
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 283-294.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00023
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hongling Yang1( ), Bo Yao1,2, Yongzhong Su1(
), Bo Yao1,2, Yongzhong Su1( ), Yulin Li1(
), Yulin Li1( )
)
Received:2023-12-03
Revised:2024-02-18
Online:2024-03-20
Published:2024-03-19
Contact:
Yongzhong Su,Yulin Li
CLC Number:
Hongling Yang, Bo Yao, Yongzhong Su, Yulin Li. Distribution pattern of soil physical and chemical properties of plantation forest in northern agro-pastoral ecotone[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(2): 283-294.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00023
| 项目 | 乔木林 | 灌木林 |
|---|---|---|
| 样点个数 | 167 | 68 |
| 优势种 | 杨树(Populus przewalskii)、樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var.mongolica)、油松(Pinus tabulaeformis) | 锦鸡儿属(Caragana)、山杏(Prunus sibirica)、黄柳(Salix gordejevii) |
| 经度/(°E) | 107.76—122.57 | 107.45—122.22 |
| 纬度/(°N) | 37.49—46.10 | 37.36—45.65 |
| 海拔/m | 351~1628 | 307~1566 |
| 年均气温/℃ | 1.82~8.94 | 3.59~8.83 |
| 年降水量/mm | 336.72~507.23 | 357.42~442.23 |
| 干燥度指数 | 1.01~1.71 | 1.14~1.62 |
| 胸径/cm | 29.51~98.04 | — |
| 树高/m | 6.29~21.68 | 1.63~6.81 |
Table 1 Basic informetion of sample sites of plantation forests in the agro-pastoral ecotone of Northern China
| 项目 | 乔木林 | 灌木林 |
|---|---|---|
| 样点个数 | 167 | 68 |
| 优势种 | 杨树(Populus przewalskii)、樟子松(Pinus sylvestris var.mongolica)、油松(Pinus tabulaeformis) | 锦鸡儿属(Caragana)、山杏(Prunus sibirica)、黄柳(Salix gordejevii) |
| 经度/(°E) | 107.76—122.57 | 107.45—122.22 |
| 纬度/(°N) | 37.49—46.10 | 37.36—45.65 |
| 海拔/m | 351~1628 | 307~1566 |
| 年均气温/℃ | 1.82~8.94 | 3.59~8.83 |
| 年降水量/mm | 336.72~507.23 | 357.42~442.23 |
| 干燥度指数 | 1.01~1.71 | 1.14~1.62 |
| 胸径/cm | 29.51~98.04 | — |
| 树高/m | 6.29~21.68 | 1.63~6.81 |
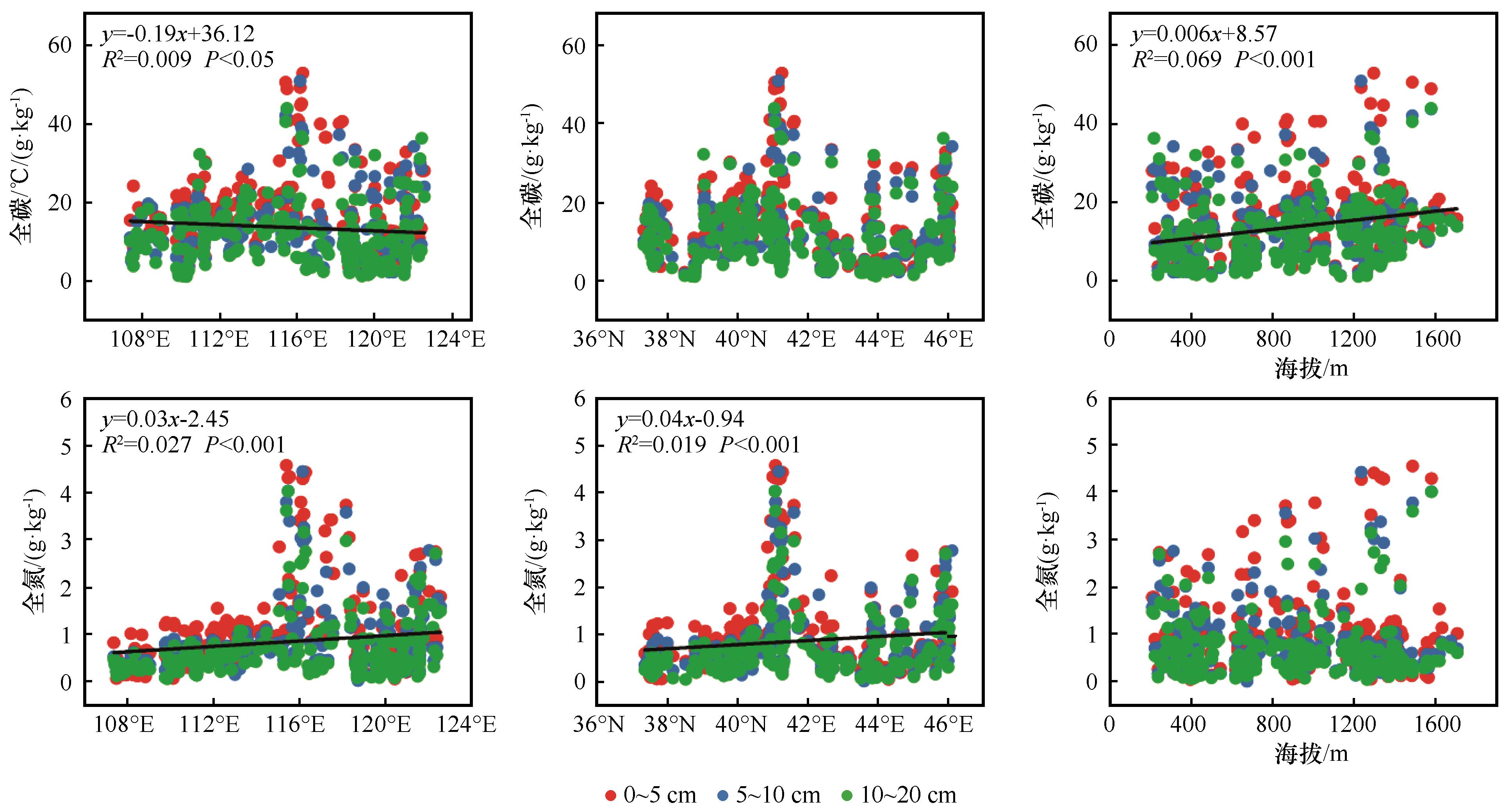
Fig.6 Spatial distribution characteristics of soil total carbon and nitrogen content of plantation forest in the agro-pastoral ecotone of Northern China
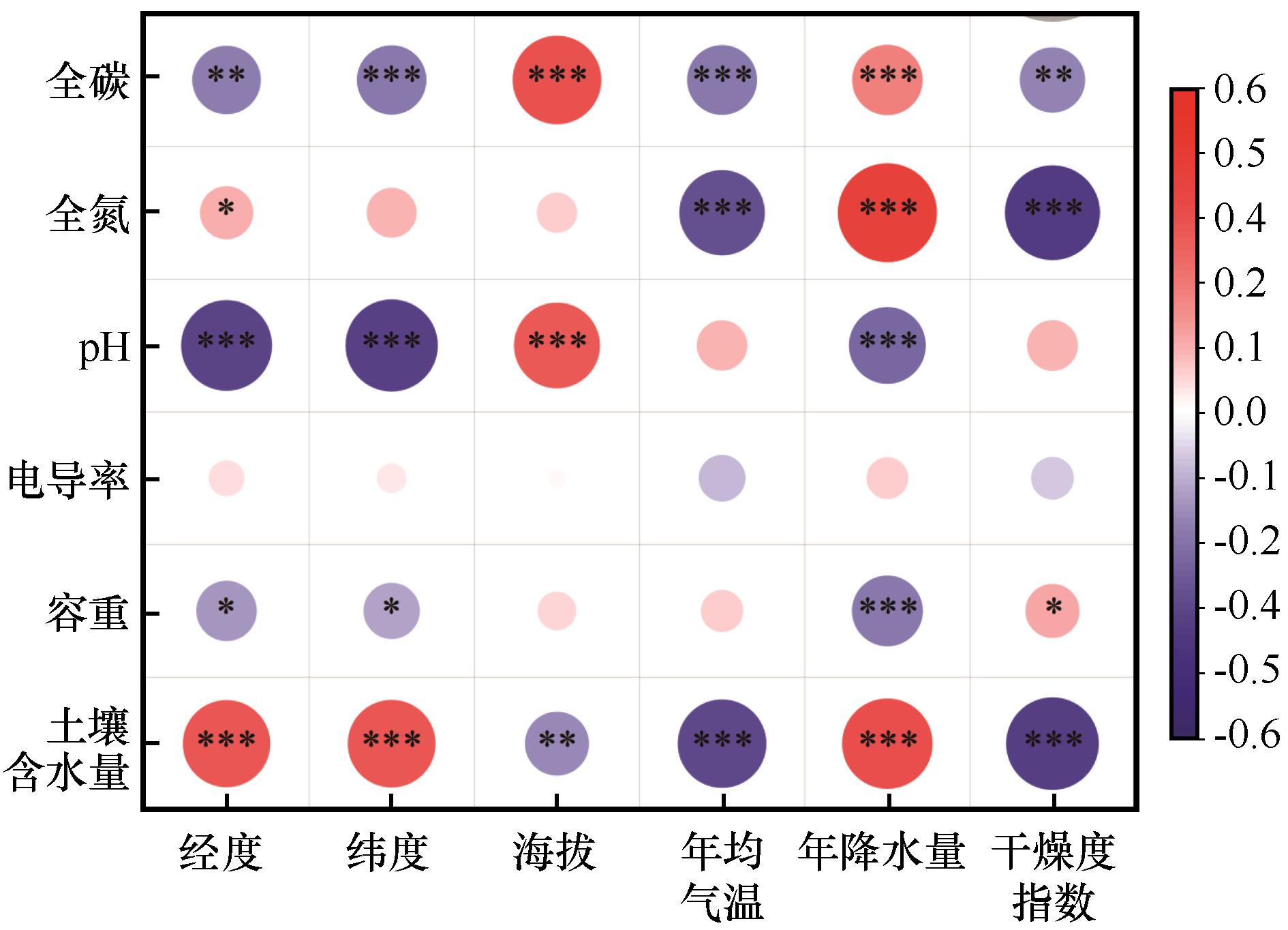
Fig.9 Correlations between soil physicochemical properties and environmental factors of plantation forest in the agro-pastoral ecotone of Northern China
| 1 | Zhang L, Sun P, Huettmann F,et al.Where should China practice forestry in a warming world?[J].Global Change Biology,2022,28(7):2461-2475. |
| 2 | Fang J, Chen A, Peng C,et al.Changes in forest biomass carbon storage in China between 1949 and 1998[J].Science,2001,292(5525):2320-2322. |
| 3 | Del Lugo A, Ball J, Carle J.Global Planted Forests Thematic Study: Results and Analysis[M].Rome,Italy:FAO,2006. |
| 4 | 王旭洋.北方农牧交错带土壤有机碳时空动态及其影响机制[D].北京:中国科学院大学,2019. |
| 5 | 赵哈林,赵学勇,张铜会,等.北方农牧交错带的地理界定及其生态问题[J].地球科学进展,2002,17:739-747. |
| 6 | 赵哈林,周瑞莲,赵学勇,等.呼伦贝尔沙质草地土壤理化特性的沙漠化演变规律及机制[J].草业学报,2012,21(2): 1-12. |
| 7 | 国家林业和草原局.三北防护林体系建设40年发展报告:1978-2018[R].北京:中国林业出版社,2018. |
| 8 | Jug A, Makeschin F, Rehfuess K E,et al.Short-rotation plantations of balsam poplars,aspen and willows on former arable land in the Federal Republic of Germany.III.soil ecological effects[J].Forest Ecology and Management,1999,121(1):85-99. |
| 9 | Guo Y, Abdalla M, Espenberg M,et al.A systematic analysis and review of the impacts of afforestation on soil quality indicators as modified by climate zone,forest type and age[J].Science of Total Environment,2021,757:143824. |
| 10 | Yao Y, Wang X, Zeng Z,et al.The Effect of afforestation on soil moisture content in Northeastern China[J].PLoS One,2016,11(8):e0160776. |
| 11 | Slessarev E W, Lin Y, Bingham N L,et al.Water balance creates a threshold in soil pH at the global scale[J].Nature,2016,540(7634):567-569. |
| 12 | Deng L, Peng C, Kim D G,et al.Drought effects on soil carbon and nitrogen dynamics in global natural ecosystems[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2021,214:103501. |
| 13 | 赵冬辉,申聪聪,张志明,等.土壤功能与环境因素在海拔梯度的耦合关系:以梅里雪山为例[J].环境科学,2022,44(2):924-931. |
| 14 | Dacal M, García-Palacios P, Asensio S,et al.Climate change legacies contrastingly affect the resistance and resilience of soil microbial communities and multifunctionality to extreme drought[J].Functional Ecology,2022,36(4):908-920. |
| 15 | Aerts R.Climate,leaf litter chemistry and leaf litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems:a triangular relationship[J].Oikos,1997,79(3):439-449. |
| 16 | 赵明范.论灌木林在“三北”防护林建设中的作用[J].中国沙漠,1993,13(3):53-57. |
| 17 | Laganière J, Angers D, Paré D.Carbon accumulation in agricultural soils after afforestation: a meta-analysis[J].Global Change Biology,2010,16(1):439-453. |
| 18 | Paul K I, Polglase P J, Nyakuengama J G,et al.Change in soil carbon following afforestation[J].Forest Ecology and Management,2002,168(1):241-257. |
| 19 | Deng L, Zhu G Y, Tang Z S,et al.Global patterns of the effects of land-use changes on soil carbon stocks[J].Global Ecology and Conservation,2016,5:127-138. |
| 20 | 巩杰,陈利顶,傅伯杰,等.黄土丘陵区小流域土地利用和植被恢复对土壤质量的影响[J].应用生态学报,2004,12:2292-2296. |
| 21 | Jackson R B, Canadell J, Ehleringer J R,et al.A global analysis of root distributions for terrestrial biomes[J].Oecologia,1996,108(3):389-411. |
| 22 | Kong W, Wei X, Wu Y,et al.Afforestation can lower microbial diversity and functionality in deep soil layers in a semiarid region[J].Global Chang Biology,2022(7):6086-6101. |
| 23 | Hong S, Piao S, Chen A,et al.Afforestation neutralizes soil pH[J].Nature Communications,2018,9(1):520. |
| 24 | Hong S B, Yin GD, Piao S L,et al.Divergent responses of soil organic carbon to afforestation[J].Nature Sustainability,2020,3(9):694. |
| 25 | Li D, Niu S, Luo Y.Global patterns of the dynamics of soil carbon and nitrogen stocks following afforestation: a meta-analysis[J].New Phytologist,2012,195(1):172-181. |
| 26 | Cao S, Chen L, Shankman D,et al.Excessive reliance on afforestation in China's arid and semi-arid regions: lessons in ecological restoration[J].Earth Science Reviews,2011,104(4): 240-245. |
| 27 | 石晓丽,史文娇.北方农牧交错带界线的变迁及其驱动力研究进展[J].农业工程学报,2018,34(20):1-11. |
| 28 | Singh K, Singh B, Singh R R.Changes in physico-chemical,microbial and enzymatic activities during restoration of degraded sodic land: ecological suitability of mixed forest over monoculture plantation[J].Catena,2012,96:57-67. |
| 29 | Chytrý M, Danihelka J, Ermakov N,et al.Plant species richness in continental southern Siberia: effects of pH and climate in the context of the species pool hypothesis[J].Global Ecology and Biogeography,2007,16(5):668-678. |
| 30 | Jo I, Fridley J D, Frank D A.Rapid leaf litter decomposition of deciduous understory shrubs and lianas mediated by mesofauna[J].Plant Ecology,2019,221(1):63-68. |
| 31 | 梁燊,刘亚斌,石川,等.黄土区不同龄期灌木柠条锦鸡儿根系的分布特征及其固土护坡效果[J].农业工程学报,2023,39(15):114-124. |
| 32 | 马金豪,栾军伟,王晖,等.乔木根系和凋落物对南亚热带3种人工林土壤线虫群落的差异化影响[J].生态学报,2023,43(18):7367-7380. |
| 33 | 马晓明,李丹,雷佳,等.不同降水年型下耕作方式结合覆盖对旱地土壤物理性质和马铃薯产量的影响[J].应用生态学报,2024:10.13287/j.1001-9332.202402.012. |
| 34 | Smith P.How long before a change in soil organic carbon can be detected[J].Global Change Biology,2004,10(11):1878-1883. |
| 35 | Shi S, Peng C, Wang M,et al.A global meta-analysis of changes in soil carbon,nitrogen,phosphorus and sulfur,and stoichiometric shifts after forestation[J].Plant and Soil,2016,407(1):323-340. |
| 36 | 左李娜,盛建东,张凯,等.新疆温性草原土壤pH特征及影响因素[J].草业科学,2022,39(7):1341-1353. |
| 37 | Zhou S, Wang J, Chen L,et al.Microbial community structure and functional genes drive soil priming effect following afforestation[J].Science of the Total Environment,2022,825:153925. |
| 38 | 张立恒,李清雪,王学全,等.高寒沙地中间锦鸡儿人工林根系分布及林下土壤特性研究[J].土壤通报,2019,50(4):1-10. |
| 39 | 樊如月,李青丰,贺一鸣.农牧交错区小叶锦鸡儿(Caragana microphylla)人工灌木林土壤碳氮磷化学计量特征[J].土壤通报,2019,50:437-443. |
| 40 | 刘希瑶,刘澎,刘驰.典型黑土中有机质和养分元素的变化分析[J].地质与资源,2022,31(1):500-507. |
| 41 | 任雯丽,任亮,赵贵宾,等.黄土高原半干旱地区休耕条件下深翻次数对土壤理化性状的影响[J].农业科技与信息,2023(2):4-9. |
| 42 | 明姣,杨光,赵允格,等.放牧对降雨条件下黄土高原退耕草地土壤水分补给的影响[J].应用生态学报,2023,34(6):1555-1562. |
| 43 | Hou G, Delang C O, Lu X,et al.A meta-analysis of changes in soil organic carbon stocks after afforestation with deciduous broadleaved,sempervirent broadleaved,and conifer tree species[J].Annals of Forest Science,2020,77(4):1324-1352. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech