
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 142-152.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00099
Zhenmin Niu( ), Naiang Wang(
), Naiang Wang( ), Penghui Wen, Xianbao Su, Xinran Yu, Wenjia Zhang
), Penghui Wen, Xianbao Su, Xinran Yu, Wenjia Zhang
Received:2021-04-02
Revised:2021-08-12
Online:2022-03-20
Published:2022-03-30
Contact:
Naiang Wang
CLC Number:
Zhenmin Niu, Naiang Wang, Penghui Wen, Xianbao Su, Xinran Yu, Wenjia Zhang. Interdune lakes affects the water content of shallow sand layer: a situ observation from the Badain Jaran Sand Sea, China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(2): 142-152.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00099
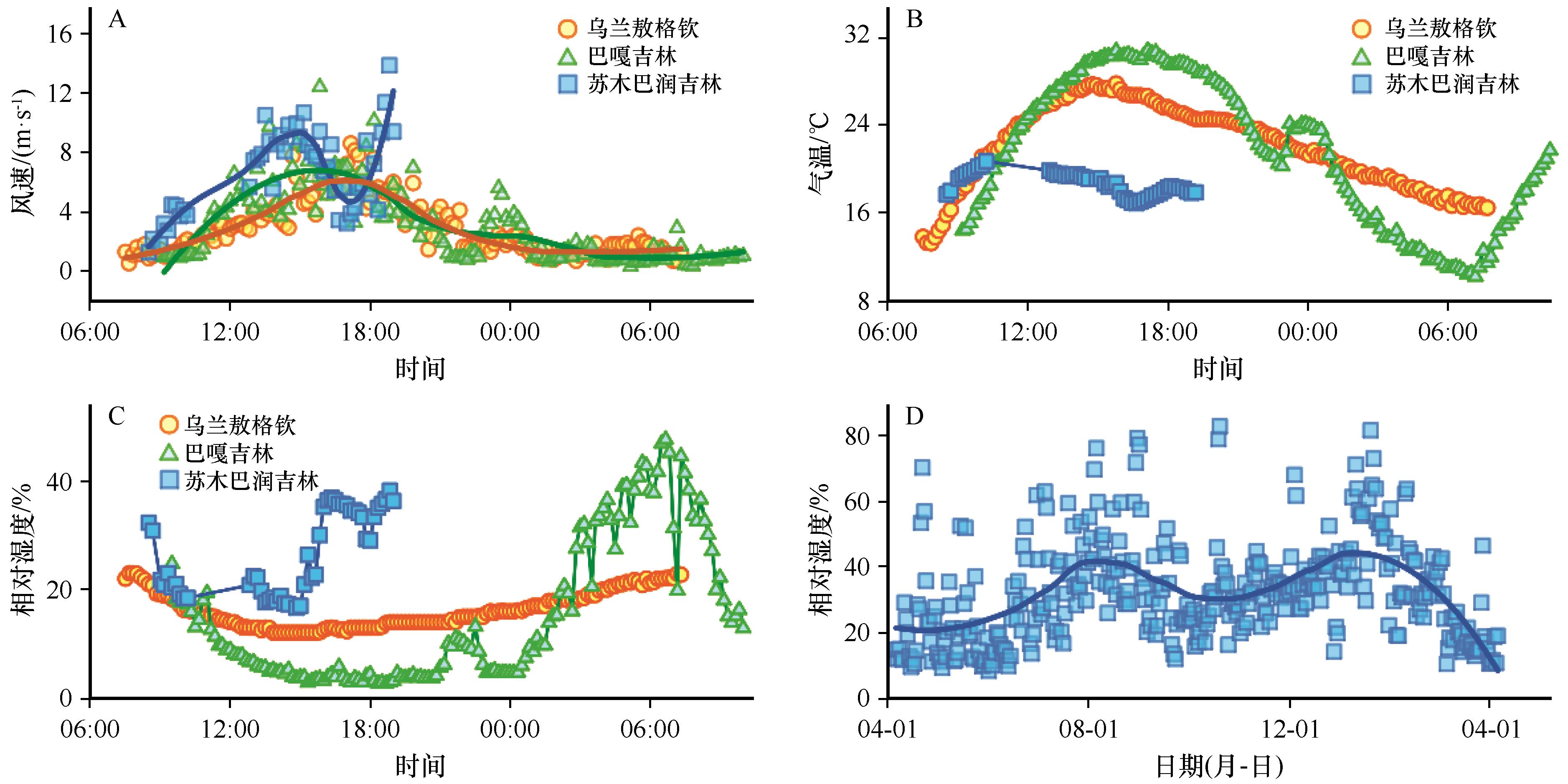
Fig.2 Comparison of wind speed, temperature and relative air humidity in Sumubarunjilin, Bagajilin and Wulanaogeqin, and the daily average relative humidity from the automatic weather station
| 项目 | 苏木巴润吉林 | 巴嘎吉林 | 乌兰敖格钦 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 参数a | 3 073.39 | 160.19 | 49.77 |
| 参数b | -0.26 | -0.12 | -0.05 |
| R2 | 0.50 | 0.52 | 0.50 |
| P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
Table 1 Fitting parameters and statistics of test for relative humidity and air temperature
| 项目 | 苏木巴润吉林 | 巴嘎吉林 | 乌兰敖格钦 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 参数a | 3 073.39 | 160.19 | 49.77 |
| 参数b | -0.26 | -0.12 | -0.05 |
| R2 | 0.50 | 0.52 | 0.50 |
| P | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
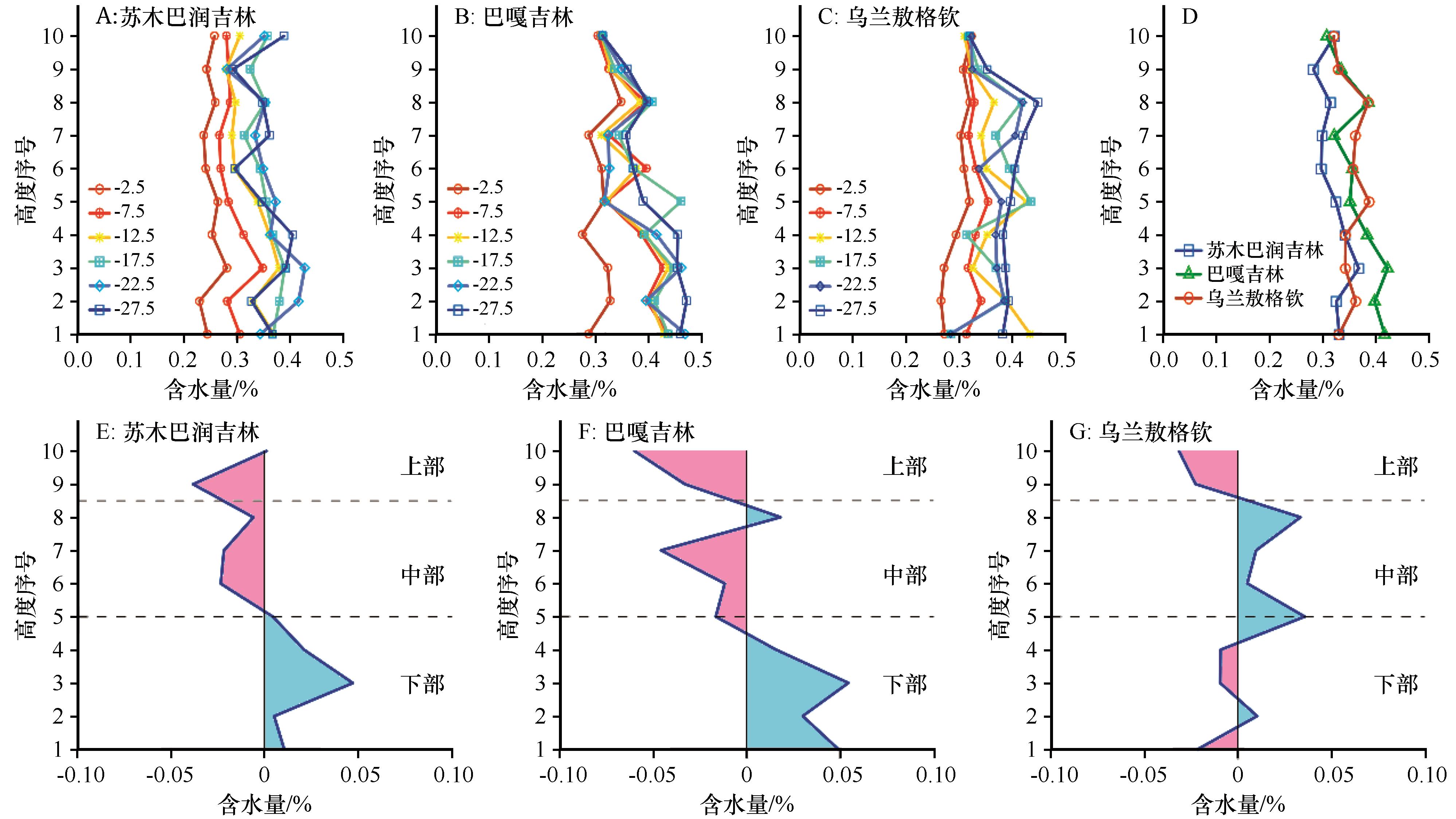
Fig.4 Variation of water content with height in shallow sand layer. A, B, and C are the soil water content at each depth in Sumubarunjilin, Bagajilin, and Wulanaogeqin, respectively; D Variation of the average water content of 0-30 cm depths in Sumubarunjilin, Bagajilin, and Wulanaogeqin; E, F, and G are the variation of anomaly value of the average water content in 0-30 cm depths with height in Sumubarunjilin, Bagajilin and Wulanaogeqin, respectively
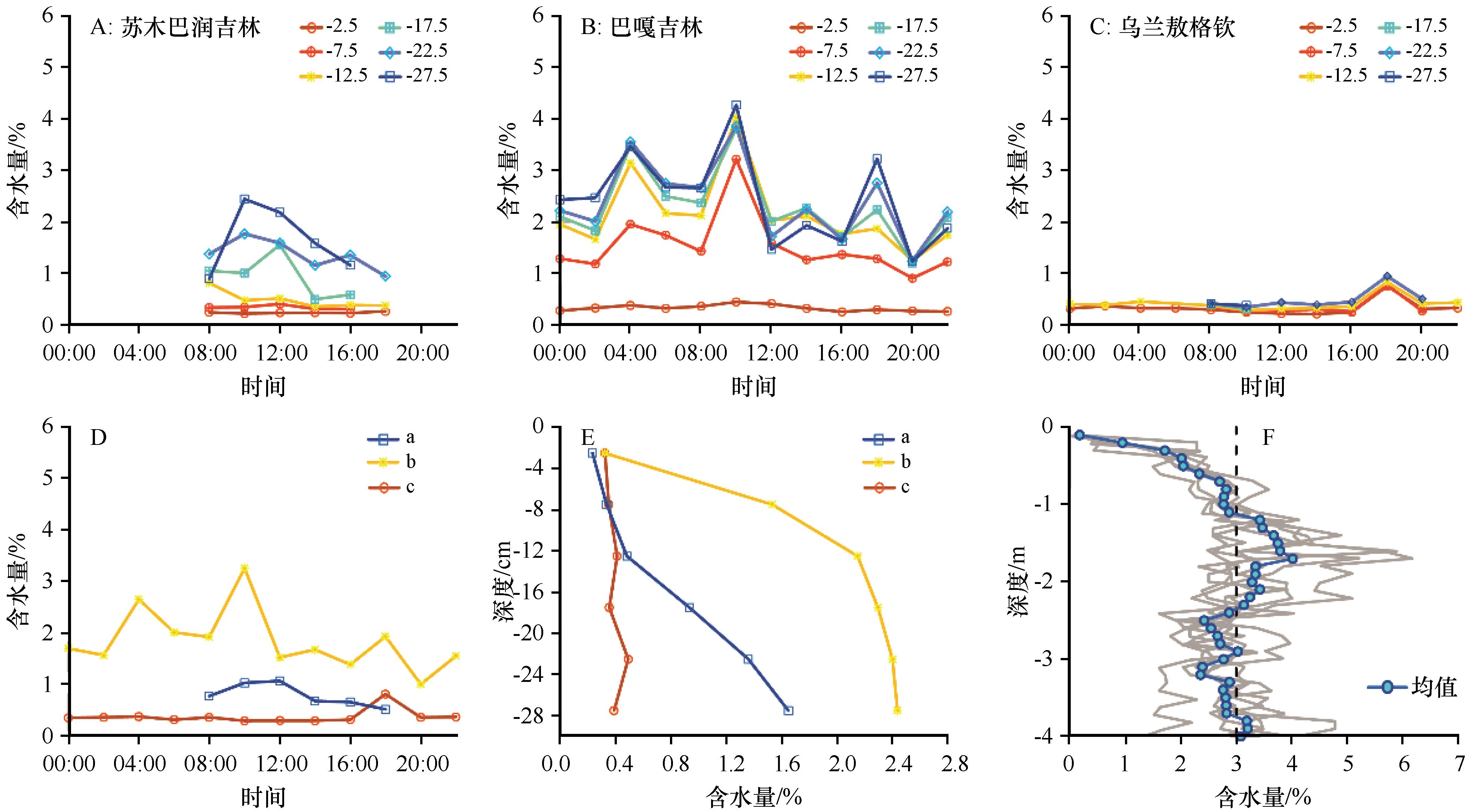
Fig.5 Variation of soil water content over time and depth. A, B and C are the soil water content at different depths within 30 cm in Sumubarunjilin, Bagajilin and Wulanaogeqin, respectively, where "-2.5" represents 0-5 cm depths, "-7.5" represents 5-10 cm depths, and so on; D is variation of the average soil water content within 30 cm over time in Sumubarunjilin, Bagajilin and Wulanaogeqin; E is variation of the average soil water content with depth of each layer within 30 cm in Sumubarunjilin, Bagajilin and Wulanaogeqin; in D and E, “a” represents Sumubarunjilin, “b” represents Bagajilin and “c” represents Wulanaogeqin; F is the variation of soil water content with depth and the average value of 6 profiles within the leeward slope of mega-dunes from 0 to 4 m (revised from literature [35])

Fig.6 The relationship between water content of shallow sand at different depths and wind speed, air temperature and relative humidity, where, "-2.5" represents 0-5 cm depths, "-7.5" represents 5-10 cm depths, and so on
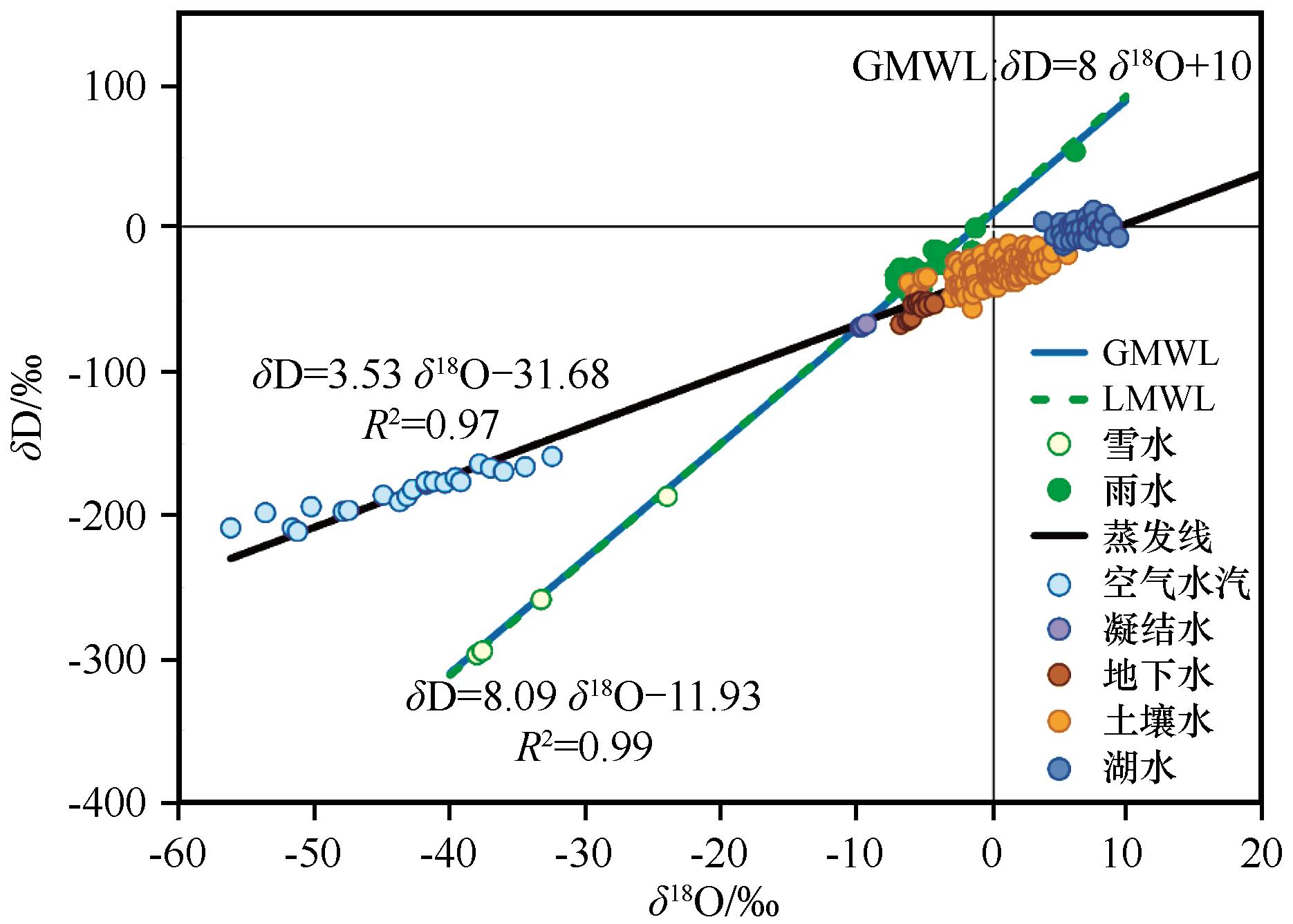
Fig.7 Isotope δD-δ18O composition of the Global Meteoric Water Line (GMWL), local meteoric water line (rainfall and snow water), evaporation line, rainfall, snow water, atmospheric water vapor, condensate water, groundwater, soil water, and lake water in the lake group area of Badain Jaran Sand Sea (Modified from literature [33])
| 1 | 朱震达,吴正,刘恕,等.中国沙漠概论[M].北京:科学出版社,1980:56-89. |
| 2 | Mckee E D.A Study of Global Sand Seas [M].Washington,USA:United States Government Printing Office,1979. |
| 3 | 王乃昂,宁凯,李卓仑,等.巴丹吉林沙漠全新世的高湖面与泛湖期[J].中国科学:地球科学,2016,46(8):1106-1115. |
| 4 | 楼桐茂.甘肃民勤至巴丹吉林庙间沙漠成因及其改造利用[M]//中国科学院治沙队.治沙研究(第三号).北京:科学出版社,1962:90-95. |
| 5 | 孙培善,孙德钦.内蒙古高原西部水文地质初步研究[M]//中国科学院治沙队.治沙研究(第六号).北京:科学出版社,1964:245-317. |
| 6 | 谭见安.内蒙古阿拉善荒漠的地方类型[M]//中国科学院地理研究所.地理集刊(第八号).北京:科学出版社,1964. |
| 7 | 王涛.巴丹吉林沙漠形成演变的若干问题[J].中国沙漠,1990,10(1):29-40. |
| 8 | 杨小平.近3万年来巴丹吉林沙漠的景观发育与雨量变化[J].科学通报,2000(4):428-434. |
| 9 | Yang X, Liu T, Xiao H.Evolution of megadunes and lakes in the Badain Jaran Desert,Inner Mongolia,China during the last 31,000 years[J].Quaternary International,2003,104:99-112. |
| 10 | Dong Z, Wang T, Wang X.Geomorphology of the megadunes in the Badain Jaran Desert [J].Geomorphology,2004,60:191-203. |
| 11 | Jakel D.The Badain Jaran Desert:its origin and development [J].Geowissenschaften,1996,14:272-274. |
| 12 | 李孝泽,王振亭,陈发虎,等.巴丹吉林沙漠横向沙山沉积GPR雷达探测研究[J].第四纪研究,2009(4):145-153. |
| 13 | Chen J, Li L, Wang J,et al.Groundwater maintains dune landscape[J].Nature,2004,432:459-460. |
| 14 | 陈建生,赵霞,盛雪芬,等.巴丹吉林沙漠湖泊群与沙山形成机理研究[J].科学通报,2006,51(23):2789-2796. |
| 15 | 任伟,金胜.应用音频大地电磁法探测内蒙古巴丹吉林高大沙山结构及成因[J].现代地质,2011,25(6):1167-1173. |
| 16 | 闫满存,王光谦,李保生,等.巴丹吉林沙漠高大沙山的形成发育研究[J].地理学报,2001,68(1):223-235. |
| 17 | 闫满存,王光谦,董光荣,等.巴丹吉林沙漠沙山发育与环境演变研究[J].中国沙漠,2001,21(4):361-366. |
| 18 | Dong Z, Qian G, Luo W,et al.Geomorphological hierarchies for complex mega-dunes and their implications for mega-dune evolution in the Badain Jaran Desert[J].Geomorphology,2009,106:180-185. |
| 19 | Warren A.Dunes:Dynamics,Morphology,History[M].West Sussex,UK:Wiley-Blackwell,2013. |
| 20 | Yang X, Scuderi L, Liu T,et al.Formation of the highest sand dunes on Earth[J].Geomorphology,2011,135:108-16. |
| 21 | Liang X, Zhao L, Niu Z,et al.Warm island effect in the Badain Jaran Desert lake group region inferred from the accumulated temperature [J].Atmosphere,2020,153(11):1265-1277. |
| 22 | Liang X, Zhao L, Xu X,et al.Plant phenological responses to the warm island effect in the lake group region of the Badain Jaran Desert,northwestern China [J].Ecological Informatics,2020,57:101066. |
| 23 | Zhang K, Cai D, Ao Y,et al.Local circulation maintains the coexistence of lake-dune pattern in the Badain Jaran Desert[J].Scientific Reports,2017,7:40238. |
| 24 | 朱金峰,王乃昂,陈红宝,等.基于遥感的巴丹吉林沙漠范围与面积分析[J].地理科学进展,2010,29(9):1087-1094. |
| 25 | 张振瑜,王乃昂,马宁,等.近40 a巴丹吉林沙漠腹地湖泊面积变化及其影响因素[J].中国沙漠,2012,32(6):1743-1750. |
| 26 | 马宁,王乃昂,朱金峰,等.巴丹吉林沙漠周边地区近50 a来气候变化特征[J].中国沙漠,2011,31(6):1541-1547. |
| 27 | Zhang X, Wang N A, Xie Z,et al.Water loss due to increasing planted vegetation over the Badain Jaran Desert,China[J].Remote Sensing,2018,134:1-21. |
| 28 | 胡文峰,王乃昂,赵力强,等.巴丹吉林沙漠典型湖泊湖气界面水-热交换特征[J].地理科学进展,2015,34(8):1061-1071. |
| 29 | Sun J, Hu W, Wang N A,et al.Eddy covariance measurements of water vapor and energy flux over a lake in the Badain Jaran Desert,China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2018,10(4):517-533. |
| 30 | 张文佳,王乃昂,于昕冉,等.基于地下水动态和经验模型的巴丹吉林沙漠潜水蒸发量级:以苏木吉林湖区为例[J].干旱区研究,2020,37(5):1215-1222. |
| 31 | 马宁,王乃昂,赵力强,等.巴丹吉林沙漠腹地降水事件后的沙山蒸发观测[J].科学通报,2014,59(7):615-622. |
| 32 | 蒋进,王雪芹,雷加强.古尔班通古特沙漠工程防护体系内土壤水分变化规律[J].水土保持学报,2003(3):74-77. |
| 33 | Zhang J, Wang N A, Niu Z,et al.Stable isotope analysis of water sources for Tamarix laxa in the mega-dunes of the Badain Jaran Desert,China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2018,10(6):821-832. |
| 34 | 陈世训,陈创买.气象学[M].北京:农业出版社,1981:20-23. |
| 35 | 赵景波,陈志青,马延东,等.巴丹吉林沙漠沙山区高含量薄膜水与水分平衡研究[J].地理科学,2017,37(6):960-966. |
| 36 | 胡隐樵.沙漠、戈壁中的一种特殊气象现象:冷岛效应[J].自然杂志,1989(10):773-777. |
| 37 | Wu Y, Wang N A, Zhao L,et al.Hydrochemical characteristics and recharge sources of Lake Nuoertu in the Badain Jaran Desert[J].Science Bulletin,2014,59(9):886-895. |
| 38 | 顾慰祖,陈建生,汪集旸,等.巴丹吉林高大沙山表层孔隙水现象的疑义[J].水科学进展,2004,15(6):695-699. |
| 39 | Subramaniam A R, Rao A V R K.Dew fall in sand dune areas of India[J].International Journal of Biometeorology,1983,27(3):271-280. |
| 40 | Zangvil A.Six years of dew observations in the Negev Desert,Israel[J].Journal of Arid Environments,1996,32(4):361-371. |
| 41 | Li X.Effects of gravel and sand mulches on dew deposition in the semiarid region of China[J].Journal of Hydrology,2002,260:151-160. |
| 42 | Pan Y, Wang X, Zhang Y,et al.Dew formation characteristics at annual and daily scale in xerophyte shrub plantations at Southeast margin of Tengger Desert,Northern China[J].Ecohydrology,2018:e1968. |
| 43 | 张兴鲁.干旱地区沙丘水汽凝结及其意义[J].水文地质工程地质,1986(6):39-42. |
| 44 | Kaseke K F, Mills A J, Brown R,et al.A method for direct assessment of the "Non Rainfall" atmospheric water cycle:input and evaporation from the soil [J].Pure and Applied Geophysics,2012,169:847-857. |
| 45 | Rollins L R.Movement of soil moisture under a thermal gradient[J].Highway Research Board Proceeding,1954,33:492-508. |
| 46 | Kosmas C, Danalatos N G, Poesen J,et al.The effect of water vapour adsorption on soil moisture content under Mediterranean climatic conditions [J].Agricultural Water Management,1998,36(2):157-168. |
| 47 | Jacobs A F G, Heusinkveld B G, Berkowicz S M.Dew deposition and drying in a desert system:a simple simulation model[J].Journal of Arid Environments,1999,42(3):211-222. |
| 48 | 黄兵兵,赵力强,程弘毅,等.巴丹吉林沙漠腹地地温变化特征[J].中国沙漠,2017,37(3):530-535. |
| [1] | Zhimin Liu, Haibin Yu. Discussion on ecological management of Horqin Sandy Land under the concept of "a living community of montains, waters, forests, farmlands, lakes, grasslands and sandylands" [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 34-40. |
| [2] | Wenzhi Zhao, Xuelian Bai, Chan Liu. Research on vegetation sand control around the south edge of Badain Jaran Sand Sea, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(1): 5-11. |
| [3] | Dongxue Chen, Ruijie Lu, Zhiyong Ding, Xiaokang Liu. Mid-late Holocene environmental changes recorded by fluvio-lacustrine and aeolian sediments in the eastern sandy land of Qinghai Lake [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 99-110. |
| [4] | Haiyun Yu, Zhengcai Zhang, Zhijun Wang. Sediment grain size characteristics at extinct lakes in the south Alxa, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(4): 177-184. |
| [5] | Lichao Zhuang, Naiang Wang, Xunhe Zhang, Liqiang Zhao, Xianbao Su. Analysis on the difference of the spatial model of lake ice freezing and melting in the Badain Jaran Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(3): 214-223. |
| [6] | Yahong Li, Chongfeng Bu, Qi Guo, Yingxin Wei. Ecological functions comparison of moss crust and algae crust in the Mu Us Sand Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 138-144. |
| [7] | Sarina, Zhibao Dong, Weige Nan. The Aesthetic Value of Mega-dune Lines in the Badain Jaran Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 221-230. |
| [8] | Yunhua Ma, Tu Feng, Yangzheng Li, Qingqing Jin. Adaptability of the Hippophae rhamnoides seedlings on different degrees of soil dressing for rocky desertification [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 228-233. |
| [9] | Liuwen Dong, Jialong Han, Wenzhi Zhao, Jiliang Liu, Yibin Ba. Comparison of ground arthropod community between Lake Wetland and adjacent sand dune in Heihe River Basin [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(6): 250-258. |
| [10] | Zhun Liang, Lü Ping, Zhengyao Liu, Nan Xiao, Wei Liang, Mingjing Xu, Miaoyan Feng. The relationship between wind regime and yardang morphology in the Duck Lake Area of Qaidam Basin, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(5): 42-48. |
| [11] | Changzhen Yan, Sen Li, Junfeng Lu, Lichao Liu. Lake number and area in the Tengger Desert during 1975-2015 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 183-189. |
| [12] | Quanlin Ma, Jinchun Zhang, Fang Chen, Dekui Zhang, Linyuan Wei. Mechanism and dynamics for succession of artificial Hedysarum scoparium sand-binding forests at the southern edge of Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 206-215. |
| [13] | Zhang Kehai, Hu Guanglu, Fang Qiao, Zhang Yujia, Li Haoran. Water content in the root zone of sand-fixation vegetation in desert-oasis ecotone in the middle reaches of the Heihe River [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(3): 33-42. |
| [14] | Wang Lixiang, Cai Mingyu, Bai Xuelian, Qiao Rongrong, Ji Shuxin, Chang Xueli. Lake fluctuation and driving factors in the Wulanbuhe Desert of China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(2): 59-67. |
| [15] | Hong Chang, Han Xujiao, Dai Jiadong, Liu Lianyou, Zhang Guoming. The physicochemical characteristics of the surface sediments on dry lake bed in Buzhai-nur Lake, Mu Us Sandy Land, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(2): 86-93. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech