
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 129-141.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00170
Ying Liu1( ), Rende Wang2(
), Rende Wang2( ), Hongjun Jiang2, Qing Li2, Yixiao Yuan2, Ruchun Zhang2, Tao Zhang2
), Hongjun Jiang2, Qing Li2, Yixiao Yuan2, Ruchun Zhang2, Tao Zhang2
Received:2024-10-28
Revised:2024-12-06
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-26
Contact:
Rende Wang
CLC Number:
Ying Liu, Rende Wang, Hongjun Jiang, Qing Li, Yixiao Yuan, Ruchun Zhang, Tao Zhang. Aeolian activity characteristics and influencing factors of the dry lakebed of Chahan Lake on the Bashang Plateau[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(2): 129-141.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00170
| 年份 | 观测时段编号 | 观测起止日期 | 时长/d |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | NO.1 | 4月24日至5月5日 | 12 |
| NO.2 | 5月6日至5月21日 | 16 | |
| 2023 | NO.3 | 3月31日至4月27日 | 28 |
| NO.4 | 4月28日至5月15日 | 18 |
Table 1 Aeolian activity observation time information
| 年份 | 观测时段编号 | 观测起止日期 | 时长/d |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | NO.1 | 4月24日至5月5日 | 12 |
| NO.2 | 5月6日至5月21日 | 16 | |
| 2023 | NO.3 | 3月31日至4月27日 | 28 |
| NO.4 | 4月28日至5月15日 | 18 |
| 观测 点号 | 观测时间 | 观测 点号 | 观测时间 | 观测 点号 | 观测时间 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO.1开始时刻 | NO.2开始时刻 | NO.1开始时刻 | NO.2开始时刻 | NO.3开始时刻 | NO.4开始时刻 | |||
| A1 | 4.47 | 11.40 | A16 | 21.69 | 16.22 | B1 | 6.42 | 0.55 |
| A2 | 18.93 | 16.61 | A17 | 5.24 | 22.21 | B2 | 24.71 | 3.03 |
| A3 | 10.96 | 28.17 | A18 | 13.49 | 20.25 | B3 | 22.60 | 5.45 |
| A4 | 11.32 | 24.93 | A19 | 8.93 | 27.14 | B4 | 26.57 | 3.24 |
| A5 | 8.12 | 23.06 | A20 | 4.17 | 18.96 | B5 | 19.98 | 3.95 |
| A6 | 6.44 | 10.24 | A21 | 5.53 | 12.31 | B6 | 27.41 | 2.74 |
| A7 | 10.66 | 11.00 | B7 | 23.78 | 2.40 | |||
| A8 | 6.52 | 12.21 | B8 | 29.43 | 2.24 | |||
| A9 | 8.91 | 10.35 | B9 | 26.21 | 4.68 | |||
| A10 | 2.23 | 9.41 | B10 | 28.50 | 7.21 | |||
| A11 | 1.23 | 8.49 | B11 | 25.80 | 4.81 | |||
| A12 | 2.51 | 8.33 | B12 | 34.63 | 9.95 | |||
| A13 | 16.61 | 8.11 | B13 | 17.30 | 3.14 | |||
| A14 | 21.52 | 18.04 | B14 | 32.90 | 17.36 | |||
| A15 | 25.02 | 13.12 | B15 | 21.19 | 3.59 | |||
Table 2 Soil moisture content (0-2.5 cm) at different time periods
| 观测 点号 | 观测时间 | 观测 点号 | 观测时间 | 观测 点号 | 观测时间 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO.1开始时刻 | NO.2开始时刻 | NO.1开始时刻 | NO.2开始时刻 | NO.3开始时刻 | NO.4开始时刻 | |||
| A1 | 4.47 | 11.40 | A16 | 21.69 | 16.22 | B1 | 6.42 | 0.55 |
| A2 | 18.93 | 16.61 | A17 | 5.24 | 22.21 | B2 | 24.71 | 3.03 |
| A3 | 10.96 | 28.17 | A18 | 13.49 | 20.25 | B3 | 22.60 | 5.45 |
| A4 | 11.32 | 24.93 | A19 | 8.93 | 27.14 | B4 | 26.57 | 3.24 |
| A5 | 8.12 | 23.06 | A20 | 4.17 | 18.96 | B5 | 19.98 | 3.95 |
| A6 | 6.44 | 10.24 | A21 | 5.53 | 12.31 | B6 | 27.41 | 2.74 |
| A7 | 10.66 | 11.00 | B7 | 23.78 | 2.40 | |||
| A8 | 6.52 | 12.21 | B8 | 29.43 | 2.24 | |||
| A9 | 8.91 | 10.35 | B9 | 26.21 | 4.68 | |||
| A10 | 2.23 | 9.41 | B10 | 28.50 | 7.21 | |||
| A11 | 1.23 | 8.49 | B11 | 25.80 | 4.81 | |||
| A12 | 2.51 | 8.33 | B12 | 34.63 | 9.95 | |||
| A13 | 16.61 | 8.11 | B13 | 17.30 | 3.14 | |||
| A14 | 21.52 | 18.04 | B14 | 32.90 | 17.36 | |||
| A15 | 25.02 | 13.12 | B15 | 21.19 | 3.59 | |||
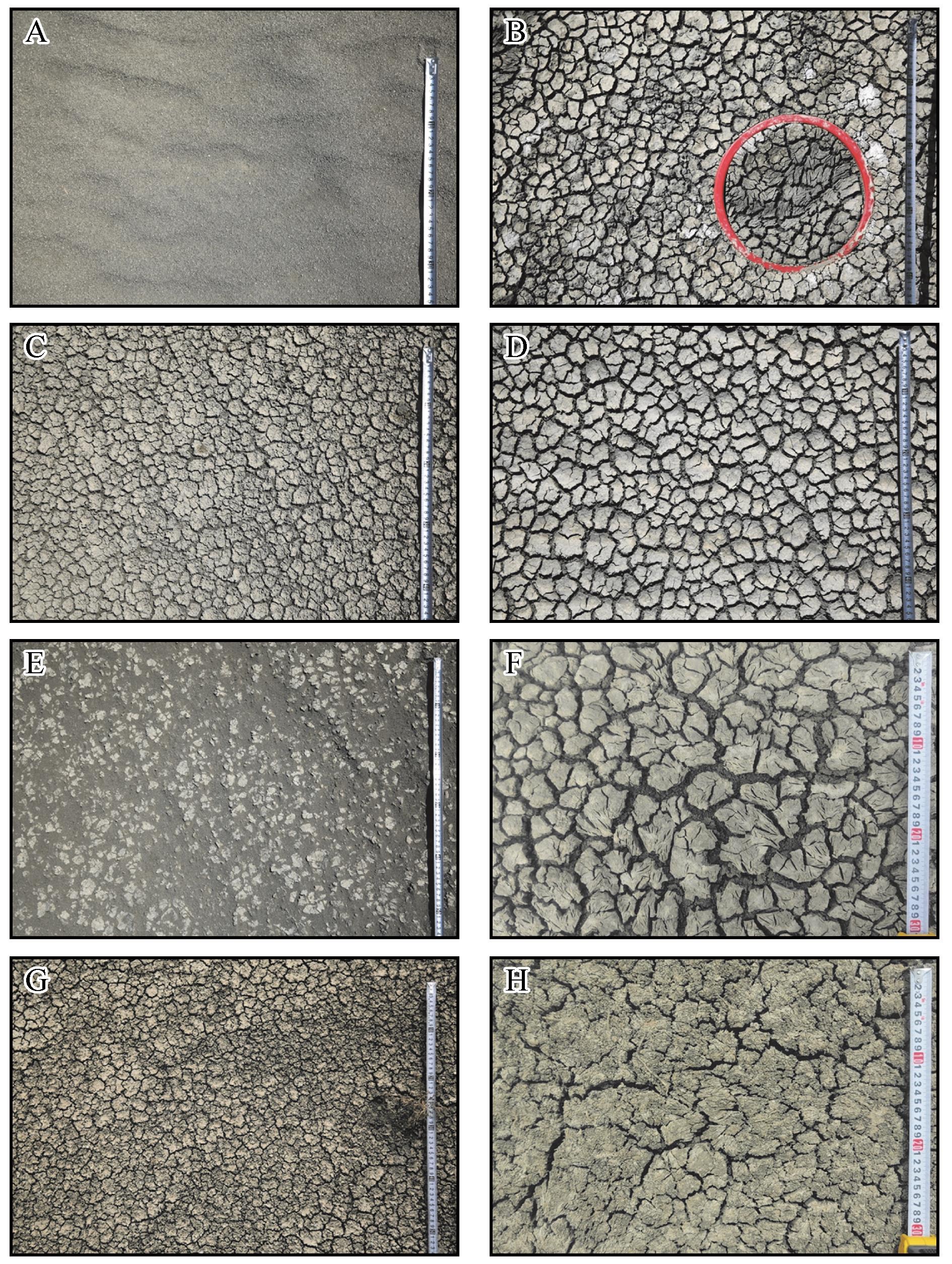
Fig.7 Surface salt crust development at the start of different time periods (A and B show the surface conditions at the A5 observation point in the lake center at the start of the first and second periods in 2021; C and D show the surface conditions at the A8 observation point on the lake edge at the start of the first and second periods in 2021; E and F show the surface conditions at the B7 observation point in the lake center at the start of the first and second periods in 2023; G and H show the surface conditions at the B12 observation point on the lake edge at the start of the first and second periods in 2023)
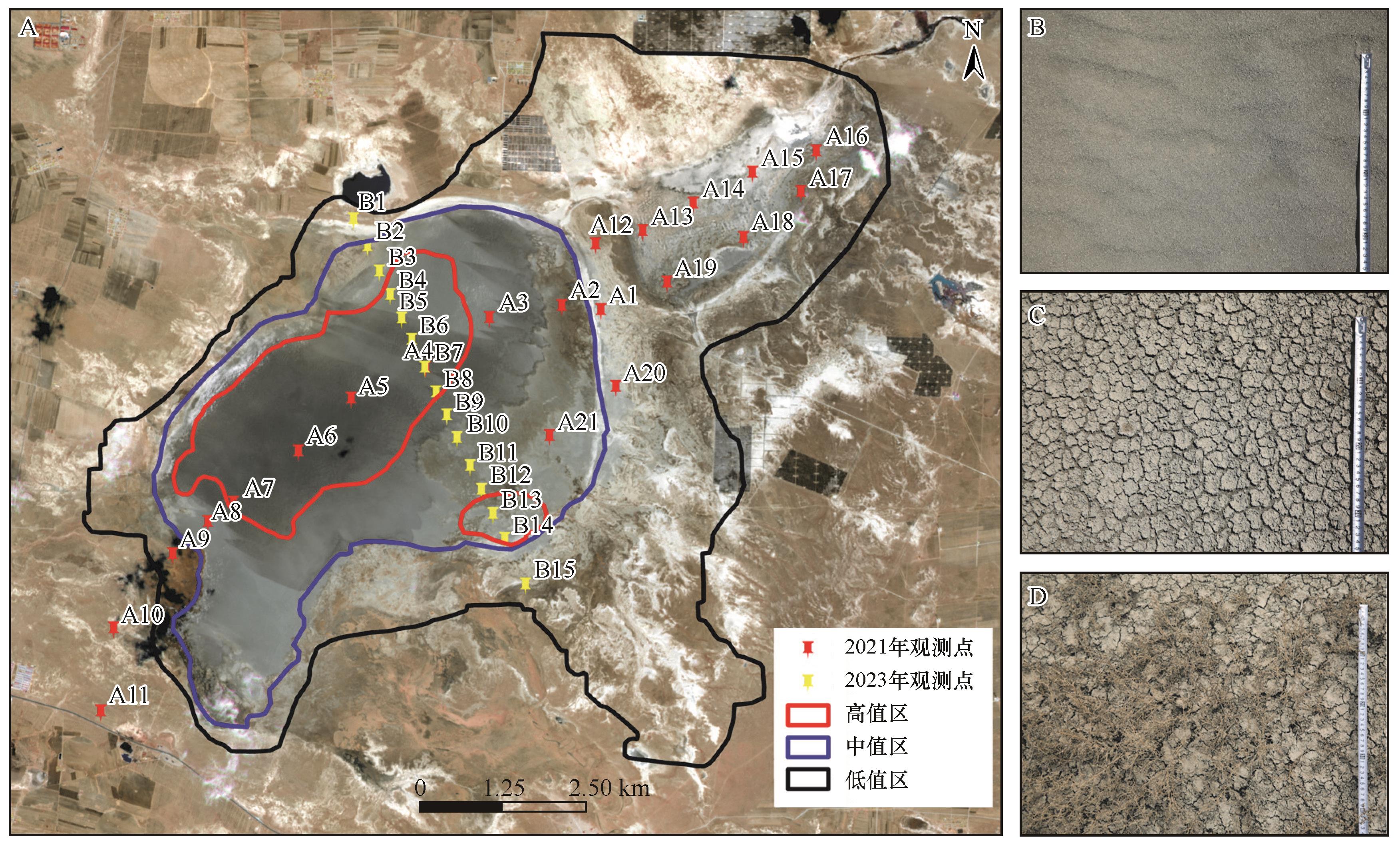
Fig.9 Risk distribution map (A) and surface conditions in high (B), medium (C), and low (D) risk of salt-dust release from the dry lakebed of Chahan Lake
| 1 | 胡汝骥,姜逢清,王亚俊,等.论中国干旱区湖泊研究的重要意义[J].干旱区研究,2007(2):137-140. |
| 2 | 张语克.半干旱草原区近40年来湖泊面积变化及干涸的原因[D].北京:北京大学,2010. |
| 3 | 韩进军,陈亮,王建萍,等.近44年我国盐湖面积变化及其影响因素研究[J].盐湖研究,2024(5):1-12. |
| 4 | Wurtsbaugh W A, Miller C, Null S E,et al.Decline of the world’s saline lakes[J].Nature Geoscience,2017,10(11):816-821. |
| 5 | 刘东伟,吉力力·阿不都外力,雷加强,等.盐尘暴及其生态效应[J].中国沙漠,2011,31(1):168-173. |
| 6 | Darvishi Boloorani A, Papi R, Soleimani M,et al.Water bodies changes in Tigris and Euphrates basin has impacted dust storms phenomena[J].Aeolian Research,2021,50:100698. |
| 7 | Alizadeh Motaghi F, Hamzehpour N, Mola Ali Abasiyan S,et al.The wind erodibility in the newly emerged surfaces of Urmia Playa Lake and adjacent agricultural lands and its determining factors[J].CATENA,2020,194:104675. |
| 8 | Mahowald N M, Bryant R G, Del Corral J,et al.Ephemeral lakes and desert dust sources[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2003,30(2):2002GL016041. |
| 9 | 王仁德,李庆,常春平,等.土壤风蚀中粉尘释放问题的研究进展[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(2):85-103. |
| 10 | 肖雨婷,张国明,洪畅,等.巴丹吉林沙漠西缘不同地表沙尘水平通量[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(2):104-113. |
| 11 | Sun X, Wang F, Fan Y,et al.Transformation of lakebed into a major soluble-salt-bearing dust source for Asia since the mid-pleistocene[J].Global and Planetary Change,2023,230:104282. |
| 12 | Quick D J, Chadwick O A.Accumulation of salt-rich dust from Owens Lake playa in nearby alluvial soils[J].Aeolian Research,2011,3(1):23-29. |
| 13 | 吐尔逊·吐尔洪.盐尘降落对植物生理特性的影响:以新疆艾比湖盐尘扩散区为例[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆农业大学,2019. |
| 14 | Grineski S E, Mallia D V, Collins T W,et al.Harmful dust from drying lakes:preserving Great Salt Lake (USA) water levels decreases ambient dust and racial disparities in population exposure[J].One Earth,2024,7(6):1056-1067. |
| 15 | 吉力力·阿不都外力.干旱区湖泊与盐尘暴[M].北京:中国环境科学出版社,2012. |
| 16 | Sweeney M R, Zlotnik V A, Joeckel R M,et al.Geomorphic and hydrologic controls of dust emissions during drought from Yellow Lake playa,west Texas,USA[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2016,133:37-46. |
| 17 | Singer A, Zobeck T, Poberezsky L,et al.The PM10 and PM2.5 dust generation potential of soils/sediments in the Southern Aral Sea Basin,Uzbekistan[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2003,54(4):705-728. |
| 18 | Gill T E.Dust generation resulting from desiccation of playa systems:studies on Mono and Owens Lakes,California[D].Davis,USA:University of California,Davis,1995. |
| 19 | 阿布拉·吐合提.中亚咸海干涸湖床粉尘扩散的时空特征、影响因素及其健康效应[D].乌鲁木齐:新疆大学,2022. |
| 20 | Wang L, Zhao Z, Shomurodov K,et al.Address the Aral Sea crisis with cooperation[J].Science,2023,380(6650):1114. |
| 21 | 杨恕,孙凌霄,何婧,等.咸海变迁:危机和现状[J].干旱区地理,2024,47(2):181-191. |
| 22 | Mu G, Yan S, Jilil A,et al.Wind erosion at the dry-up bottom of Aiby Lake[J].Science in China Series D:Earth Sciences,2002,45(1):157-164. |
| 23 | 葛拥晓.艾比湖干涸湖床风扬粉尘的发生及其潜在扩散特征研究[D].乌鲁木齐:中国科学院新疆生态与地理研究所,2016. |
| 24 | Cahill T A, Gill T E, Reid J S,et al.Saltating particles,playa crusts and dust aerosols at Owens(dry) Lake,California[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,1996,21(7):621-639. |
| 25 | Gillette D, Ono D, Richmond K.A combined modeling and measurement technique for estimating windblown dust emissions at Owens (dry) Lake,California[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface,2004,109(F1):JF000025. |
| 26 | Gillette D A, Hardebeck E, Parker J.Large-scale variability of wind erosion mass flux rates at Owens Lake:2.role of roughness change,particle limitation,change of threshold friction velocity,and the Owen effect[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,1997,102(D22):25989-25998. |
| 27 | King J, Etyemezian V, Sweeney M,et al.Dust emission variability at the Salton Sea,California,USA[J].Aeolian Research,2011,3(1):67-79. |
| 28 | Buck B J, King J, Etyemezian V.Effects of salt mineralogy on dust emissions,Salton Sea,California[J].Soil Science Society of America Journal,2011,75(5):1971-1985. |
| 29 | Dickey H, Schreuder M, Schmid B,et al.Quantifying dust emission potential of playa and desert surfaces in the Salton Sea Air Basin,California,United States[J].Aeolian Research,2023,60:100850. |
| 30 | 曲书锋,张国明,刘连友,等.干涸尾闾湖盆区泥漠地表磨蚀释尘特征[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(4):81-88. |
| 31 | Liu D, Han L, Kou Z,et al.Exploration of playa surface crusts in Qehan Lake,China through field investigation and wind tunnel experiments[J].Journal of Arid Land,2023,15(5):491-507. |
| 32 | 黄红宁.查干淖尔湖地表粉尘释放特征的风洞实验研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2021. |
| 33 | 赵望龙.安固里淖干湖盆土壤风蚀特征研究[D].石家庄:河北师范大学,2017. |
| 34 | 于海云,张正偲,王志军.阿拉善高原东南部干涸湖盆沉积物粒度特征[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(4):177-184. |
| 35 | Tan L, Wang H, An Z,et al.Aeolian sand transport over a dry playa surface:sand flux density profiles,saltation layer height,and flux scaling laws and implications for dust emission dynamics[J].CATENA,2023,224:106970. |
| 36 | Argaman E, Singer A, Tsoar H.Erodibility of some crust forming soils/sediments from the Southern Aral Sea Basin as determined in a wind tunnel[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2005,31(1):47-63. |
| 37 | Gillette D A.A qualitative geophysical explanation for “Hot Spot” dust emitting source regions[J].Contributions to Atmospheric Physics,1999,72(1):67-77. |
| 38 | Gillette D A, Niemeyer T C, Helm P J.Supply-limited horizontal sand drift at an ephemerally crusted,unvegetated saline playa[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2001,106(D16):18085-18098. |
| 39 | 姚顺予,郭晏宏,白慧敏,等.干涸湖床盐碱粉尘湍流释放的大涡模拟[J].中国沙漠,2024,44(5):261-270. |
| 40 | 鄢雪英,丁建丽,李鑫,等.艾比湖湿地退化对盐尘暴发生及运移路径的影响[J].生态学报,2015,35(17):5856-5865. |
| 41 | 韩旭娇,张国明,雷洁,等.干涸湖床不同类型盐土地表净风吹蚀实验研究[J].干旱区研究,2019,36(1):262-268. |
| 42 | Zhang G, Li L, Tang W,et al.Wind erosion from crusted playa surfaces by no saltation and with saltation:a comparison through laboratory wind tunnel experiments[J].International Soil and Water Conservation Research,2023,11(3):518-527. |
| 43 | 王昆,齐雷杰.察汗淖尔只剩最后一滴泪[J].半月谈,2020(13):74-75. |
| 44 | 刘一,倪明霞,夏建新,等.坝上察汗淖尔湖水面萎缩原因及其恢复对策[J].中央民族大学学报(自然科学版),2021,30(4):53-59. |
| 45 | 王奕璇,邢世禄,丁宁.察汗淖尔湖泊面积变化及其对气候的响应分析[J].环境工程,2022,40(11):47-53. |
| 46 | 陈沫宇,李彦苍,雷晓辉,等.察汗淖尔流域地下水位时空演变特征及驱动因子定量评估[J].干旱区资源与环境,2022,36(11):105-111. |
| 47 | 陈鹏,张冰,马荣,等.坝上高原察汗淖尔湖泊面积变化及驱动要素分析[J].科学技术与工程,2023,23(26):11108-11117. |
| 48 | 蒋红军,王仁德,张茹春,等.坝上地区察汗淖尔湖流域盐尘暴形成风险研究[J].盐湖研究,2024(1):1-8. |
| 49 | 邹学勇,张春来,程宏,等.土壤风蚀模型中的影响因子分类与表达[J].地球科学进展,2014,29(8):875-889. |
| [1] | Haokun Mo, Guangyin Hu, Huicong Meng. Research progress on aeolian activity in the Qinghai Lake area, northeastern Tibetan Plateau [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(6): 197-209. |
| [2] | Hong Jia, Zhiyan Sun, Jinming Xie, Jie Chen, Yinghua Zheng, Mingrui Qiang. Environmental changes recorded by aeolian deposits in the coasts of China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(3): 51-62. |
| [3] | Mei Shao, Wanyin Luo, Xuehua Che, Fang Wang, Junfeng Lu, Songbing Zou. Aeolian sand transport and its potential amount into Longyangxia Reservoir in 1987-2019 based on COSI-Corr [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 249-261. |
| [4] | Lichao Zhuang, Naiang Wang, Xunhe Zhang, Liqiang Zhao, Xianbao Su. Analysis on the difference of the spatial model of lake ice freezing and melting in the Badain Jaran Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(3): 214-223. |
| [5] | Li Tengfei, Li Jinfeng, Lu Ruijie, Liu Xiaokang, Chen Lu. Extraction of Grain-size Components with Environmentally Sensitivity of Aeolian Sediments in Eastern Shore of Qinghai Lake and Their Palaeoclimatic Implications [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2017, 37(5): 878-884. |
| [6] | Zhang Liqiu, Zhang Hong, Li Jiao, Li Jinchang. Climate Change in Sandy Desertification Area of the Northern Shanxi from 1980 to 2014 [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2016, 36(4): 1116-1125. |
| [7] | ZHANG Zheng-cai, DONG Zhi-bao. Field Observation of Aeolian Sediment Flux in the Southeast Tengger Desert [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2013, 33(4): 973-980. |
| [8] | GE Yong-xiao1,2, ABUDUWAILI Jilili1, LIU Dong-wei3, ABULIMITI Mireban1,4. Fractal Characteristics of Particle Size Distribution in Salt-rich Sediments from Different Depths under Six Different Types of Landscapes in the Playa of the Ebinur Lake [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2013, 33(3): 804-812. |
| [9] | ZHANG Zheng-cai;DONG Zhi-bao;ZHAO Ai-guo;QIAN Guang-qiang. Relationship between Sand Transport and Sand Drift Potential [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2011, 31(4): 824-827. |
| [10] | WANG Ren-de;;ZOU Xue-yong;ZHAO Jing-yan;. Field Observation of Farmland Wind-erosion around Beijing [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2011, 31(2): 400-406. |
| [11] | Jilili-Abudouwaili;LIU Dong-wei;XU Jun-rong. Wind Tunnel Study of Wind Erosion and Dust Flux on Different Surfaces in Dry Ebinur Lake, Xinjiang, China [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2009, 29(1): 63-67. |
| [12] | LI Zhen-shan;WANG Yi;HE Li-min. Vegetation-Erosion Process in Semiarid Region: Ⅰ. Dynamical Models [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2009, 29(1): 23-30. |
| [13] | MA Yao-ming, MA Wei-qiang, LI Mao-shan, SUN Fang-lin, WAN Jie-min. Remote Sensing Parameterization of Land Surface Heat Fluxes over the Middle Reaches of the Heihe River [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2004, 24(4): 392-399. |
| [14] | YAO De-liang, LI Jia-chun, LI Xin-rong, ZHANG Jing-guang, LIU Li-chao. Field Study on Terrestrial Processes in Arid Areas [J]. JOURNAL OF DESERT RESEARCH, 2001, 21(3): 254-259. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech