
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 104-113.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00110
Yuting Xiao1,2,3( ), Guoming Zhang1,2,4,5(
), Guoming Zhang1,2,4,5( ), Chang Hong1,2,3, Lianyou Liu1,2,3, Yanyan Yang6, Yu Gu1,2,3, Yong Liu1,2,3, Mingzhu Xiang1,2,3, Shufeng Qu1,2,3, Xuran Sun1,2,3
), Chang Hong1,2,3, Lianyou Liu1,2,3, Yanyan Yang6, Yu Gu1,2,3, Yong Liu1,2,3, Mingzhu Xiang1,2,3, Shufeng Qu1,2,3, Xuran Sun1,2,3
Received:2022-05-04
Revised:2022-09-05
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2023-04-12
Contact:
Guoming Zhang
CLC Number:
Yuting Xiao, Guoming Zhang, Chang Hong, Lianyou Liu, Yanyan Yang, Yu Gu, Yong Liu, Mingzhu Xiang, Shufeng Qu, Xuran Sun. Sand-dust horizontal flux of different surfaces in the western margin of Badain Jaran Desert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 104-113.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00110
| 地表类型 | 2019-02—2019-07 | 2019-07—2019-12 | 2019-12—2020-07 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y1 | y2 | y3 | ||||||||||||
| c | b | a | R2 | c | b | a | R2 | c | b | a | R2 | |||
| 芦苇滩地 | 7.66 | -10.90 | 14 887.09 | 0.9958 | 7.36 | -12.49 | 3 208.11 | 0.9999 | 9.13 | -11.71 | 4 757.25 | 0.9885 | ||
| 干涸湖床 | -4.70 | 0.46 | 58 240.00 | 0.9898 | -3.14 | -3.03 | 52 352.60 | 0.9988 | 1.38 | -5.86 | 82 441.94 | 0.9956 | ||
| 盐碱滩地 | 5.98 | -8.89 | 5 798.77 | 0.9976 | 7.53 | -11.48 | 2 141.38 | 0.9999 | 7.85 | -10.80 | 5 465.93 | 0.9955 | ||
| 流动沙地 | -11.12 | 2.38 | 58 131.80 | 0.9956 | -9.88 | -0.44 | 68 364.59 | 0.9996 | -16.22 | 4.39 | 34 085.22 | 0.9995 | ||
| 灌丛沙堆 | 3.54 | -6.26 | 3 526.89 | 0.9986 | 2.87 | -6.10 | 714.96 | 0.9999 | 4.59 | -6.99 | 875.65 | 0.9934 | ||
Table 1 Fitting coefficients of the horizontal distribution function of sand-dust flux with height over different surfaces
| 地表类型 | 2019-02—2019-07 | 2019-07—2019-12 | 2019-12—2020-07 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y1 | y2 | y3 | ||||||||||||
| c | b | a | R2 | c | b | a | R2 | c | b | a | R2 | |||
| 芦苇滩地 | 7.66 | -10.90 | 14 887.09 | 0.9958 | 7.36 | -12.49 | 3 208.11 | 0.9999 | 9.13 | -11.71 | 4 757.25 | 0.9885 | ||
| 干涸湖床 | -4.70 | 0.46 | 58 240.00 | 0.9898 | -3.14 | -3.03 | 52 352.60 | 0.9988 | 1.38 | -5.86 | 82 441.94 | 0.9956 | ||
| 盐碱滩地 | 5.98 | -8.89 | 5 798.77 | 0.9976 | 7.53 | -11.48 | 2 141.38 | 0.9999 | 7.85 | -10.80 | 5 465.93 | 0.9955 | ||
| 流动沙地 | -11.12 | 2.38 | 58 131.80 | 0.9956 | -9.88 | -0.44 | 68 364.59 | 0.9996 | -16.22 | 4.39 | 34 085.22 | 0.9995 | ||
| 灌丛沙堆 | 3.54 | -6.26 | 3 526.89 | 0.9986 | 2.87 | -6.10 | 714.96 | 0.9999 | 4.59 | -6.99 | 875.65 | 0.9934 | ||
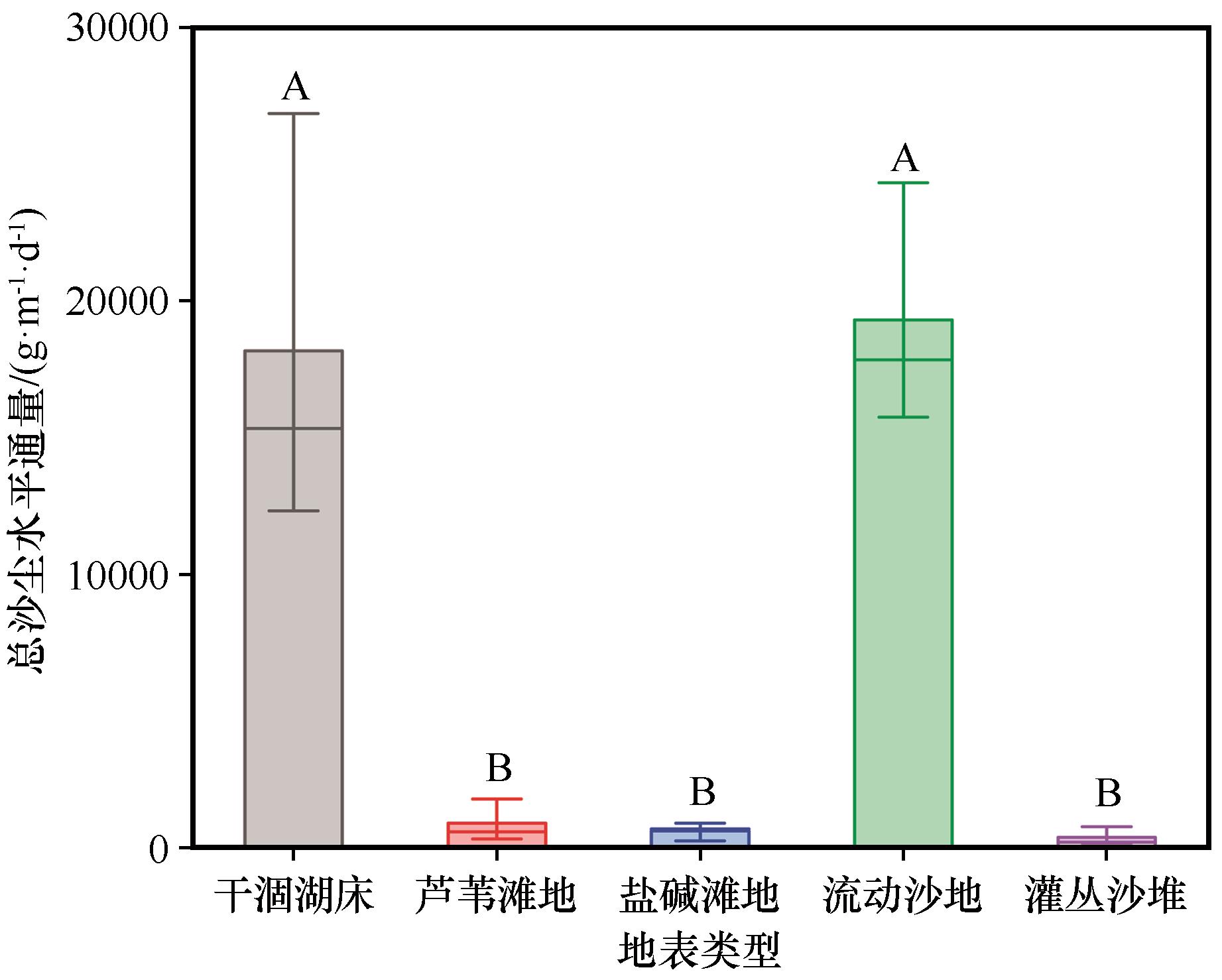
Fig. 5 The derived total horizontal sand-dust flux from MWAC sediment samplers in different areas show an average from February of 2019 to July of 2020 (Significant difference is denoted by the A and B symbols,P<0.01)
| 1 | Yang X P.Geomorphologische untersuchungen in trockenrumen NW-Chinas unter besonderer berücksichtigung von Badanjilin und Takelamagan[J].Gottinger Geographische Abhandlungen,1991,96:1-36. |
| 2 | 闫满存,王光谦,李保生,等.巴丹吉林沙漠高大沙山的形成发育研究[J].地理学报,2001,56(1):83-91. |
| 3 | Mischke S.New evidence for origin of Badain Jaran Desert of Inner Mongolia from granulometry and thermoluminescence dating[J].Journal of Palaeogeography,2005,7(1):79-97. |
| 4 | 宁凯,王乃昂,李卓仑,等.基于CMB模型的巴丹吉林沙漠沙源区分析[J].干旱区地理,2021,44(2):389-399. |
| 5 | Hu F G, Yang X P.Geochemical and geomorphological evidence for the provenance of aeolian deposits in the Badain Jaran Desert,northwestern China[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2016,131:179-192. |
| 6 | 武建军,何丽红,郑晓静.跃移层中沙粒浓度分布特征的研究[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2002,38(3):15-21. |
| 7 | 董治宝,孙宏义,赵爱国.WITSEG集沙仪:风洞用多路集沙仪[J].中国沙漠,2003,23(6):111-117. |
| 8 | 常兆丰,赵建林,刘世增,等.集沙仪开发研究现状、问题及突破点[J].生态学杂志,2018,37(9):2834-2839. |
| 9 | Breshears D D, Whicker J J, Johansen M P,et al.Wind and water erosion and transport in semi-arid shrubland,grassland and forest ecosystems:quantifying dominance of horizontal wind-driven transport[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2010,28(11):1189-1209. |
| 10 | 康永德,杨兴华,肖让,等.基于精细化观测的沙尘通量分布特征[J].地球环境学报,2020,11(3):255-264. |
| 11 | Etyemezian V, Nikolich G, Ahonen S,et al.The Portable In Situ Wind Erosion Laboratory (PI-SWERL):a new method to measure PM10 windblown dust properties and potential for emissions[J].Atmospheric Environment,2007,41(18):3789-3796. |
| 12 | Baddock M C, Zobeck T M, Pelt R S V,et al.Dust emissions from undisturbed and disturbed,crusted playa surfaces:cattle trampling effects[J].Aeolian Research,2011,3(1):31-41. |
| 13 | Sankey J B, Germino M J, Glenn N F.Dust supply varies with sagebrush microsites and time since burning in experimental erosion events[J].Journal of Geophysical Research (Biogeosciences),2012,117:G01013. |
| 14 | Zhao Y, Huang A, Zhu X,et al.The impact of the winter North Atlantic Oscillation on the frequency of spring dust storms over Tarim Basin in northwest China in the past half-century[J].Environmental Research Letters,2013,8(2):24026. |
| 15 | Yang X H, Shen S H, Yang F,et al.Spatial and temporal variations of blowing dust events in the Taklimakan Desert[J].Theoretical and Applied Climatology,2016,125:669-677. |
| 16 | 黄雨晖,韩小元,赵健,等.新疆戈壁地区风沙流结构及其粒径特征研究[J].气象与减灾研究,2019,42(3):199-205. |
| 17 | 张克存,屈建军,俎瑞平,等.戈壁-流沙地表风沙流特性研究[J].干旱区资源与环境,2008,22(10):55-59. |
| 18 | Huo W, He Q, Yang F,et al.Observed particle sizes and fluxes of Aeolian sediment in the near surface layer during sand-dust storms in the Taklamakan Desert[J].Theoretical and Applied Climatology,2017,130:735-746. |
| 19 | 屈建军,黄宁,拓万全,等.戈壁风沙流结构特性及其意义[J].地球科学进展,2005,20(1):19-23. |
| 20 | 张克存,屈建军,俎瑞平,等.戈壁风沙流结构和风速廓线特征研究[J].水土保持研究,2005,12(1):54-55. |
| 21 | 杨帆,郑新倩,努尔阿米娜·依明,等.巴丹吉林沙漠北缘沙尘天气过程中近地面气象要素变化及风沙流结构分析[J].沙漠与绿洲气象,2015,9(4):67-74. |
| 22 | 刘旭阳,宁文晓,王振亭.两种戈壁地表风沙流特征的野外观测[J].干旱区研究,2020,37(4):1087-1094. |
| 23 | Farrell E J, Sherman D J, Ellis J T,et al.Vertical distriburion of grain size for wind blown sand[J].Aeolian Research,2012,7:51-61. |
| 24 | 屈建军,张克存,张伟民,等.几种典型戈壁床面风沙流特性比较[J].中国沙漠,2012,32(2):285-290. |
| 25 | 郭树江,杨自辉,王强强,等.青土湖干涸湖底风沙流结构及输沙粒径特征[J].生态学杂志,2021,40(4):1166-1176. |
| 26 | 杨兴华,何清,程玉景,等.策勒绿洲-荒漠过渡带风沙前沿近地表沙尘水平通量观测[J].干旱区研究,2013,30(6):1100-1105. |
| 27 | 韩菲.中国北方沙漠鸣沙特征对比及其成因研究[D].北京:中国地质大学(北京),2017. |
| 28 | 何清,胡文峰,杨兴华,等.巴丹吉林沙漠拐子湖地区贴地层风速廓线和风沙流结构特征[J].干旱区研究,2012,29(3):517-523. |
| 29 | 赵文智,白雪莲,刘婵.巴丹吉林沙漠南缘的植物固沙问题[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(1):5-11. |
| 30 | 刘鑫,焦健,王婷,等.巴丹吉林沙漠南缘沙地芦苇种群生态特征[J].干旱区研究,2022,39(1):220-229. |
| 31 | 马瑞,赵锦梅,马彦军,等.巴丹吉林沙漠南缘近流沙区白刺灌丛沙堆形态特征与空间分布[J].水土保持学报,2021,35(4):217-221. |
| 32 | 何青华.巴丹吉林沙漠湖泊沉积与泥炭层植硅体记录的全新世环境演变研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2021. |
| 33 | 张律吕.巴丹吉林沙漠全新世湖泊沉积记录及其演变机制探讨[D].兰州:兰州大学,2019. |
| 34 | 白旸,王乃昂,何瑞霞,等.巴丹吉林沙漠湖相沉积的探地雷达图像及光释光年代学证据[J].中国沙漠,2011,31(4):842-847. |
| 35 | 朱金峰,王乃昂,陈红宝,等.基于遥感的巴丹吉林沙漠范围与面积分析[J].地理科学进展,2010,29(9):1087-1094. |
| 36 | Yang X, Ma N, Dong J,et al.Recharge to the inter-dune lakes and Holocene climatic changes in the Badain Jaran Desert,western China[J].Quaternary Research,2010,73(1):10-19. |
| 37 | 刘红梅,吕世杰,任倩楠,等.巴丹吉林沙漠梭梭林下沙质土壤的粒径变化和空间分布特征研究[J].草地学报,2021,29(6):1249-1256. |
| 38 | Fryrear D W.A field dust sampler[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,1986,41:117-120. |
| 39 | Kirkby M J, Morgan R P C.Soil Erosion[M].Chichester,USA: John Wiley & Sons,1980:217-251. |
| 40 | Li J, Okin G S, Alvarez L,et al.Quantitative effects of vegetation cover on wind erosion and soil nutrient loss in a desert grassland of southern New Mexico,USA[J].Biogeochemistry,2007,85:317-332. |
| 41 | Shao Y P, Raupach M R.The overshoot and equilibration of saltation[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,1992,97(20):559-564. |
| 42 | Bhattachan A, D'Odorico P, Okin G S,et al.Potential dust emissions from the southern Kalahari’s dunelands[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface,2013,118:307-314. |
| 43 | Dukes D, Gonzales H B, Ravi S,et al.Quantifying postfire aeolian sediment transport using rare earth element tracers[J].Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences,2018,123(1):288-299. |
| 44 | 张克存,屈建军,董治宝,等.风沙流中风速脉动对输沙量的影响[J].中国沙漠,2006,26(3):336-340. |
| 45 | 王自龙,赵明,冯向东,等.民勤绿洲外围不同下垫面条件下风沙流结构的观测研究[J].水土保持学报,2009,23(4):72-75. |
| 46 | 王金国,安志山,张克存,等.乌玛高速公路中卫段风沙环境及输移规律[J].水土保持研究,2021,28(6):183-189. |
| 47 | 吴晓旭,邹学勇,王仁德,等.毛乌素沙地不同下垫面的风沙运动特征[J].中国沙漠,2011,31(4):828-835. |
| 48 | 邳华伟,冯广龙.塔里木盆地西北部3种典型下垫面风沙活动特征[J].干旱区研究,2016,33(2):441-448. |
| 49 | 洛桑曲加,张焱,马鹏飞,等.雅鲁藏布江中游不同地表输沙量特征[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(2):6-13. |
| 50 | 胡文峰.巴丹吉林沙漠拐子湖地区春季风沙观测研究[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆师范大学,2012. |
| 51 | 鲁涛,刘维,徐玉波,等.台特玛湖干涸湖盆区风蚀起沙研究[J].干旱区资源与环境,2021,35(11):119-126. |
| 52 | 王洪涛,董治宝,张晓航.风沙流中沙粒浓度分布的实验研究[J].地球科学进展,2004,19(5):732-735. |
| 53 | Dong Z B, Lv P, Zhang Z C,et al.Aeolian transport over a developing transverse dune[J].Journal of Arid Land,2014,6(3):243-254. |
| 54 | 陶彬彬,哈斯额尔敦,乌格特茉勒,等.库布齐沙漠南缘抛物线形沙丘表面风速与输沙率的变异[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(6):1445-1452. |
| 55 | 李菁菁,李得禄,满多清,等.不同年代退耕地上2种积沙仪风沙流特征比较[J].中国农学通报,2021,37(8):60-65. |
| 56 | 刘芳,郝玉光,辛智鸣,等.乌兰布和沙漠东北缘地表风沙流结构特征[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(5):1200-1207. |
| 57 | 管雪薇,杨采怡,刘广明,等.吉兰泰盐湖防护体系阻沙效应及输沙粒度特征[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(4):50-59. |
| 58 | Field J P, Breshears D D, Whicker J J,et al.Sediment capture by vegetation patches:implications for desertification and increased resource redistribution[J].Journal of Geophysical Research: Biogeosciences,2012,117(1):G01033. |
| 59 | Okin G S, Gillette D A.Distribution of vegetation in wind-dominated landscapes:implications for wind erosion modeling and landscape processes[J].Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres,2001,106(D9):9673-9683. |
| 60 | 刘铮瑶,董治宝,王建博,等.巴丹吉林沙漠边缘地区植被特征[J].中国沙漠,2016,36(5):1348-1356. |
| 61 | 崔徐甲,董治宝,逯军峰,等.巴丹吉林沙漠高大沙山区植被特征与地貌形态的关系[J].水土保持通报,2014,34(5):278-283. |
| 62 | 王兆云,牛改红,柳本立.风沙活动强度3种估算指标对比及适用性分析[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(3):118-126. |
| 63 | 董玉祥,马骏.风速对海岸沙丘表面风沙流结构影响的实证研究[J].干旱区资源与环境,2009,23(9):179-183. |
| 64 | Zhang Z C, Dong Z B, Li C X.Wind regime and sand transport in China's Badain Jaran Desert[J].Aeolian Research,2015,17:1-13. |
| 65 | Liu X, Kang Y, Chen H,et al.Application of a high-precision aeolian sand collector in field wind and sand surveys[J].International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2021,18(14):7393. |
| 66 | 毛东雷,雷加强,王翠,等.新疆策勒县沙漠-绿洲过渡带风沙流结构及输沙粒度特征[J].水土保持通报,2015,35(1):25-33. |
| 67 | 张克存,奥迎焕,屈建军,等.巴丹吉林沙漠湖泊-沙山近地表风沙动力环境[J].干旱区地理,2013,36(5):790-794. |
| [1] | Yanxia Pan, Rong Hui, Xinrong Li. Distribution and characteristics of microorganisms in deserts of China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(1): 244-256. |
| [2] | Meng Wang, Junfeng Lu, Peng Fu, Zhibao Dong. Characteristics of soil nutrients and grain size around Badain Jaran Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 232-244. |
| [3] | Yunfeng Zhang, Yijuan Ma, Zhizhu Su, Aimin Liang, Xin Zhang, Yingying Cui. Dune movement in the joint zone of the Badain Jaran Desert and Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 82-91. |
| [4] | Heng Ren, Wenzhi Zhao, Zhitao Wang, Jiang Zhao. Spatial pattern of Psammochloa villosa population in patch landscape in dune habitat [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 89-98. |
| [5] | Hui Zhao, Hongyu Yang, Xingfan Wang, Keqi Wang. Geochronology of the typical sediments in the Badain Jaran Desert: the progress and issues [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 57-65. |
| [6] | Lichao Zhuang, Naiang Wang, Xunhe Zhang, Liqiang Zhao, Xianbao Su. Analysis on the difference of the spatial model of lake ice freezing and melting in the Badain Jaran Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(3): 214-223. |
| [7] | Sarina, Zhibao Dong, Weige Nan. The Aesthetic Value of Mega-dune Lines in the Badain Jaran Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 221-230. |
| [8] | Chunyan Zhao, Jianhua Si, Qi Feng, Huan Luo, Jie Qin. Transformation of livelihood strategy for herdsman in Badain Jaran Desert and its impact on ecological environment [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 34-42. |
| [9] | Keqi Wang, Hui Zhao, Yongwei Sheng, Shengan Zhang, Xingfan Wang, Hongyu Yang, Qian Chao. Distribution and morphological parameters of dunes in the Badain Jaran Desert based on DEM [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 81-94. |
| [10] | Jiang Yingsha, Gao Yanhong, Pan Yongjie, Li Xia. Spatial and Seasonal Distributions of Sand Dusts in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and Its Surrounding Areas [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(4): 83-91. |
| [11] | Liu Chan, Zhao Wenzhi, Liu Bing, Meng Yangyang. Distribution Characteristics and Dynamic Changes of Vegetation in Badain Jaran Desert: Based on UAV and MODIS Data [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(4): 92-102. |
| [12] | Zheng Xinqian, Yang Fan, Li Chaofan, Pan Honglin, Ji Chunrong, Ali Mamtimin, Huo Wen, Yang Xinghua, Zhou Chenglong. The Turbulence Intensity of Surface Layer and Land Surface Processes over Guaizi Lake Shifting Sandy Land on the Northern Margin of Badain Jaran Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(4): 103-112. |
| [13] | Xu Xingbin, Wang Naiang, Liang Xiaoyan, Niu Zhenmin, Zhao Liqiang, Wang Yixin. Temperature, Humidity Profiles and Heat Balance in the Megadune Surface Layer of the Badain Jaran Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(6): 1303-1312. |
| [14] | Liu Zhengyao, Dong Zhibao, Sarina, Yang Junhuai, Chen Guoxiang, Liu Yonglin, Luo Wanyin, Yang Zhuanling, Xiao Nan. Grain size and Micro-morphology Characteristics of the Surface Sediments in the Marginal Area of the Badan Jaran Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(5): 945-953. |
| [15] | Yang Yang, Yang Fan, Ali Mamtimin, Yang Xinghua, Huo Wen, Zhou Chenglong, He Qing, Chen Shuai. Comparative Analyses on Surface Radiation Characteristic in Tazhong of the Taklamakan Desert and Guaizihu Lake of the Badain Jaran Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2018, 38(5): 1068-1077. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech