
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 70-78.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00049
Previous Articles Next Articles
Hongji Zhou1( ), Fanmin Mei1(
), Fanmin Mei1( ), Mengji Pu1, Chuan Lin1, Jin Su2, Jinguang Chen3
), Mengji Pu1, Chuan Lin1, Jin Su2, Jinguang Chen3
Received:2024-03-11
Revised:2024-05-12
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-12-06
Contact:
Fanmin Mei
CLC Number:
Hongji Zhou, Fanmin Mei, Mengji Pu, Chuan Lin, Jin Su, Jinguang Chen. Ensemble models for identifying automatically aeolian saltating tracks driven by datasets[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(6): 70-78.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00049
| 变量 | 定义 |
|---|---|
| 瞬时水平速度的平均值(m·s-1) | |
| 瞬时垂直速度的平均值(m·s-1) | |
| 瞬时合速度的平均值(m·s-1) | |
| 轨迹抛物线方程拟合曲线的决定系数, |
Table 1 Parameterized features of saltating track samples
| 变量 | 定义 |
|---|---|
| 瞬时水平速度的平均值(m·s-1) | |
| 瞬时垂直速度的平均值(m·s-1) | |
| 瞬时合速度的平均值(m·s-1) | |
| 轨迹抛物线方程拟合曲线的决定系数, |
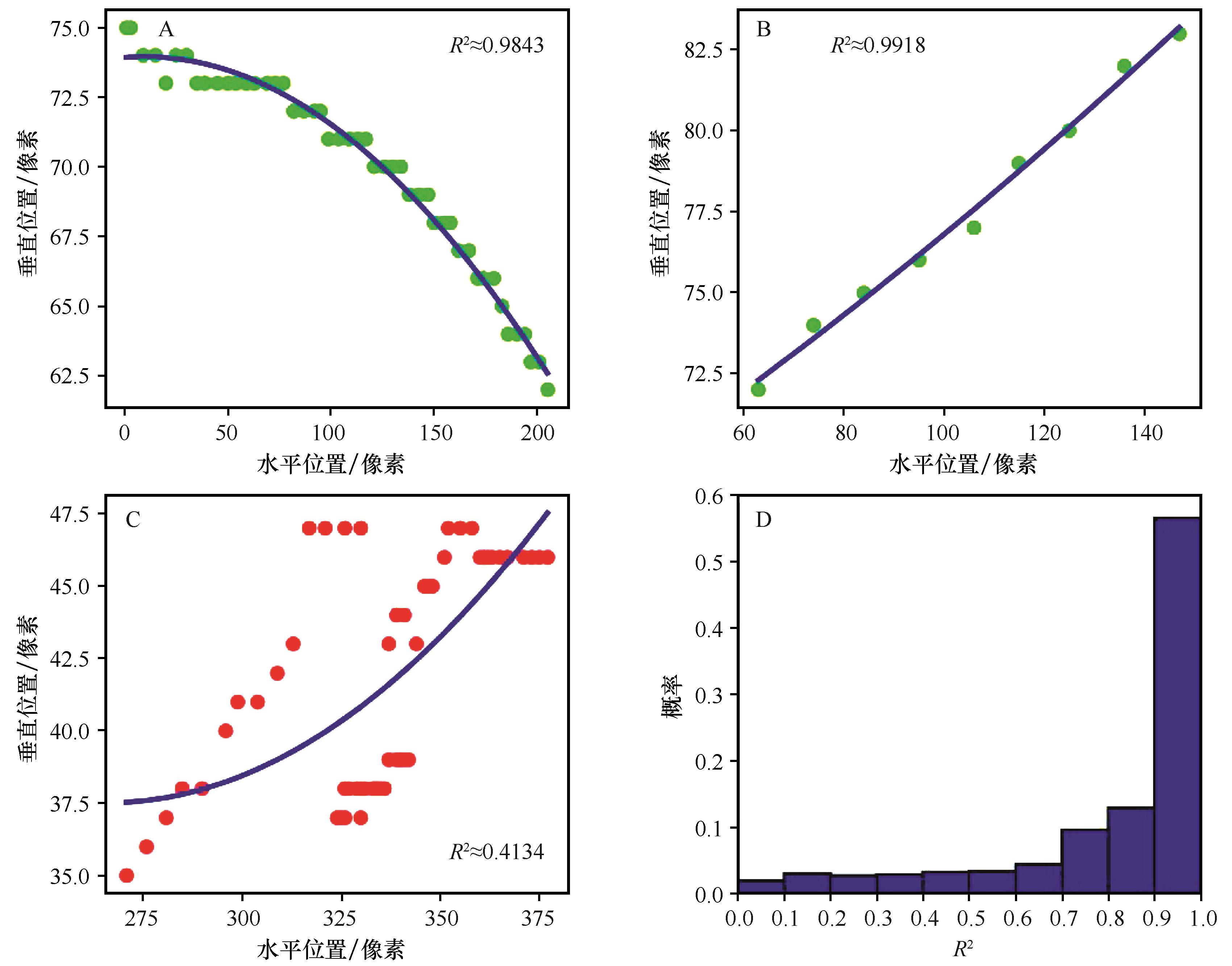
Fig.2 The 27th true ascent trajectory (A), the 7th true descent trajectory (B) and the 16th false trajectory (C)in video M1 extracted by the KF-H algorithm, respectively; Probability distribution of the determination coefficient (R2 ) for fitting quadratic curves of 5 756 true trajectories (D)
| 算法 | HP1 | HP2 | HP3 | HP4 | HP5 | HP6 | HP7 | HP8 | HP9 | HP10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 随机森林 | True | -1 | True | 180 | 18 | True | “sqrt” | “gini” | ||
| 梯度提升决策树 | True | -1 | True | 210 | 3 | 0.3 | ||||
| XGBoost | True | -1 | 70 | 6 | 0.3 | 0.5 | ||||
| 极度随机树 | True | -1 | True | 186 | 21 | 0.1 | True | None | “entropy” |
Table 2 Final hyperparameter settings for each model optimized by Tree-structured Parzen Estimator
| 算法 | HP1 | HP2 | HP3 | HP4 | HP5 | HP6 | HP7 | HP8 | HP9 | HP10 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 随机森林 | True | -1 | True | 180 | 18 | True | “sqrt” | “gini” | ||
| 梯度提升决策树 | True | -1 | True | 210 | 3 | 0.3 | ||||
| XGBoost | True | -1 | 70 | 6 | 0.3 | 0.5 | ||||
| 极度随机树 | True | -1 | True | 186 | 21 | 0.1 | True | None | “entropy” |

Fig.4 Correlation matrix of features and label (the value of each matrix element represents the P-value of the significance test and the corresponding color represents the correlation coefficient)
| 模型 | 准确率 | 精准度 | 召回率 | F1分数 | MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 随机森林 | 0.8923 | 0.8939 | 0.8923 | 0.8857 | 0.7056 |
| 极度随机树 | 0.9035 | 0.9030 | 0.9035 | 0.8995 | 0.7378 |
| 梯度提升决策树 | 0.8976 | 0.8970 | 0.8976 | 0.8929 | 0.7207 |
| XGBoost | 0.8995 | 0.9012 | 0.8995 | 0.8939 | 0.7267 |
Table 3 Predictive performance of four ensemble models
| 模型 | 准确率 | 精准度 | 召回率 | F1分数 | MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 随机森林 | 0.8923 | 0.8939 | 0.8923 | 0.8857 | 0.7056 |
| 极度随机树 | 0.9035 | 0.9030 | 0.9035 | 0.8995 | 0.7378 |
| 梯度提升决策树 | 0.8976 | 0.8970 | 0.8976 | 0.8929 | 0.7207 |
| XGBoost | 0.8995 | 0.9012 | 0.8995 | 0.8939 | 0.7267 |
| 优化数据集 | 准确率 | 精确度 | 召回率 | F1分数 | MCC | AUC分数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 原始数据集 | 0.9035 | 0.9030 | 0.9035 | 0.8995 | 0.7378 | 0.9179 |
| 原始数据集+瞬时水平速度的方差 | 0.9332 | 0.9327 | 0.9332 | 0.9329 | 0.8241 | 0.9506 |
| 原始数据集+瞬时水平速度的方差+瞬时垂直速度的方差 | 0.9379 | 0.9372 | 0.9379 | 0.9374 | 0.8356 | 0.9697 |
Table 4 Performances of the trained Extremely Randomized Trees by optimized datasets
| 优化数据集 | 准确率 | 精确度 | 召回率 | F1分数 | MCC | AUC分数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 原始数据集 | 0.9035 | 0.9030 | 0.9035 | 0.8995 | 0.7378 | 0.9179 |
| 原始数据集+瞬时水平速度的方差 | 0.9332 | 0.9327 | 0.9332 | 0.9329 | 0.8241 | 0.9506 |
| 原始数据集+瞬时水平速度的方差+瞬时垂直速度的方差 | 0.9379 | 0.9372 | 0.9379 | 0.9374 | 0.8356 | 0.9697 |
| 1 | Bagnold R A.The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes[M].Netherlands:Springer,1942. |
| 2 | Wang D, Wang Y, Yang B,et al.Statistical analysis of sand grain/bed collision process recorded by high‐speed digital camera[J].Sedimentology,2008,55(2):461-470. |
| 3 | Jiang C W, Parteli E J R, Dong Z B,et al.Wind-tunnel experiments of aeolian sand transport reveal a bimodal probability distribution function for the particle lift-off velocities[J].Catena,2022,217:106496. |
| 4 | Zhang Y, Wang Y, Jia P.Measuring the kinetic parameters of saltating sand grains using a high-speed digital camera[J].Science China Physics,Mechanics Astronomy,2014,57:1137-1143. |
| 5 | O'Brien P, Neuman C M K.PTV measurement of the spanwise component of aeolian transport in steady state[J].Aeolian Research,2016,20:126-138. |
| 6 | O'Brien P, Neuman C M K.An experimental study of the dynamics of saltation within a three-dimensional framework[J].Aeolian Research,2018,31:62-71. |
| 7 | Yang B, Wang Y, Zhang Y.The 3-D spread of saltation sand over a flat bed surface in aeolian sand transport[J].Advanced Powder Technology,2009,20(4):303-309. |
| 8 | O'Brien P, McKenna Neuman C.Experimental validation of the near‐bed particle‐borne stress profile in aeolian transport systems[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface,2019,124(11):2463-2474. |
| 9 | Kang L Q, Zou X Y, Zhao G D,et al.Wind tunnel investigation of horizontal and vertical sand fluxes of ascending and descending sand particles in aeolian sand transport[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2016,41(12):1647-1657. |
| 10 | Ho T D, Valance A, Dupont P,et al.Scaling laws in aeolian sand transport[J].Physical Review Letters,2011,106(9):094501. |
| 11 | Zhang Y, Li M, Wang Y,et al.Reinvestigation of the scaling law of the windblown sand launch velocity with a wind tunnel experiment[J].Journal of Arid Land,2019,11:664-673. |
| 12 | Creyssels M, Dupont P, El Moctar A O,et al.Saltating particles in a turbulent boundary layer:experiment and theory[J].Journal of Fluid Mechanics,2009,625:47-74. |
| 13 | Mei F M, Zhou H J, Su J,et al.A new hybrid algorithm based on Kalman filter-Hungarian algorithm for tracking aeolian saltating particle in the high-speed video[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2024, . |
| 14 | Breiman L.Random forests[J].Machine Learning,2001,45:5-32. |
| 15 | Geurts P, Ernst D, Wehenkel L.Extremely randomized trees[J].Machine Learning,2006,63:3-42. |
| 16 | Friedman J H.Greedy function approximation:a gradient boosting machine[J].Annals of Statistics,2001:1189-1232. |
| 17 | Chen T, Guestrin C.Xgboost:a scalable tree boosting system[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd Acm Sigkdd International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining.2016:785-794. |
| 18 | Boroughani M, Pourhashemi S, Gholami H,et al.Predicting of dust storm source by combining remote sensing,statistic-based predictive models and game theory in the Sistan watershed,southwestern Asia[J].Journal of Arid Land,2021,13(11):1103-1121. |
| 19 | Boroughani M, Pourhashemi S, Hashemi H,et al.Application of remote sensing techniques and machine learning algorithms in dust source detection and dust source susceptibility mapping[J].Ecological Informatics,2020,56:101059. |
| 20 | Choubin B, Hosseini F S, Rahmati O,et al.Mapping of salty aeolian dust-source potential areas:Ensemble model or benchmark models?[J].Science of The Total Environment,2023,877:163419. |
| 21 | Gholami H, Mohamadifar A, Sorooshian A,et al.Machine-learning algorithms for predicting land susceptibility to dust emissions:the case of the Jazmurian Basin,Iran[J].Atmospheric Pollution Research,2020,11(8):1303-1315. |
| 22 | Rahmati O, Mohammadi F, Ghiasi S S,et al.Identifying sources of dust aerosol using a new framework based on remote sensing and modelling[J].Science of The Total Environment,2020,737:139508. |
| 23 | Iban M C, Bilgilioglu S S.Snow avalanche susceptibility mapping using novel tree-based machine learning algorithms (XGBoost,NGBoost,and LightGBM) with eXplainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) approach[J].Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment,2023,37(6):2243-2270. |
| 24 | Zafari A, Zurita-Milla R, Izquierdo-Verdiguier E.Land cover classification using extremely randomized trees:a kernel perspective[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters,2019,17(10):1702-1706. |
| 25 | 李森,颜长珍.基于ChinaCover数据集的绿洲结构数据制图:以河西内陆河流域为例[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(3):230-242. |
| 26 | 蒋小芳,徐青霞,段翰晨,等.黄河景电灌区土壤盐渍化反演的多模型对比[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(5):18-30. |
| 27 | 吴敏,温小虎,冯起,等.基于随机森林模型的干旱绿洲区张掖盆地地下水水质评价[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(3):657-663. |
| 28 | 张亦然,刘廷玺,童新,等.基于多源遥感和机器学习方法的科尔沁沙地植被覆盖度反演[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(3):187-195. |
| 29 | Houghton J E, Nichols T E, Griffiths J,et al.Automated classification of estuarine sub‐depositional environment using sediment texture[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface,2023,128(2):e2022JF006891. |
| 30 | Nichols T E, Worden R H, Houghton J E,et al.Sediment texture and geochemistry as predictors of sub-depositional environment in a modern estuary using machine learning:a framework for investigating clay-coated sand grains[J].Sedimentary Geology,2023,458:106530. |
| 31 | Zheng,D Y, Hou M C, Chen A Q,et al.Application of machine learning in the identification of fluvial-lacustrine lithofacies from well logs:a case study from Sichuan Basin,China[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering,2022,215,110610. |
| 32 | Bergstra J, Bardenet R, Bengio Y,et al.Algorithms for hyper-parameter optimization[C]//International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.2011. |
| 33 | Beguería S.Validation and evaluation of predictive models in hazard assessment and risk management[J].Natural Hazards,2006,37:315-329. |
| 34 | Fawcett T.An introduction to ROC analysis[J].Pattern recognition letters,2006,27(8):861-874. |
| 35 | al Pedregosaet.Scikit-learn:machine learning in python[J].Journal of Machine Learning Research,2011,12:2825-2830. |
| 36 | Canbek G, Sagiroglu S, Temizel T T,et al.Binary classification performance measures/metrics:a comprehensive visualized roadmap to gain new insights[C]//2017 International Conference on Computer Science and Engineering(UBMK).IEEE,2017:821-826. |
| 37 | Chicco D, Jurman G.The advantages of the Matthews correlation coefficient(MCC)over F1 score and accuracy in binary classification evaluation[J].BMC Genomics,2020,21(1):1-13. |
| 38 | Silla C N, Freitas A A.A survey of hierarchical classification across different application domains[J].Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery,2011,22:31-72. |
| 39 | Akay H.Spatial modeling of snow avalanche susceptibility using hybrid and ensemble machine learning techniques[J].CATENA,2021,206:105524. |
| 40 | Yang J M, He Q, Liu Y.Winter-Spring prediction of snow avalanche susceptibility using optimisation multi-source heterogeneous factors in the Western Tianshan Mountains,China[J].Remote Sensing,2022,14(6):1340. |
| 41 | Duan T, Anand A, Ding D Y,et al.Ngboost:natural gradient boosting for probabilistic prediction[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning.PMLR,2020:2690-2700. |
| 42 | MacQueen J.Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations[C]//Proceedings of the Fifth Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics and Probability.1967:281-297. |
| 43 | Ester M, Kriegel H P, Sander J,et al.A density-based algorithm for discovering clusters in large spatial databases with noise[C]//KDD'96:Proceedings of the Second International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining.1996:226-231. |
| 44 | Bian J, Tian D, Tang Y,et al.Trajectory data classification:a review[J].ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology(TIST),2019,10(4):1-34. |
| [1] | Ting Ning, Dinghai Zhang, Youyi Zhao, Jing Jiang. Relationship between soil moisture and topography and vegetation in the Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(5): 133-142. |
| [2] | Fanmin Mei, Qianwen Yang, Wang Li, Jin Su. An overview of analytical models of saltation [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(4): 14-23. |
| [3] | Teng Zhang, Yunfa Miao, Yaguo Zou, Ziyue Zhang, Guoping Feng. Classification and changes of vegetation in Sugan Lake wetland in the extreme arid region [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(4): 81-90. |
| [4] | Wu Min, Wen Xiaohu, Feng Qi, Yin Zhengliang, Yang Linshan. Assessment of Groundwater Quality Based on Random Forest Model in Arid Oasis Area [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(3): 657-663. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech