
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 197-209.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00150
Haokun Mo( ), Guangyin Hu(
), Guangyin Hu( ), Huicong Meng
), Huicong Meng
Received:2023-09-26
Revised:2023-10-23
Online:2023-11-20
Published:2023-11-30
Contact:
Guangyin Hu
CLC Number:
Haokun Mo, Guangyin Hu, Huicong Meng. Research progress on aeolian activity in the Qinghai Lake area, northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(6): 197-209.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00150
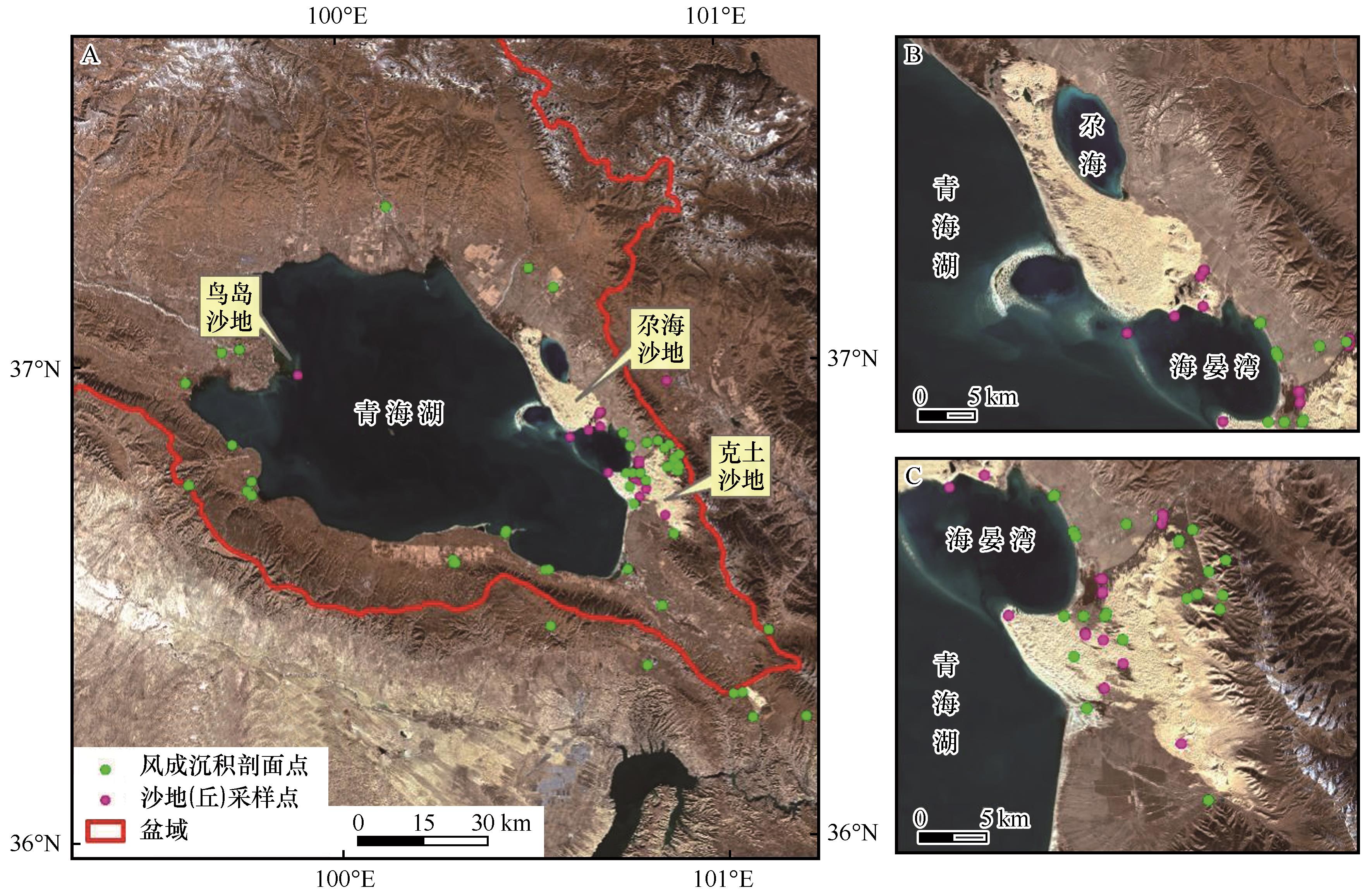
Fig.2 Some published aeolian sedimentary profiles and sampling sites of sandy land (hills) in Qinghai Lake area (A) and in Gahai Dunefield (B), Ketu Dunefield (C)
| 1 | 潘保田,李吉均.青藏高原:全球气候变化的驱动机与放大器:Ⅲ.青藏高原隆起对气候变化的影响[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版),1996,32(1):108-115. |
| 2 | 郑度,李炳元.青藏高原自然地理研究的进展[J].地理学报,1990,45(2):235-244. |
| 3 | Dong Z B, Hu G Y, Qian G Q,et al.High-altitude aeolian research on the Tibetan Plateau[J].Reviews of Geophysics,2017,55:864-901. |
| 4 | Dong Z W, Brahney J, Kang S C,et al.Aeolian dust transport,cycle and influences in high-elevation cryosphere of the Tibetan Plateau region:new evidences from alpine snow and ice[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2020,211:103408. |
| 5 | 薛红盼.青海湖北部地区全新世风成沉积记录的环境变化[D].西宁:中国科学院青海盐湖研究所,2021. |
| 6 | Stauch G.Geomorphological and palaeoclimate dynamics recorded by the formation of aeolian archives on the Tibetan Plateau[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2015,150:393-408. |
| 7 | 赵亚娟.末次冰消期以来青海湖西岸风成沉积记录的高密度光释光年代学及环境演变[D].西宁:青海师范大学,2017. |
| 8 | E C Y, Zhang J, Chen Z Y,et al.High resolution OSL dating of aeolian activity at Qinghai Lake,Northeast Tibetan Plateau[J].Catena,2019,183:104180. |
| 9 | 鄂崇毅,曹广超,侯光良,等.青海湖江西沟黄土记录的环境演变研究[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质,2013,33(4):193-200. |
| 10 | Lu H Y, Zhao C F, Mason J,et al.Holocene climatic changes revealed by aeolian deposits from the Qinghai Lake area (northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau) and possible forcing mechanisms[J].The Holocene,2010,21(2):297-304. |
| 11 | 安芷生,吴国雄,李建平,等.全球季风动力学与气候变化[J].地球环境学报,2015,6(6):341-381. |
| 12 | 陈骥.青海湖现代沉积体系研究[D].北京:中国地质大学(北京),2016. |
| 13 | 边千韬,刘嘉麒,罗小全,等.青海湖的地质构造背景及形成演化[J].地震地质,2000,22(1):20-26. |
| 14 | 陈克造,黄第藩,梁狄刚.青海湖的形成和发展[J].地理学报,1964,30(3):214-233. |
| 15 | 陈骥,张万益,姜在兴,等.环青海湖地区风场特征及其对沉积体系的影响[J].中国地质,2021,48(6):1935-1946. |
| 16 | 师永民,王新民,宋春晖.青海湖湖区风成沙堆积[J].沉积学报,1996,14():234-238. |
| 17 | Hu G Y, Dong Z B, Zhang Z C,et al.Wind regime and aeolian landforms on the eastern shore of Qinghai Lake,Northeastern Tibetan Plateau,China[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2021,188:104451. |
| 18 | 张登山,王彬.青海湖中沙堤的形成及其对湖水位的影响[J].干旱区资源与环境,1991,5(1):96-102. |
| 19 | 姚正毅,李晓英,肖建华.青海湖滨土地沙漠化驱动机制[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(6):1429-1437. |
| 20 | 宋春晖,方小敏,师永民,等.青海湖西岸风成沙丘特征及成因[J].中国沙漠,2000,20(4):443-446. |
| 21 | 侯光良,许长军.利用(RS)和(GIS)对青海湖环湖沙地分布等情况的调查研究[J].青海环境,2005,15(3):105-107. |
| 22 | 何东宁,赵鸿斌,张登山,等.青海湖盆地沙地特征及风沙化趋势[J].地理科学,1993,13(4):382-388. |
| 23 | 张兆康.高密度光释光测年揭示青海湖流域千年尺度气候演变[D].西宁:青海师范大学,2023. |
| 24 | 胡梦珺,田丽慧,张登山,等.遥感与GIS支持下近30 a来青海湖环湖区土地沙漠化动态变化研究[J].中国沙漠,2012,32(4):901-909. |
| 25 | Cui B L, Xiao B, Li X Y,et al.Exploring the geomorphological processes of Qinghai Lake and surrounding lakes in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau,using multitemporal landsat imagery (1973-2015)[J].Global and Planetary Change,2017,152:167-175. |
| 26 | 杨璟,丁明涛,李振洪,等.Google Earth Engine支持下的青海湖空间格局演变分析[J].测绘地理信息,2022,48(5):1-6. |
| 27 | 祁苗苗,姚晓军,刘时银,等.1973-2018年青海湖岸线动态变化[J].湖泊科学,2020,32(2):573-586. |
| 28 | 祝存兄,史飞飞,乔斌,等.基于高分1号卫星数据的青海湖扩张及湖滨沙地变化特征分析[J].干旱区研究,2022,39(4):1076-1089. |
| 29 | Chen F H, Wu D, Chen J H,et al.Holocene moisture and East Asian summer monsoon evolution in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau recorded by Lake Qinghai and its environs:a review of conflicting proxies[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2016,154:111-129. |
| 30 | Liu X J, Lai Z P, Yu L P,et al.Luminescence chronology of aeolian deposits from the Qinghai Lake area in the Northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau and its palaeoenvironmental implications(CPCI-S)[J].Quaternary Geochronology,2012,10(7):37-43. |
| 31 | 李娜娜.色度和粘土矿物记录的末次冰期间冰阶以来青海湖地区的环境演变[D].兰州:西北师范大学,2021. |
| 32 | 胡梦珺,李娜娜,张亚云,等.近32 ka以来青海湖古风成砂-古土壤序列色度参数变化特征及环境演变[J].第四纪研究,2020,40(5):1105-1117. |
| 33 | 袁宝印,陈克造, Bowler J M,等.青海湖的形成与演化趋势[J].第四纪研究,1990,10(3):233-243. |
| 34 | 贾玉连,施雅风,范云崎.四万年以来青海湖的三期高湖面及其降水量研究[J].湖泊科学,2000,12(3):211-218. |
| 35 | David R, Ma H Z, David B M,et al.Paleoenvironmental and archaeological investigations at Qinghai Lake,western China:geomorphic and chronometric evidence of lake level history[J].Quaternary International,2010,218(1/2):29-44. |
| 36 | 胡梦珺,李森,高尚玉,等.风成沉积物粒度特征及其反映的青海湖周边近32 ka以来土地沙漠化演变过程[J].中国沙漠,2012,32(5):1240-1247. |
| 37 | Stephen C P, Ashok S, An Z S,et al.Luminescence age and palaeoenvironmental implications of a late Pleistocene ground wedge on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J].Permafrost and Periglacial Processes,2001,12(2):203-210. |
| 38 | Huang C, Lai Z P, Liu X J,et al.Lake-level history of Qinghai Lake on the NE Tibetan Plateau and its implications for Asian monsoon pattern:a review[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2021,273:107258. |
| 39 | David B M, Ma H Z, David R,et al.Age constraints on the late Quaternary evolution of Qinghai Lake,Tibetan Plateau[J].Quaternary Research,2008,69(2):316-325. |
| 40 | 王中,刘向军,丛禄.青海湖东岸末次冰期冰盛期和早全新世沙漠范围重建[J].盐湖研究,2017,25(2):67-75. |
| 41 | Shen J, Liu X Q, Ryo M,et al.A high-resolution climatic change since the Late Glacial Age inferred from multi-proxy of sediments in Qinghai Lake[J].Science in China (Series D:Earth Sciences),2005,48(6):742-751. |
| 42 | Wang Z, Zhang F, Li X Z,et al.Changes in the depth of Lake Qinghai since the last deglaciation and asynchrony between lake depth and precipitation over the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J].Global and Planetary Change,2020,188:103156. |
| 43 | Jin Z D, An Z S, Yu J M,et al.Lake Qinghai sediment geochemistry linked to hydroclimate variability since the last glacial[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2015,122:63-73. |
| 44 | Colman S M, Yu S Y, An Z S,et al.Late Cenozoic climate changes in China's western interior:a review of research on Lake Qinghai and comparison with other records[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2007,26(17/18):2281-2300. |
| 45 | Lu R J, Jia F F, Gao S Y,et al.Holocene aeolian activity and climatic change in Qinghai Lake basin,northeastern Qingha-Tibetan Plateau[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2015,430:1-10. |
| 46 | Shang Y, Lu R J, Jia F F,et al.Paleoclimatic evolution indicated by major geochemical elements from aeolian sediments on the east of Qinghai Lake[J].Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions,2013,5(3):301-308. |
| 47 | Lai Z P, Kaiser K, Brückner H.Luminescence-dated aeolian deposits of late Quaternary age in the southern Tibetan Plateau and their implications for landscape history[J].Quaternary Research,2009,72(3):421-430. |
| 48 | Sun J M, Li S H, Muhs D R,et al.Loess sedimentation in Tibet:provenance,processes,and link with Quaternary glaciations[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2007,26(17/18):2265-2280. |
| 49 | 常秋芳,芦宝良,赖忠平,等.青海南山风成沉积光释光年代学研究[J].盐湖研究,2016,24(2):54-61. |
| 50 | 陈发虎,汪世兰,张维信,等.青海湖南岸全新世黄土剖面、气候信息及湖面升降探讨[J].地理科学,1991,11(1):76-85. |
| 51 | Ding Z Y, Lu R J, Lyu Z Q,et al.Geochemical characteristics of Holocene aeolian deposits east of Qinghai Lake,China,and their paleoclimatic implications[J].Science of The Total Environment,2019,692:917-929. |
| 52 | Shen J, Liu X Q, Wang S M,et al.Palaeoclimatic changes in the Qinghai Lake area during the last 18,000 years[J].Quaternary International,2005,136(1):131-140. |
| 53 | An Z S, Colman S M, Zhou W J,et al.Interplay between the Westerlies and Asian monsoon recorded in Lake Qinghai sediments since 32 ka[J].Scientific Reports,2012,2(1):619. |
| 54 | Zhang J R, Liu Q, Yang L H,et al.Regional hydroclimates regulate the Holocene aeolian accumulation processes of the Qinghai Lake basin on the northeastern Tibetan plateau[J].Catena,2022,210:105866. |
| 55 | Xue H P, Zeng F M.Holocene environmental evolution in the Qinghai Lake area recorded by aeolian deposits[J].Quaternary International,2021,580:67-77. |
| 56 | 薛红盼,曾方明.青海湖东岸全新世风成沉积地球化学特征及其古气候意义[J].沉积学报,2021,39(5):1198-1207. |
| 57 | Ji J F, Shen J, Balsam W,et al.Asian monsoon oscillations in the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau since the late glacial as interpreted from visible reflectance of Qinghai Lake sediments[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2005,233(1/2):61-70. |
| 58 | 葛全胜,刘健,方修琦,等.过去2000年冷暖变化的基本特征与主要暖期[J].地理学报,2013,68(5):579-592. |
| 59 | Wei H C, E C Y, Zhang J,et al.Climate change and anthropogenic activities in Qinghai Lake basin over the last 8500 years derived from pollen and charcoal records in an aeolian section[J].Catena,2020,193:104616. |
| 60 | Liu X J, Lai Z P, Madsen D,et al.Last deglacial and Holocene lake level variations of Qinghai Lake,north-eastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J].Journal of Quaternary Science,2015,30(3):245-257. |
| 61 | 赵存法,鹿化煜,周亚利,等.青海湖地区冰消期以来气候变化的黄土记录[J].高校地质学报,2009,15(1):135-140. |
| 62 | 唐道斌,杨坤美,曾兰华,等.2.0 ka以来青藏高原东北部风沙活动增强的时空差异[J].地理学报,2023,78(9):1-15. |
| 63 | Li X Z, Liu X J, He Y X,et al.Summer moisture changes in the Lake Qinghai area on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau recorded from a meadow section over the past 8400 yrs[J].Global and Planetary Change,2018,161:1-9. |
| 64 | Xu H, Hou Z H, Ai L,et al.Precipitation at Lake Qinghai,NE Qinghai-Tibet Plateau,and its relation to Asian summer monsoons on decadal/interdecadal scales during the past 500 years[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2007,254(3/4):541-549. |
| 65 | Yan D D, Wünnemann B, Hu Y B,et al.Wetland evolution in the Qinghai Lake area,China,in response to hydrodynamic and eolian processes during the past 1100 years[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2017,162:42-59. |
| 66 | Wu D, Zhou A F, Zhang J W,et al.Temperature-induced dry climate in basins in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau during the early to middle Holocene[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2020,237:106311. |
| 67 | Yang L H, Long H, Cheng H Y,et al.OSL dating of a mega-dune in the eastern Lake Qinghai basin (northeastern Tibetan Plateau) and its implications for Holocene aeolian activities[J].Quaternary Geochronology,2019,49:165-171. |
| 68 | Stauch G, IJmker J, Pötsch S,et al.Aeolian sediments on the north-eastern Tibetan Plateau[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2012,57:71-84. |
| 69 | Wang X Y, Yi S W, Lu H Y,et al.Aeolian process and climatic changes in loess records from the northeastern Tibetan Plateau:response to global temperature forcing since 30 ka[J].Paleoceanography,2015,30(6):612-620. |
| 70 | 张晶,鄂崇毅,赵亚娟.青海湖黑马河黄土的高密度光释光测年[J].地球环境学报,2018,9(6):557-568. |
| 71 | 王训明,周娜,郎丽丽,等.风沙活动对陆地生态系统影响研究进展[J].地球科学进展,2015,30(6):627-635. |
| 72 | 董治宝,吕萍.70年来中国风沙地貌学的发展[J].地理学报,2020,75(3):509-528. |
| 73 | 陈骥,姜在兴,张万益,等.“源-汇”沉积体系主导下的现代风成相发育模式探讨:以青海湖东岸为例[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(5):999-1008. |
| 74 | Liu X J, Cong L, An F Y,et al.Downwind aeolian sediment accumulations associated with lake-level variations of the Qinghai Lake during the Holocene,Northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J].Environmental Earth Sciences,2019,78(1):19. |
| 75 | 曾方明.青海湖地区晚第四纪黄土的物质来源[J].地球科学,2016,41(1):131-138. |
| 76 | 陈东雪,鲁瑞洁,丁之勇,等.青海湖湖东沙地河湖-风成沉积记录的中晚全新世以来环境变化[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(6):99-110. |
| 77 | 曾方明,刘向军,叶秀深,等.青海湖种羊场风成沉积的常量元素组成及其化学风化指示[J].盐湖研究,2015,23(1):1-7. |
| 78 | 郭晓宁,王钰,朱宝文,等.基于HYSPLIT模式的青海东部次浮尘污染过程的气象特征分析[C]//中国环境科学学会2021年科学技术年会论文集(一).天津:中国环境科学学会,2021. |
| 79 | 姚振,张亚峰,董峻麟,等.青海省东部地区大气降尘地球化学特征[J].中国矿业,2017,26():170-172. |
| 80 | 席永帅.青藏高原东北缘大气降尘的时空分异特征[D].西宁:青海师范大学,2016. |
| 81 | Wan D J, Jin Z D, Wang Y X.Geochemistry of eolian dust and its elemental contribution to Lake Qinghai sediment[J].Applied Geochemistry,2012,27(8):1546-1555. |
| 82 | 李璠,徐维新,祁栋林,等.1961-2015年青海沙尘天气时空变化特征[J].干旱区研究,2018,35(2):412-417. |
| 83 | Liu Z Y, Liu D, Huang J P,et al.Airborne dust distributions over the Tibetan Plateau and surrounding areas derived from the first year of CALIPSO lidar observations[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussions,2008,8(2):5957-5977. |
| 84 | 汪海娇,田丽慧,张登山,等.青海湖东岸沙地风沙活动特征[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(1):49-56. |
| 85 | 张登山,张佩,吴汪洋,等.青海湖东克土沙区风沙运动规律及防治对策[J].中国沙漠,2016,36(2):274-280. |
| 86 | 张乐春,张登山,汪海娇,等.青海湖湖东沙区风季起沙风况及输沙势特征[J].干旱区资源与环境,2023,37(3):91-97. |
| 87 | 吴汪洋,张登山,田丽慧,等.青海湖沙地人工治理沙丘的风速廓线变化特征[J].水土保持研究,2013,20(6):162-167. |
| 88 | 白敏,鲁瑞洁,丁之勇,等.青海湖湖东沙地粒度端元分析及其指示意义[J].第四纪研究,2020,40(5):1203-1215. |
| 89 | 徐树建.风成沉积物环境敏感粒度指标的提取及意义[J].干旱区资源与环境,2007,21(3):95-98. |
| 90 | 李腾飞,李金凤,鲁瑞洁,等.青海湖东岸沙地风成沉积物粒度敏感组分及其古气候意义[J].中国沙漠,2017,37(5):878-884. |
| 91 | Sun D H, Bloemendal J, Rea D K,et al.Grain-size distribution function of polymodal sediments in hydraulic and aeolian environments,and numerical partitioning of the sedimentary components[J].Sedimentary Geology,2002,152(3/4):263-277. |
| 92 | 姜莹莹.末次冰消期以来青海湖地区风成沉积记录的环境演变[D].西宁:青海师范大学,2015. |
| 93 | 展秀丽,严平,王宁,等.环青海湖固沙治理区与流动沙丘土壤特征研究[J].生态环境学报,2011,20(2):292-297. |
| 94 | 袁杰,曹广超,鄂崇毅,等.环青海湖表层土壤沉积物粒度分布特征及其指示意义[J].水土保持研究,2015,22(3):150-154. |
| 95 | 吕志强,鲁瑞洁,刘小槺,等.青海湖湖东沙地沉积记录的全新世以来风沙活动变化[J].干旱区地理,2018,41(3):536-544. |
| 96 | 张登山,田丽慧,鲁瑞洁,等.青海湖湖东沙地风沙沉积物的粒度特征[J].干旱区地理,2013,36(2):203-211. |
| 97 | 展秀丽,严平.青海湖沙区风沙土土壤机械组成特征[J].甘肃农业大学学报,2016,51(1):107-113. |
| 98 | 鲁瑞洁,唐清亮,桑艳礼,等.青海湖克土沙区不同类型沙丘土壤水分的动态变化[J].水土保持研究,2012,19(2):111-115. |
| 99 | 杨龙,孙永娟,鄂崇毅,等.江西沟1号风成剖面地球化学元素特征及古环境意义[J].盐湖研究,2016,24(2):44-53. |
| 100 | 周笃珺,马海州,高东林,等.青海湖南岸全新世黄土地球化学特征及气候环境意义[J].中国沙漠,2004,24(2):144-148. |
| 101 | 尚媛,鲁瑞洁,贾飞飞,等.青海湖湖东风成剖面化学元素特征及其环境指示意义[J].中国沙漠,2013,33(2):463-469. |
| 102 | Wang L D, Lu R J, Ding Z Y,et al.Holocene aeolian activity in the Ganzihe sandy land,Qinghai Lake basin[J].Quaternary International,2021,598:56-65. |
| 103 | Zeng F M, Liu X J, Li X Z,et al.Aquatic species dominate organic matter in Qinghai Lake during the Holocene:evidence from eolian deposits around the lake[J].Journal of Earth Science,2017,28(3):484-491. |
| 104 | 杜婧,鲁瑞洁,刘小槺,等.青海湖湖东沙地全新世风成沉积物磁化率特征及其环境意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质,2018,38(2):175-184. |
| 105 | 铁生年,马丽莉,杨兴学.青海湖周边沙漠化沙粒表面性质研究[J].青海大学学报(自然科学版),2011,29(5):17-20. |
| 106 | 铁生年,姜雄.青海湖周边沙漠化沙粒基本性能研究[J].硅酸盐通报,2014,33(4):715-719. |
| 107 | 史运坤,鄂崇毅,张晶,等.青海湖地区不同海拔黄土磁化率环境指示意义[J].地球环境学报,2021,12(3):256-268. |
| 108 | 董吉宝,安芷生,卢凤艳.湖泊沉积物中风成和水成组分定量判据的初步研究:以青海湖为例[J].地质力学学报,2010,16(4):402-411. |
| 109 | Jin Z D, You C F, Yu J M,et al.Seasonal contributions of catchment weathering and eolian dust to river water chemistry,northeastern Tibetan Plateau:chemical and Sr isotopic constraints[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,2011,116(F4):F002002. |
| 110 | Jin Z D, You C F, Yu J M.Toward a geochemical mass balance of major elements in Lake Qinghai,NE Tibetan Plateau:a significant role of atmospheric deposition[J].Applied Geochemistry,2009,24(10):1901-1907. |
| 111 | Hu G Y, Hu J J, Dong Z B,et al.Seasonal ice-covered lake surface likely caused the spatial heterogeneity of aeolian sediment grain-size in the source region of Yellow River,northeastern Tibetan Plateau,China[J].Frontiers in Earth Science,2023,11:1150585. |
| 112 | 徐叔鹰,徐德馥.青海湖东岸的风沙堆积[J].中国沙漠,1983,3(3):11-17. |
| 113 | Dong M, Yan P, Liu B L,et al.Distribution patterns and morphological classification of climbing dunes in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J].Aeolian Research,2018,35:58-68. |
| 114 | 鲁瑞洁,唐清亮,张登山,等.青海湖湖东克土沙区固定沙丘土壤水分动态变化的初步研究[J].地球环境学报,2010,1(3):183-188. |
| 115 | 鲁瑞洁,唐清亮,魏殿生,等.青海湖湖东沙地不同沙丘降雨入渗研究[J].中国沙漠,2013,33(3):797-803. |
| 116 | Wu W Y, Zhang D S, Tian L H,et al.Morphological change and migration of revegetated dunes in the Ketu Sandy Land of the Qinghai Lake,China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2023,15(7):827-841. |
| 117 | 李森,董玉祥,董光荣,等.青藏高原土地沙漠化区划[J].中国沙漠,2001,21(4):418-427. |
| 118 | 宋春晖,方小敏,师永民,等.青海湖现代三角洲沉积特征及形成控制因素[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2001,37(3):112-120. |
| 119 | 林建才.青海湖周围地区荒漠化土地动态问题的探讨[J].青海农林科技,2003(4):25-27. |
| 120 | 赵超,鲁瑞洁,李金凤.青海湖流域土地沙漠化及表土粒度特征[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(2):276-283. |
| 121 | 赵明月,赵文武,靳婷,等.青海湖流域土地沙漠化敏感性评价[J].中国农学通报,2012,28(32):237-242. |
| 122 | 张慧超,沙占江,张婷婷,等.20年来环青海湖区沙漠化土地的空间变化及其驱动力分析[J].干旱区资源与环境,2011,25(3):59-64. |
| 123 | 李小雁,许何也,马育军,等.青海湖流域土地利用/覆被变化研究[J].自然资源学报,2008,32(2):285-296. |
| 124 | 张明.基于遥感数据的青海湖流域土地沙漠化评价研究[J].国土与自然资源研究,2016(3):35-37. |
| 125 | 郭丽红,沙占江,马燕飞,等.环青海湖区20年来沙漠化土地景观格局空间变化分析[J].中国人口·资源与环境,2010,20(3):119-123. |
| 126 | 马燕飞,沙占江,牛志宁,等.环青海湖区沙漠化土地景观格局自相关分析[J].干旱区研究,2010,27(6):954-961. |
| 127 | 王静洁,蔡延玲.青海湖及其周围地区沙化土地变化动态研究[J].湖南林业科技,2016,43(6):81-89. |
| 128 | Wang H B, Ma M G, Geng L Y.Monitoring the recent trend of aeolian desertification using Landsat TM and Landsat 8 imagery on the north-east Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in the Qinghai Lake basin[J].Natural Hazards,2015,79:1753-1772. |
| 129 | 李庆,张春来,周娜,等.青藏高原沙漠化土地空间分布及区划[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(4):690-700. |
| 130 | 铁生年,李星,李昀珺.青海湖周边地区沙化现状和治理措施[J].青海科技,2009,16(1):22-26. |
| 131 | Yang M X, Wang S L, Yao T D,et al.Desertification and its relationship with permafrost degradation in Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau[J].Cold Regions Science and Technology,2004,39(1):47-53. |
| 132 | 马慧榕,肖锋军,董治宝,等.2000-2020年青海省共和县土地沙漠化动态及其驱动因素[J].干旱区资源与环境,2022,36(6):139-148. |
| 133 | 张慧超.环青海湖区沙漠化土地变化及其成因分析[D].西宁:青海师范大学,2011. |
| 134 | 田丽慧,张登山,胡梦珺,等.1976-2007年青海省刚察县土地沙漠化驱动力分析[J].中国沙漠,2013,33(2):493-500. |
| [1] | Ying Wang, Shuangwen Yi, Zhiwei Xu, Haochen Zhang, Xusheng Li. Quartz OSL and K-feldspar pIRIR dating of typical sediments over the past 20 000 years from the Tengger Desert, northern China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(3): 69-85. |
| [2] | Mengjun Hu, Jing Zhuang, Wenli Sun, Dengyou Zheng, Tianqi Ji, Aokang Xu. Geochemical characteristics of major elements and environmental evolution in the Holocene in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 11-20. |
| [3] | Aihua Hao, Xian Xue, Quangang You, Chaoyang Gou. Review on precipitation change over the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau in recent 60 years [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 43-52. |
| [4] | Yaofang Hou, Shengkui Cao, Guangchao Cao, Zhigang Wang, Youcai Wang, Ligang Kang. Relationship between hydrogen and oxygen stable isotope compositions of soil water and soil water storage in Shaliuhe River Basin of Qinghai Lake [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 153-164. |
| [5] | Jingjing Hu, Guangyin Hu, Zhibao Dong. Particle size characteristics of aeolian desertified land in Madoi Basin of the source region of Yellow River [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(4): 242-252. |
| [6] | Hong Jia, Zhiyan Sun, Jinming Xie, Jie Chen, Yinghua Zheng, Mingrui Qiang. Environmental changes recorded by aeolian deposits in the coasts of China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(3): 51-62. |
| [7] | Mei Shao, Wanyin Luo, Xuehua Che, Fang Wang, Junfeng Lu, Songbing Zou. Aeolian sand transport and its potential amount into Longyangxia Reservoir in 1987-2019 based on COSI-Corr [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 249-261. |
| [8] | Fangming Zeng, Hongpan Xue. The dataset of elemental compositions of the late Pleistocene loess-paleosol deposits on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 262-264. |
| [9] | Dongxue Chen, Ruijie Lu, Zhiyong Ding, Xiaokang Liu. Mid-late Holocene environmental changes recorded by fluvio-lacustrine and aeolian sediments in the eastern sandy land of Qinghai Lake [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 99-110. |
| [10] | Yan Zhang, Pengfei Ma, Lin Zeng, Aimin Liang, Zhengcai Zhang. Study on silt and clay provenance in the Yarlung Zangbo River middle reaches using sediment physicochemical characteristics [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(3): 92-100. |
| [11] | Pengfei Ma, Zhengcai Zhang, Qunpei Lunzhu, Jiajia Gao, Rui Dai, Wang Ci, Kaijia Pan. Analysis on the sand transport wind power conditions and suggestions on the sand disaster preventions in the middle reaches of Yarlung Zangbo River, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 10-18. |
| [12] | Guangyin Hu, Zhibao Dong, Zhengcai Zhang, Ming Zhou, Lunyu Shang. The regime of sand driving wind and sand drift potential in Zoige Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(5): 20-24. |
| [13] | Xixi Ma, Jianhua Xiao, Zhengyi Yao. A comparative study on the three calculation methods of grain-size parameters for aeolian sediments [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 95-102. |
| [14] | Yang Yufan, Cao Shengkui, Feng Qi, Cao Guangchao, Liu Ying, Lei Yizhen. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Composition of Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes of Shallow Groundwater in Shaliu River Basin of Qinghai Lake [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(5): 45-53. |
| [15] | Yao Huiru, Li Dongliang. The Gale Concentration Period and Degree over the Tibetan Plateau and Related Atmospheric Circulation during the Windy Period [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(2): 122-133. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech