
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 153-164.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00053
Yaofang Hou( ), Shengkui Cao(
), Shengkui Cao( ), Guangchao Cao, Zhigang Wang, Youcai Wang, Ligang Kang
), Guangchao Cao, Zhigang Wang, Youcai Wang, Ligang Kang
Received:2021-10-19
Revised:2022-04-06
Online:2022-11-20
Published:2023-01-09
Contact:
Shengkui Cao
CLC Number:
Yaofang Hou, Shengkui Cao, Guangchao Cao, Zhigang Wang, Youcai Wang, Ligang Kang. Relationship between hydrogen and oxygen stable isotope compositions of soil water and soil water storage in Shaliuhe River Basin of Qinghai Lake[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 153-164.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00053
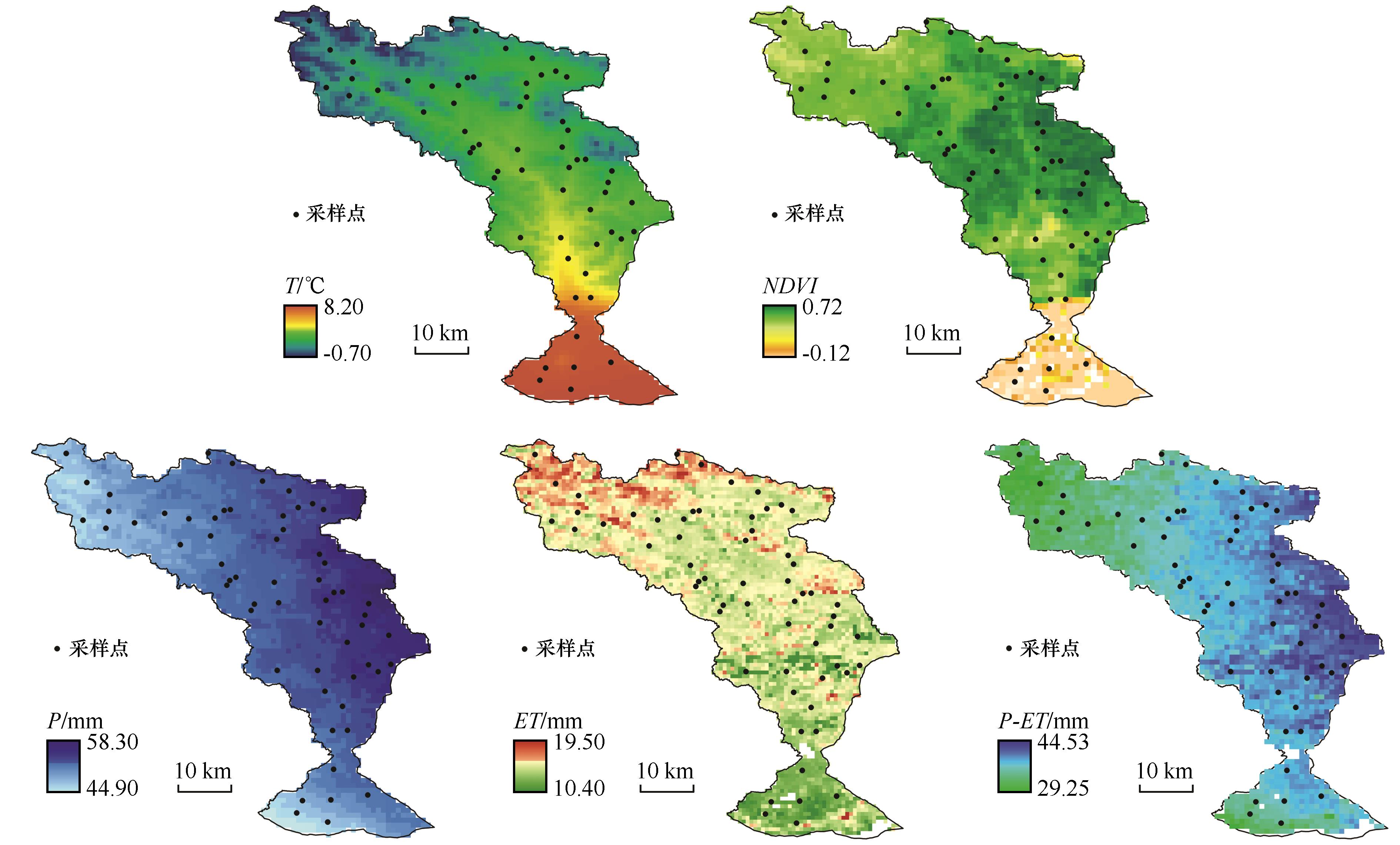
Fig.2 Distribution map of temperature (T), Normalized Vegetation Index (NDVI), monthly precipitation(P), monthly evapotranspiration (ET), difference between monthly precipitation and evapotranspiration (P-ET) in the Shaliu River Basin in September 2020
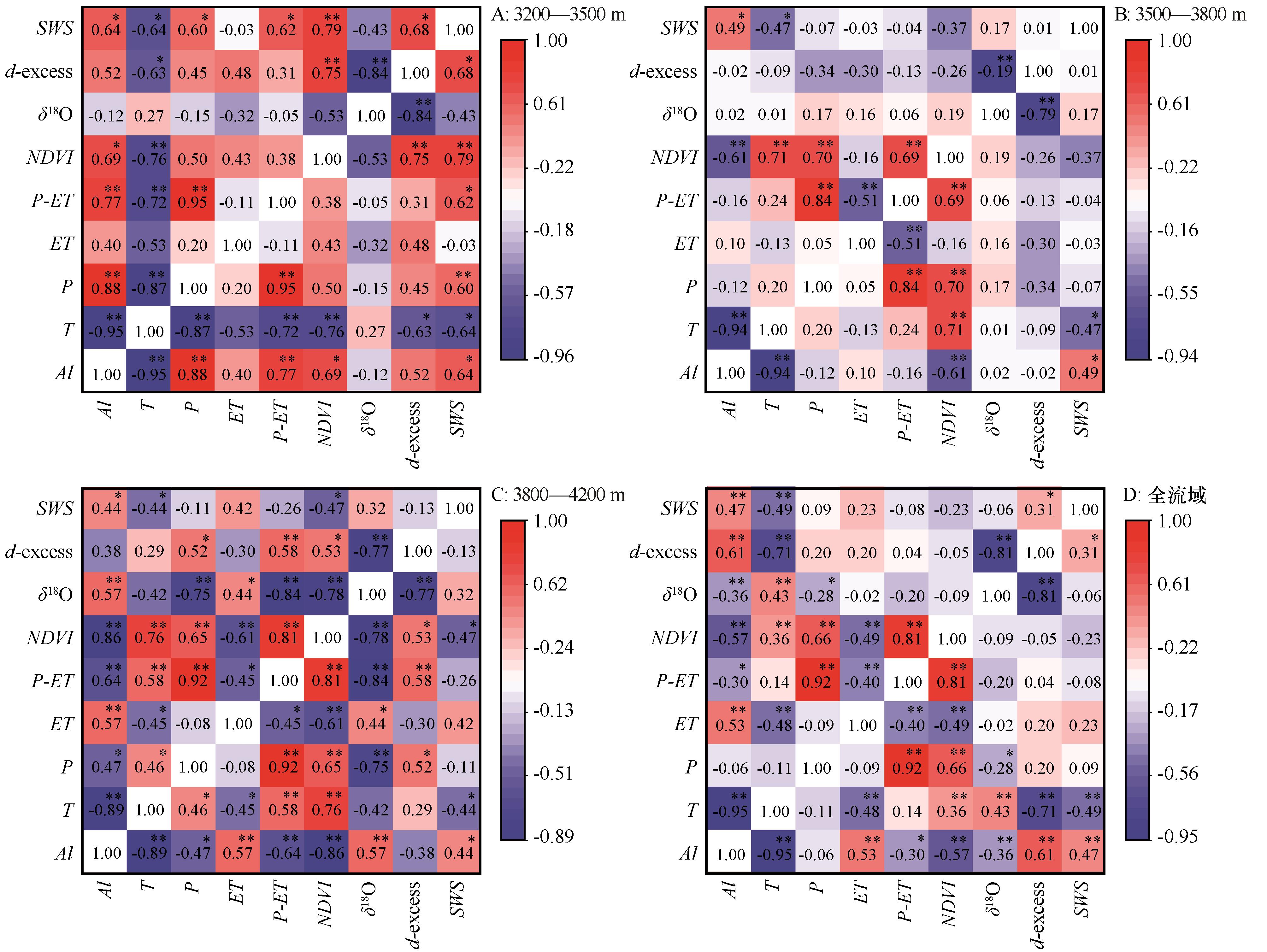
Fig.7 Correlations between soil water δ18O, d-excess value, soil water storage and environmental factors in different height zones 3 200-3 500 m (A), 3 500-3 800 m (B), 3 800-4 200 m(C), and the whole basin (D) in the Shaliu River Basin
| SWS | Al | T | P | ET | NDVI | δ18O | d-excess |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 cm, SWS≤30 mm | 0.60** | -0.70** | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.12 | -0.34* | 0.58** |
| 10—20 cm, SWS≤30 mm | 0.43** | -0.52** | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.10 | -0.53** | 0.63** |
| 20—30 cm, SWS≤30 mm | 0.42** | -0.48** | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.09 | -0.39** | 0.58** |
| 0—30 cm, SWS≤100 mm | 0.56** | -0.65** | 0.35* | 0.09 | 0.19 | -0.64** | 0.77** |
Table 1 Correlations between soil water storage and different environmental factors in the Shaliu River Basin in September 2020
| SWS | Al | T | P | ET | NDVI | δ18O | d-excess |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 cm, SWS≤30 mm | 0.60** | -0.70** | 0.30 | 0.29 | 0.12 | -0.34* | 0.58** |
| 10—20 cm, SWS≤30 mm | 0.43** | -0.52** | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.10 | -0.53** | 0.63** |
| 20—30 cm, SWS≤30 mm | 0.42** | -0.48** | 0.28 | 0.21 | 0.09 | -0.39** | 0.58** |
| 0—30 cm, SWS≤100 mm | 0.56** | -0.65** | 0.35* | 0.09 | 0.19 | -0.64** | 0.77** |
| 土壤储水量 (SWS) | 土层/cm | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 | 10—20 | 20—30 | |
| ≤30 mm | 0.79 | 0.81 | 0.79 |
| ≥30 mm | 0.54 | 0.51 | 0.53 |
Table 2 Relation of soil water storage to vertical decrease rate of temperature in Shaliu River Basin in September 2020
| 土壤储水量 (SWS) | 土层/cm | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0—10 | 10—20 | 20—30 | |
| ≤30 mm | 0.79 | 0.81 | 0.79 |
| ≥30 mm | 0.54 | 0.51 | 0.53 |
| 1 | 史志华,朱华德,陈佳,等.小流域土壤水分空间异质性及其与环境因子的关系[J].应用生态学报,2012,23(4):889-895. |
| 2 | Li H Q, Wang C Y, Zhang F W,et al.Atmospheric water vapor and soil moisture jointly determine the spatiotemporal variations of CO2 fluxes and evapotranspiration across the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau grasslands[J].Science of the Total Environment,2021,791:145379. |
| 3 | 朱磊,田军仓,孙骁磊.基于全耦合的地表径流与土壤水分运动数值模拟[J].水科学进展,2015,26(3):322-330. |
| 4 | Xie H Y, Jiang X W, Tan S C,et al.Interaction of soil water and groundwater during the freezing-thawing cycle:field observations and numerical modeling[J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2021,25(8):4243-4257. |
| 5 | 李雨芊,孟玉川,宋泓苇,等.典型林区水分氢氧稳定同位素在土壤-植物-大气连续体中的分布特征[J].应用生态学报,2021,32(6):1928-1934. |
| 6 | 戴军杰,章新平,吕殿青,等.南方红壤丘陵区樟树林土壤水分动态变化[J].水土保持研究,2019,26(4):123-131. |
| 7 | Pu H M, Song W F, Wu J K.Using soil water stable isotopes to investigate soil water movement in a water conservation forest in Hani Terrace[J].Water,2020,12(12):3520. |
| 8 | 王锐,刘文兆,宋献方.黄土塬区土壤水分运动的氢氧稳定同位素特征研究[J].水土保持学报,2014,28(3):134-137,184. |
| 9 | 周海,郑新军,唐立松,等.盐生荒漠土壤水稳定氢、氧同位素组成季节动态[J].中国沙漠,2014,34(1):162-169. |
| 10 | 雷义珍,曹生奎,曹广超,等.基于氢氧稳定同位素和水化学的青藏高原高寒内陆流域水文过程示踪研究[J].地理研究,2021,40(5):1239-1252. |
| 11 | 邱菊,蒋勇军,吕同汝,等.典型岩溶槽谷区土壤水和地下水氢氧稳定同位素对隧道建设的响应[J].地球科学,2021,47(2):717-728. |
| 12 | 吴华武,李小雁,蒋志云,等.基于δD和δ 18O的青海湖流域芨芨草水分利用来源变化研究[J].生态学报,2015,35(24):8174-8183. |
| 13 | 李宁,周海,任珩,等.不同地下水位处梭梭(Haloxylon ammodendron)水分来源特征[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(4):79-86. |
| 14 | 郝帅,李发东.艾比湖流域典型荒漠植被水分利用来源研究[J].地理学报,2021,76(7):1649-1661. |
| 15 | 闫建梅,何丙辉,田太强,等.川中丘陵区不同土地利用方式土壤入渗与贮水特征[J].水土保持学报,2014,28(1):53-57,62. |
| 16 | 王明明,刘新平,李玉霖,等.不同植被盖度沙质草地生长季土壤水分动态[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(5):54-61. |
| 17 | 索立柱,黄明斌,段良霞,等.黄土高原不同土地利用类型土壤含水量的地带性与影响因素[J].生态学报,2017,37(6):2045-2053. |
| 18 | 贺慧丹,祝景彬,未亚西,等.高寒草甸土壤贮水量对封育措施的响应[J].水土保持研究,2018,25(3):210-216,223. |
| 19 | Baroni G, Ortuani B, Facchi A,et al.The role of vegetation and soil properties on the spatiotemporal variability of the surface soil moisture in a maize cropped field[J].Journal of Hydrology,2013,489:148-159. |
| 20 | 常学尚,常国乔.干旱半干旱区土壤水分研究进展[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(1):156-163. |
| 21 | Perry M, Niemann J.Analysis and estimation of soil moisture at the catchment scale using EOFs[J].Journal of Hydrology,2007,334:388-404. |
| 22 | 董立国,李生宝,蒋齐,等.宁夏半干旱黄土丘陵区不同土地利用类型土壤贮水量变化分析[J].干旱区资源与环境,2011,25(10):184-189. |
| 23 | 刘磊,李小雁,蒋志云,等.青海湖流域不同海拔高度土壤水分时空变化特征[J].资源科学,2017,39(2):263-275. |
| 24 | 姚雪玲,傅伯杰,吕一河.黄土丘陵沟壑区坡面尺度土壤水分空间变异及影响因子[J].生态学报,2012,32(16):4961-4968. |
| 25 | 吴丽丽,刘丹一,杨文斌,等.降雨量、土壤蓄水量对流动沙地土壤水分深层渗漏的影响[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(3):210-218. |
| 26 | 王家鑫,张明军,张宇,等.基于稳定同位素示踪的黄河兰州段河漫滩土壤水特征分析[J].干旱区地理,2021,44(5):1449-1458. |
| 27 | 肖雄,李小雁,吴华武,等.青海湖流域高寒草甸壤中流水分来源研究[J].水土保持学报,2016,30(2):230-236. |
| 28 | 马延东,赵景波,邵天杰,等.青海环湖地区草原土壤含水量及富集规律[J].中国农业科学,2015,48(10):1982-1995. |
| 29 | 蒋志云,李小雁,张思毅,等.基于电磁感应成像植被斑块土壤水盐效应研究[J].生态学报,2019,39(24):9188-9199. |
| 30 | 田丽慧,汪海娇,张登山,等.高寒沙地典型固沙植物在沙丘不同地貌部位的水分利用特征[J].生态学报,2021,41(15):1-12. |
| 31 | 赵国琴,李小雁,吴华武,等.青海湖流域具鳞水柏枝植物水分利用氢同位素示踪研究[J].植物生态学报,2013,37(12):1091-1100. |
| 32 | 杨羽帆,曹生奎,冯起,等.青海湖沙柳河流域浅层地下水氢氧稳定同位素分布特征[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(5):45-53. |
| 33 | Cui B L, Li X Y.Runoff processes in the Qinghai Lake Basin,northeast Qinghai-Tibet Plateau,China:insights from stable isotope and hydrochemistry[J].Quaternary International,2015,380/381:123-132. |
| 34 | 刚察县志编纂委员会.刚察县志[M].西安:陕西人民出版社,1998:95-97. |
| 35 | 陈桂琛,彭敏.青海湖地区植被及其分布规律[J].植物生态学与地植物学学报,1993,17(1):73-83. |
| 36 | 孙永亮,李小雁,汤佳,等.青海湖流域气候变化及其水文效应[J].资源科学,2008,30(3):354-362. |
| 37 | 孟春红,夏军.“土壤水库”贮水量的研究[J].节水灌溉,2004(4):8-10. |
| 38 | Craig H.Isotopic variations in meteoric water[J].Science,1961,133(3465):1702-1703. |
| 39 | Dansgaard W.Stable isotopes in precipitation[J].Tellus,1964,16(4):436-468. |
| 40 | 杨羽帆.基于氢氧稳定同位素技术的青海湖沙柳河流域降水径流过程研究[D].西宁:青海师范大学,2019. |
| 41 | 顾慰祖.同位素水文学[M].北京:科学出版社,2011:53. |
| 42 | 吴华武,李小雁,赵国琴,等.青海湖流域降水和河水中δ 18O和δD变化特征[J].自然资源学报,2014,29(9):1552-1564. |
| 43 | 张翔,邓志民,潘国艳,等.鄱阳湖湿地土壤水稳定同位素变化特征[J].生态学报,2015,35(22):7580-7589. |
| 44 | 刘保清,刘志民,钱建强,等.科尔沁沙地南缘主要固沙植物旱季水分来源[J].应用生态学报,2017,28(7):2093-2101. |
| 45 | 田立德,姚檀栋, Tsujimura M,等.青藏高原中部土壤水中稳定同位素变化[J].土壤学报,2002,39(3):289-295. |
| 46 | 侯士彬,宋献方,于静洁,等.太行山区典型植被下降水入渗的稳定同位素特征分析[J].资源科学,2008,30(1):86-92. |
| 47 | 汪星,周玉红,汪有科,等.黄土高原半干旱区山地密植枣林土壤水分特性研究[J].水利学报,2015,46(3):263-270. |
| 48 | 林莎,贺康宁,王莉,等.基于地统计学的黄土高寒区典型林地土壤水分盈亏状况研究[J].生态学报,2020,40(2):728-737. |
| 49 | 王春敏.基于NDVI的三江源植被变化及影响因素分析[D].北京:中国地质大学(北京),2018. |
| 50 | 靳宇蓉,鲁克新,李鹏,等.基于稳定同位素的土壤水分运动特征[J].土壤学报,2015,52(4):792-801. |
| 51 | 李嘉竹,刘贤赵.氢氧稳定同位素在SPAC水分循环中的应用研究进展[J].中国沙漠,2008,28(4):787-794. |
| [1] | Yali Liu, Jianhua Bai, Wei Xiong, Yuqing Han, Honglin Lian, Hao Guo, Zhiming Xin, Xiangjie Liu, Huaiyuan Liu. The characteristics of branch nocturnal sap flow and its environmental driving mechanism of Haloxylon ammodendron artificial shrub in the Ulan Buh Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(5): 195-203. |
| [2] | Zhenmin Niu, Naiang Wang, Penghui Wen, Xianbao Su, Xinran Yu, Wenjia Zhang. Interdune lakes affects the water content of shallow sand layer: a situ observation from the Badain Jaran Sand Sea, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(2): 142-152. |
| [3] | Chengpeng Sun, Wenzhi Zhao. Effect of land use on soil infiltration in the desert-oasis of Hexi Corridor [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 148-156. |
| [4] | Dongxue Chen, Ruijie Lu, Zhiyong Ding, Xiaokang Liu. Mid-late Holocene environmental changes recorded by fluvio-lacustrine and aeolian sediments in the eastern sandy land of Qinghai Lake [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 99-110. |
| [5] | Wenbing Yang, Tao Wang, Wei Xiong, Hui Zou, Wei Feng, Yiben Cheng, Honglin Lian. Overview of hydrological principle of low vegetation coverage sand control [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(3): 75-80. |
| [6] | Yahong Li, Chongfeng Bu, Qi Guo, Yingxin Wei. Ecological functions comparison of moss crust and algae crust in the Mu Us Sand Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 138-144. |
| [7] | Yunhua Ma, Tu Feng, Yangzheng Li, Qingqing Jin. Adaptability of the Hippophae rhamnoides seedlings on different degrees of soil dressing for rocky desertification [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 228-233. |
| [8] | Quanlin Ma, Jinchun Zhang, Fang Chen, Dekui Zhang, Linyuan Wei. Mechanism and dynamics for succession of artificial Hedysarum scoparium sand-binding forests at the southern edge of Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 206-215. |
| [9] | Zhang Kehai, Hu Guanglu, Fang Qiao, Zhang Yujia, Li Haoran. Water content in the root zone of sand-fixation vegetation in desert-oasis ecotone in the middle reaches of the Heihe River [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(3): 33-42. |
| [10] | Wu Lili, Liu Danyi, Yang Wenbin, Wang Tao, Li Wei, Feng Jinchao, Feng Wei. Relationship between precipitation and soil water storage and soil deep percolation in mobile sand land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(3): 210-218. |
| [11] | Li Minlan, Qu Jianjun, Tang Ximing, Dun Yaoquan, Chen Xiaoying, Wu Ting, Song Naiping. Influence of HDPE honeycomb sand fixation on soil moisture [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(1): 136-144. |
| [12] | Yang Yufan, Cao Shengkui, Feng Qi, Cao Guangchao, Liu Ying, Lei Yizhen. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Composition of Stable Hydrogen and Oxygen Isotopes of Shallow Groundwater in Shaliu River Basin of Qinghai Lake [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(5): 45-53. |
| [13] | Yan Jialiang, Zhao Wenzhi, Liu Jiliang, Feng Lan. Characteristics of Soil Water Repellency and Its Causes in Oasis Cropland [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(5): 174-181. |
| [14] | Li Yunfei, Xie Ting, Shi Wanli, Li Xiaojun. Response of Topsoil Organic Carbon Mineralization to Litter Addition in the Revegetation Area in the Southeastern Fringe of the Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(5): 200-209. |
| [15] | Meng Yangyang, Liu Bing, Liu Chan. Dynamic Process of Water-Heat-Salt in Soil and the Mechanism in the Desert Oasis Wetland [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(1): 149-160. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech