
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 82-91.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00020
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yunfeng Zhang1( ), Yijuan Ma1, Zhizhu Su2, Aimin Liang3(
), Yijuan Ma1, Zhizhu Su2, Aimin Liang3( ), Xin Zhang3, Yingying Cui3
), Xin Zhang3, Yingying Cui3
Received:2021-12-30
Revised:2022-03-04
Online:2022-09-20
Published:2022-09-22
Contact:
Aimin Liang
CLC Number:
Yunfeng Zhang, Yijuan Ma, Zhizhu Su, Aimin Liang, Xin Zhang, Yingying Cui. Dune movement in the joint zone of the Badain Jaran Desert and Tengger Desert[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 82-91.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00020
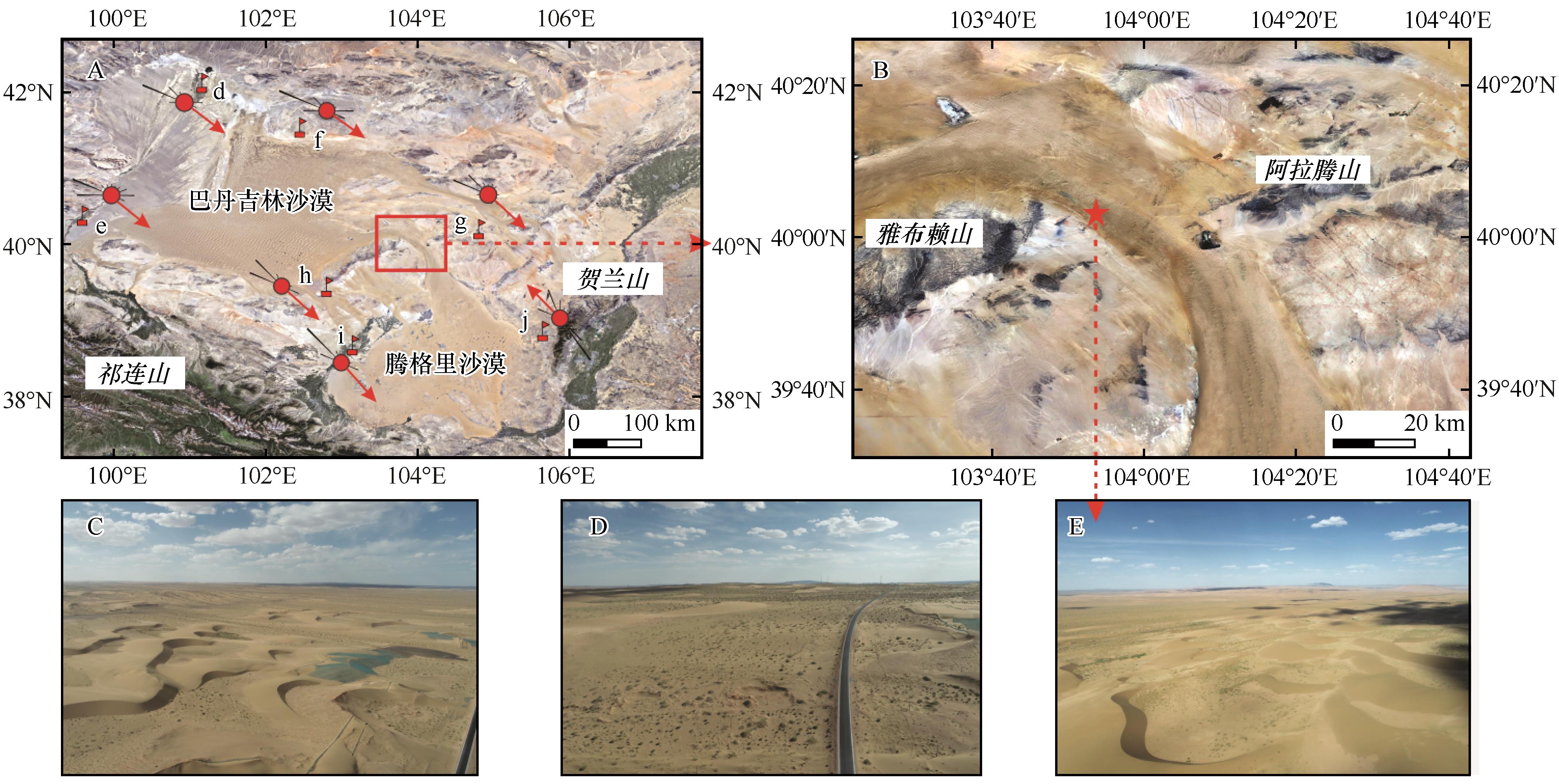
Fig.1 Location (A), surface landscape (B) of the study area and the drift potential of the area around the study area and its landscape (C, D, E).d:Ejina Banner; e:Dingxin; f:Guaizihu; g:Bayanor Gong; h:Yabrai; i:Minqin; j:Alxa Left Banner
| 项 目 | 迎风坡 | 丘顶 | 背风坡 | 北翼 | 南翼 | 沙丘 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 移动速率 | 北部A (11个) | 范围/(m·a-1) | 4.80—22.25 | 7.67—19.68 | 7.69—19.11 | 6.03—19.04 | 5.60—22.16 | 7.87—19.55 |
| 均值/(m·a-1) | 10.44 | 11.43 | 11.07 | 10.79 | 12.19 | 11.19 | ||
| 标准差 | 4.32 | 3.34 | 3.18 | 4.01 | 4.58 | 3.24 | ||
中部B (28个) | 范围/(m·a-1) | 5.75—12.35 | 5.49—14.16 | 5.44—13.81 | 5.36—13.69 | 3.87—15.82 | 5.88—13.25 | |
| 均值/(m·a-1) | 9.31 | 9.94 | 9.60 | 9.58 | 10.76 | 9.84 | ||
| 标准差 | 1.79 | 1.92 | 1.91 | 1.82 | 2.92 | 1.77 | ||
南部C (15个) | 范围/(m·a-1) | 4.99—14.06 | 6.16—13.59 | 6.14—13.25 | 6.22—13.91 | 5.27—17.13 | 6.21—13.45 | |
| 均值/(m·a-1) | 9.30 | 9.48 | 9.31 | 9.11 | 10.50 | 9.54 | ||
| 标准差 | 2.40 | 2.12 | 2.10 | 2.24 | 3.37 | 2.21 | ||
全部沙丘 (54个) | 范围/(m·a-1) | 4.80—22.25 | 5.49—19.68 | 5.44—19.11 | 5.36—19.04 | 3.87—22.16 | 5.88—19.55 | |
| 均值/(m·a-1) | 9.54 | 10.12 | 9.82 | 9.69 | 10.98 | 10.03 | ||
| 标准差 | 2.62 | 2.38 | 2.31 | 2.53 | 3.42 | 2.27 | ||
| 移动方向 | 北部A (11个) | 范围/(°) | 111—131 | 112—141 | 112—140 | 106—132 | 109—132 | 113-127 |
| 均值/(°) | 119 | 119 | 118 | 114 | 121 | 118 | ||
| 标准差 | 6.35 | 8.61 | 8.41 | 7.51 | 7.77 | 3.83 | ||
中部B (28个) | 范围/(°) | 107—139 | 111—133 | 110—136 | 110—130 | 103—138 | 113—130 | |
| 均值(°) | 125 | 123 | 124 | 120 | 123 | 123 | ||
| 标准差 | 7.43 | 6.43 | 7.03 | 5.51 | 8.45 | 5.32 | ||
南部C (15个) | 范围/(°) | 112—149 | 109—136 | 109—136 | 110—132 | 100—134 | 109—135 | |
| 均值/(°) | 128 | 124 | 125 | 120 | 122 | 124 | ||
| 标准差 | 10.30 | 7.12 | 7.89 | 6.69 | 8.75 | 6.57 | ||
全部沙丘 (54个) | 范围/(°) | 107—149 | 109—141 | 109—140 | 106—132 | 100—138 | 109—135 | |
| 均值/(°) | 125 | 123 | 123 | 119 | 122 | 122 | ||
| 标准差 | 8.58 | 7.25 | 7.78 | 6.60 | 8.31 | 5.73 | ||
Table 1 Movement law of barchan dune
| 项 目 | 迎风坡 | 丘顶 | 背风坡 | 北翼 | 南翼 | 沙丘 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 移动速率 | 北部A (11个) | 范围/(m·a-1) | 4.80—22.25 | 7.67—19.68 | 7.69—19.11 | 6.03—19.04 | 5.60—22.16 | 7.87—19.55 |
| 均值/(m·a-1) | 10.44 | 11.43 | 11.07 | 10.79 | 12.19 | 11.19 | ||
| 标准差 | 4.32 | 3.34 | 3.18 | 4.01 | 4.58 | 3.24 | ||
中部B (28个) | 范围/(m·a-1) | 5.75—12.35 | 5.49—14.16 | 5.44—13.81 | 5.36—13.69 | 3.87—15.82 | 5.88—13.25 | |
| 均值/(m·a-1) | 9.31 | 9.94 | 9.60 | 9.58 | 10.76 | 9.84 | ||
| 标准差 | 1.79 | 1.92 | 1.91 | 1.82 | 2.92 | 1.77 | ||
南部C (15个) | 范围/(m·a-1) | 4.99—14.06 | 6.16—13.59 | 6.14—13.25 | 6.22—13.91 | 5.27—17.13 | 6.21—13.45 | |
| 均值/(m·a-1) | 9.30 | 9.48 | 9.31 | 9.11 | 10.50 | 9.54 | ||
| 标准差 | 2.40 | 2.12 | 2.10 | 2.24 | 3.37 | 2.21 | ||
全部沙丘 (54个) | 范围/(m·a-1) | 4.80—22.25 | 5.49—19.68 | 5.44—19.11 | 5.36—19.04 | 3.87—22.16 | 5.88—19.55 | |
| 均值/(m·a-1) | 9.54 | 10.12 | 9.82 | 9.69 | 10.98 | 10.03 | ||
| 标准差 | 2.62 | 2.38 | 2.31 | 2.53 | 3.42 | 2.27 | ||
| 移动方向 | 北部A (11个) | 范围/(°) | 111—131 | 112—141 | 112—140 | 106—132 | 109—132 | 113-127 |
| 均值/(°) | 119 | 119 | 118 | 114 | 121 | 118 | ||
| 标准差 | 6.35 | 8.61 | 8.41 | 7.51 | 7.77 | 3.83 | ||
中部B (28个) | 范围/(°) | 107—139 | 111—133 | 110—136 | 110—130 | 103—138 | 113—130 | |
| 均值(°) | 125 | 123 | 124 | 120 | 123 | 123 | ||
| 标准差 | 7.43 | 6.43 | 7.03 | 5.51 | 8.45 | 5.32 | ||
南部C (15个) | 范围/(°) | 112—149 | 109—136 | 109—136 | 110—132 | 100—134 | 109—135 | |
| 均值/(°) | 128 | 124 | 125 | 120 | 122 | 124 | ||
| 标准差 | 10.30 | 7.12 | 7.89 | 6.69 | 8.75 | 6.57 | ||
全部沙丘 (54个) | 范围/(°) | 107—149 | 109—141 | 109—140 | 106—132 | 100—138 | 109—135 | |
| 均值/(°) | 125 | 123 | 123 | 119 | 122 | 122 | ||
| 标准差 | 8.58 | 7.25 | 7.78 | 6.60 | 8.31 | 5.73 | ||
| 年份 | 迎风坡长度/m (范围/均值) | 高度/m (范围/均值) | 宽度/m (范围/均值) | 周长/m (范围/均值) | 底面积/m2 (范围/均值) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 39.67—169.79/81.17 | 6.31—18.77/11.65 | 94.72—400.97/182.71 | 419—1 327/709 | 6 870—70 671/20 025 |
| 2014 | 42.39—213.54/87.63 | 5.47—18.56/9.56 | 91.90—400.32/195.07 | 386—1 444/738 | 5 612—62 357/20 573 |
Table 2 Dune morphological parameters change
| 年份 | 迎风坡长度/m (范围/均值) | 高度/m (范围/均值) | 宽度/m (范围/均值) | 周长/m (范围/均值) | 底面积/m2 (范围/均值) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2003 | 39.67—169.79/81.17 | 6.31—18.77/11.65 | 94.72—400.97/182.71 | 419—1 327/709 | 6 870—70 671/20 025 |
| 2014 | 42.39—213.54/87.63 | 5.47—18.56/9.56 | 91.90—400.32/195.07 | 386—1 444/738 | 5 612—62 357/20 573 |
| 年份 | 苗条 | 正常 | 矮胖 | 胖 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量/个 | 占比/% | 数量/个 | 占比/% | 数量/个 | 占比/% | 数量/个 | 占比/% | |
| 2003 | 36 | 66.67 | 16 | 29.63 | 2 | 3.70 | — | — |
| 2014 | 38 | 70.37 | 11 | 20.37 | 4 | 7.41 | 1 | 1.85 |
Table 3 Barchan dune shape changes
| 年份 | 苗条 | 正常 | 矮胖 | 胖 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数量/个 | 占比/% | 数量/个 | 占比/% | 数量/个 | 占比/% | 数量/个 | 占比/% | |
| 2003 | 36 | 66.67 | 16 | 29.63 | 2 | 3.70 | — | — |
| 2014 | 38 | 70.37 | 11 | 20.37 | 4 | 7.41 | 1 | 1.85 |
| 沙丘编号 | 植被覆盖情况 | 沙丘密度 | 高度/m | 宽度/m | 移动速率/( m?a-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2号 (北部) | 裸露平坦 无植被覆盖 | 以新月形沙丘为主 沙丘密度较低 | 10.06 | 107.07 | 19.55 |
43号 (南部) | 灌丛沙包 分布于丘间地 | 新月形沙丘链分布 沙丘密度较高 | 10.48 | 112.05 | 9.64 |
Table 4 Comparison of dune movement rate under different conditions
| 沙丘编号 | 植被覆盖情况 | 沙丘密度 | 高度/m | 宽度/m | 移动速率/( m?a-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2号 (北部) | 裸露平坦 无植被覆盖 | 以新月形沙丘为主 沙丘密度较低 | 10.06 | 107.07 | 19.55 |
43号 (南部) | 灌丛沙包 分布于丘间地 | 新月形沙丘链分布 沙丘密度较高 | 10.48 | 112.05 | 9.64 |
| 1 | Livingstone I, Warren A.Aeolian Geomorphology:A New Introduction[M].Hoboken,USA:John Wiley & Sons,2019. |
| 2 | Yang Z L, Qian G Q, Dong Z B,et al.Migration of barchan dunes and factors that influence migration in the Sanlongsha dune field of the northern Kumtagh Sand Sea,China[J].Geomorphology,2021,378(3):107615. |
| 3 | 杨岩岩,刘连友,屈志强,等.新月形沙丘研究进展[J].地理科学,2014,34(1):76-83. |
| 4 | 李志中.新月形沙丘研究进展综述[J].干旱区地理,1994(4):81-87. |
| 5 | Hunter R E, Richmond B M, Alpha T R.Storm-controlled oblique dunes of the Oregon coast[J].Geological Society of America Bulletin,1983,94(12):1450. |
| 6 | 王宁波,李生宇,王海峰,等.塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地垄间地上覆沙丘形态的空间变化特征及其成因[J].干旱区地理,2014,37(1):89-96. |
| 7 | Dong Z B, Qian G Q, Lv P,et al.Investigation of the sand sea with the tallest dunes on Earth:China's Badain Jaran Sand Sea[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2013,120:20-39. |
| 8 | 哈斯,董光荣,王贵勇.腾格里沙漠东南缘格状沙丘的形态-动力学研究[J].中国科学D辑:地球科学,1999(5):466-471. |
| 9 | Yang Y Y, Qu Z Q, Shi P J,et al.Wind regime and sand transport in the corridor between the Badain Jaran and Tengger Deserts,central Alxa Plateau,China[J].Aeolian Research,2014,12:143-156. |
| 10 | 张诚.阿拉善沙漠风积砂重矿物组成及物源分析[D].兰州:兰州大学,2020. |
| 11 | 董治宝,吕萍.70年来中国风沙地貌学的发展[J].地理学报,2020,75(3):509-528. |
| 12 | 贺大良.风沙地貌形成机制的几个问题[J].中国沙漠,1985,5(1):35-39. |
| 13 | 杨军怀.塔克拉玛干沙漠沙丘移动研究[D].西安:陕西师范大学,2019. |
| 14 | 刘羽,王秀红,张雪芹,等.巴丹吉林-腾格里沙漠间沙丘活化带发展过程及其驱动力分析[J].干旱区研究,2011,28(6):957-966. |
| 15 | 宁文晓,刘旭阳,王振亭.巴丹吉林沙漠气温和降水特征及空间分层异质性[J].中国科学院大学学报,2021,38(1):103-113. |
| 16 | 刘婵,赵文智,刘冰,等.基于无人机和MODIS数据的巴丹吉林沙漠植被分布特征与动态变化研究[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(4):92-102. |
| 17 | 李建军,焦菊英,曹雪,等.柴达木盆地沙丘移动的空间分异及对形态参数的响应[J].农业工程学报,2021,37(7):309-314. |
| 18 | 王静璞,刘连友,沈玲玲.基于Google Earth的毛乌素沙地新月形沙丘移动规律研究[J].遥感技术与应用,2013,28(6):1094-1100. |
| 19 | 王静璞,王光镇,韩柳,等.毛乌素沙地不同固沙措施下沙丘的移动特征[J].甘肃农业大学学报,2017,52(2):54-60. |
| 20 | 许明静,吕萍,肖南,等.毛乌素沙地西北部植被覆盖对沙丘移动的影响[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(4):71-80. |
| 21 | 刘其悦,余涛,高海亮,等.遥感卫星几何产品真实性检验方法与应用[J].测绘工程,2018,27(10):7-10. |
| 22 | Katsuki A, Kikuchi M.Simulation of barchan dynamics with inter-dune sand streams[J].New Journal of Physics,2011,13(6):63049. |
| 23 | 刘建宝,王乃昂,程弘毅,等.沙丘沙休止角影响因素实验研究[J].中国沙漠,2010,30(4):758-762. |
| 24 | Yang J H, Dong Z B, Liu Z Y,et al.Migration of barchan dunes in the western Quruq Desert,northwestern China[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2019,44(10):2016-2029. |
| 25 | Fryberger S G.Dunes forms and wind regime,a study of global sand seas[M]//Mckee E D.A Study of Global Sand Seas.Washington,USA:US Government Printing Office,1979. |
| 26 | Bullard J E.A Note on the Use of the Fryberger Method "for evaluating Potential Sand transport by wind"[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research,1997,67(3):499-501. |
| 27 | 朱震达,陈治平,吴正,等.塔克拉玛干沙漠风沙地貌研究[M].北京:科学出版社,1981. |
| 28 | Long J T, Sharp R P.Barchan-dune movement in Imperial Valley,California[J].Geological Society of America Bulletin,1964,75(2):149-156. |
| 29 | Laity J.Deserts and Desert Environments[M].Hoboken,USA:John Wiley & Sons,2008. |
| 30 | Bagnold R A.The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dune[M].London,UK:Methuen,1941. |
| 31 | 朱秉启.中纬度荒漠区河西走廊沙丘地貌的演化特征及其环境指示[J].地理学报,2021,76(11):2710-2729. |
| 32 | Buckley R.The effect of sparse vegetation on the transport of dune sand by wind[J].Nature,1987,325:426-428. |
| 33 | Wasson R J, Hyde R.Factors determining desert dune type[J].Nature,1983,304(5924):337-339. |
| 34 | Lancaster N.Geomorphology of Desert Dunes[M].London,UK:Taylor & Francis e-Library,2005. |
| 35 | Wilson I G.Aeolian bedforms-their development and origins[J].Sedimentology,2010,19(3/4):173-210. |
| 36 | Yang Y Y, Liu L Y, Shi P J,et al.Morphology,spatial pattern and sediment of Nitraria tangutorum nebkhas in barchans interdune areas at the southeast margin of the Badain Jaran Desert,China[J].Geomorphology,2015,232:182-192. |
| 37 | Laksono A, Saputri A A, Izumi B,et al.Vegetation covers change and its impact on Barchan Dune morphology in Parangtritis Coast,Indonesia[C]//The 1st Geosciences and Environmental Sciences Symposium (ICST 2020),2020. |
| 38 | Finkel H J.The Barchans of Southern Peru[J].The Journal of Geology,1959,67(6):614-647. |
| 39 | Vermeesch P, Drake N.Remotely sensed dune celerity and sand flux measurements of the world's fastest barchans(Bodele,Chad)[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2008,35:1-6. |
| 40 | Bagnold R A.The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes[M].London,UK:Methuen,1942. |
| 41 | 杨军怀,董治宝,刘铮瑶,等.库鲁克沙漠风沙地貌与沙丘移动[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(4):1-8. |
| [1] | Aibaidoula Gulayisaimu, Feng Zhang, Feng Wu, Shixin Wu, Jianghua Zheng, Tao Sun. Grain size characteristics of dune sands and spatial variation in the Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 133-145. |
| [2] | Meng Wang, Junfeng Lu, Peng Fu, Zhibao Dong. Characteristics of soil nutrients and grain size around Badain Jaran Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 232-244. |
| [3] | Min Chen, Baosheng Li, Fengnian Wang, Dongfeng Niu, Xiaohao Wen, Peixian Shu, Yuejun Si, Qinjiang Yang, Chen Wang. High-resolution monsoonal environment change in MIS3 based on trace elements in the Tumen Section on the southweest edge of Tegger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 253-263. |
| [4] | Heng Ren, Wenzhi Zhao, Zhitao Wang, Jiang Zhao. Spatial pattern of Psammochloa villosa population in patch landscape in dune habitat [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 89-98. |
| [5] | Hui Zhao, Hongyu Yang, Xingfan Wang, Keqi Wang. Geochronology of the typical sediments in the Badain Jaran Desert: the progress and issues [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 57-65. |
| [6] | Lichao Zhuang, Naiang Wang, Xunhe Zhang, Liqiang Zhao, Xianbao Su. Analysis on the difference of the spatial model of lake ice freezing and melting in the Badain Jaran Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(3): 214-223. |
| [7] | Sarina, Zhibao Dong, Weige Nan. The Aesthetic Value of Mega-dune Lines in the Badain Jaran Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 221-230. |
| [8] | Wenfan Wang, Rentao Liu, Zhixia Guo, Yonghong Feng, Jiayu Jiang. Physical and chemical properties and fractal dimension distribution of soil under shrubs in the southern area of Tengger Dseart [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 209-218. |
| [9] | Haotian Yang, Xinrong Li, Peijie Yan, Yunfei Li, Quanlin Ma. Soil types and spatial distribution in Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 154-162. |
| [10] | Bingyao Wang, Xingchen Liu, Lichao Liu. Characteristics of precipitation in the surrounding area of Tengger Desert in 1957-2017 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 163-170. |
| [11] | Yingwu Chen, Qingxiao Chen, Haotian Yang. Diversity and fauna of terrestrial wild vertebrate in Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 171-182. |
| [12] | Changzhen Yan, Sen Li, Junfeng Lu, Lichao Liu. Lake number and area in the Tengger Desert during 1975-2015 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 183-189. |
| [13] | Quanlin Ma, Jinchun Zhang, Fang Chen, Dekui Zhang, Linyuan Wei. Mechanism and dynamics for succession of artificial Hedysarum scoparium sand-binding forests at the southern edge of Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 206-215. |
| [14] | Yingwu Chen, Qingxiao Chen, Haotian Yang. Diversity and fauna of terrestrial wild vertebrates in the Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 216-222. |
| [15] | Delu Li, Quanlin Ma, Jinchun Zhang, Fang Chen, Xinrong Li, Hongbo Yuan, Linyuan Wei, Haotian Yang, Zhong Zhang. Vegetation characteristics of the Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 223-233. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech