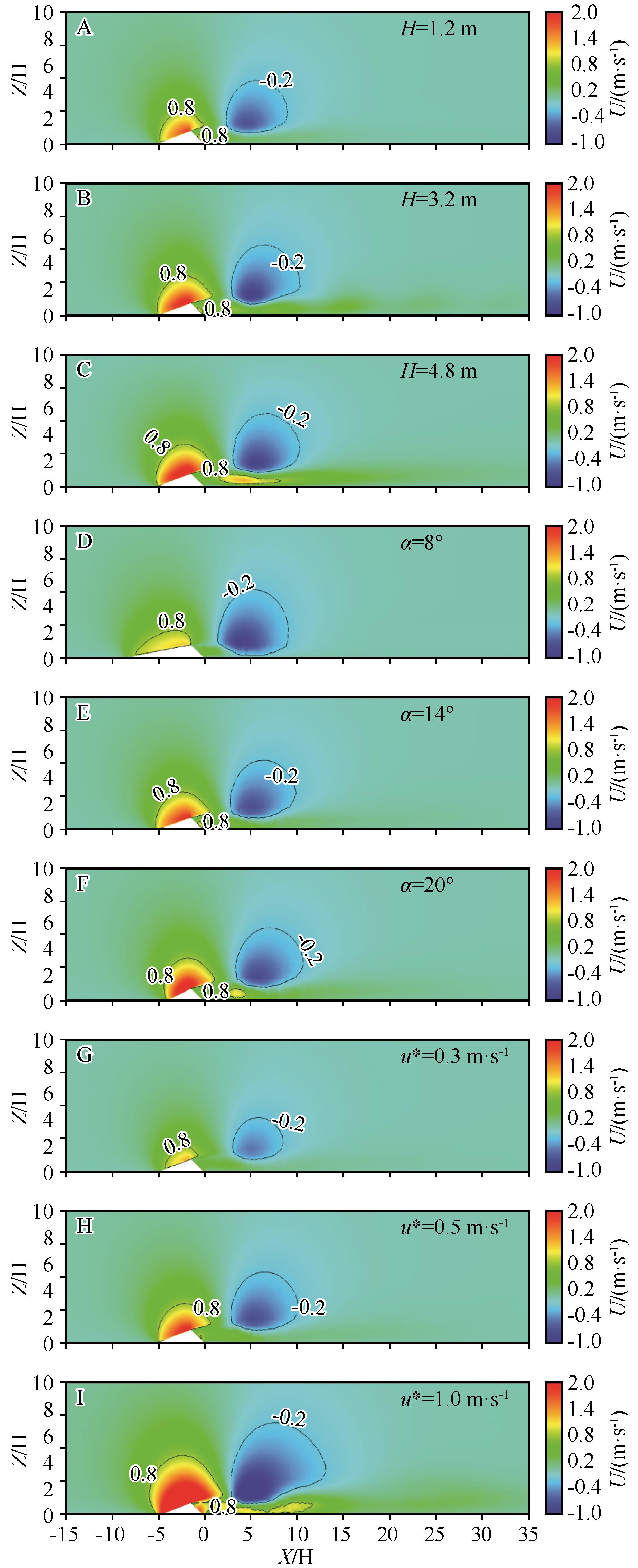
Fig. 5 Cloud map of vertical velocity distribution of barchan dunes under different working conditions. A-C: Different dune heights;D-F: Different windward slope gradients;G-I: Different inlet velocities
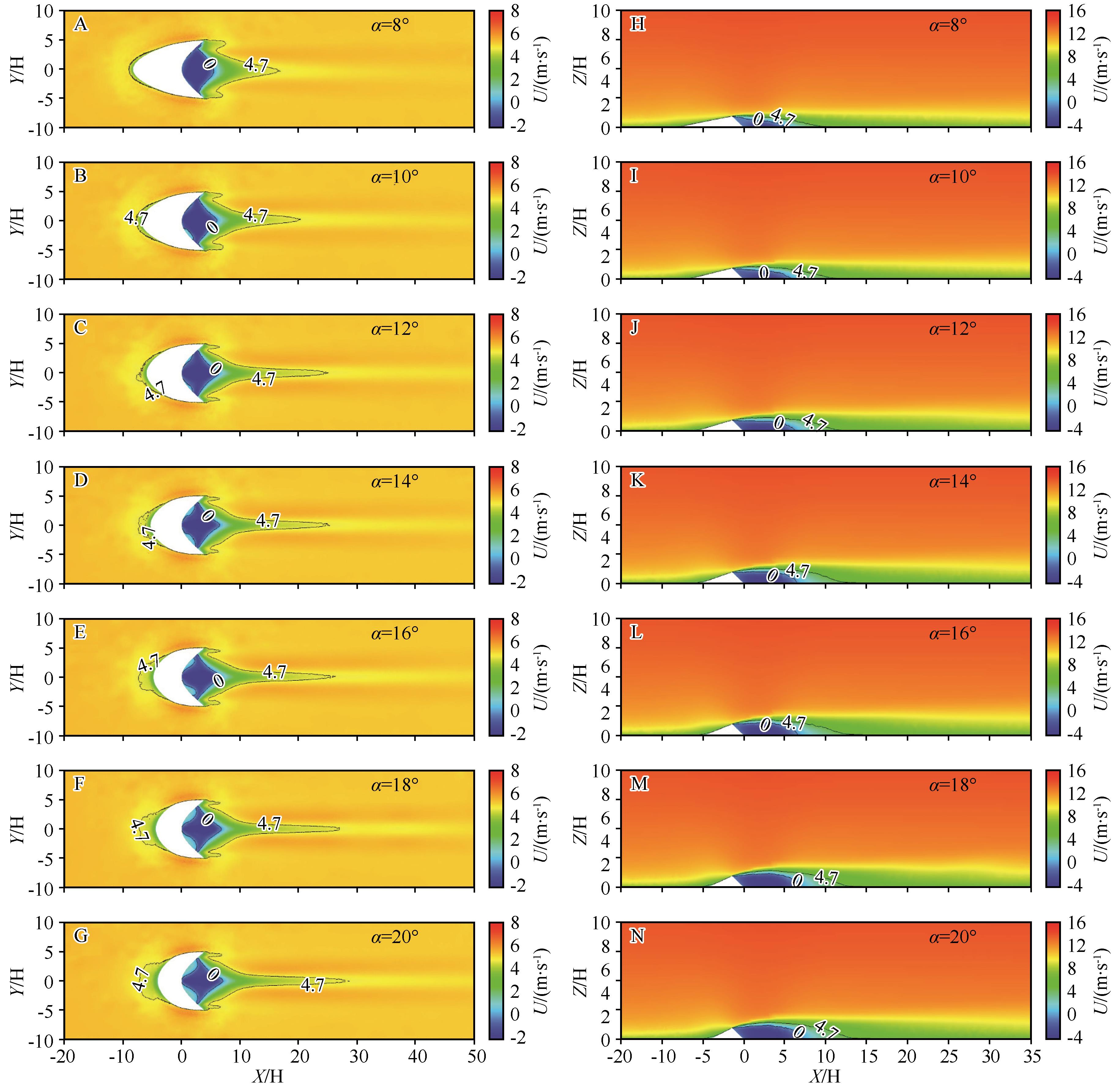
Fig. 6 Cloud map of horizontal velocity distribution of Barchan dunes with different windward slope gradients. A-G are horizontal velocity distribution cloud map at 0.1 m from the surface; H-N are horizontal velocity distribution cloud map at the longitudinal profile of the central axis of the dunes
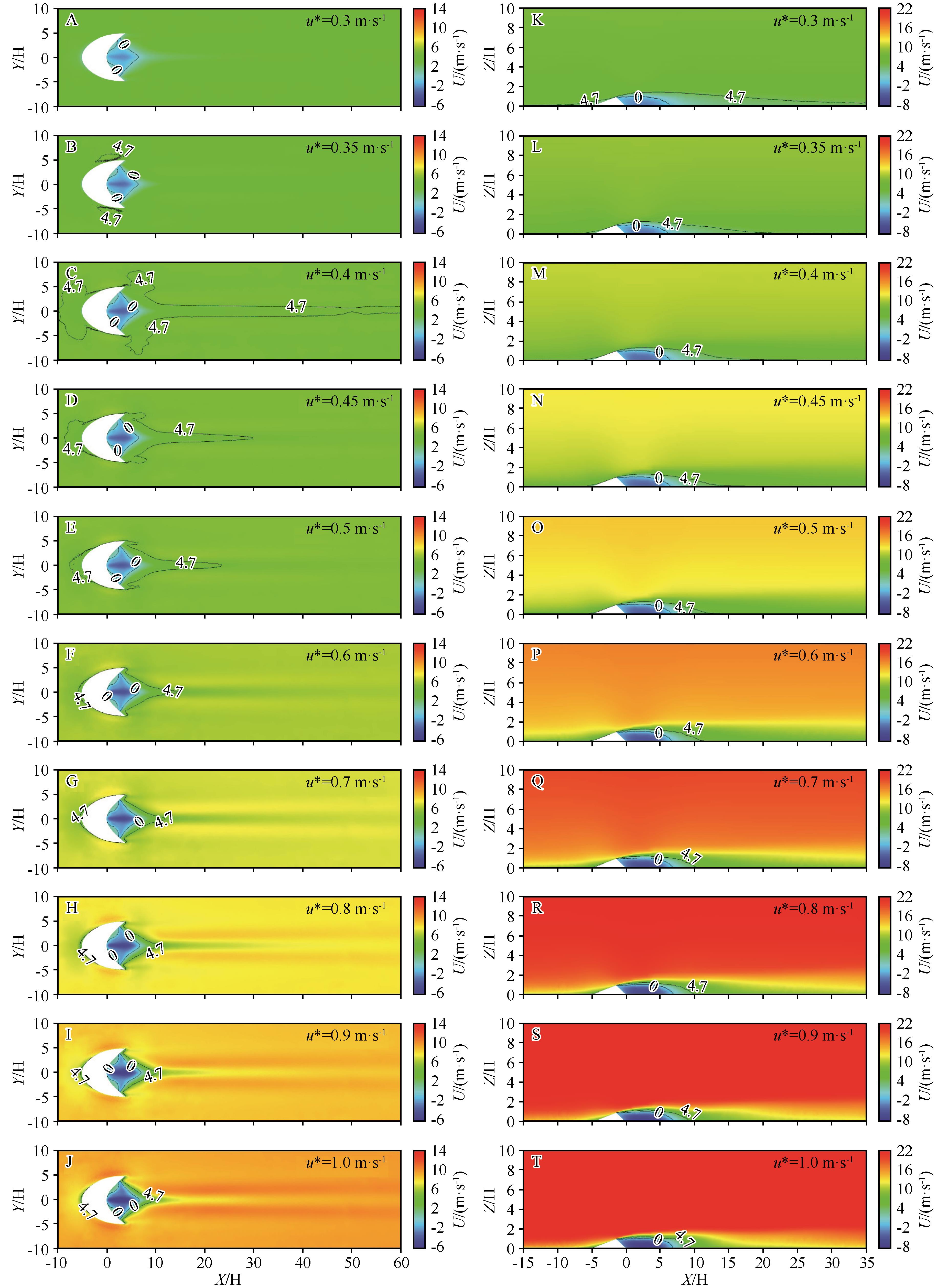
Fig. 7 Cloud map of horizontal velocity distribution of barchan dunes under different inlet velocities. A-J are horizontal velocity distribution cloud map at 0.1 m from the surface; K-T are horizontal velocity distribution cloud map at the longitudinal profile of the central axis of the dunes
| 1 | Charru F, Andreotti B, Claudin P.Sand ripples and dunes[J].Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics,2013,45:469. |
| 2 | Anderson R S.Grit and grain[J].Nature,1991,351(6329):706. |
| 3 | Hunter R E, Richmond B M, Alpha T R.Storm-controlled oblique dunes of the Oregon coast[J].Geological Society of America Bulletin,1983,94(12):1450-1465. |
| 4 | 丁国栋.风沙物理学[M].北京:中国林业出版社,2010:100-102. |
| 5 | Howard A D, Morton J B, Gad-El-Hak M,et al.Sand transport model of barchan dune equilibrium[J].Sedimentology,1978,25(3):307-338. |
| 6 | 吴正.风沙地貌学[M].北京:科学出版社,1987:87-89. |
| 7 | Faria R, Ferreira A D, Sismeiro J L,et al.Wind tunnel and computational study of the stoss slope effect on the aeolian erosion of transverse sand dunes[J].Aeolian Research,2011,3(3):303-314. |
| 8 | 李恒鹏,陈广庭,李波.新月形沙丘迎风坡气流加速模拟[J].中国沙漠,2001,21(1):27-30. |
| 9 | Cai D, Li S, Gao X,et al.Wind tunnel simulation of the aeolian erosion on the leeward side of barchan dunes and its implications for the spatial distribution patterns of barchan dunes[J].Catena,2021,207:105583. |
| 10 | Liu B, Qu J, Zhang W,et al.Numerical simulation of wind flow over transverse and pyramid dunes[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2011,99(8):879-888. |
| 11 | 钱广强,董治宝,罗万银,等.横向沙丘背风侧气流重附风洞模拟[J].中国沙漠,2008,28(1):16-20. |
| 12 | Baddock M C, Livingstone I, Wiggs G F S.The geomorphological significance of airflow patterns in transverse dune interdunes[J].Geomorphology,2007,87(4):322-336. |
| 13 | Venditti J G, Bauer B O.Turbulent flow over a dune:Green River,Colorado[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2005,30(3):289-304. |
| 14 | Walker I J, Nickling W G.Simulation and measurement of surface shear stress over isolated and closely spaced transverse dunes in a wind tunnel[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2003,28(10):1111-1124. |
| 15 | Hesp P A, Hastings K, Hesp P A.Width,height and slope relationships and aerodynamic maintenance of barchans[J].Geomorphology,1998,22(2):193-204. |
| 16 | Stam J M T.On the modelling of two-dimensional aeolian dunes[J].Sedimentology,1997,44(1):127-141. |
| 17 | Frank A, Kocurek G.Toward a model for airflow on the lee side of aeolian dunes[J].Sedimentology,1996,43(3):451-458. |
| 18 | McLean S R, Nelson J M, Wolfe S R.Turbulence structure over two-dimensional bed forms; implications for sediment transport[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Oceans,1994,99(C6):12729-12747. |
| 19 | Nelson J M, McLean S R, Wolfe S R.Mean flow and turbulence fields over two-dimensional bed forms[J].Water Resources Research,1993,29(12):3935-3953. |
| 20 | Weng W S, Hunt J C R, Carruthers D J,et al.Air flow and sand transport over sand-dunes[J].Acta Mechanica,1991:1-22. |
| 21 | Wippermann F K, Gross G.The wind-induced shaping and migration of an isolated dune:a numerical experiment[J].Boundary-layer Meteorology,1986,36(4):319-334. |
| 22 | 冯净雪,丁占良,尤莉,等.科尔沁沙地西部横向沙丘间的风况和输沙势[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(4):110-119. |
| 23 | 殷婕,哈斯额尔敦,安晶,等.鄂尔多斯高原油蒿(Artemisia ordosica)灌丛沙堆风沙气流结构及其地貌学意义[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(1):184-195. |
| 24 | 潘凯佳,张正偲,梁爱民.反向沙丘近地层气流变化及其对沙丘形态的影响[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(2):1-8. |
| 25 | 王晓旭,严平,王勇,等.坡度和坡形对爬坡沙丘形成影响的风洞模拟实验[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(6):118-126. |
| 26 | 刘旭阳,宁文晓,王振亭.新月形沙丘脊线处的风沙流结构[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(6):76-82. |
| 27 | Dong Z, Qinan G, Lu P,et al.Turbulence fields in the lee of two-dimensional transverse dunes simulated in a wind tunnel[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2009,34(2):204-216. |
| 28 | 杨岩岩,刘连友,屈志强,等.新月形沙丘研究进展[J].地理科学,2014,34(1):76-83. |
| 29 | Parsons D R, Wiggs G F S, Walker I J,et al.Numerical modelling of airflow over an idealised transverse dune[J].Environmental Modelling & Software:with Environment Data News,2004,19(2):153-162. |
| 30 | Smyth T A G, Jackson D W T, Cooper J A G,et al.Computational fluid dynamic modelling of three-dimensional airflow over dune blowouts[J].Journal of Coastal Research,2011,SI(64):314-318. |
| 31 | Smith A B, Jackson D W T, Cooper J A G.Three-dimensional airflow and sediment transport patterns over barchan dunes[J].Geomorphology,2017,278:28-42. |
| 32 | Launder B E, Spalding D B.The numerical computation of turbulent flows[J].Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering,1974,3(2):269-289. |
| 33 | Smyth T A G.A review of Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) airflow modelling over aeolian landforms[J].Aeolian Research,2016,22:153-164. |
| 34 | Yakhot V, Thangam S, GatskI T B,et al.Development of turbulence models for shear flows by a double expansion technique[J].Physics of Fluids,1992,4(7):1510-1520. |
| 35 | Yakhot V, Orszag S A.Renormalization group analysis of turbulence:I.basic theory[J].Journal of Scientific Computing,1986,1(1):3-51. |
| 36 | Hargreaves D M, Wright N G.On the use of the k-ε model in commercial CFD software to model the neutral atmospheric boundary layer[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2007,95(5):355-369. |
| 37 | Richards P J, Norris S E.Appropriate boundary conditions for computational wind engineering models revisited[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2011,99(4):257-266. |
| 38 | Bagnold R A.The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes[M].London,UK:Chapmann and Hall,1941:85-95. |
| 39 | Sauermann G, Rognon P, Poliakov A,et al.The shape of the barchan dunes of Southern Morocco[J].Geomorphology,2000,36(1/2):47-62. |
| 40 | Sweet M L, Kocurek G.An empirical-model of aeolian dune lee-face air-flow[J].Sedimentology,1990,37(6):1023-1038. |
| 41 | Walker I J, Nickling W G.Dynamics of secondary airflow and sediment transport over and in the lee of transverse dunes[J].Progress in Physical Geography-Earth and Environment,2002,26(1):47-75. |
| 42 | Hersen P, Andersen K H, Elbelrhiti H,et al.Corridors of barchan dunes:stability and size selection[J].Physical Review E,2004,69(1):11304. |
| 43 | Duran O, Parteli E J R, Herrmann H J.A continuous model for sand dunes;review,new developments and application to barchan dunes and barchan dune fields[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2010,35(13):1591-1600. |
| 44 | Worman S L, Murray A B, Littlewood R,et al.Modeling emergent large-scale structures of barchan dune fields[J].Geology,2013,41(10):1059-1062. |
| 45 | Elbelrhiti H, Claudin P, Andreotti B.Field evidence for surface-wave-induced instability of sand dunes[J].Nature,2005,437(7059):720-723. |
| 46 | Katsuki A, Kikuchi M.Simulation of barchan dynamics with inter-dune sand streams[J].New Journal of Physics,2011,13(6):63049. |
| [1] | Tong Zou, Zhuanling Yang, Jinzhi Wei, Yingying Liao, Xuegang Xing, Guangqiang Qian, Xiaolei Liang. Migration and influencing factors of barchan dunes in southwestern Qaidam Basin, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(1): 212-221. |
| [2] | Li Zhixing, Li Zhizhong, Jin Jianhui, Zheng Fei, Zhang Wenjing, Bai Li. Spatial-temporal variation of drift potential and dune morphology evolution during 2008-2018 in Changli coast of Hebei, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(3): 94-105. |
| [3] | Chen Guoxiang, Dong Zhibao, Li Chao, Xiao Weiqiang, Yang Junhuai, Shi Weikang, Zhang Yuemin. Surface Texture of Quartz Grains from Dune Sediments of Northern Qarhan Salt Lake of China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(5): 954-962. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech