
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 172-184.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00164
Hanyong Ding1( ), Hanqing Kang1,2(
), Hanqing Kang1,2( ), Jingjing Lv1
), Jingjing Lv1
Received:2023-08-24
Revised:2023-11-24
Online:2024-03-20
Published:2024-03-19
Contact:
Hanqing Kang
CLC Number:
Hanyong Ding, Hanqing Kang, Jingjing Lv. Impact of soil moisture products on the simulation results of super sandstorms during March of 2021 in North China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(2): 172-184.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00164
| 数据产品 | 产品简介 | 分辨率 | 研究变量 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 时间 | 空间 | |||
| 基于卫星反演产品 | ||||
| AMSR2-JAXA | 日本宇宙航空研究开发机构(JAXA)根据搭载在全球变化观测任务——水资源1号卫星(GCOM-W1)上的用于测量地球表面的先进微波扫描辐射计(AMSR),基于频率和偏振指数查找表的算法开发的土壤湿度产品[ | ~12 h | 0.1° | Geophysical Data |
| AMSR2-LPRM | 荷兰阿姆斯特丹自由大学联合美国航空航天局(NASA)根据AMSR数据开发的陆表参数反演模型算法(LPRM)土壤湿度产品 | ~12 h | 0.1° | soil_moisture_x |
| SMAP L3 | 土壤湿度主-被动探测卫星(SMAP)基于L2观测数据的“每日增强全球复合射频”土壤湿度数据(SMAP_L3_SM_P_E) | 1 d | 9 km | soil_moisture_scav |
| SMOS | 土壤湿度与海洋盐度(SMOS)是ESA地球探索者(Earth Explorers)项目的第二项任务,观测陆地表层(前几厘米)的土壤湿度和海洋表面盐度[ | ~1 h | ~40 km | Soil_Moisture |
| “开放环”模型产品 | ||||
| EAR5-Land | 欧洲中期天气预报中心(ECMWF)第五代陆面再分析数据集(ERA5-Land)是专门针对陆地过程的高分辨率再分析数据产品,受到ERA5气象场的驱动,在用于陆地表面交换的单一碳-水分块状欧洲中心方案模型(CHTESSEL)模拟下生成,未与集成预报系统(IFS)的大气模块或海洋波浪模型耦合[ | 1 h | 0.1° | swvl1 |
| GLDAS | 全球陆面数据同化系统 (GLDAS) 由NASA、戈达德太空飞行中心(GSFC)、美国国家海洋和大气管理局(NOAA)和国家环境预报中心(NCEP)的科学家共同开发[ | 3 h | 0.25° | SoilMoi0_10cm_inst |
| 经过卫星数据同化的模型产品 | ||||
| ERA5 | 欧洲中期天气预报中心(ECMWF)发布的第五代再分析数据集[ | 1 h | 0.25° | SWVL1_GDS0_DBLY |
| GLEAM | 全球陆地蒸发阿姆斯特丹模型(GLEAM)是一套专门用于通过卫星数据估算陆地蒸发和根区土壤湿度的算法。在GLEAM中,土壤湿度的卫星观测值与方程预测的第一土壤层的模拟水分含量同化[ | 1 d | 0.25° | SMsurf |
| NCEP/FNL | 美国国家环境预报中心再分析数据集(NCEP/FNL),基于全球陆面数据同化系统(GLDAS) | 6 h | 0.25° | SOILW_P0_2L106_GLL0 |
| SMAP L4 | 土壤湿度主-被动探测卫星(SMAP)L4产品通过将SMAP数据集中的亮温数据同化到陆面模型中而获得[ | 3 h | 9 km | sm_surface_analysis |
Table 1 Classification and attributes of soil moisture product datasets
| 数据产品 | 产品简介 | 分辨率 | 研究变量 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 时间 | 空间 | |||
| 基于卫星反演产品 | ||||
| AMSR2-JAXA | 日本宇宙航空研究开发机构(JAXA)根据搭载在全球变化观测任务——水资源1号卫星(GCOM-W1)上的用于测量地球表面的先进微波扫描辐射计(AMSR),基于频率和偏振指数查找表的算法开发的土壤湿度产品[ | ~12 h | 0.1° | Geophysical Data |
| AMSR2-LPRM | 荷兰阿姆斯特丹自由大学联合美国航空航天局(NASA)根据AMSR数据开发的陆表参数反演模型算法(LPRM)土壤湿度产品 | ~12 h | 0.1° | soil_moisture_x |
| SMAP L3 | 土壤湿度主-被动探测卫星(SMAP)基于L2观测数据的“每日增强全球复合射频”土壤湿度数据(SMAP_L3_SM_P_E) | 1 d | 9 km | soil_moisture_scav |
| SMOS | 土壤湿度与海洋盐度(SMOS)是ESA地球探索者(Earth Explorers)项目的第二项任务,观测陆地表层(前几厘米)的土壤湿度和海洋表面盐度[ | ~1 h | ~40 km | Soil_Moisture |
| “开放环”模型产品 | ||||
| EAR5-Land | 欧洲中期天气预报中心(ECMWF)第五代陆面再分析数据集(ERA5-Land)是专门针对陆地过程的高分辨率再分析数据产品,受到ERA5气象场的驱动,在用于陆地表面交换的单一碳-水分块状欧洲中心方案模型(CHTESSEL)模拟下生成,未与集成预报系统(IFS)的大气模块或海洋波浪模型耦合[ | 1 h | 0.1° | swvl1 |
| GLDAS | 全球陆面数据同化系统 (GLDAS) 由NASA、戈达德太空飞行中心(GSFC)、美国国家海洋和大气管理局(NOAA)和国家环境预报中心(NCEP)的科学家共同开发[ | 3 h | 0.25° | SoilMoi0_10cm_inst |
| 经过卫星数据同化的模型产品 | ||||
| ERA5 | 欧洲中期天气预报中心(ECMWF)发布的第五代再分析数据集[ | 1 h | 0.25° | SWVL1_GDS0_DBLY |
| GLEAM | 全球陆地蒸发阿姆斯特丹模型(GLEAM)是一套专门用于通过卫星数据估算陆地蒸发和根区土壤湿度的算法。在GLEAM中,土壤湿度的卫星观测值与方程预测的第一土壤层的模拟水分含量同化[ | 1 d | 0.25° | SMsurf |
| NCEP/FNL | 美国国家环境预报中心再分析数据集(NCEP/FNL),基于全球陆面数据同化系统(GLDAS) | 6 h | 0.25° | SOILW_P0_2L106_GLL0 |
| SMAP L4 | 土壤湿度主-被动探测卫星(SMAP)L4产品通过将SMAP数据集中的亮温数据同化到陆面模型中而获得[ | 3 h | 9 km | sm_surface_analysis |
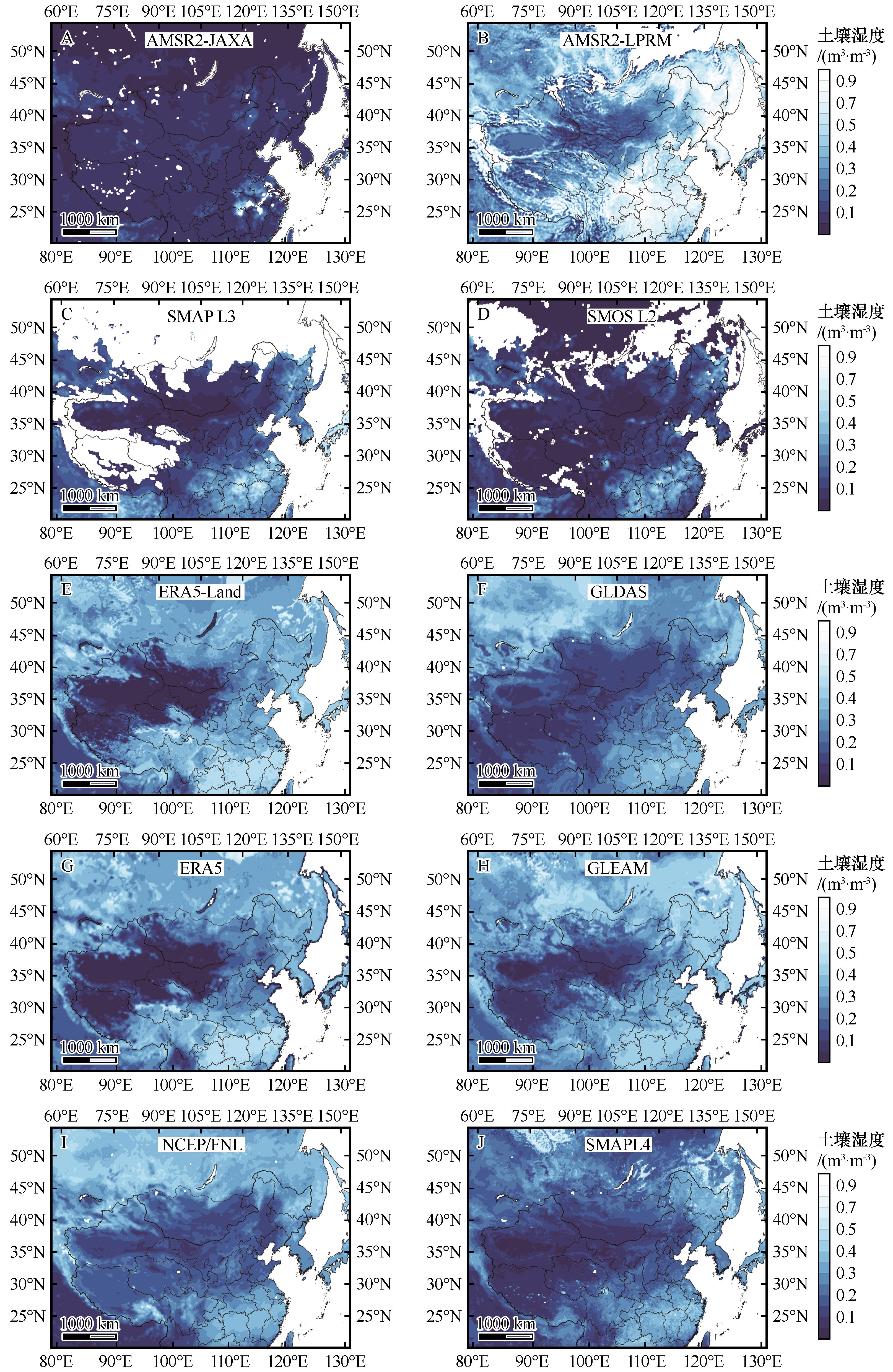
Fig.2 Average spatial distribution of soil moisture for the products AMSR2-JAXA (A),AMSR2-LPRM (B), SMAP L3 (C), SMOS L2 (D), ERA5-Land (E), GLDAS (F), ERA5 (G), GLEAM (H), NCEP/FNL (I), SMAP L4(J) from March 7 to March 31, 2021
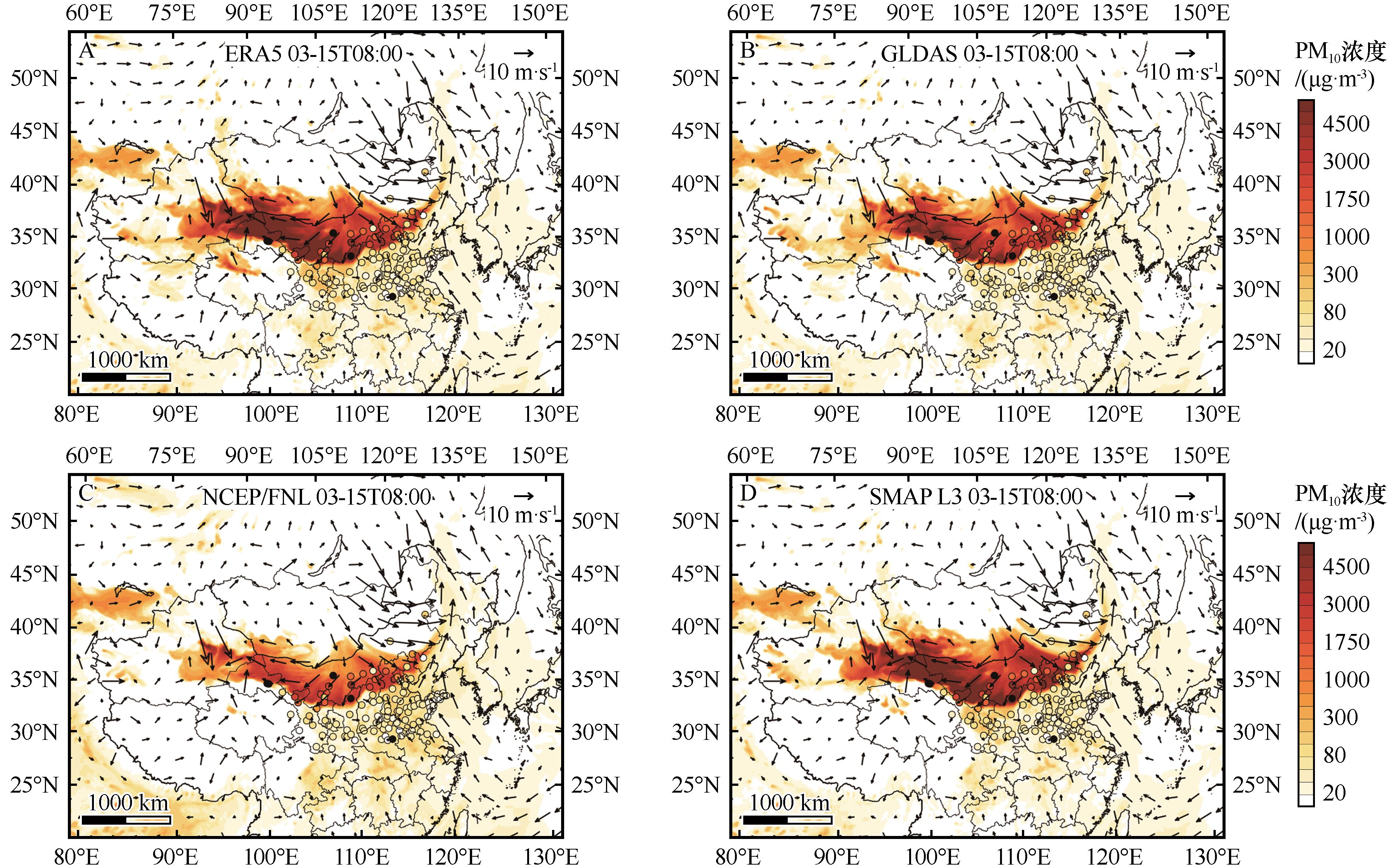
Fig.4 The PM10 concentration simulation results of ERA5(A), GLDAS(B), NCEP/FNL(C), SMAP L3 (D) on March 15, 2021 at 08:00, compared with the observed values at 110 sites (the circles in the figure represent the observed results at city sites, the colored contours represents the simulation results, using a common color bar)
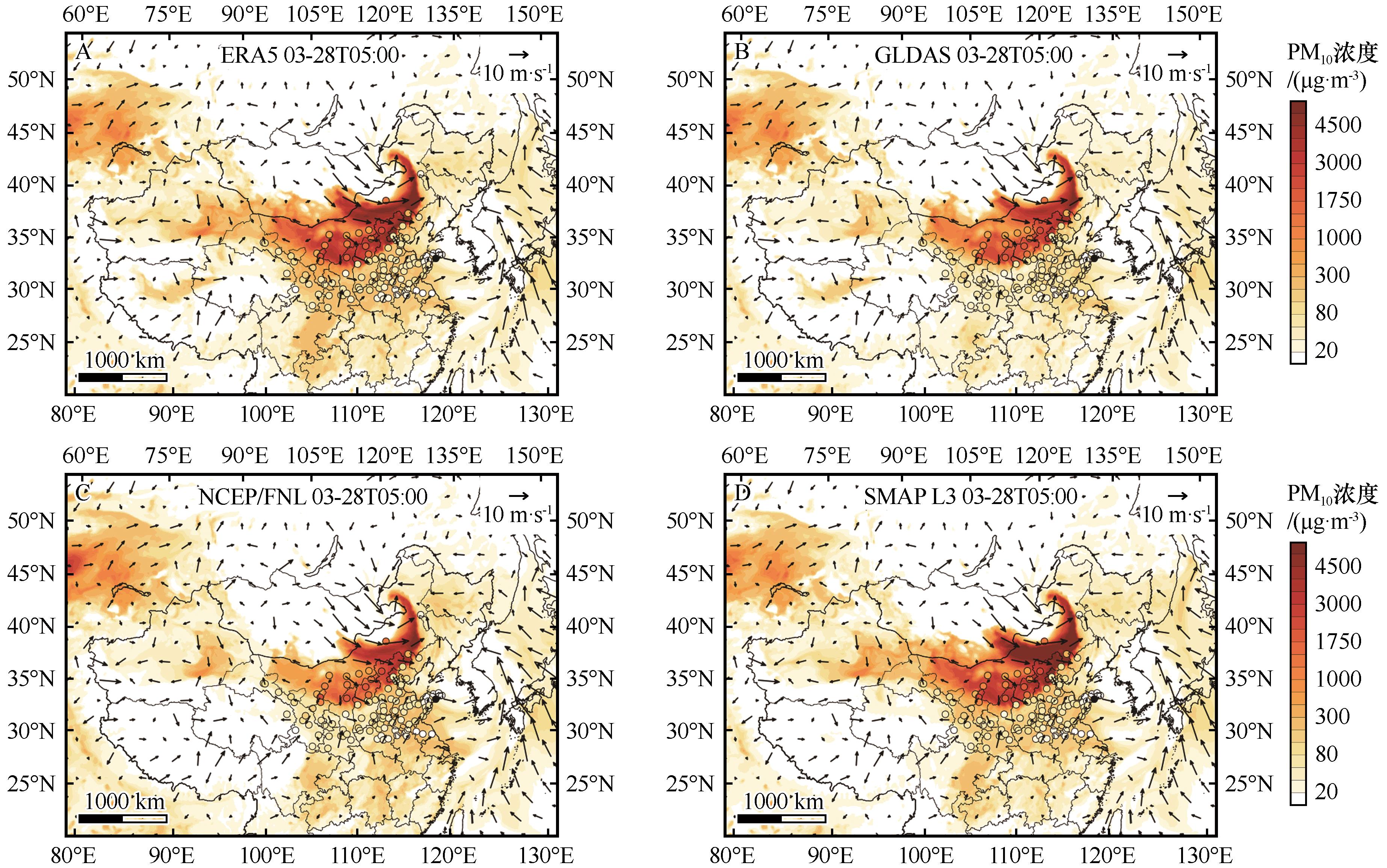
Fig.5 The PM10 concentration simulation results of ERA5 (A), GLDAS (B), NCEP/FNL (C), SMAP L3 (D) on March 28, 2021 at 05:00, compared with the observed values at 110 sites (the circles in the figure represent the observed results at city sites, the colored contours represents the simulation results, using a common color bar)
土壤湿度 数据产品 | 第一次沙尘暴过程 | 第二次沙尘暴过程 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | Bias /(μg·m-3) | RMSE /(μg·m-3) | NMB /% | FGE | R | Bias /(μg·m-3) | RMSE /(μg·m-3) | NMB /% | FGE | |
| ERA5 | 0.55 | -199.27 | 915.72 | -32.08 | 0.14 | 0.76 | 86.84 | 535.14 | 26.86 | 0.11 |
| GLDAS | 0.60 | -278.67 | 879.84 | -37.31 | 0.15 | 0.78 | -139.72 | 501.01 | -28.88 | 0.16 |
| NCEP/FNL | 0.54 | -434.60 | 965.30 | -58.64 | 0.19 | 0.75 | -161.01 | 550.59 | -31.74 | 0.18 |
| SMAP L3 | 0.61 | -82.28 | 895.02 | -7.16 | 0.12 | 0.77 | 120.35 | 587.95 | 35.55 | 0.12 |
Table 2 R, Bias, RMSE, NMB, and FGE of PM10 between model simulations and observations in two sandstorm events
土壤湿度 数据产品 | 第一次沙尘暴过程 | 第二次沙尘暴过程 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | Bias /(μg·m-3) | RMSE /(μg·m-3) | NMB /% | FGE | R | Bias /(μg·m-3) | RMSE /(μg·m-3) | NMB /% | FGE | |
| ERA5 | 0.55 | -199.27 | 915.72 | -32.08 | 0.14 | 0.76 | 86.84 | 535.14 | 26.86 | 0.11 |
| GLDAS | 0.60 | -278.67 | 879.84 | -37.31 | 0.15 | 0.78 | -139.72 | 501.01 | -28.88 | 0.16 |
| NCEP/FNL | 0.54 | -434.60 | 965.30 | -58.64 | 0.19 | 0.75 | -161.01 | 550.59 | -31.74 | 0.18 |
| SMAP L3 | 0.61 | -82.28 | 895.02 | -7.16 | 0.12 | 0.77 | 120.35 | 587.95 | 35.55 | 0.12 |
土壤湿度 数据产品 | 第一次沙尘暴过程 | 第二次沙尘暴过程 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | Bias /(μg·m-3) | RMSE /(μg·m-3) | NMB /% | FGE | R | Bias /(μg·m-3) | RMSE /(μg·m-3) | NMB /% | FGE | |
| ERA5 | 0.79 | -159.96 | 719.95 | -24.52 | 0.10 | 0.82 | 91.36 | 519.97 | 29.77 | 0.10 |
| GLDAS | 0.79 | -249.22 | 721.24 | -30.67 | 0.11 | 0.80 | -139.71 | 468.18 | -27.70 | 0.15 |
| NCEP/FNL | 0.78 | -425.65 | 840.49 | -53.88 | 0.15 | 0.77 | -163.52 | 520.33 | -30.95 | 0.17 |
| SMAP L3 | 0.80 | -34.76 | 724.65 | -0.13 | 0.10 | 0.81 | 130.64 | 577.98 | 40.51 | 0.11 |
Table 3 R, Bias, RMSE, NMB, and FGE of PM10 between model simulations and observations in two sandstorm events after synchronous peak adjustment
土壤湿度 数据产品 | 第一次沙尘暴过程 | 第二次沙尘暴过程 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | Bias /(μg·m-3) | RMSE /(μg·m-3) | NMB /% | FGE | R | Bias /(μg·m-3) | RMSE /(μg·m-3) | NMB /% | FGE | |
| ERA5 | 0.79 | -159.96 | 719.95 | -24.52 | 0.10 | 0.82 | 91.36 | 519.97 | 29.77 | 0.10 |
| GLDAS | 0.79 | -249.22 | 721.24 | -30.67 | 0.11 | 0.80 | -139.71 | 468.18 | -27.70 | 0.15 |
| NCEP/FNL | 0.78 | -425.65 | 840.49 | -53.88 | 0.15 | 0.77 | -163.52 | 520.33 | -30.95 | 0.17 |
| SMAP L3 | 0.80 | -34.76 | 724.65 | -0.13 | 0.10 | 0.81 | 130.64 | 577.98 | 40.51 | 0.11 |
| 1 | Filonchyk M.Characteristics of the severe March 2021 Gobi Desert dust storm and its impact on air pollution in China[J].Chemosphere,2022,287(3):132219. |
| 2 | Yin Z C, Wan Y, Zhang Y J,et al.Why super sandstorm 2021 in North China?[J].National Science Review,2022,9(3):nwab165. |
| 3 | 高美玲,杨桂芳.我国北方沙尘暴的成因分析及防治对策[J].科协论坛(下半月),2012(4):125-126. |
| 4 | 张莉,李继峰,常春平,等.风速分辨率对土壤风蚀模数计算结果的影响[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(3):21-30. |
| 5 | Shao Y P.A model for mineral dust emission[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2001,106(D17):20239-20254. |
| 6 | Shao Y P.Physics and Modelling of Wind Erosion[M].Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer,2008. |
| 7 | Shao Y, Raupach M R, Findlater P A.Effect of saltation bombardment on the entrainment of dust by wind[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,1993,98(D7):12719-12726. |
| 8 | Alfaro S C, Gaudichet A, Gomes L,et al.Modeling the size distribution of a soil aerosol produced by sandblasting[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,1997,102(D10):11239-11249. |
| 9 | Kok J F, Parteli E J, Michaels T I,et al.The physics of wind-blown sand and dust[J].Reports on Progress in Physics,2012,75(10):106901. |
| 10 | Vova O, Kappas M, Rafiei Emam A.Comparison of satellite soil moisture products in Mongolia and their relation to grassland condition[J].Land,2019,8(9):142. |
| 11 | Wang A H, Zeng X B, Guo D L.Estimates of global surface hydrology and heat fluxes from the Community Land Model (CLM4.5) with four atmospheric forcing datasets[J].Journal of Hydrometeorology,2016,17(9):2493-2510. |
| 12 | Wang A H, Shi X L.A multilayer soil moisture dataset based on gravimetric method in China and its characteristics[J].Journal of Hydrometeorology,2019,20(8):1721-1736. |
| 13 | 魏巍,张稳定,陈焕盛,等.库布齐沙漠治理对京津冀地区空气质量影响:2017年5月3-6日沙尘天气模拟[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(1):77-87. |
| 14 | 陈思宇,贯雅雯,赵丹,等.东亚沙尘气候效应对地面温度日较差影响的数值模拟[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(3):127-138. |
| 15 | Beck H E, Pan M, Miralles D G,et al.Evaluation of 18 satellite-and model-based soil moisture products using in situ measurements from 826 sensors[J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2021,25(1):17-40. |
| 16 | Liu W C, Wang J X, Xu F L,et al.Validation of four satellite-derived soil moisture products using ground-based in situ observations over Northern China[J].Remote Sensing,2022,14(6):1419. |
| 17 | 刘冲,赵天良,熊洁,等.1991-2010年全球沙尘气溶胶排放量气候特征及其大气环流影响因子[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(4):959-970. |
| 18 | Yu X, Wang T J, Liu C,et al.Numerical studies on a severe dust storm in East Asia using WRF-Chem[J].Atmospheric and Climate Sciences,2017,7(1):92-116. |
| 19 | Zeng Y, Wang M H, Zhao C,et al.WRF-Chem v3.9 simulations of the East Asian dust storm in May 2017:modeling sensitivities to dust emission and dry deposition schemes[J].Geoscientific Model Development,2020,13(4):2125-2147. |
| 20 | Lee J H, Lee S H.Modeling a severe wintertime Asian dust event observed in the East Asia region:sensitivity of the WRF-Chem dust emission schemes[J].Atmospheric Pollution Research,2022,13(12):101599. |
| 21 | Zhao J Q, Ma X Y, Wu S Q,et al.Dust emission and transport in Northwest China:WRF-Chem simulation and comparisons with multi-sensor observations[J].Atmospheric Research,2020,241(1):104978. |
| 22 | Ma S Q, Zhang X L, Gao C,et al.Multimodel simulations of a springtime dust storm over northeastern China:implications of an evaluation of four commonly used air quality models (CMAQ v5.2.1,CAMx v6.50,CHIMERE v2017r4,and WRF-Chem v3.9.1)[J].Geoscientific Model Development,2019,12(11):4603-4625. |
| 23 | Kim S, Liu Y Y, Johnson F M,et al.A global comparison of alternate AMSR2 soil moisture products:Why do they differ?[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2015,161:43-62. |
| 24 | Kerr Y H, Waldteufel P, Wigneron J P,et al.Soil moisture retrieval from space:the Soil Moisture and Ocean Salinity (SMOS) mission[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2001,39(8):1729-1735. |
| 25 | Kerr Y H, Waldteufel P, Wigneron J P,et al.The SMOS mission:new tool for monitoring key elements of the global water cycle[J].Proceedings of the IEEE,2010,98(5):666-687. |
| 26 | 杨娜,汤燕杰,张宁馨,等.基于SMOS、SMAP数据的青藏高原季风及植被生长季土壤水分长消特征研究[J].遥感技术与应用,2022,37(6):1373-1384. |
| 27 | 曲学斌,林聪,辛孝飞,等.ERA5-Land、MERRA2再分析资料在呼伦贝尔地区的适用性研究[J].沙漠与绿洲气象,2022,16(5):24-30. |
| 28 | Rodell M, Houser P R, Jambor U,et al.The global land data assimilation system[J].Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society,2004,85(3):381-394. |
| 29 | Miralles D G, Holmes T R H, De Jeu R A M,et al.Global land-surface evaporation estimated from satellite-based observations[J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2011,15(2):453-469. |
| 30 | Nadeem A A, Zha Y Y, Shi L S,et al.Multi-scale assessment of SMAP level 3 and level 4 soil moisture products over the soil moisture network within the ShanDian River (SMN-SDR) Basin,China[J].Remote Sensing,2022,14(4):982. |
| 31 | Foroutan H, Young J, Napelenok S,et al.Development and evaluation of a physics-based windblown dust emission scheme implemented in the CMAQ modeling system[J].Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems,2017,9(1):585-608. |
| 32 | Li M, Zhang Q, Kurokawa J I,et al.MIX:a mosaic Asian anthropogenic emission inventory under the international collaboration framework of the MICS-Asia and HTAP[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2017,17(2):935-963. |
| 33 | Guenther A B, Jiang X, Heald C L,et al.The Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature version 2.1 (MEGAN2.1):an extended and updated framework for modeling biogenic emissions[J].Geoscientific Model Development,2012,5(6):1471-1492. |
| 34 | 陈泓羽,吴静,李纯斌,等.卫星土壤水分产品在青藏高原地区的适用性评价[J].生态学报,2020,40(24):9195-9207. |
| 35 | Shrestha K L, Kondo A, Kaga A,et al.High-resolution modeling and evaluation of ozone air quality of Osaka using MM5-CMAQ system[J].Journal of Environmental Sciences,2009,21(6):782-789. |
| 36 | Spyrou C, Solomos S, Bartsotas N S,et al.Development of a dust source map for WRF-Chem model based on MODIS NDVI[J].Atmosphere,2022,13(6):868. |
| 37 | Wu Q S, Liu H X, Wang L,et al.Evaluation of AMSR2 soil moisture products over the contiguous United States using in situ data from the International soil moisture network[J].International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation,2016,45(B):187-199. |
| 38 | 陆峥,韩孟磊,卢麾,等.基于AMSR2多频亮温的黑河流域中上游土壤水分估算研究[J].遥感技术与应用,2020,35(1):33-47. |
| 39 | Gomis-Cebolla J, Rattayova V, Salazar-Galán S,et al.Evaluation of ERA5 and ERA5-land reanalysis precipitation datasets over Spain (1951-2020)[J].Atmospheric Research,2023,284(15):106606. |
| 40 | Liang P, Chen B, Yang X P,et al.Revealing the dust transport processes of the 2021 mega dust storm event in northern China[J].Science Bulletin,2022,67(1):21-24. |
| 41 | Kong K, Nandintsetseg B, Shinoda M,et al.Seasonal variations in threshold wind speed for saltation depending on soil temperature and vegetation:a case study in the Gobi Desert[J].Aeolian Research,2021,52:1-10. |
| 42 | Mccarthy C, Sternberg T, Hoshino B,et al.Preserving the Gobi:identifying potential UNESCO world heritage in Mongolia's Gobi Desert[J].Journal of Asia-Pacific Biodiversity,2022,15(4):500-517. |
| 43 | Heiner M, Galbadrakh D, Kiesecker J.Encyclopedia of the World's Biomes[M].Berlin,Germany:Elsevier,2020:78-84. |
| [1] | Siyu Chen, Shikang Du, Hongru Bi, Dan Zhao, Yue Zhang, Yu Chen, Gaotong Lou, Junyan Chen. Review on identification and forecasting of dusty weather [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(1): 11-21. |
| [2] | Zhaoen Han, Wei Cui, Jinrong Li, Guodong Tang, Jun Zhang. Effect of soil moisture content on wind erosion rate of frozen aeolian sand [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(1): 228-234. |
| [3] | Chengxian Liao, Haibing Wang, Xiya Liu, Yue Li. Simulation of movement characteristics of wind and sand two-phase flow on the gobi surface based on CFD technology [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(6): 71-78. |
| [4] | Yanxia Pan, Yang Zhao, Zhishan Zhang. The influence of eco-mat laying on sand fixation and soil temperature and humidity [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(5): 186-193. |
| [5] | Yayun Li, Wei Cheng, Ning Wang, Xin Li, Rui Gao. Comparative study on the characteristic of spring sandstorms and the related meteorological factors of the Taklimakan Desert and Gobi Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 1-9. |
| [6] | Yuxi Wei, Lijuan Chen, Haiyang Xi, Chengqi Zhang, Kaiyuan Gan, Tian Yong, Jinxia Zhang. Spatial differentiation of soil moisture and conductivity in Shiyang River Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 264-273. |
| [7] | Jingping Chen, Ziying Yu, Fan Yang, Mi Wang, Han Hu, Guanzhong Ni, Xin Gao, Xin Wang. Particle size characteristics of sandstorm and surface sand at Tazhong area of Taklimakan Desert, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 150-158. |
| [8] | Jiapeng Pan, Kecun Zhang, Zhishan An, Hongxue Zhang, Chengjie Xue. Analysis of comprehensive benefits of wind-blown sand control projects: a case study of Heishanzui, Dunhuang, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 233-242. |
| [9] | Guangyu Hong, Xiaojiang Wang, Tieshan Liu, Hailong, Zhenting Wu, Huercha, Xiaowei Gao, Haifeng Yang, Zhuofan Li, Zihao Li, Siqin, Lejun Wang. Applicability of Hydrus-1D Model in simulating the soil moisture in Hedysarum leave in Mu Us Sandy Land, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 233-242. |
| [10] | Lin Li, Hu Liu, Chengpeng Sun, Wenzhi Zhao. Groundwater evapotranspiration estimation based on soil moisture and water table measurements [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 277-287. |
| [11] | Haojun Qin, Xiaojun Yang, Li Ma, Yicheng Wang, Zhao Fu, Junxia Zhang, Zhengqi Lu. Characteristics and causes of regional sandstorms in Northwest of China from 2000 to 2020 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 53-64. |
| [12] | Chunyan Zhao, Jie Qin, Xiaohui He, Dongmeng Zhou. Effects of sand burial on typical desert plants [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 63-72. |
| [13] | Shiyang Chen, Rong Yang, Yongzhong Su, Zeyu Du. Characteristics of soil respiration in farmland of Hexi oasis and its response to long-term fertilization [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(3): 178-186. |
| [14] | Wenzhi Zhao, Xuelian Bai, Chan Liu. Research on vegetation sand control around the south edge of Badain Jaran Sand Sea, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 5-11. |
| [15] | Feiyao Liu, Quangang You, Siyuan Wu, Cuihua Huang, Jing Pan, Shaoxiu Ma, Xiaojie Chen, Xian Xue. Effects of abandonment and recultivation of farmland on soil hydraulic properties in a typical oasis of arid regions [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 169-178. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech