中国沙漠 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 11-20.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00103
收稿日期:2022-04-20
修回日期:2022-07-07
出版日期:2023-03-20
发布日期:2023-04-12
作者简介:胡梦珺(1974—),女,甘肃庆阳人,博士,副教授,主要研究方向为寒旱区环境演变与元素地球化学。E-mail: lele200466@163.com
基金资助:
Mengjun Hu( ), Jing Zhuang, Wenli Sun, Dengyou Zheng, Tianqi Ji, Aokang Xu
), Jing Zhuang, Wenli Sun, Dengyou Zheng, Tianqi Ji, Aokang Xu
Received:2022-04-20
Revised:2022-07-07
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2023-04-12
摘要:
对青藏高原东北部风成砂-古土壤序列泽库剖面(ZK剖面)常量元素氧化物含量及其比值进行分析,结合14C测年,揭示其常量元素地球化学特征,探讨了青藏高原东北部全新世环境演变。结果表明:(1)剖面沉积物的化学组成以SiO2、Al2O3、CaO为主,其中SiO2和CaO的标准差较高,对气候变化较为敏感。(2)自剖面底部向上SiO2含量和残积系数呈现先减少后增加的趋势,高值指示冷干的气候意义,CaO含量和退碱系数则相反,高值指示温湿的气候意义。(3)9.4 ka BP以来青藏高原东北部的气候经历了由温湿向冷干的转变过程,可划分为9.4~4.2 ka BP气候温湿期和4.2 ka BP至今气候冷干期;其中在6.6~6.2 ka BP、2.4~2.0 ka BP和1.7~1.5 ka BP存在次一级的气候波动。
中图分类号:
胡梦珺, 庄静, 孙文丽, 郑登友, 吉天琪, 许澳康. 青藏高原东北部全新世常量元素地球化学特征及环境演变[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 11-20.
Mengjun Hu, Jing Zhuang, Wenli Sun, Dengyou Zheng, Tianqi Ji, Aokang Xu. Geochemical characteristics of major elements and environmental evolution in the Holocene in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(2): 11-20.
| 深度/cm | 地层 | 特征描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 0~34 | 表土层(ZK1) | 灰褐色粉砂-细砂,块状结构,稍紧实,多现代植物根系 |
| 34~73 | 风成砂层(ZK2) | 暗灰色,稍紧实,可见植物根系 |
| 73~99 | 弱砂质古土壤层(ZK3) | 暗褐色粉砂-细砂,块状结构,较紧实,可见少量植物根系 |
| 99~129 | 风成砂层(ZK4) | 浅灰色,稍紧实 |
| 129~176 | 弱砂质古土壤层(ZK5) | 暗褐色粉砂-细砂,块状结构,稍紧实,可见少量植物根系 |
| 176~213 | 风成砂层(ZK6) | 灰黄色,稍紧实 |
| 213~267 | 弱砂质古土壤层(ZK7) | 暗褐色粉砂-细砂,块状结构,稍紧实,可见少量菌丝体 |
| 267~282 | 风成砂层(ZK8) | 暗灰色,稍紧实 |
| 282~338 | 弱砂质古土壤层(ZK9) | 暗褐色粉砂-细砂,块状结构,稍紧实,可见少量菌丝体 |
表1 ZK剖面地层特征
Table 1 Stratigraphic characteristic of ZK profile
| 深度/cm | 地层 | 特征描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 0~34 | 表土层(ZK1) | 灰褐色粉砂-细砂,块状结构,稍紧实,多现代植物根系 |
| 34~73 | 风成砂层(ZK2) | 暗灰色,稍紧实,可见植物根系 |
| 73~99 | 弱砂质古土壤层(ZK3) | 暗褐色粉砂-细砂,块状结构,较紧实,可见少量植物根系 |
| 99~129 | 风成砂层(ZK4) | 浅灰色,稍紧实 |
| 129~176 | 弱砂质古土壤层(ZK5) | 暗褐色粉砂-细砂,块状结构,稍紧实,可见少量植物根系 |
| 176~213 | 风成砂层(ZK6) | 灰黄色,稍紧实 |
| 213~267 | 弱砂质古土壤层(ZK7) | 暗褐色粉砂-细砂,块状结构,稍紧实,可见少量菌丝体 |
| 267~282 | 风成砂层(ZK8) | 暗灰色,稍紧实 |
| 282~338 | 弱砂质古土壤层(ZK9) | 暗褐色粉砂-细砂,块状结构,稍紧实,可见少量菌丝体 |
| 深度/cm | 样品编号 | δ13C/‰ | pMC/% | 14C年龄/a BP | 校正年代 /a BP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ13C | 误差(1σ) | pMC | 误差(1σ) | 14C年龄 | 误差(1σ) | |||
| 30~34 | XA12698 | -25.58 | 0.14 | 92.09 | 0.36 | 662 | 31 | 664 |
| 73~75 | XA12699 | -24.68 | 0.09 | 82.45 | 0.31 | 1 550 | 30 | 1 513 |
| 99~103 | XA12700 | -24.64 | 0.08 | 80.16 | 0.27 | 1 777 | 27 | 1 709 |
| 171~176 | XA12701 | -24.52 | 0.09 | 74.22 | 0.24 | 2 395 | 26 | 2 461 |
| 213~218 | XA12702 | -24.79 | 0.09 | 62.11 | 0.30 | 3 826 | 39 | 4 290 |
| 262~267 | XA12703 | -25.88 | 0.10 | 51.07 | 0.20 | 5 399 | 31 | 6 277 |
| 282~286 | XA12704 | -24.94 | 0.08 | 48.51 | 0.22 | 5 811 | 36 | 6 665 |
| 332~337 | XA12705 | -26.16 | 0.09 | 35.18 | 0.19 | 8 393 | 43 | 9 480 |
表2 ZK剖面 14C测年数据
Table 2 The data of 14C ages of the ZK profile
| 深度/cm | 样品编号 | δ13C/‰ | pMC/% | 14C年龄/a BP | 校正年代 /a BP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δ13C | 误差(1σ) | pMC | 误差(1σ) | 14C年龄 | 误差(1σ) | |||
| 30~34 | XA12698 | -25.58 | 0.14 | 92.09 | 0.36 | 662 | 31 | 664 |
| 73~75 | XA12699 | -24.68 | 0.09 | 82.45 | 0.31 | 1 550 | 30 | 1 513 |
| 99~103 | XA12700 | -24.64 | 0.08 | 80.16 | 0.27 | 1 777 | 27 | 1 709 |
| 171~176 | XA12701 | -24.52 | 0.09 | 74.22 | 0.24 | 2 395 | 26 | 2 461 |
| 213~218 | XA12702 | -24.79 | 0.09 | 62.11 | 0.30 | 3 826 | 39 | 4 290 |
| 262~267 | XA12703 | -25.88 | 0.10 | 51.07 | 0.20 | 5 399 | 31 | 6 277 |
| 282~286 | XA12704 | -24.94 | 0.08 | 48.51 | 0.22 | 5 811 | 36 | 6 665 |
| 332~337 | XA12705 | -26.16 | 0.09 | 35.18 | 0.19 | 8 393 | 43 | 9 480 |
| 氧化物 | 地 层 | 全剖面 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZK1 | ZK2 | ZK3 | ZK4 | ZK5 | ZK6 | ZK7 | ZK8 | ZK9 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变化范围 | |
| SiO2 | 68.92 | 69.83 | 69.31 | 69.42 | 68.65 | 67.76 | 65.72 | 65.71 | 66.23 | 67.85 | 1.85 | 63.73~71.62 |
| Al2O3 | 9.72 | 9.92 | 9.90 | 9.70 | 10.03 | 9.94 | 10.06 | 9.89 | 9.90 | 9.91 | 0.27 | 9.44~10.58 |
| Fe2O3 | 3.02 | 3.07 | 3.09 | 3.09 | 3.21 | 3.12 | 3.14 | 3.17 | 3.21 | 3.13 | 0.10 | 2.92~3.42 |
| MgO | 1.08 | 1.09 | 1.10 | 1.07 | 1.17 | 1.19 | 1.30 | 1.26 | 1.24 | 1.18 | 0.11 | 1.00~1.47 |
| CaO | 4.22 | 3.92 | 3.97 | 3.84 | 4.31 | 5.10 | 5.44 | 5.09 | 4.90 | 4.59 | 0.65 | 3.49~6.28 |
| Na2O | 2.39 | 2.37 | 2.41 | 2.40 | 2.38 | 2.37 | 2.40 | 2.40 | 2.40 | 2.39 | 0.03 | 2.27~2.55 |
| K2O | 1.87 | 1.92 | 1.90 | 1.86 | 1.92 | 1.91 | 1.91 | 1.89 | 1.90 | 1.90 | 0.05 | 1.77~2.00 |
表3 ZK剖面常量元素氧化物含量(%)
Table 3 Content of major element oxides of the ZK profile
| 氧化物 | 地 层 | 全剖面 | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZK1 | ZK2 | ZK3 | ZK4 | ZK5 | ZK6 | ZK7 | ZK8 | ZK9 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变化范围 | |
| SiO2 | 68.92 | 69.83 | 69.31 | 69.42 | 68.65 | 67.76 | 65.72 | 65.71 | 66.23 | 67.85 | 1.85 | 63.73~71.62 |
| Al2O3 | 9.72 | 9.92 | 9.90 | 9.70 | 10.03 | 9.94 | 10.06 | 9.89 | 9.90 | 9.91 | 0.27 | 9.44~10.58 |
| Fe2O3 | 3.02 | 3.07 | 3.09 | 3.09 | 3.21 | 3.12 | 3.14 | 3.17 | 3.21 | 3.13 | 0.10 | 2.92~3.42 |
| MgO | 1.08 | 1.09 | 1.10 | 1.07 | 1.17 | 1.19 | 1.30 | 1.26 | 1.24 | 1.18 | 0.11 | 1.00~1.47 |
| CaO | 4.22 | 3.92 | 3.97 | 3.84 | 4.31 | 5.10 | 5.44 | 5.09 | 4.90 | 4.59 | 0.65 | 3.49~6.28 |
| Na2O | 2.39 | 2.37 | 2.41 | 2.40 | 2.38 | 2.37 | 2.40 | 2.40 | 2.40 | 2.39 | 0.03 | 2.27~2.55 |
| K2O | 1.87 | 1.92 | 1.90 | 1.86 | 1.92 | 1.91 | 1.91 | 1.89 | 1.90 | 1.90 | 0.05 | 1.77~2.00 |
| 元素比值 | ZK1 | ZK2 | ZK3 | ZK4 | ZK5 | ZK6 | ZK7 | ZK8 | ZK9 | 全剖面 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 | 均值 | ||||||||||
| 化学蚀变指数CIA | 49.59 | 50.12 | 49.83 | 49.44 | 50.32 | 50.20 | 50.20 | 49.84 | 49.85 | 47.77~51.39 | 49.98 |
| Na2O/K2O | 1.94 | 1.88 | 1.93 | 1.96 | 1.88 | 1.89 | 1.92 | 1.94 | 1.92 | 1.77~2.19 | 1.91 |
| Sa | 12.05 | 11.95 | 11.88 | 12.15 | 11.63 | 11.58 | 11.10 | 11.28 | 11.35 | 10.46~12.78 | 11.62 |
| Ki | 0.81 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.82 | 0.74 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.65~0.93 | 0.79 |
| W | 1.19 | 1.11 | 1.13 | 1.13 | 1.17 | 1.32 | 1.38 | 1.34 | 1.30 | 1.00~1.49 | 1.24 |
表4 ZK剖面常量元素氧化物比值
Table 4 Ratio of major element oxides of the ZK profile
| 元素比值 | ZK1 | ZK2 | ZK3 | ZK4 | ZK5 | ZK6 | ZK7 | ZK8 | ZK9 | 全剖面 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 范围 | 均值 | ||||||||||
| 化学蚀变指数CIA | 49.59 | 50.12 | 49.83 | 49.44 | 50.32 | 50.20 | 50.20 | 49.84 | 49.85 | 47.77~51.39 | 49.98 |
| Na2O/K2O | 1.94 | 1.88 | 1.93 | 1.96 | 1.88 | 1.89 | 1.92 | 1.94 | 1.92 | 1.77~2.19 | 1.91 |
| Sa | 12.05 | 11.95 | 11.88 | 12.15 | 11.63 | 11.58 | 11.10 | 11.28 | 11.35 | 10.46~12.78 | 11.62 |
| Ki | 0.81 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.82 | 0.74 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.75 | 0.65~0.93 | 0.79 |
| W | 1.19 | 1.11 | 1.13 | 1.13 | 1.17 | 1.32 | 1.38 | 1.34 | 1.30 | 1.00~1.49 | 1.24 |
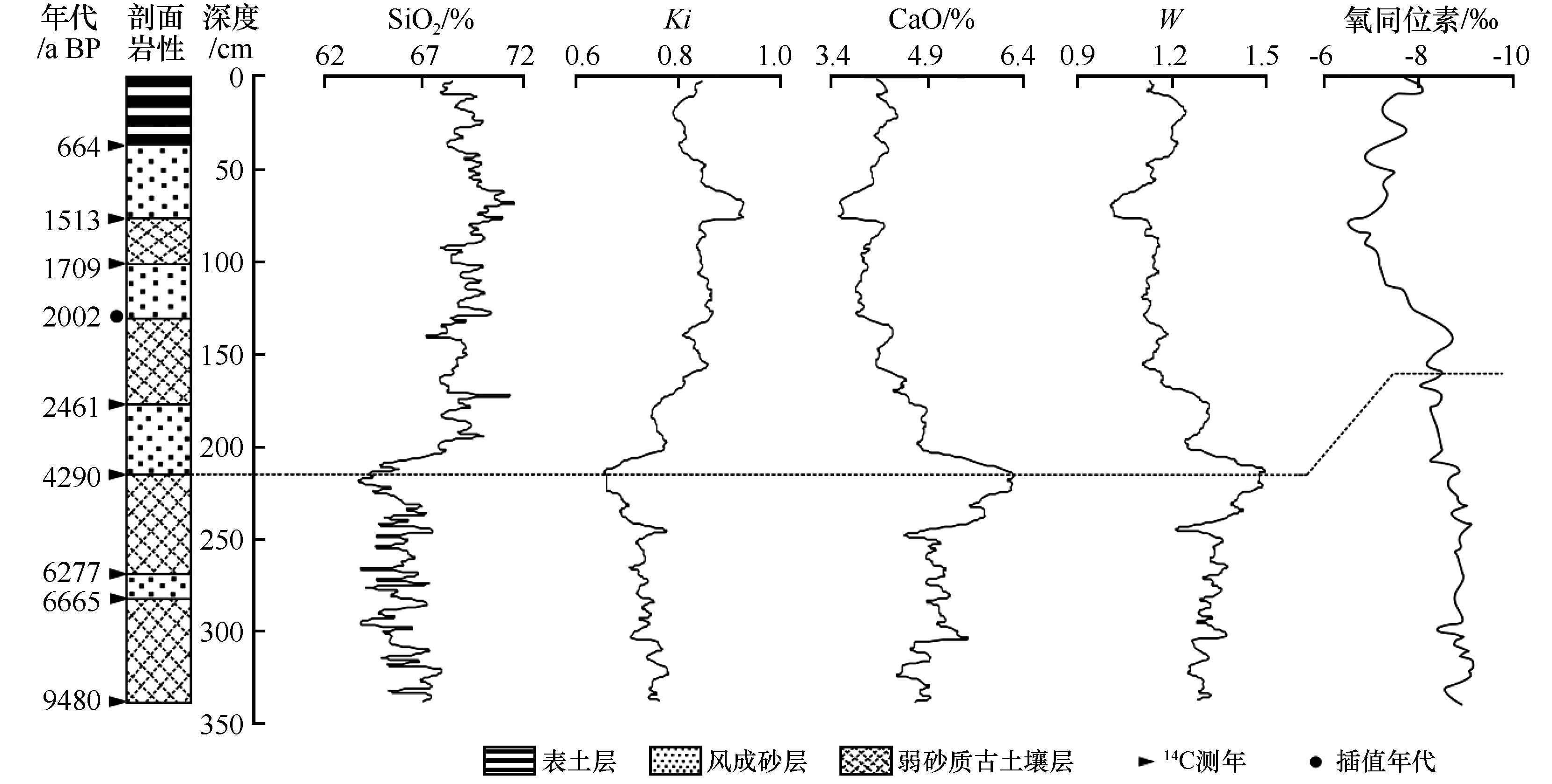
图4 ZK剖面地球化学指标与董哥洞石笋氧同位素[54]揭示的气候变化
Fig.4 Climate change revealed by geochemical indexes of ZK profile and oxygen isotope from the stalagmite in Dongge Cave[54]
| 1 | Bryson R A.Airstream Climatology of Asia[M].Boston,USA:American Meteorological Society,1986. |
| 2 | Henderson A C, Holmes A, Leng M J.Late Holocene isotope hydrology of lake Qinghai,NE Tibetan Plateau:effective moisture variability and atmospheric circulation changes[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2010,29(17):2215-2223. |
| 3 | 刘东生,卢演俦,郑洪汉,等.黄土与环境[M].北京:科学出版社,1985. |
| 4 | 王昭武.全新世气候变化[M].北京:气象出版社,2011:43-136. |
| 5 | 程波,陈发虎,张家武.共和盆地末次冰消期以来的植被和环境演变[J].地理学报,2010,65(11):1336-1344. |
| 6 | 刘冰,靳鹤龄,孙忠,等.青藏高原东北部泥炭沉积粒度与元素记录的全新世千年尺度的气候变化[J].冰川冻土,2013,35(3):609-620. |
| 7 | 胡梦珺,冯淑琴,李向锋.马四剖面揭示的共和盆地12 ka以来的环境演变[J].地层学杂志,2019,43(1):101-108. |
| 8 | 杜乃秋,孔昭宸,山发寿.青海湖QH85-14C钻孔孢粉分析及其古气候古环境的初步探讨[J].植物学报,1989,31(10):803-814. |
| 9 | 陈发虎,汪世兰,张维信,等.青海湖南岸全新世黄土剖面、气候信息及湖面升降探讨[J].地理科学,1991,11(1):76-85. |
| 10 | Lu R J, Jia F F, Gao S Y,et al.Holocene aeolian activity and climatic change in Qinghai Lake basin,northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2015,430:1-10. |
| 11 | 薛红盼,曾方明.青海湖东岸全新世风成沉积地球化学特征及其古气候意义[J].沉积学报,2021,39(5):1198-1207. |
| 12 | 曹广超,马海州,张璞,等.11.5 ka BP以来尕海沉积物氧化物地球化学特征及其环境意义[J].沉积学报,2009,27(2):360-366. |
| 13 | 王素萍,贾国东,赵艳,等.柴达木盆地克鲁克湖全新世气候变化的正构烷烃分子记录[J].第四纪研究,2010,30(6):1097-1104. |
| 14 | Yu L P, Lai Z P.Holocene climate change inferred from stratigraphy and OSL chronology of aeolian sediments in the Qaidam Basin,northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J].Quaternary Research,2014,81(3):488-499. |
| 15 | 刘冰,靳鹤龄,孙忠,等.青藏高原东北部风成沉积微量元素揭示的全新世千年尺度气候变化[J].古地理学报,2013,15(3):423-433. |
| 16 | 吕志强,鲁瑞洁,刘小槺,等.青海湖湖东沙地沉积记录的全新世以来风沙活动变化[J].干旱区地理,2018,41(3):536-544. |
| 17 | Gordeev V V, Sidorov I S.Concentrations of major elements and their outflow into the Laptev Sea by the Lena River[J].Marine Chemistry,1993,43(1/4):33-45. |
| 18 | 陈骏,季峻峰,仇纲,等.陕西洛川黄土化学风化程度的地球化学研究[J].中国科学D辑:地球科学,1997,27(6):531-536. |
| 19 | 刁桂仪,文启忠.黄土风化成土过程中主要元素迁移序列[J].地质地球化学,1999,27(1):21-26. |
| 20 | Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J].Nature,1982,299(5885):715-717. |
| 21 | 杨劲松,王永,赵红梅.晚更新世以来萨拉乌苏河流域主元素的地球化学特征及古环境意义[J].干旱区资源与环境,2016,30(11):148-153. |
| 22 | 陈旸,陈骏,刘连文.甘肃西峰晚第三纪红粘土的化学组成及化学风化特征[J].地质力学学报,2001,7(2):167-175. |
| 23 | 牛东风,李保生,王丰年,等.微量元素记录的毛乌素沙漠全新世气候波动:以萨拉乌苏流域DGS1层段为例[J].沉积学报,2015,33(4):735-743. |
| 24 | 杨红瑾,黄春长,庞奖励,等.宁夏长城塬全新世黄土-土壤剖面元素地球化学特征研究[J].地理科学,2010,30(1):134-140. |
| 25 | 陈玉美,舒强,张茂恒,等.南京下蜀黄土记录的250~100 ka期间的环境演化信息[J].地质科学情报,2014,33(6):55-59. |
| 26 | 胡梦珺,杨爱丽,张文丽.常量元素氧化物含量及其比值揭示的中晚全新世以来玛曲高原的环境演变[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(2):313-321. |
| 27 | 文启忠,耿安松,刁桂仪,等.中国黄土地球化学[M].北京:科学出版社,1989:1-285. |
| 28 | 靳鹤龄,李明启,苏志珠,等.220 ka BP 来萨拉乌苏河流域地质剖面地球化学特征及其对全球气候变化的响应[J].冰川冻土,2005,27(6):861-868. |
| 29 | Vital H, Stattegger K.Major and trace element of stream sediments from the lowermost Amazon River[J].Chemical Geology,2000,168(1/2):151-168. |
| 30 | 黄汝昌.陆相沉积中古气候演变及元素的迁移、聚集和演化[C]//中国科学院兰州地质研究所所刊.北京:科学出版社,1982:137-160. |
| 31 | 高尚玉,董光荣,李保生,等.萨拉乌苏河第四纪地层中化学元素的迁移和聚集与古气候的关系[J].地球化学,1985(3):269-275. |
| 32 | 陈渭南,高尚玉,孙忠,等.毛乌素沙地全新世地层化学元素特点及其古气候意义[J].中国沙漠,1994,14(1):22-30. |
| 33 | 秦小光,殷志强,汪美华,等.青藏高原东北缘共和-贵德盆地全新世气候变化[J].地质学报,2017,91(1):266-286. |
| 34 | 侯光良,刘峰贵,刘翠华,等.中全新世甘青地区古文化变迁的环境驱动[J].地理学报,2009,64(1):53-58. |
| 35 | 赵佳玉,王淑贤, Darin Andrey,等.新疆阿尔泰全新世双湖沉积物正构烷烃分布及其环境意义[J].第四纪研究,2021,41(4):965-975. |
| 36 | 陈璐,鲁瑞洁,刘小槺,等.萨拉乌苏河流域全新世气候变化的元素地球化学记录[J].北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2017,53(3):308-315. |
| 37 | 周家兴,吴利杰,于娟,等.铜川地区11.4~1.5 ka B.P.期间黄土地球化学风化特征及其古气候意义[J].地球与环境,2019,47(1):64-73. |
| 38 | Zhou W J, Lu X F, Wu Z C,et al.Climate change of Zoige Plateau since Holocene and AMS radiocarbon[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2001,46(12):1040-1044. |
| 39 | 段克勤,姚檀栋,王宁练,等.青藏高原中部全新世气候不稳定性的高分辨率冰芯记录[J].中国科学D辑:地球科学,2012,42(9):1441-1449. |
| 40 | 张菀漪,张静雅,郑淇,等.青藏高原东北缘冬给错纳湖全新世湖面波动[J].第四纪研究,2019,39(4):1018-1033. |
| 41 | 刘俊余,查小春,黄春长,等.甘肃天水全新世黄土粒度、磁化率特征及其古气候意义[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2020,56(2):180-186. |
| 42 | Sun A Z, Feng Z D.Holocene climatic reconstructions from the fossil pollen record at Qigai Nuur in the southern Mongolian Plateau[J].Holocene,2013,23(10):1391-1402. |
| 43 | 秦小光,张磊,穆燕.中国东部南北方过渡带淮河半湿润区全新世气候变化[J].第四纪研究,2015,35(6):1509-1524. |
| 44 | 赵黎,孙庆峰.青藏高原共和盆地 14.5 cal ka BP以来粘土矿物响应的气候变化模式[J].岩石矿物学杂志,2014,33(4):681-692. |
| 45 | 陈东雪,鲁瑞洁,丁之勇,等.青海湖湖东沙地河湖-风成沉积记录的中晚全新世以来环境变化[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(6):1-12. |
| 46 | 余英浩,金映豫,徐德克,等.青海可鲁克湖孢粉记录的14 cal ka BP以来植被和气候演化历史[J].第四纪研究,2021,41(5):1229-1243. |
| 47 | 王娜,春喜.乌兰布和沙漠晚第四纪以来环境演化研究进展[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(1):175-183. |
| 48 | 王琳栋,杨太保,梁烨,等.会宁地区全新世黄土沉积粒度特征及其古气候意义[J].干旱区研究,2016,33(6):1150-1156. |
| 49 | Wang W, Feng Z D.Holocene moisture evolution across the Mongolian Plateau and its surrounding areas:a synthesis of climatic records[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2013,122:38-57. |
| 50 | 杜婧,鲁瑞洁,刘小槺,等.青海湖湖东沙地全新世风成沉积物磁化率特征及其环境意义[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质,2018,38(2):175-184. |
| 51 | 林勇杰,郑绵平,王海雷.青藏高原中部色林错矿物组合特征对晚全新世气候的响应[J].科技导报,2014,32(35):35-40. |
| 52 | 陈秀玲,李志忠,凌智永,等.新疆伊犁河谷晚全新世以来的风砂沉积与环境演化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质,2010,30(6):35-42. |
| 53 | 黄振辉,马春梅,齐士峥,等.台湾头社盆地湖沼相沉积孢粉记录的6.2~1.3 cal ka BP以来气候研究[J].高校地质学报,2020,26(5):592-600. |
| 54 | 张美良,程海,林玉石,等.贵州荔波1.5万年以来石笋高分辨率古气候环境记录[J].地球化学,2004(1):65-74. |
| 55 | 刘冰,靳鹤龄,孙忠,等.共和盆地开额泥炭剖面粒度敏感组分提取与全新世气候环境变化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质,2013,33(4):125-134. |
| 56 | 张亚云,胡梦珺,李娜娜,等.共和盆地马四剖面12 cal ka BP以来的成壤环境演变[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(6):66-75. |
| [1] | 柳欣滢, 金明, 杨帆, 马亚鹏, 刘慧, 孙小云, 夏敦胜. 毛乌素沙地东缘中全新世以来环境变化及其对文明演化的影响初探[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 92-100. |
| [2] | 周维鑫, 温小浩, 李保生, 王晨, 田梦圆, 邱明昆. 萨拉乌苏河流域干沟子剖面全新世湖相沉积的地球化学元素特征及其反映的物源变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 114-122. |
| [3] | 胡梦珺, 郑登友, 吉天琪, 庄静, 孙文丽. 晚更新世早期共和盆地湖相沉积常量元素地化学特征及环境演变[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 147-157. |
| [4] | 曾方明, 薛红盼. 青藏高原东北部晚第四纪黄土-古土壤元素组成数据集[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(6): 262-264. |
| [5] | 陈东雪, 鲁瑞洁, 丁之勇, 刘小槺. 青海湖湖东沙地河湖-风成沉积记录的中晚全新世以来环境变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(6): 99-110. |
| [6] | 马晓慧, 庞奖励, 刘小槺, 丁丹, 岳晓晓, 贾飞飞. 瓦窑沟剖面记录的早中全新世毛乌素沙地东南缘气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 71-80. |
| [7] | 曾方明, 薛红盼. 青藏高原东北部晚第四纪黄土-古土壤的元素组成及其物源指示[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(6): 105-117. |
| [8] | 白旸, 陈佳升, 程延, 张甜. 广东全新世海岸风沙沉积分布[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(6): 71-81. |
| [9] | 张彩霞, 娄俊鹏, 蔡迪文. 荒漠地区15种植物的元素含量[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(4): 18-23. |
| [10] | 李想, 苏志珠, 马义娟, 张彩霞, 柳苗苗. 毛乌素沙地东南缘全新世气候不稳定性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 109-117. |
| [11] | 张亚云, 胡梦珺, 李娜娜, 王佳, 李春艳. 共和盆地马四剖面12 cal ka BP以来的成壤环境演变[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(6): 66-75. |
| [12] | 刘荔昀, 鲁瑞洁, 刘小槺. 风成沉积物色度记录的毛乌素沙漠全新世以来气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(6): 83-89. |
| [13] | 雷晨, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 查小春, 周亚利, 温瑞艳, 炊郁达. 渭河上游地区樊家城黄土-古土壤剖面Rb、Sr、Ba存留特征及意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(6): 90-98. |
| [14] | 薛文萍, 靳鹤龄, 刘冰, 孙良英, 刘振宇. 中国季风边缘区全新世沙地演化及其驱动机制研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(3): 163-171. |
| [15] | 韩瑞, 苏志珠, 李想, 柳苗苗, 马义娟. 粒度和磁化率记录的毛乌素沙地东缘全新世气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(2): 105-114. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
