
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 120-128.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2020.00115
Previous Articles Next Articles
Ziting Wang1,2( ), Lei Yang3, Guang Li1(
), Lei Yang3, Guang Li1( ), Chunshan Chai2, Yangdong Zhang2, Donghao Liu2
), Chunshan Chai2, Yangdong Zhang2, Donghao Liu2
Received:2020-07-06
Revised:2020-11-06
Online:2021-03-20
Published:2021-03-26
Contact:
Guang Li
CLC Number:
Ziting Wang, Lei Yang, Guang Li, Chunshan Chai, Yangdong Zhang, Donghao Liu. Distribution and diversity of herbage under Caragana korshinskii plantation at hillslope scale in the semi-arid loess hilly region[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 120-128.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2020.00115
| 样地 | 海拔/m | 坡度/(°) | 坡向/(°) | 土壤容重/(g·cm-3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阴坡 | 上坡位 | 2 079 | 25° | 291° | 1.14±0.05 |
| 中坡位 | 2 041 | 33° | 264° | 1.09±0.10 | |
| 下坡位 | 2 012 | 22° | 282° | 1.15±0.05 | |
| 半阳坡 | 上坡位 | 2 106 | 34° | 332° | 1.23±0.04 |
| 中坡位 | 2 061 | 30° | 323° | 1.10±0.04 | |
| 下坡位 | 2 017 | 28° | 342° | 1.08±0.01 | |
| 阳坡 | 上坡位 | 2 068 | 33° | 0° | 1.15±0.02 |
| 中坡位 | 2 043 | 30° | 4° | 1.14±0.06 | |
| 下坡位 | 2 003 | 27° | 0° | 1.15±0.02 | |
Table 1 Basic description of experimental sites
| 样地 | 海拔/m | 坡度/(°) | 坡向/(°) | 土壤容重/(g·cm-3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阴坡 | 上坡位 | 2 079 | 25° | 291° | 1.14±0.05 |
| 中坡位 | 2 041 | 33° | 264° | 1.09±0.10 | |
| 下坡位 | 2 012 | 22° | 282° | 1.15±0.05 | |
| 半阳坡 | 上坡位 | 2 106 | 34° | 332° | 1.23±0.04 |
| 中坡位 | 2 061 | 30° | 323° | 1.10±0.04 | |
| 下坡位 | 2 017 | 28° | 342° | 1.08±0.01 | |
| 阳坡 | 上坡位 | 2 068 | 33° | 0° | 1.15±0.02 |
| 中坡位 | 2 043 | 30° | 4° | 1.14±0.06 | |
| 下坡位 | 2 003 | 27° | 0° | 1.15±0.02 | |
| 物种 | 阴坡 | 半阳坡 | 阳坡 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上坡位 | 中坡位 | 下坡位 | 上坡位 | 中坡位 | 下坡位 | 上坡位 | 中坡位 | 下坡位 | |
| 赖草(Leymus secalinus) | 0.201±0.071 | 0.179±0.061 | 0.161±0.056 | 0.363±0.124 | 0.205±0.066 | 0.342±0.116 | 0.039±0.034 | ||
| 长芒草(Stipa bungeana) | 0.126±0.050 | 0.033±0.029 | 0.266±0.003 | 0.155±0.068 | 0.210±0.048 | 0.201±0.107 | 0.296±0.059 | 0.336±0.034 | 0.134±0.054 |
| 中华隐子草(Cleistogenes chinensis) | 0.006±0.005 | 0.020±0.018 | |||||||
| 狗尾草(Setaria viridis) | 0.068±0.036 | 0.054±0.041 | 0.019±0.017 | 0.052±0.016 | 0.054±0.014 | 0.058±0.020 | |||
| 灰绿藜(Chenopodium glaucum) | 0.020±0.018 | 0.012±0.010 | |||||||
| 大花蚓果芥(Torularia humilis) | 0.002±0.002 | 0.024±0.012 | 0.033±0.013 | 0.030±0.003 | 0.045±0.016 | 0.034±0.017 | 0.022±0.019 | 0.032±0.016 | |
| 二裂委陵菜(Potentilla bifurca) | 0.041±0.016 | 0.021±0.018 | 0.053±0.027 | ||||||
| 西山委陵菜(Potentilla sischanensis) | 0.004±0.003 | 0.010±0.006 | 0.021±0.012 | 0.004±0.003 | 0.014±0.005 | 0.023±0.013 | |||
| 伏毛山莓草(Sibbaldia adpressa) | 0.041±0.020 | 0.057±0.020 | 0.028±0.020 | 0.011±0.006 | 0.059±0.010 | 0.052±0.021 | 0.054±0.029 | 0.080±0.029 | 0.098±0.032 |
| 糙叶黄耆(Astragalus scaberrimus) | 0.013±0.011 | ||||||||
| 甘肃棘豆(Oxytropis kansuensis) | 0.021±0.012 | ||||||||
| 天蓝苜蓿(Medicago lupulina) | 0.069±0.047 | 0.003±0.003 | 0.018±0.015 | 0.010±0.009 | |||||
| 野亚麻(Linum stelleroides) | 0.005±0.004 | 0.019±0.010 | |||||||
| 骆驼蓬(Peganum harmala) | 0.054±0.027 | 0.048±0.019 | 0.022±0.019 | 0.040±0.021 | 0.043±0.022 | 0.035±0.031 | |||
| 远志(Polygala tenuifolia) | 0.031±0.018 | ||||||||
| 裂叶堇菜(Viola dissecta) | 0.029±0.009 | 0.010±0.008 | |||||||
| 早开堇菜(Viola prionantha) | 0.003±0.003 | ||||||||
| 北方獐牙菜(Swertia diluta) | 0.021±0.018 | ||||||||
| 鹅绒藤(Cynanchum chinense) | 0.006±0.005 | ||||||||
| 地梢瓜(Cynanchum thesioides) | 0.029±0.025 | 0.014±0.012 | 0.019±0.016 | 0.029±0.025 | 0.017±0.015 | 0.056±0.029 | |||
| 田旋花(Convolvulus arvensis) | 0.036±0.032 | ||||||||
| 蒙古芯芭(Cymbaria mongolica) | 0.009±0.008 | 0.005±0.005 | 0.019±0.010 | 0.022±0.019 | |||||
| 角蒿(Incarvillea sinensis) | 0.033±0.029 | 0.067±0.046 | |||||||
| 阿尔泰狗娃花(Heteropappus altaicus) | 0.073±0.022 | 0.047±0.024 | 0.159±0.025 | 0.094±0.009 | 0.238±0.070 | 0.128±0.050 | 0.225±0.051 | 0.245±0.076 | 0.300±0.100 |
| 铁杆蒿(Artemisia sacrorum) | 0.068±0.059 | 0.028±0.024 | 0.118±0.102 | 0.007±0.006 | 0.061±0.042 | 0.019±0.016 | |||
| 茵陈蒿(Artemisia capillaris) | 0.248±0.050 | 0.343±0.108 | 0.067±0.034 | 0.112±0.057 | 0.012±0.010 | ||||
| 冷蒿(Artemisia frigida) | 0.061±0.036 | 0.0214±0.019 | 0.053±0.046 | 0.085±0.060 | 0.032±0.028 | 0.014±0.012 | |||
| 束伞亚菊(Ajania parviflora) | 0.023±0.013 | 0.167±0.060 | 0.040±0.035 | 0.034±0.030 | 0.144±0.048 | 0.072±0.040 | 0.239±0.051 | ||
| 大蓟(Cirsium japonicum) | 0.046±0.040 | ||||||||
| 抱茎风毛菊(Saussurea chingiana) | 0.001±0.001 | ||||||||
| 苦荬菜(Ixeris polycephala) | 0.020±0.010 | 0.006±0.005 | |||||||
| 小苦荬(Ixeridium dentatum) | 0.005±0.004 | ||||||||
Table 2 Importance values of herbs at different slope positions of three slope aspects in Caragana korshinskii plantation (Mean±S.E.)
| 物种 | 阴坡 | 半阳坡 | 阳坡 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上坡位 | 中坡位 | 下坡位 | 上坡位 | 中坡位 | 下坡位 | 上坡位 | 中坡位 | 下坡位 | |
| 赖草(Leymus secalinus) | 0.201±0.071 | 0.179±0.061 | 0.161±0.056 | 0.363±0.124 | 0.205±0.066 | 0.342±0.116 | 0.039±0.034 | ||
| 长芒草(Stipa bungeana) | 0.126±0.050 | 0.033±0.029 | 0.266±0.003 | 0.155±0.068 | 0.210±0.048 | 0.201±0.107 | 0.296±0.059 | 0.336±0.034 | 0.134±0.054 |
| 中华隐子草(Cleistogenes chinensis) | 0.006±0.005 | 0.020±0.018 | |||||||
| 狗尾草(Setaria viridis) | 0.068±0.036 | 0.054±0.041 | 0.019±0.017 | 0.052±0.016 | 0.054±0.014 | 0.058±0.020 | |||
| 灰绿藜(Chenopodium glaucum) | 0.020±0.018 | 0.012±0.010 | |||||||
| 大花蚓果芥(Torularia humilis) | 0.002±0.002 | 0.024±0.012 | 0.033±0.013 | 0.030±0.003 | 0.045±0.016 | 0.034±0.017 | 0.022±0.019 | 0.032±0.016 | |
| 二裂委陵菜(Potentilla bifurca) | 0.041±0.016 | 0.021±0.018 | 0.053±0.027 | ||||||
| 西山委陵菜(Potentilla sischanensis) | 0.004±0.003 | 0.010±0.006 | 0.021±0.012 | 0.004±0.003 | 0.014±0.005 | 0.023±0.013 | |||
| 伏毛山莓草(Sibbaldia adpressa) | 0.041±0.020 | 0.057±0.020 | 0.028±0.020 | 0.011±0.006 | 0.059±0.010 | 0.052±0.021 | 0.054±0.029 | 0.080±0.029 | 0.098±0.032 |
| 糙叶黄耆(Astragalus scaberrimus) | 0.013±0.011 | ||||||||
| 甘肃棘豆(Oxytropis kansuensis) | 0.021±0.012 | ||||||||
| 天蓝苜蓿(Medicago lupulina) | 0.069±0.047 | 0.003±0.003 | 0.018±0.015 | 0.010±0.009 | |||||
| 野亚麻(Linum stelleroides) | 0.005±0.004 | 0.019±0.010 | |||||||
| 骆驼蓬(Peganum harmala) | 0.054±0.027 | 0.048±0.019 | 0.022±0.019 | 0.040±0.021 | 0.043±0.022 | 0.035±0.031 | |||
| 远志(Polygala tenuifolia) | 0.031±0.018 | ||||||||
| 裂叶堇菜(Viola dissecta) | 0.029±0.009 | 0.010±0.008 | |||||||
| 早开堇菜(Viola prionantha) | 0.003±0.003 | ||||||||
| 北方獐牙菜(Swertia diluta) | 0.021±0.018 | ||||||||
| 鹅绒藤(Cynanchum chinense) | 0.006±0.005 | ||||||||
| 地梢瓜(Cynanchum thesioides) | 0.029±0.025 | 0.014±0.012 | 0.019±0.016 | 0.029±0.025 | 0.017±0.015 | 0.056±0.029 | |||
| 田旋花(Convolvulus arvensis) | 0.036±0.032 | ||||||||
| 蒙古芯芭(Cymbaria mongolica) | 0.009±0.008 | 0.005±0.005 | 0.019±0.010 | 0.022±0.019 | |||||
| 角蒿(Incarvillea sinensis) | 0.033±0.029 | 0.067±0.046 | |||||||
| 阿尔泰狗娃花(Heteropappus altaicus) | 0.073±0.022 | 0.047±0.024 | 0.159±0.025 | 0.094±0.009 | 0.238±0.070 | 0.128±0.050 | 0.225±0.051 | 0.245±0.076 | 0.300±0.100 |
| 铁杆蒿(Artemisia sacrorum) | 0.068±0.059 | 0.028±0.024 | 0.118±0.102 | 0.007±0.006 | 0.061±0.042 | 0.019±0.016 | |||
| 茵陈蒿(Artemisia capillaris) | 0.248±0.050 | 0.343±0.108 | 0.067±0.034 | 0.112±0.057 | 0.012±0.010 | ||||
| 冷蒿(Artemisia frigida) | 0.061±0.036 | 0.0214±0.019 | 0.053±0.046 | 0.085±0.060 | 0.032±0.028 | 0.014±0.012 | |||
| 束伞亚菊(Ajania parviflora) | 0.023±0.013 | 0.167±0.060 | 0.040±0.035 | 0.034±0.030 | 0.144±0.048 | 0.072±0.040 | 0.239±0.051 | ||
| 大蓟(Cirsium japonicum) | 0.046±0.040 | ||||||||
| 抱茎风毛菊(Saussurea chingiana) | 0.001±0.001 | ||||||||
| 苦荬菜(Ixeris polycephala) | 0.020±0.010 | 0.006±0.005 | |||||||
| 小苦荬(Ixeridium dentatum) | 0.005±0.004 | ||||||||
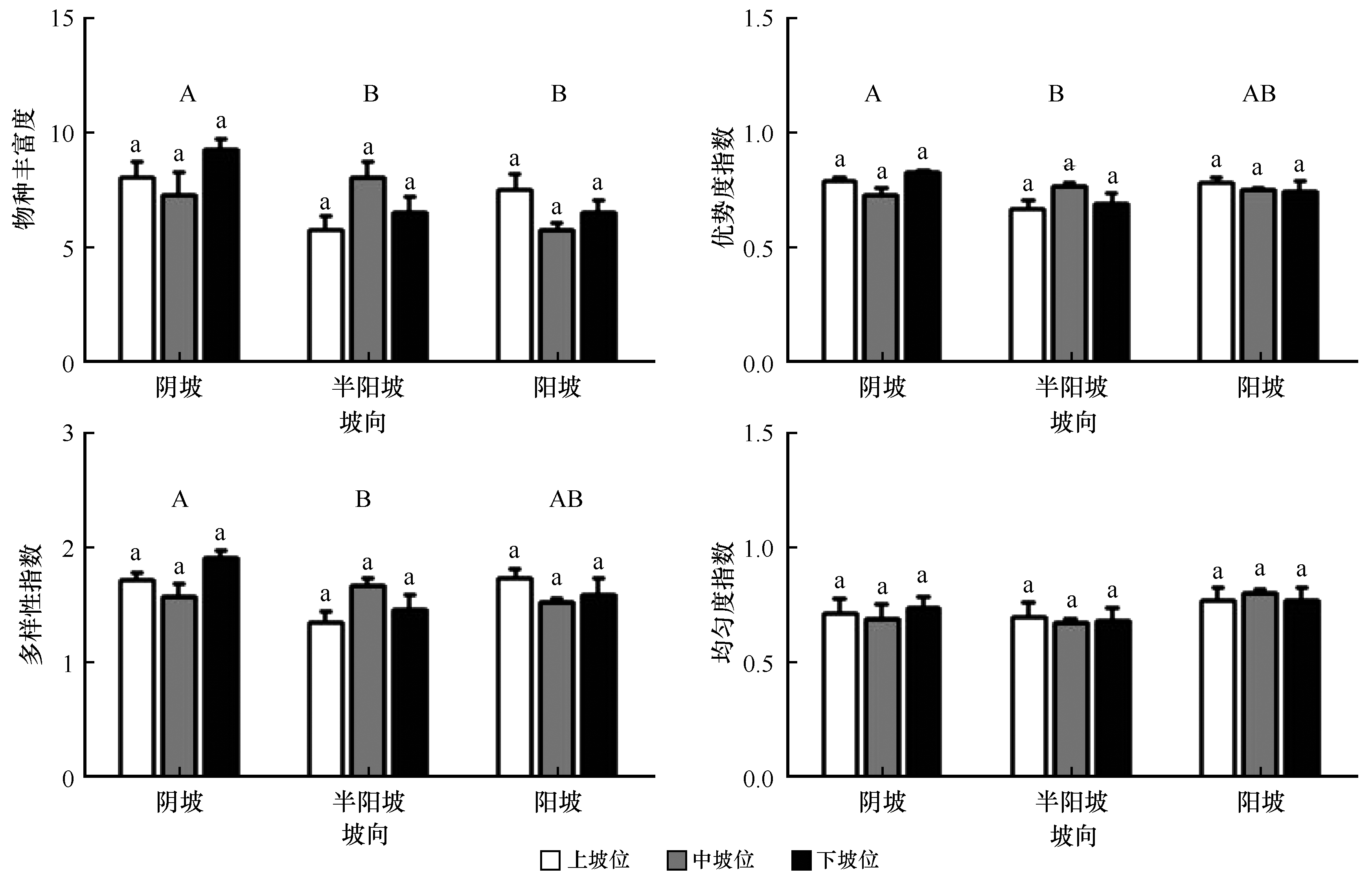
Fig.3 Species richness, Simpson, Shannon-Wiener and Pielouon index of herb community at different slope positions of three slope aspects in Caragana korshinskii plantation
| 指标 | 草本地上 生物量 | 灌木 密度 | 0—40 cm 土壤水分 含量 | 40—200 cm 土壤水分 含量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 草本地上生物量 | 1 | -0.355n.s. | 0.197n.s. | 0.433n.s. |
| 灌木密度 | 1 | -0.034* | 0.130n.s. | |
| 0—40 cm土壤水分含量 | 1 | 0.38n.s. | ||
| 40—200 cm土壤水分含量 | 1 |
Table 3 Pearson correlation of herbaceous biomass with shrub density and soil water content
| 指标 | 草本地上 生物量 | 灌木 密度 | 0—40 cm 土壤水分 含量 | 40—200 cm 土壤水分 含量 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 草本地上生物量 | 1 | -0.355n.s. | 0.197n.s. | 0.433n.s. |
| 灌木密度 | 1 | -0.034* | 0.130n.s. | |
| 0—40 cm土壤水分含量 | 1 | 0.38n.s. | ||
| 40—200 cm土壤水分含量 | 1 |
| 1 | 王晗生.黄土高原植被恢复策略回顾[J].中国水土保持科学,2004,2(1):42-45. |
| 2 | 张金屯.黄土高原植被恢复与建设的理论和技术问题[J].水土保持学报,2004,18(5):120-124. |
| 3 | 张文辉,刘国彬.黄土高原植被恢复与建设策略[J].中国水土保持,2009(1):24-27. |
| 4 | 郭忠升.水资源紧缺地区土壤水分植被承载力论述[J].林业科学,2011,47(5):143-147. |
| 5 | Guo Z S,Shao M A.Impact of afforestation density on soil and water conservation of the semi-arid Loess Plateau,China[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,2013,68(5):401-410. |
| 6 | 周萍,刘国彬,侯喜禄.黄土丘陵区不同坡形及坡位草本群落生物量及多样性研究[J].中国水土保持科学,2009,7(1):67-73. |
| 7 | 崔静,黄佳健,陈云明,等.黄土丘陵区人工柠条林下草本植物物种多样性研究[J].西北林学院学报,2018,33(3):14-20. |
| 8 | 胡相明,程积民,万惠娥.黄土丘陵区人工林下草本层植物的结构特征[J].水土保持通报,2006,26(3):41-45. |
| 9 | 秦伟,朱清科,张宇清,等.陕北黄土区生态修复过程中植物群落物种多样性变化[J].应用生态学报,2009,20(2):403-409. |
| 10 | 张健,刘国彬.黄土丘陵区不同植被恢复模式对沟谷地植物群落生物量和物种多样性的影响[J].自然资源学报,2010,25(2):207-217. |
| 11 | Jia X X,Shao M A,Wei X R.Richness and composition of herbaceous species in restored shrub land and grassland ecosystems in the northern Loess Plateau of China[J].Biodiversity & Conservation,2011,20(14):3435-3452. |
| 12 | 高阳,程积民,赵钰,等.黄土区典型人工林草本层生态恢复效应[J].草地学报,2013,21(1):79-86. |
| 13 | 程积民,杜峰,万惠娥.黄土高原半干旱区集流灌草立体配置与水分调控[J].草地学报,2000,8(3): 210-219. |
| 14 | 程积民,万惠娥,杜锋.黄土高原半干旱区退化灌草植被的恢复与重建[J].林业科学,2001,37(4): 50-57. |
| 15 | Okubo S,Kamiyama A,Kitagawa Y,et al.Plant species composition of the herbaceous layer of secondary woodlands and their verges in relation to micro-scale landform in the Tama Hills,Central Japan[J].Landscape Research Japan Online,2003,66(5):537-542. |
| 16 | Zhao W J,Zhang Y,Zhu Q K,et al.Effects of microtopography on spatial point pattern of forest stands on the semi-arid Loess Plateau,China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2015(3):370-380. |
| 17 | 寇萌,焦菊英,杜华栋,等.黄土丘陵沟壑区不同立地条件草本群落物种多样性与生物量研究[J].西北林学院学报,2013,28(1):12-18. |
| 18 | 马克平,黄建辉,于顺利,等.北京东灵山地区植物群落多样性的研究Ⅱ丰富度、均匀度和物种多样性指数[J].生态学报,1995,15(3):268-277. |
| 19 | 朱云云,王孝安,王贤,等.坡向因子对黄土高原草地群落功能多样性的影响[J].生态学报,2015,36(21):6823-6833. |
| 20 | 汝海丽,张海东,焦峰,等.黄土丘陵区微地形条件下草本群落特征与土壤水分及养分关系分析[J].草地学报,2016,24(4):776-782. |
| 21 | 王子婷,杨磊,蔡国军,等.半干旱黄土区坡面尺度柠条生长状况及影响要素分析[J].生态学报,2017,37(23):115-124. |
| 22 | Gong X,Brueck H,Giese K M,et al.Slope aspect has effects on productivity and species composition of hilly grassland in the Xilin River Basin,Inner Mongolia,China[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2008,72(4):483-493. |
| 23 | 王子婷,杨磊,李广,等.半干旱黄土区苜蓿退化对坡面草本植物分布及多样性的影响[J].生态学报,2019,39(10):3720-3729. |
| 24 | 郑江坤,魏天兴,郑路坤,等.坡面尺度上地貌对α生物多样性的影响[J].生态环境学报,2009,8(6):2254-2259. |
| 25 | Yang L,Wei W,Chen L D,et al.Response of temporal variation of soil moisture to vegetation restoration in semi-arid Loess Plateau,China[J].Catena,2014,115(4):123-133. |
| 26 | 刘丙霞,任健,邵明安,等.黄土高原北部人工灌草植被土壤干燥化过程研究[J].生态学报,2020,40(11):3795-3803. |
| 27 | 贾希洋,周静静,宿婷婷,等.平茬密度对荒漠草原人工柠条林间生境的影响[J].生态学报,2020,40(12):4126-4136. |
| 28 | 刘燕萍,马驰,莫保儒,等.柠条人工林下草本植被特征与土壤特性相关性研究[J].草地学报,2020,28(2):468-473. |
| 29 | 樊如月,李青丰,贺一鸣,等.柠条林分密度对林带间草本群落的影响[J].干旱区资源与环境,2019,33(2):177-182. |
| 30 | Yang Z B,Jin H X,Wang G.An assessment of restoration success to forests planted for ecosystem restoration in loess plateau,Northwestern China[J].Environmental Monitoring & Assessment,2010,164(1):357-368. |
| [1] | Di Deng, Zebin Zhao, Yuan Ma. Modeling of species distribution with GIS in arid regions: take Caragana korshinskii for example [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(5): 74-80. |
| [2] | Wang Wenxing, Yang Tiqiang, Wang Gongyi, Liu Xiangyu, Zhao Qingchun, Li Wei. Sensitivity to Drought Stress of Caragana korshinskii Seeds Treated With Electric Field [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(5): 1310-1314. |
| [3] | Wang Linlong, Liu Minghu, Li Qinghe, Xu Jun. Architecture Characteristics of Helianthemum songaricum under Different Habitats [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(3): 651-658. |
| [4] | Zhu Meng, Liu Wei, Qin Yanyan, Cao Jianjun, Li Huiya, Zhao Yu. Distribution of Soil Organic Carbon at Hillslope Scale in Forest-steppe Zone of Qilian Mountains [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(3): 741-748. |
| [5] | Bao Jingting, Wang Jin, Su Jieqiong. Photosynthetic Properties and Water Use Characteristics in Caragana korshinskii in Different Ages [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(1): 199-205. |
| [6] | Pan Yanxia, Wang Xinping, Zhang Yafeng, Hu Rui. Influence of Topography on Formation Characteristics of Hygroscopic and Condensate Water in Shapotou, Ningxia, China [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2014, 34(1): 118-124. |
| [7] | WANG Xin-ping, LI Xin-rong, ZHANG Jing-guang. Infiltration Processes of Precipitation in a Revegetated Sand Dune with Caragana korshinskii Shrub [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2002, 22(6): 534-540. |
| [8] | ZHOU Hai-yan, ZHANG Jing-guang, ZHAO Liang, WANG Gang. Gas Exchange Characteristics and Regulation Mechanism of Several Caragana Shrubs Under Wet Condition [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2002, 22(4): 316-320. |
| [9] | Wang Bangxi, Huang Jiuchang, Wang hu. EFFECTS OF LIGHT INTENSITY AND TEMPERATURE ON PHOTOSYNTHESIS AND RESPIRATION IN LEAVES OF CARAGANA KORSHINSKII KOM. DURING DIFFERENT GROWTH SEASONS [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 1996, 11(2): 145-148. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech