
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 50-60.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00074
Previous Articles Next Articles
Meng Zhang( ), Liqiang Kang(
), Liqiang Kang( ), Xiaomei Wang
), Xiaomei Wang
Received:2023-03-28
Revised:2023-05-16
Online:2024-01-20
Published:2023-12-26
Contact:
Liqiang Kang
CLC Number:
Meng Zhang, Liqiang Kang, Xiaomei Wang. Effect of staggered and square arrangements on surface shear stress and sand transport rate on tree vegetated surface[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(1): 50-60.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00074
| 排列方式 | 植株密度/(株·m-2) | 行距/m | 株距/m |
|---|---|---|---|
| 交错 | 18 | 0.167 | 0.333 |
| 32 | 0.125 | 0.250 | |
| 50 | 0.100 | 0.200 | |
| 矩形 | 18 | 0.236 | 0.236 |
| 32 | 0.177 | 0.177 | |
| 50 | 0.141 | 0.141 |
Table 1 The row spacing and plant spacing under different plant densities and arrangements
| 排列方式 | 植株密度/(株·m-2) | 行距/m | 株距/m |
|---|---|---|---|
| 交错 | 18 | 0.167 | 0.333 |
| 32 | 0.125 | 0.250 | |
| 50 | 0.100 | 0.200 | |
| 矩形 | 18 | 0.236 | 0.236 |
| 32 | 0.177 | 0.177 | |
| 50 | 0.141 | 0.141 |
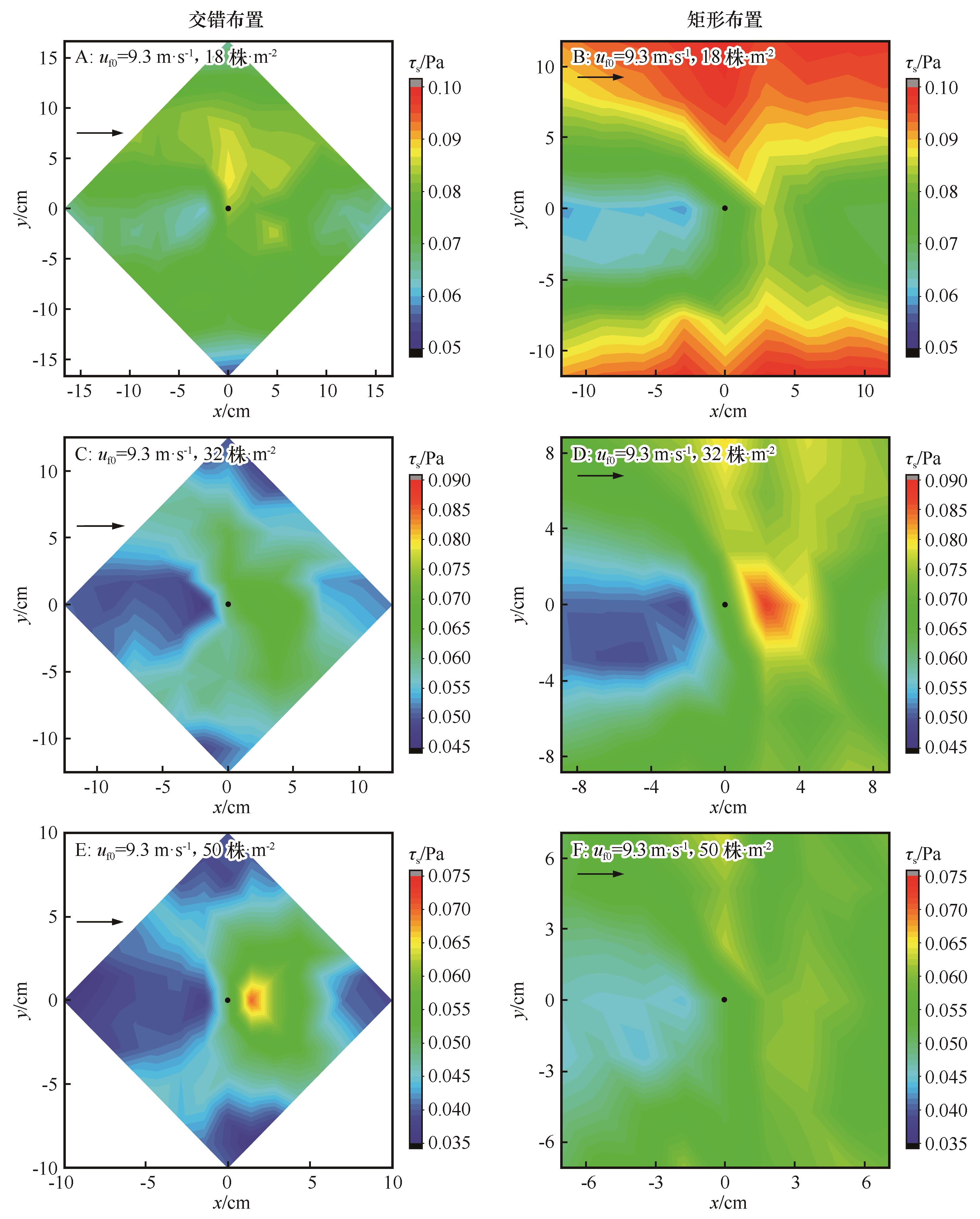
Fig.6 Comparison of surface shear stress distribution between staggered (A, C, E) and square (B, D, F) arrangements in different plant densities (the black dot is the position of plant model, uf0 is the incoming wind speed, τs is the surface shear stress)
| 植株密度 /(株·m-2) | uf0 /(m·s-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | 8.0 | 0.915 | 1.035 | 1.017 |
| 9.3 | 0.899 | 1.038 | 1.017 | |
| 10.8 | 0.902 | 1.037 | 1.018 | |
| 12.2 | 0.903 | 1.037 | 1.018 | |
| 13.6 | 0.881 | 1.040 | 1.017 | |
| 32 | 8.0 | 0.862 | 1.071 | 1.050 |
| 9.3 | 0.844 | 1.064 | 1.042 | |
| 10.8 | 0.836 | 1.055 | 1.035 | |
| 12.2 | 0.839 | 1.049 | 1.029 | |
| 13.6 | 0.835 | 1.043 | 1.024 | |
| 50 | 8.0 | 0.828 | 1.101 | 1.081 |
| 9.3 | 0.833 | 1.102 | 1.083 | |
| 10.8 | 0.846 | 1.103 | 1.086 | |
| 12.2 | 0.835 | 1.105 | 1.088 | |
| 13.6 | 0.847 | 1.105 | 1.089 |
Table 2 Ratios of average surface shear stress, shear stress acting on roughness elements and total shear stress in staggered array to that in square array
| 植株密度 /(株·m-2) | uf0 /(m·s-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | 8.0 | 0.915 | 1.035 | 1.017 |
| 9.3 | 0.899 | 1.038 | 1.017 | |
| 10.8 | 0.902 | 1.037 | 1.018 | |
| 12.2 | 0.903 | 1.037 | 1.018 | |
| 13.6 | 0.881 | 1.040 | 1.017 | |
| 32 | 8.0 | 0.862 | 1.071 | 1.050 |
| 9.3 | 0.844 | 1.064 | 1.042 | |
| 10.8 | 0.836 | 1.055 | 1.035 | |
| 12.2 | 0.839 | 1.049 | 1.029 | |
| 13.6 | 0.835 | 1.043 | 1.024 | |
| 50 | 8.0 | 0.828 | 1.101 | 1.081 |
| 9.3 | 0.833 | 1.102 | 1.083 | |
| 10.8 | 0.846 | 1.103 | 1.086 | |
| 12.2 | 0.835 | 1.105 | 1.088 | |
| 13.6 | 0.847 | 1.105 | 1.089 |
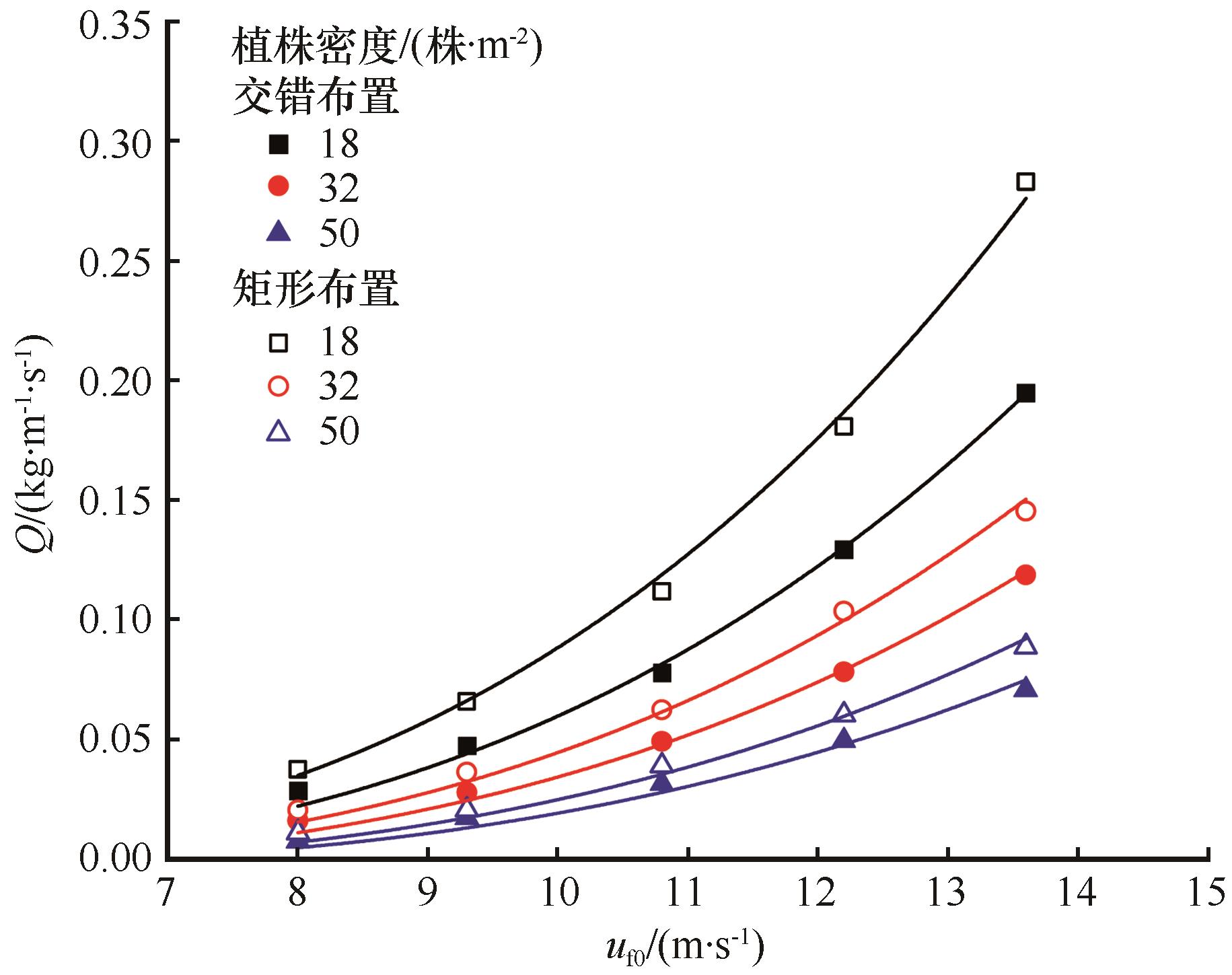
Fig.12 Variation of sand transport rate on vegetated surface with the incoming wind speed in staggered and square arrays (the fitting curve is Eq.(3))
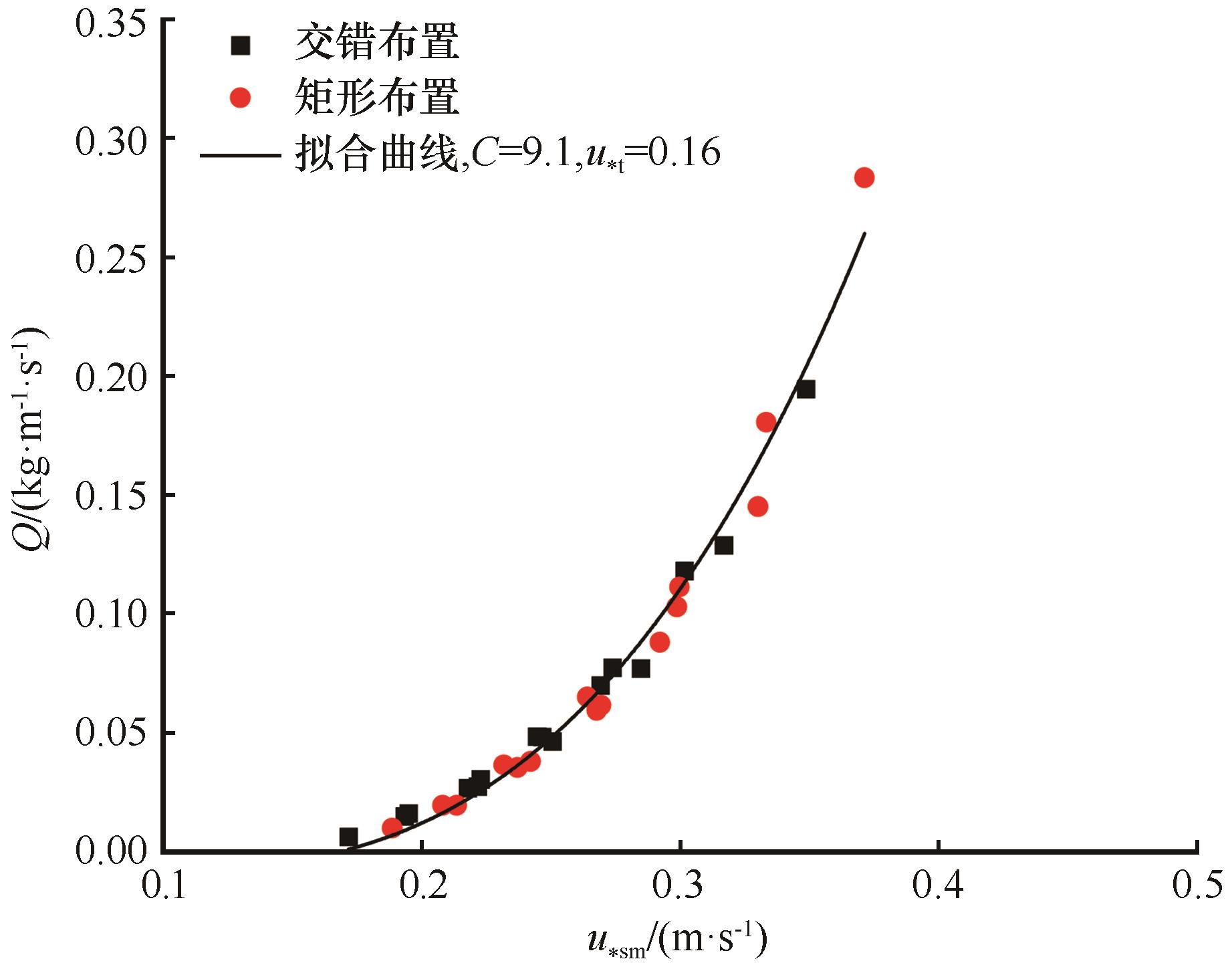
Fig.14 Variation of sand transport rate on vegetated surface with the average surface friction velocity in staggered and square arrays (the fitting curve is Eq.(4))
| 1 | Wolfe S A, Nickling W G.The protective role of sparse vegetation in wind erosion[J].Progress in Physical Geography,1993,17(1):50-68. |
| 2 | Cheng H, Liu C C, Kang L Q.Experimental study on the effect of plant spacing,number of rows and arrangement on the airflow field of forest belt in a wind tunnel[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2020,178:104169. |
| 3 | 屈志强,张莉,丁国栋,等.不同配置方式沙蒿灌丛对土壤风蚀影响的对比分析[J].水土保持学报,2008,22(3):1-4. |
| 4 | 夏建新,石学峰,吉祖稳.植被覆盖条件下地表输沙率模型[J].应用基础与工程科学学报,2006,14(2):218-227. |
| 5 | 杨文斌,卢琦,吴波,等.低覆盖度不同配置灌丛内风流结构与防风效果的风洞实验[J].中国沙漠,2007,27(5):791-796. |
| 6 | 杨文斌,杨红艳,卢琦,等.低覆盖度灌木群丛的水平配置格局与固沙效果的风洞试验[J].生态学报,2008,28(7):2998-3007. |
| 7 | 徐高兴,徐先英,王立,等.梭梭不同密度与配置固沙效果风洞模拟试验[J].干旱区资源与环境,2019,33(9):189-195. |
| 8 | Brown S, Nickling W G, Gillies J A.A wind tunnel examination of shear stress partitioning for an assortment of surface roughness distributions[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,2008,113:F02S06. |
| 9 | Cheng H, Liu C C, Zou X Y,et al.Wind erosion rate for vegetated soil cover:a prediction model based on surface shear strength[J].Catena,2020,187:104398. |
| 10 | Webb N P, Chappell A, LeGrand S L,et al.A note on the use of drag partition in aeolian transport models[J].Aeolian Research,2020,42:100560. |
| 11 | Walter B, Voegeli C, Horender S.Estimating sediment mass fluxes on surfaces sheltered by live vegetation[J].Boundary-Layer Meteorology,2017,163:273-286. |
| 12 | Zou X Y, Li H R, Kang L Q,et al.Soil wind erosion rate on rough surfaces:a dynamical model derived from an invariant pattern of the shear-stress probability density function of the soil surface[J].Catena,2022,219:106633. |
| 13 | Webb N P, Okin G S, Brown S.The effect of roughness elements on wind erosion:the importance of surface shear stress distribution[J].Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres,2014,119:6066-6084. |
| 14 | Kang L Q, Zhang J J, Yang Z C,et al.Experimental investigation on shear-stress partitioning for flexible plants with approximately zero basal-to-frontal area ratio in a wind tunnel[J].Boundary-Layer Meteorology,2018,169:251-273. |
| 15 | Raupach M R, Gillette D A, Leys J F.The effect of roughness elements on wind erosion threshold [J].Journal of Geophysical Research,1993,98:3023-3029. |
| 16 | Marshall J K.Drag measurements in roughness arrays of varying density and distribution[J].Agricultural Meteorology,1971,8:269-292. |
| 17 | Crawley D M, Nickling W G.Drag partition for regularly-arrayed rough surfaces[J].Boundary-Layer Meteorology,2002,107:445-468. |
| 18 | Walter B, Gromke C, Lehning M.Shear-stress partitioning in live plant canopies and modifications to Raupach's model[J].Boundary-Layer Meteorology,2012,144:217-241. |
| 19 | Musick H B, Trujillo S M, Truman C R.Wind-tunnel modelling of the influence of vegetation structure on saltation threshold[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,1996,21:589-605. |
| [1] | Liqiang Kang, Qin Zhang, Meng Zhang. Characteristics of surface shear stress distribution around a slender flexible plant model in wind tunnel boundary layer [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 128-134. |
| [2] | Zhengcai Zhang, Kaijia Pan, Yan Zhang, Lanying Han. Sand transport characteristics above gobi surface during a dust storm in northern China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 130-138. |
| [3] | Liqiang Kang, Caiyun Li, Junjie Zhang, Xueyong Zou. Characteristics of instantaneous surface shear stress distribution at flexible plant surface [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(5): 49-56. |
| [4] | Yang Huan, Li Yuqiang, Wang Xuyang, Niu Yayi, Gong Xiangwen, Yu Peidong. Characteristics of Aeolian Sediment Flux Structure over Different Underlying Surfaces in Semi-arid Area [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(6): 1144-1152. |
| [5] | Liu Fang, Hao Yuguang, Xin Zhiming, Chen Hailing, Xu Jun, Zhao Yingming. The Surface Aeolian-sand Flow Structure in the Northeastern Margin of the Ulanbuh Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2014, 34(5): 1200-1207. |
| [6] | Wu Shengzhi, Guo Weijin. Numerical Simulation of Saltation on the Windward Side of Sand Dunes [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2014, 34(2): 307-311. |
| [7] | . A Wind Tunnel Experiment of Aeolian Sand Transport over Wetted Coastal Sand Surface [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2012, 32(6): 1512-1521. |
| [8] | LI De-Lu, MAN Duo-qing, ZHU Guo-qing, WEI Lin-yuan, TANG Jin-nian. Aeolian-sand Flow Structure Characteristics at Different Positions in Inter-dune Lowland [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2012, 32(5): 1210-1215. |
| [9] | XU Man-hou, LIU Tong, ZHAO Xin-jun, ZHANG Wei-bin. Study on the Collaborative Windbreak Effect and Optimization Configuration Model of Shelterbelt and Natural Vegetation in an Oasis-desert Ecotone in Junggar Basin [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2012, 32(5): 1224-1232. |
| [10] | WU Xiao-xu;ZOU Xue-yong;WANG Ren-de;ZHAO Jing-yan;CHENG Hong;QIAN Jiang. Aeolian Movement Characteristics over Different Underlying Surfaces in Mu Us Sandy Land [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2011, 31(4): 828-835. |
| [11] | HU Wen-wen;WANG Ping. A General Model Predicting the Streamwise Sand Transport Rate with Saltating Sand Charged [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2011, 31(3): 613-617. |
| [12] | LIU Ben-li;ZHANG Wei-min;LIU Xiao-ning;ZHANG Guo-bin;QIU Fei;ZHAN Hong-tao. Field Measurements of Sand Transport Rate Change under Easterly Wind Condition over Gobi Land atop Mogao Grottoes [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2010, 30(3): 516-521. |
| [13] | ZHAO Man-quan;FU Li-hong;WANG Jin-lian;DONG Mei. Experimental Study on Sampler Efficiency of Whirl Type Separation Sand Sampler in Wind Tunnel [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2009, 29(6): 1009-1014. |
| [14] | LIU Shu-lin;WANG Tao;GUO Jian. Characteristics of Blown Sand Activities in Hunshandake Sandy Land in Spring [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2006, 26(3): 356-361. |
| [15] | LI Zhen-shan;ZHANG Qi-feng. Evolution of Streamwise Sand Transport with Distance [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2006, 26(2): 189-193. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech