中国沙漠 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (6): 243-254.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00063
• • 上一篇
张琦1,2( ), 苏永红1(
), 苏永红1( ), 冯起1, 鱼腾飞1, 马小红3
), 冯起1, 鱼腾飞1, 马小红3
收稿日期:2021-12-27
修回日期:2022-04-12
出版日期:2022-11-20
发布日期:2023-01-09
通讯作者:
苏永红
作者简介:苏永红(E-mail: syh@lzb.ac.cn)基金资助:
Qi Zhang1,2( ), Yonghong Su1(
), Yonghong Su1( ), Qi Feng1, Tengfei Yu1, Xiaohong Ma3
), Qi Feng1, Tengfei Yu1, Xiaohong Ma3
Received:2021-12-27
Revised:2022-04-12
Online:2022-11-20
Published:2023-01-09
Contact:
Yonghong Su
摘要:
基于2014年和2020年地下水位监测数据,估算了黑河下游额济纳绿洲七道桥胡杨(Populus euphratica)林生态系统生长季旺盛期的地下水蒸散发(ETg),并与从涡度观测系统测定的蒸散发(ET)作比较,同时分析了不同模型的估算结果及其主要影响因素。结果表明:(1)基于昼夜水位波动法(White、Hays和Soylu方法)估算的ETg均与生态系统ET变化趋势一致且显著相关,经过对比分析得出,Hays方法精度最高,推荐使用该方法计算ETg。(2)地下水位、太阳辐射、气温和饱和水汽压差是影响ETg的主要因子,风速对ETg无显著影响。(3)生长季,ETg占生态系统ET的比例随干旱时间的增大而增大。
中图分类号:
张琦, 苏永红, 冯起, 鱼腾飞, 马小红. 以地下水位估算的荒漠河岸胡杨( Populus euphratica )林生态系统地下水蒸散发[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(6): 243-254.
Qi Zhang, Yonghong Su, Qi Feng, Tengfei Yu, Xiaohong Ma. Estimation of groundwater evapotranspiration of Populus euphratica forest ecosystem along desert river banks based on groundwater level dynamics[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(6): 243-254.
| 植被覆盖度 /% | 植株密度 /(株·hm-2) | 树高 /m | 胸径 /cm | 林龄 /a | 土壤质地 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—60 cm | 60—120 cm | 120—150 cm | |||||
| 75 | 350 | 10.1±1.7 | 22.9±4.8 | 30—60 | 沙壤土 | 沙土 | 沙、黏土混合 |
表1 胡杨林分特征和土壤质地
Table 1 Populus euphratica forest stand characteristics and soil texture
| 植被覆盖度 /% | 植株密度 /(株·hm-2) | 树高 /m | 胸径 /cm | 林龄 /a | 土壤质地 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0—60 cm | 60—120 cm | 120—150 cm | |||||
| 75 | 350 | 10.1±1.7 | 22.9±4.8 | 30—60 | 沙壤土 | 沙土 | 沙、黏土混合 |
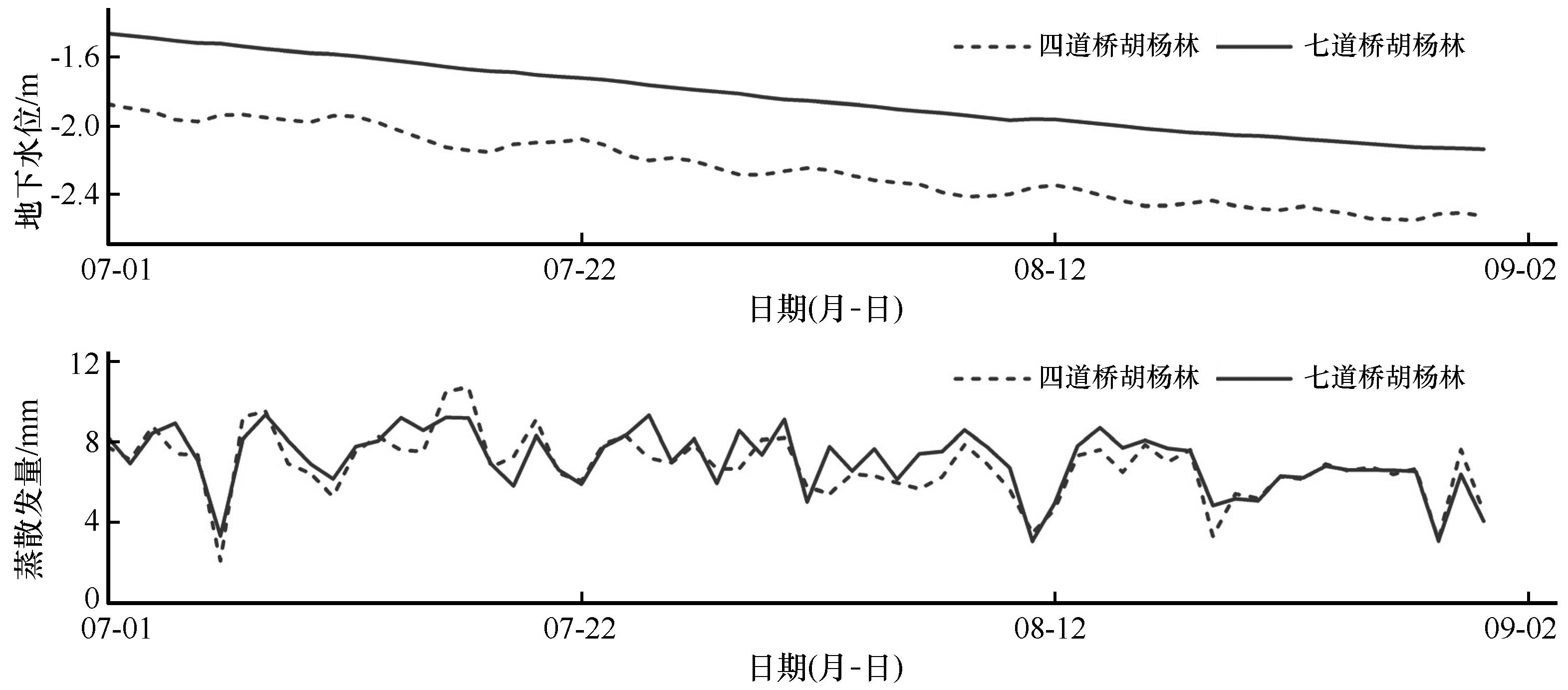
图2 2014年四道桥和七道桥胡杨林地下水位和蒸散发同期对照变化
Fig.2 Contrast changes of groundwater depth and evapotranspiration in the Populus euphratica forests in Sidaoqiao and Qidaoqiao in 2014
| 仪器 | 名 称 | 观测及采集对象 | 采样间隔及频率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 观测仪器 | 三维超声风速仪(CSAT3, Campbell Co, 美国) | 风速 | — |
| 开路式CO2/H2O分析仪(Li-7500A, LI-COR, 美国) | 水汽和CO2浓度 | ||
| 四分净辐射仪(CNR4, Kipp & Zonen, 荷兰) | 净辐射(Rn) | ||
| 相对温湿度传感器( HMP45C, Campbell,美国) | 气温(Ta)、湿度(RH) | ||
| 土壤热通量板( HFP, Hukse Flux Thermal Sensors B.V. , Delft, 荷兰。埋设在地下5 cm处,水平间隔0.5 m) | 土壤热通量(G) | ||
| 数据采集仪器 | CR3000数据采集器 | 通量观测数据、净辐射(Rn)、气温(Ta)、相对湿度(RH) | 采样间隔:30 min 采样频率:10 Hz |
表2 涡度观测数据及仪器
Table 2 Eddy observation data and instruments
| 仪器 | 名 称 | 观测及采集对象 | 采样间隔及频率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 观测仪器 | 三维超声风速仪(CSAT3, Campbell Co, 美国) | 风速 | — |
| 开路式CO2/H2O分析仪(Li-7500A, LI-COR, 美国) | 水汽和CO2浓度 | ||
| 四分净辐射仪(CNR4, Kipp & Zonen, 荷兰) | 净辐射(Rn) | ||
| 相对温湿度传感器( HMP45C, Campbell,美国) | 气温(Ta)、湿度(RH) | ||
| 土壤热通量板( HFP, Hukse Flux Thermal Sensors B.V. , Delft, 荷兰。埋设在地下5 cm处,水平间隔0.5 m) | 土壤热通量(G) | ||
| 数据采集仪器 | CR3000数据采集器 | 通量观测数据、净辐射(Rn)、气温(Ta)、相对湿度(RH) | 采样间隔:30 min 采样频率:10 Hz |
| 年份 | 00:00—04:00 | 00:00—06:00 | 18:00—06:00 | 22:00—06:00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.33** | 0.29* | 0.30** | 0.27** |
| 2020 | 0.45** | 0.37** | 0.40** | 0.43* |
表3 2014年和2020年采用White方法基于不同时间窗口估算的 ETg 与生态系统 ET 之间的Pearson相关性分析
Table 3 Pearson correlation analysis of ecosystem ET with ETg estimated based on White′s method in different time windows in 2014 and 2020
| 年份 | 00:00—04:00 | 00:00—06:00 | 18:00—06:00 | 22:00—06:00 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.33** | 0.29* | 0.30** | 0.27** |
| 2020 | 0.45** | 0.37** | 0.40** | 0.43* |
| 年份 | 1 d | 2 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.43** | 0.31** | 0.25* | 0.21 | 0.19 |
| 2020 | 0.41** | 0.29* | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.15 |
表4 2014年和2020年基于Soylu方法不同移动窗口估算的 ETg 与生态系统 ET 之间的Pearson相关性分析
Table 4 Pearson correlation analysis of ecosystem ET with ETg estimated based on Soylu method in different moving windows in 2014 and 2020
| 年份 | 1 d | 2 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.43** | 0.31** | 0.25* | 0.21 | 0.19 |
| 2020 | 0.41** | 0.29* | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.15 |
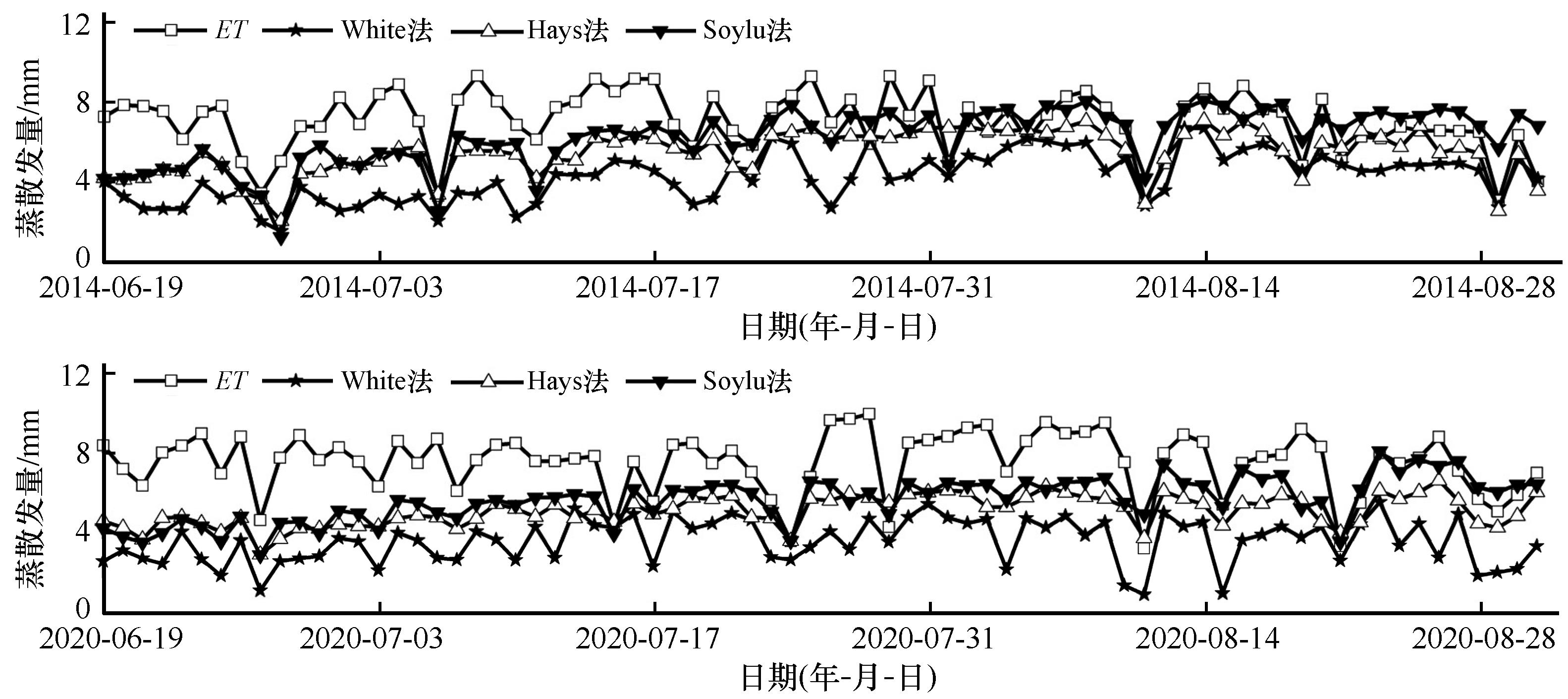
图7 2014年和2020年生长旺盛期胡杨林生态系统蒸散(ET)和地下水蒸散发(ETg)
Fig.7 Ecosystem evapotranspiration (ET) and groundwater evapotranspiration (ETg) of Populus euphratica forest during the peak of the growing season in 2014 and 2020
| 年份 | White法 | Hays法 | Soylu法 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.33** | 0.64** | 0.43** |
| 2020 | 0.45** | 0.59** | 0.41* |
表5 2014年和2020年基于White、Hays法和Soylu法估算的 ETg 与生态系统 ET 之间的Pearson相关性分析
Table 5 Pearson correlation analysis of ecosystem ET with ETg estimated based on White, Hays and Soylu methods in 2014 and 2020
| 年份 | White法 | Hays法 | Soylu法 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 0.33** | 0.64** | 0.43** |
| 2020 | 0.45** | 0.59** | 0.41* |
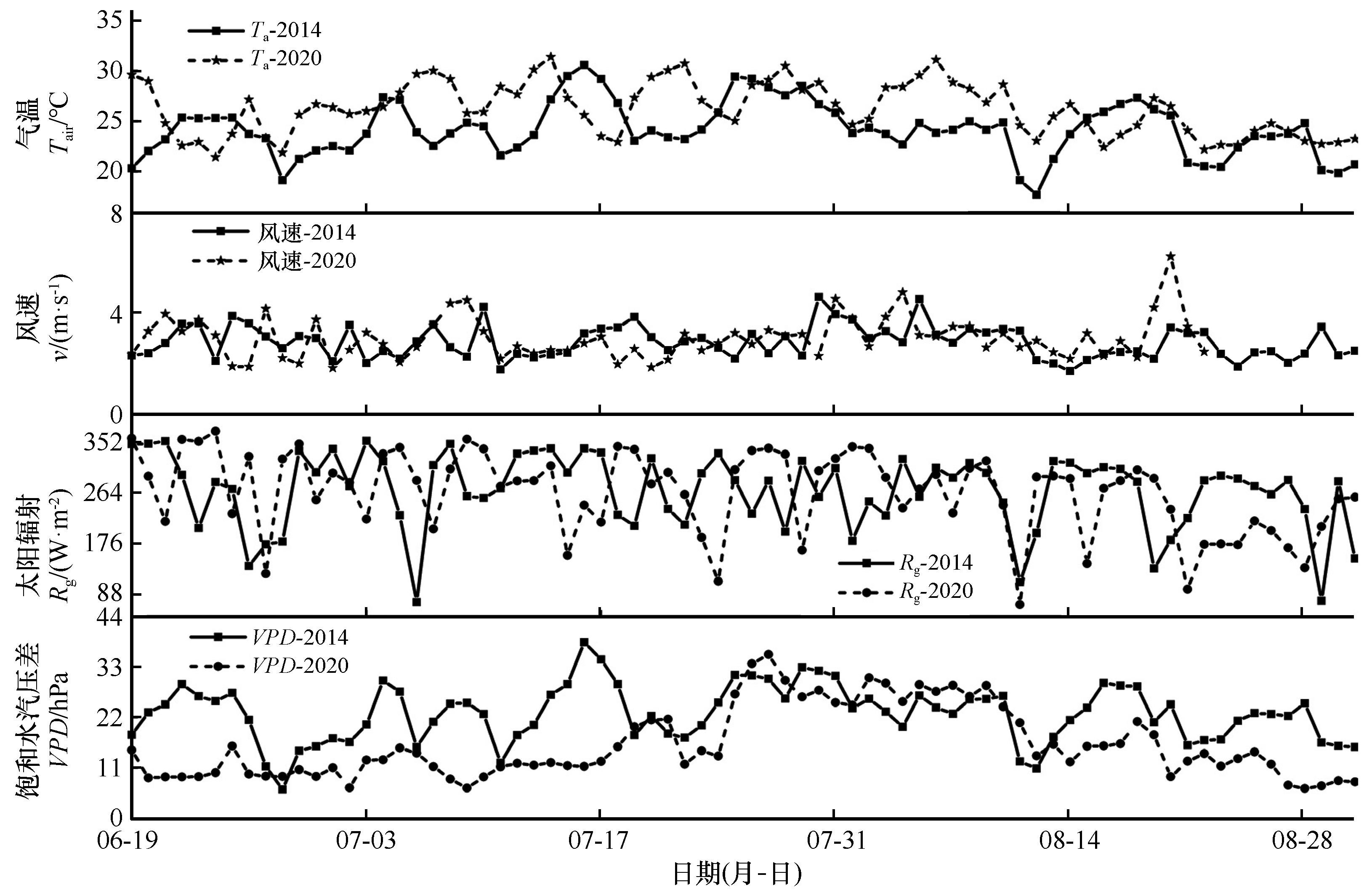
图8 2014年和2020年生长旺盛期胡杨林生态系统气象因子变化
Fig.8 Variations of meteorological factors in Populus euphratica forest ecosystem during the peak growth season in 2014 and 2020
| 年份 | 地下水位/m | 气温/℃ | 风速/(m·s-1) | 入射太阳辐射/(W·m-2) | VPD/hPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | -0.41** | 0.47** | 0.02 | 0.50** | 0.60** |
| 2020 | -0.54** | 0.19* | 0.04 | 0.36** | 0.54** |
表6 2014年和2020年 ETg 与地下水位、气温、风速、太阳辐射和 VPD 之间的Pearson相关性
Table 6 Pearson correlation analysis of ETg with groundwater level, temperature, wind speed, solar radiation or VPD in 2014 and 2020
| 年份 | 地下水位/m | 气温/℃ | 风速/(m·s-1) | 入射太阳辐射/(W·m-2) | VPD/hPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | -0.41** | 0.47** | 0.02 | 0.50** | 0.60** |
| 2020 | -0.54** | 0.19* | 0.04 | 0.36** | 0.54** |
| 年份 | 自变量 | 代表符号 | 系数 | R2 | 调整后R2 | 模型P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 地下水位/m | X1 | -2.276** | 0.685 | 0.672 | <0.01 |
| 太阳辐射/℃ | X2 | 0.008** | ||||
| 饱和水汽压差VPD/hPa | X3 | 0.081** | ||||
| 常量 | — | -2.388** | ||||
| 2020 | 地下水位/m | X1 | -2.609** | 0.706 | 0.693 | <0.01 |
| 太阳辐射/℃ | X2 | 0.006** | ||||
| 饱和水汽压差VPD/hPa | X3 | 0.021** | ||||
| 常量 | — | -2.118** |
表7 2014年和2020年地下水位、太阳辐射和 VPD 与 ETg 线性模型系数及 R2
Table 7 Groundwater level, solar radiation, VPD and ETg linear model coefficients and R2 in 2014 and 2020
| 年份 | 自变量 | 代表符号 | 系数 | R2 | 调整后R2 | 模型P值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 地下水位/m | X1 | -2.276** | 0.685 | 0.672 | <0.01 |
| 太阳辐射/℃ | X2 | 0.008** | ||||
| 饱和水汽压差VPD/hPa | X3 | 0.081** | ||||
| 常量 | — | -2.388** | ||||
| 2020 | 地下水位/m | X1 | -2.609** | 0.706 | 0.693 | <0.01 |
| 太阳辐射/℃ | X2 | 0.006** | ||||
| 饱和水汽压差VPD/hPa | X3 | 0.021** | ||||
| 常量 | — | -2.118** |
| 1 | Feng S, Fu Q.Expansion of global drylands under a warming climate[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2013,13(19):10081-10094. |
| 2 | Yin L, Zhou Y, Ge S,et al.Comparison and modification of methods for estimating evapotranspiration using diurnal groundwater level fluctuations in arid and semiarid regions[J].Journal of Hydrology,2013,496:9-16. |
| 3 | 马小红,冯起.荒漠河岸胡杨林生态系统能量分配及蒸散发[J].生态学报,2020,40(23):8683-8693. |
| 4 | Xi H, Zhang J, Feng Q,et al.How changes of groundwater level affect the desert riparian forest ecosystem in the Ejina Oasis,Northwest China[J].Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions,2019,11(1):62-80. |
| 5 | Wang X, Huo Z, Shukla M K,et al.Energy fluxes and evapotranspiration over irrigated maize field in an arid area with shallow groundwater[J].Agricultural Water Management,2020,228:105922. |
| 6 | Yu T F, Feng Q, Si J H,et al.Evapotranspiration of a Populus euphratica Oliv.forest and its controlling factors in the lower Heihe River Basin,Northwest China[J].Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions,2017,9(2):175-182. |
| 7 | Chen H, Huo Z, Dai X,et al.Impact of agricultural water-saving practices on regional evapotranspiration:the role of groundwater in sustainable agriculture in arid and semi-arid areas[J].Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2018,263:156-168. |
| 8 | Soylu M E, Lenters J D, Istanbulluoglu E,et al.On evapotranspiration and shallow groundwater fluctuations:a Fourier-based improvement to the White method[J].Water Resources Research,2012,48(6):W06506. |
| 9 | Yue W, Wang T, Franz T E,et al.Spatiotemporal patterns of water table fluctuations and evapotranspiration induced by riparian vegetation in a semiarid area[J].Water Resources Research,2016,52(3):1948-1960. |
| 10 | Cheng D H, Li Y, Chen X,et al.Estimation of groundwater evaportranspiration using diurnal water table fluctuations in the Mu Us Desert,northern China[J].Journal of Hydrology,2013,490:106-113. |
| 11 | Wang P, Grinevsky S O, Pozdniakov S P,et al.Application of the water table fluctuation method for estimating evapotranspiration at two phreatophyte-dominated sites under hyper-arid environments[J].Journal of Hydrology,2014,519:2289-2300. |
| 12 | 袁国富,罗毅,邵明安,等.塔里木河下游荒漠河岸林蒸散规律及其关键控制机制[J].中国科学:地球科学,2015,45(5):695-706. |
| 13 | White W N.A Method of Estimating Ground-water Supplies based on Discharge by Plants and Evaporation from Soil:Results of Investigations in Escalante Valley,Utah[M].Washington DC,USA:US Government Printing Office,1932. |
| 14 | Hays K B.Water use by saltcedar (Tamarix sp.) and associated vegetation on the Canadian,Colorado and Pecos Rivers in Texas[D].College Station, Texas,USA:Texas A & M University,2003. |
| 15 | Loheide II S P.A method for estimating subdaily evapotranspiration of shallow groundwater using diurnal water table fluctuations[J].Ecohydrology,2008,1(1):59-66. |
| 16 | 王京晶,刘鹄,徐宗学,等.基于昼夜水位波动法估算地下水蒸散发量的研究:以河西走廊典型绿洲为例[J].干旱区研究,2021,38(1):59-67. |
| 17 | 吴立宗,王建华,年雁云.黑河流域边界数据集(1985、1995、2000、1995、2000)[DB].国家青藏高原科学数据中心,2013.DOI:10.11888/Geogra.tpdc.270587 . |
| 18 | Idso S B.An Introduction to environmental biophysics[J].Journal of Environmental Quality,1977,6(4):474. |
| 19 | Burba G, Schmidt A, Scott R L,et al.Calculating CO2 and H2O eddy covariance fluxes from an enclosed gas analyzer using an instantaneous mixing ratio[J].Global Change Biology,2012,18(1):385-399. |
| 20 | Foken T, Göockede M, Mauder M,et al.Post-field data quality control[M]//Beverly L,Shashi V.Handbook of Micrometeorology.Dordrecht,The Netherlands:Springer,2004:181-208. |
| 21 | Vickers D, Mahrt L.Quality Control and Flux Sampling Problems for Tower and Aircraft Data[J].Journal of Atmospheric & Oceanic Technology,1997,14(3):514-526. |
| 22 | Liu S M, Xu Z W, Wang W Z,et al.A comparison of eddy-covariance and large aperture scintillometer measurements with respect to the energy balance closure problem[J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2011,15(4):1291-1306. |
| 23 | Wilson K, Goldstein A, Falge E,et al.Energy balance closure at FLUXNET sites[J].Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2002,113(1):223-243. |
| 24 | Wutzler T, Lucas-Moffat A, Migliavacca M,et al.Basic and extensible post-processing of eddy covariance flux data with REddyProc[J].Biogeosciences,2018,15(16):5015-5030. |
| 25 | Wohlfahrt G, Haslwanter A, Hörtnagl L,et al.On the consequences of the energy imbalance for calculating surface conductance to water vapour[J].Agricultural & Forest Meteorology,2009,149(9):1556-1559. |
| 26 | 尹力,赵良菊,阮云峰,等.黑河下游典型生态系统水分补给源及优势植物水分来源研究[J].冰川冻土,2012,34(6):1478-1486. |
| 27 | Loheide S P, Butler J J, Gorelick S M.Estimation of groundwater consumption by phreatophytes using diurnal water table fluctuations:a saturated-unsaturated flow assessment[J].Water Resources Research,2005,41(7):372-380. |
| 28 | 鱼腾飞,冯起,司建华,等.黑河下游柽柳根系水力提升对林分蒸散的贡献[J].生态学报,2017,37(18):6029-6037. |
| 29 | Karl Pearson.Notes on the History of Correlation[J].Biometrika,1920,13(1):25-45. |
| 30 | Fan J, Ostergaard K T, Guyot A,et al.Estimating groundwater evapotranspiration by a subtropical pine plantation using diurnal water table fluctuations:implications from night-time water use[J].Journal of Hydrology,2016,542:679-685. |
| 31 | 孙海涛,陈亚鹏,陈亚宁,等.塔里木河下游荒漠河岸林地下水蒸散发[J].干旱区研究,2020,37(1):116-125. |
| 32 | Hou P, Beeton R J, Carter R W,et al.Response to environmental flows in the lower Tarim River,Xinjiang,China:ground water[J].Journal of Environmental Management,2007,83(4):371-382. |
| 33 | 张经天,席海洋,王春林,等.基于地下水位变化的荒漠河岸林蒸散估算[J].高原气象,2019,38(1):179-186. |
| 34 | Fahle M, Dietrich O.Estimation of evapotranspiration using diurnal groundwater level fluctuations:comparison of different approaches with groundwater lysimeter data[J].Water Resources Research,2014,50(1):273-286. |
| [1] | 李倩, 马龙, 刘廷玺, 王硕. 采煤对海流兔流域大气降水-地表水-地下水-矿井水转化关系的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 146-157. |
| [2] | 陈雪萍, 赵学勇, 王瑞雄, 宁志英, 卢建男, 赵思腾. 气候变化与土地利用/覆被变化对中国北方农牧交错带水资源影响研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(3): 170-177. |
| [3] | 周生辉, 刘廷玺, 段利民, 冀如, 张春雨. 毛乌素沙地海流兔河流域水文地质特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 103-110. |
| [4] | 杨羽帆, 曹生奎, 冯起, 曹广超, 刘英, 雷义珍. 青海湖沙柳河流域浅层地下水氢氧稳定同位素分布特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(5): 45-53. |
| [5] | 岳宁, 魏国孝, 孙朋, 董军, 党慧慧, 王刚, 黄少文. 乌兰布和沙漠降水入渗补给对气候变化的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(5): 1016-1025. |
| [6] | 曹乐, 聂振龙, 刘学全, 王哲, 孟令群, 姜高磊. 巴丹吉林沙漠湖泊钙华的水化学成因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(5): 1026-1034. |
| [7] | 魏水莲, 刘新平, 赵学勇, 张铜会, 云建英, 张婧, 张建鹏, 冯静, 苏娜. 科尔沁沙地奈曼地区地下水水质时空变化特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(3): 571-579. |
| [8] | 于海姣, 温小虎, 冯起, 尹振良, 常宗强, 鱼腾飞, 牛晓宇. 运用小波变换与支持向量机耦合模型(WA-SVM)预测干旱区地下水埋深[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(5): 1435-1442. |
| [9] | 魏亚平, 范敬龙, 徐新文, 金小军, 周宏伟. 塔克拉玛干沙漠南部地下水化学演化模拟[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(3): 798-804. |
| [10] | 张竞, 王旭升, 胡晓农, 卢会婷, 巩艳萍, 万力. 巴丹吉林沙漠地下水流场的宏观特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(3): 774-782. |
| [11] | 安帅, 王乃昂, 陈会丽, 赵力强. 基于SOFM网络的巴丹吉林沙漠湖泊聚类及其地下水补给来源推断[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(2): 574-581. |
| [12] | 司建华, 冯 起, 席海洋, 鱼腾飞, 李 炜. 黑河下游额济纳绿洲生态需水关键期及需水量[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(2): 560-567. |
| [13] | 李文赞;严 平*;刘永刚;丁连刚;俄有浩. 库姆塔格沙漠东北缘浅层地下水补给来源[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(6): 1617-1622. |
| [14] | 何建华;付素静;马金珠;张清寰. 北大河流域地下水化学演化与补给特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(6): 1630-1638. |
| [15] | 魏国孝;朱锡芬;马金珠;许 翔;徐 涛. 贺兰山至吉兰泰盐湖的水化学特征及演化规律[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(5): 1330-1336. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
