中国沙漠 ›› 2022, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (3): 170-177.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00115
• • 上一篇
陈雪萍1,2, 赵学勇1( ), 王瑞雄1,2, 宁志英1,2, 卢建男1,2, 赵思腾1,2
), 王瑞雄1,2, 宁志英1,2, 卢建男1,2, 赵思腾1,2
收稿日期:2021-07-27
修回日期:2021-09-03
出版日期:2022-05-20
发布日期:2022-06-01
通讯作者:
赵学勇
作者简介:赵学勇(E-mail: zhaoxy@lzb.ac.cn)基金资助:
Xueping Chen1,2, Xueyong Zhao1( ), Ruixiong Wang1,2, Zhiying Ning1,2, Jiannan Lu1,2, Siteng Zhao1,2
), Ruixiong Wang1,2, Zhiying Ning1,2, Jiannan Lu1,2, Siteng Zhao1,2
Received:2021-07-27
Revised:2021-09-03
Online:2022-05-20
Published:2022-06-01
Contact:
Xueyong Zhao
摘要:
中国北方农牧交错带对全球变化响应敏感,研究气候变化及土地利用/覆被变化(LUCC)背景下北方农牧交错带水资源问题,对变化环境下生态脆弱区的水资源利用与管理具有重要意义。通过对北方农牧交错带气候与LUCC演变特征及其对水资源影响等方面的综合研究,总结得出:(1) 近几十年,该地区气候呈暖干化趋势,气温升高速率与降水减少速率均高于全球平均水平。(2) LUCC以农牧相互转化为主,土地利用结构未发生明显变化。(3) 该地区流域径流、地下水位与气温负相关,与降水量正相关,且降水作用更明显;近几十年来,LUCC成为影响该地区生态水文过程的主导因素,对水资源影响的贡献率越来越大。同时,针对目前研究中存在的问题及薄弱环节,提出未来研究的发展趋势和亟需重点加强的研究方向。
中图分类号:
陈雪萍, 赵学勇, 王瑞雄, 宁志英, 卢建男, 赵思腾. 气候变化与土地利用/覆被变化对中国北方农牧交错带水资源影响研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(3): 170-177.
Xueping Chen, Xueyong Zhao, Ruixiong Wang, Zhiying Ning, Jiannan Lu, Siteng Zhao. Research advances on the impact of climate change and LUCC for water resources in the northern agro-pastoral zone in China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2022, 42(3): 170-177.
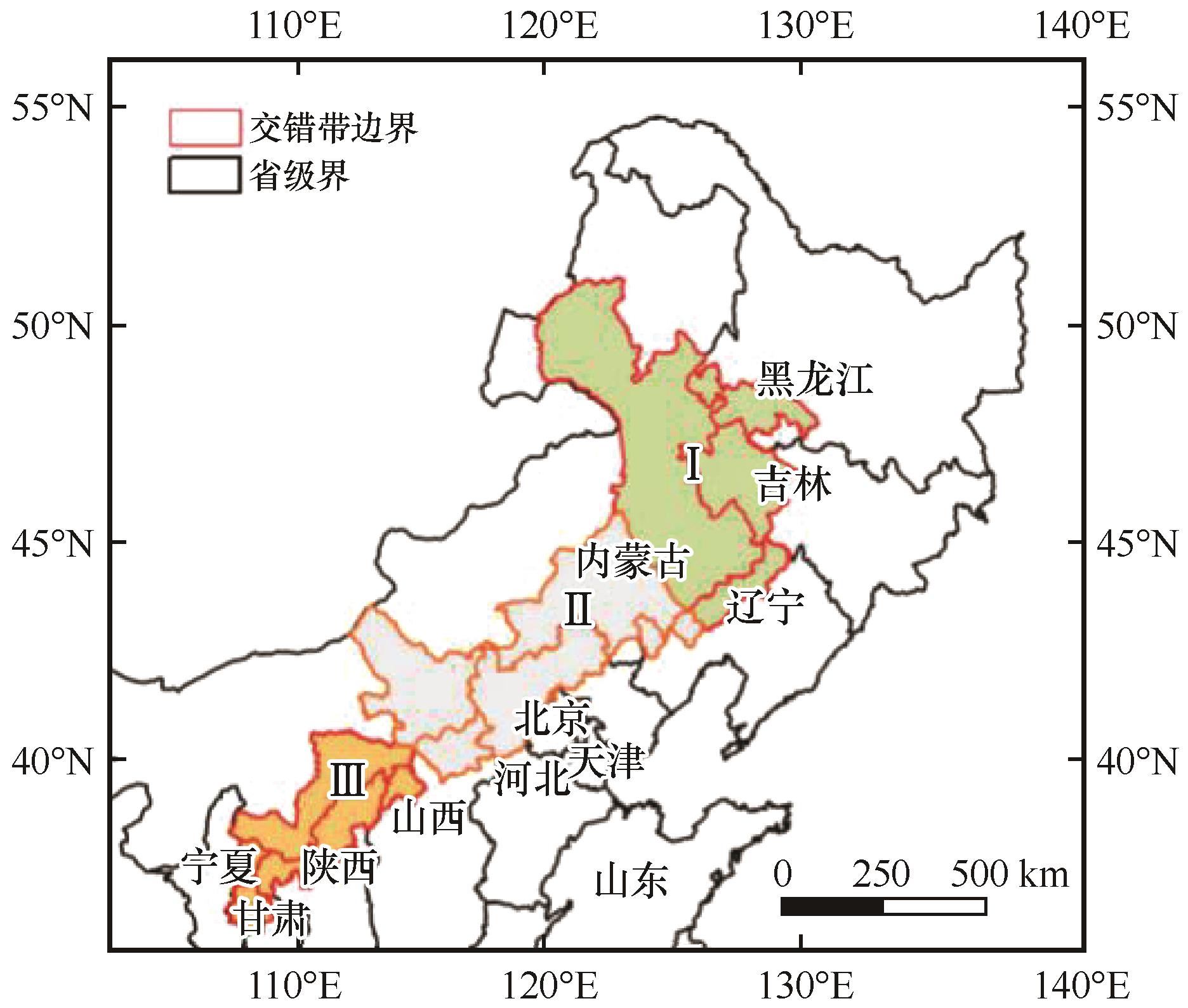
图1 中国北方农牧交错带区域位置(Ⅰ.东北段、Ⅱ.华北段、Ⅲ.西北段)
Fig.1 The location of agropastoral transitional zone of northern China (Ⅰ,Northeast part; Ⅱ,North China part; Ⅲ,Northwest part)
| 湖泊名称 | 时段(年份) | 湖泊面积/km2 | 面积变化量/km2 | 面积变化率/(km2·a-1) | 文献来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 呼伦湖 | 1961—2018 | 2 360—1739 | 621 | 72.84 | 王鹏飞等[ |
| 奈曼西湖 | 1962—2001 | 25—0 | 25 | 0.64 | 张桂英[ |
| 黄旗海 | 1975—2015 | 69—5.8 | 63.2 | 15.8 | 付意成等[ |
| 达里诺尔 | 1983—2018 | 224.8—214.3 | 10.5 | 17.4 | 木希叶乐等[ |
| 查干诺尔 | 1988—2017 | 99—29.8 | 69.2 | 2.38 | 丹旸[ |
| 岱海 | 1989—2018 | 158.8—53.64 | 62.3 | 2.15 | 刘旭隆[ |
表1 近70年中国北方农牧交错带部分湖泊面积变化
Table 1 Changes in the area of some lakes in the northern agriculture-pastoral zone of northern China in the past 70 years
| 湖泊名称 | 时段(年份) | 湖泊面积/km2 | 面积变化量/km2 | 面积变化率/(km2·a-1) | 文献来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 呼伦湖 | 1961—2018 | 2 360—1739 | 621 | 72.84 | 王鹏飞等[ |
| 奈曼西湖 | 1962—2001 | 25—0 | 25 | 0.64 | 张桂英[ |
| 黄旗海 | 1975—2015 | 69—5.8 | 63.2 | 15.8 | 付意成等[ |
| 达里诺尔 | 1983—2018 | 224.8—214.3 | 10.5 | 17.4 | 木希叶乐等[ |
| 查干诺尔 | 1988—2017 | 99—29.8 | 69.2 | 2.38 | 丹旸[ |
| 岱海 | 1989—2018 | 158.8—53.64 | 62.3 | 2.15 | 刘旭隆[ |
| 序号 | 时段(年度) | 研究区 | 每10年气温变率/℃ | 每10年降水变率/mm | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1960—2011 | 东北段 | 0.34 | -9.88 | [ |
| 2 | 1951—2006 | 华北段(科尔沁沙地) | 0.28 | — | [ |
| 3 | 1951—2015 | 华北段 | 0.26 | -15.6 | [ |
| 4 | 1955—2014 | 华北段 | 0.45 | — | [ |
| 5 | 1961—2018 | 华北段(科尔沁沙地) | 0.33 | -0.04 | [ |
| 6 | 1960—2016 | 西北段 | 0.34 | -2.7 | [ |
| 7 | 1960—2010 | 西北段 | 0.38 | — | [ |
| 8 | 1974—2006 | 西北段(榆林市) | 0.46 | -1.0 | [ |
| 9 | 1980—2013 | 西北段(武川县) | 0.50 | -0.06 | [ |
| 10 | 1961—2012 | 全区 | 0.33 | -4.98 | [ |
| 11 | 1964—2011 | 全区 | 0.40 | -2.6 | [ |
| 12 | 1971—2015 | 全区 | 0.39 | -4.60 | [ |
表2 近70年中国北方农牧交错带气候变化
Table 2 Climate changes in the northern farming-pastoral zone of northern China in the past 70 years
| 序号 | 时段(年度) | 研究区 | 每10年气温变率/℃ | 每10年降水变率/mm | 文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1960—2011 | 东北段 | 0.34 | -9.88 | [ |
| 2 | 1951—2006 | 华北段(科尔沁沙地) | 0.28 | — | [ |
| 3 | 1951—2015 | 华北段 | 0.26 | -15.6 | [ |
| 4 | 1955—2014 | 华北段 | 0.45 | — | [ |
| 5 | 1961—2018 | 华北段(科尔沁沙地) | 0.33 | -0.04 | [ |
| 6 | 1960—2016 | 西北段 | 0.34 | -2.7 | [ |
| 7 | 1960—2010 | 西北段 | 0.38 | — | [ |
| 8 | 1974—2006 | 西北段(榆林市) | 0.46 | -1.0 | [ |
| 9 | 1980—2013 | 西北段(武川县) | 0.50 | -0.06 | [ |
| 10 | 1961—2012 | 全区 | 0.33 | -4.98 | [ |
| 11 | 1964—2011 | 全区 | 0.40 | -2.6 | [ |
| 12 | 1971—2015 | 全区 | 0.39 | -4.60 | [ |
| 研究区 | 时段(年份) | 突变年份 | 减水贡献比例/% | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 气候变化 | 人类活动(LUCC) | ||||
| 密云水库 | 1960—2016 | 1980 | — | 60.00 | 黄俊雄等[ |
| 潮白河流域 | 1980—2001 | 1980 | 31.00 | 70.00 | Wang等[ |
| 无定河流域 | 1978—2010 | 1996 | 53.75 | 46.25 | 曹钧恒[ |
| 西辽河平原 | 1980—2016 | 1998 | 24.50 | 75.5 | 朱永华等[ |
| 滦河流域 | 1960—2010 | 1980 | 26.30 | 73.70 | 张利平等[ |
| 锡林郭勒河 | 1963—2015 | 1998 | 30.34 | 69.66 | 王威娜等[ |
| 皇甫川流域 | 1960—2008 | 1998 | 16.81 | 83.19 | 王随继等[ |
| 小理河流域 | 1971—2013 | 1998 | 29.80 | 70.20 | 付金霞[ |
| 泾河上游 | 1973—2012 | 1985 | 40.30 | 59.70 | 党素珍等[ |
| 北洛河流域 | 1956—2011 | 1964 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 樊晶晶等[ |
| 泾河流域 | 1971—2010 | 1985 1996 | 26.60 7.60 | 73.40 92.40 | 郑培龙等[ |
| 塔布河流域 | 1959—2018 | 2009 | 8.31 | 91.69 | 李芳芳等[ |
表3 气候变化与LUCC(人类活动)对区域水文过程影响贡献率
Table 3 The contribution rate of climate change and LUCC (human activity) to the regional hydrological process
| 研究区 | 时段(年份) | 突变年份 | 减水贡献比例/% | 文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 气候变化 | 人类活动(LUCC) | ||||
| 密云水库 | 1960—2016 | 1980 | — | 60.00 | 黄俊雄等[ |
| 潮白河流域 | 1980—2001 | 1980 | 31.00 | 70.00 | Wang等[ |
| 无定河流域 | 1978—2010 | 1996 | 53.75 | 46.25 | 曹钧恒[ |
| 西辽河平原 | 1980—2016 | 1998 | 24.50 | 75.5 | 朱永华等[ |
| 滦河流域 | 1960—2010 | 1980 | 26.30 | 73.70 | 张利平等[ |
| 锡林郭勒河 | 1963—2015 | 1998 | 30.34 | 69.66 | 王威娜等[ |
| 皇甫川流域 | 1960—2008 | 1998 | 16.81 | 83.19 | 王随继等[ |
| 小理河流域 | 1971—2013 | 1998 | 29.80 | 70.20 | 付金霞[ |
| 泾河上游 | 1973—2012 | 1985 | 40.30 | 59.70 | 党素珍等[ |
| 北洛河流域 | 1956—2011 | 1964 | 40.00 | 60.00 | 樊晶晶等[ |
| 泾河流域 | 1971—2010 | 1985 1996 | 26.60 7.60 | 73.40 92.40 | 郑培龙等[ |
| 塔布河流域 | 1959—2018 | 2009 | 8.31 | 91.69 | 李芳芳等[ |
| 1 | 刘晓,陈隽,范琳琳.等 .水资源承载力研究进展与新方法[J].北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2014,50(3):312-318. |
| 2 | 郝杰,张伟.水资源评价现状及有关问题探讨[J].海河水利,2007,23(2):48-49. |
| 3 | Nian Y, Li X, Zhou J,et al.Impact of land use change on water resource allocation in the middle reaches of the Heihe River Basin in northwestern China[J].Journal of Arid Land,2014,6(3):273-286. |
| 4 | Piao S, Ciais P, Huang Y,et al.The impacts of climate change on water resources and agriculture in China[J].Nature,2010,467(7311):43-51. |
| 5 | Wang R, Kalin L, Kuang W,et al.Individual and combined effects of land use/cover and climate change on Wolf Bay watershed streamflow in southern Alabama[J].Hydrological Processes,2014,28(22):5530-5546. |
| 6 | Walling E, Fang D.Recent trends in the suspended sediment loads of the world's rivers[J].Global and Planetary Change,2003,39(1/2):111-126. |
| 7 | Jackson C, Meister R, Prudhomme C.Modeling the effects of climate change and its uncertainty on UK chalk groundwater resources from an ensemble of global climate model projections[J].Journal of Hydrology,2011,399(1):12-28. |
| 8 | 李向应,秦大河,效存德.等 .近期气候变化研究的一些最新进展[J].科学通报,2011,56(36):3029-3040. |
| 9 | 刘启宁,辛卓航,韩建旭,等.变化环境下东北半干旱地区径流演变规律分析:以洮儿河流域为例[J].水力发电学报,2020,39(5):51-63. |
| 10 | 张建云,贺瑞敏.关于中国北方水资源问题的再认识[J].水科学进展,2013,24(3):303-310. |
| 11 | 栗士棋,刘颖,程芳芳,等.环境变化对水资源影响研究进展及其借鉴与启示[J].水利科学与寒区工程,2020,3(5):1-6. |
| 12 | Vorosmarty J, Green P, Salisbury J,et al.Global water resources:vulnerability from climate change and population growth[J].Science,2000,289(5477):284-288. |
| 13 | 史晓亮,李颖,赵凯,等.诺敏河流域土地利用与覆被变化及其对水文过程的影响[J].水土保持通报,2013,33(1):23-28. |
| 14 | 赵阳,郑江坤,武巧英.气候和土地利用变化对潮白河流域径流变化的定量影响[J].农业工程学报,2012,28(22):252-260. |
| 15 | Yin J, Gentine P, Sha Z.Large increase in global storm runoff extremes driven by climate and anthropogenic changes[J].Nature Communications,2018,9(1):233-254. |
| 16 | 田晶,郭生练,刘德地,等.气候与土地利用变化对汉江流域径流的影响[J].地理学报,2020,75(11):2307-2318. |
| 17 | 丁美慧,孙泽祥,刘志锋,等.中国北方农牧交错带城市扩展过程对植被净初级生产力影响研究:以呼包鄂地区为例[J].干旱区地理,2017,40(7):614-621. |
| 18 | 赵哈林,赵学勇,张铜会,等.北方农牧交错带的地理界定及其生态问题[J].地球科学进展,2002,35(5):739-747. |
| 19 | 史文娇,刘奕婷,石晓丽.气候变化对北方农牧交错带界线变迁影响的定量探测方法研究[J].地理学报,2017,72(3):407-419. |
| 20 | 张生军,杨改河,刘和林.北方农牧交错带水资源与生态环境问题初探[J].安徽农业科学,2006,21(9):1945-1947. |
| 21 | 周一敏,张昂,赵昕奕.未来气候变化情景下中国北方农牧交错带脆弱性评估[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2017,53(6):1099-1107. |
| 22 | 方梓行,刘志锋,赵媛媛,等.中国北方农牧交错带气候变化特点及未来趋势:基于观测和模拟资料的综合分析[J].自然资源学报,2020,35(2):358-370. |
| 23 | 殷小菡.北方农牧交错带西段退耕对生态系统主要服务功能影响研究[D].济南:山东师范大学,2019. |
| 24 | Li L, Jiang D, Hou X,et al.Simulated run off responses to land use in the middle and upstream reaches of Tao Er He River basin,Northeast China,in wet,average and dry years[J].Hydrological Processes,2013,27(24):3484-3494. |
| 25 | 李亚光,孙卫东,杨绍峰,等.赤峰市老哈河流域实测降雨量实测径流量变化趋势浅析[J].内蒙古水利,2020,23(9):12-14. |
| 26 | 安娜,于明洋,吴建华,等.西拉木伦河流域气候与径流关系[J].北方农业学报,2016,44(4):85- 89. |
| 27 | 王鹏飞,郭云艳,周康,等.1961-2018年呼伦湖水面面积变化特征及其对气候变化的响应[J].环境科学研究,2021,34(4):792-800. |
| 28 | 张桂英.奈曼西湖水库干枯后对附近降水的影响[J].内蒙古民族大学学报,2010,16(5):93-94. |
| 29 | 付意成,赵进勇,朱国平,等.基于M-K检验的黄旗海湖面面积退化成因分析[J].中国农村水利水电,2017,42(7):79-84. |
| 30 | 木希叶乐,秦福莹,布仁吉日嘎拉,等.1983-2018年内蒙古达里诺尔自然保护区水域动态变化及其驱动因素分析[J].中国农学通报,2020,36(32):62-68. |
| 31 | 丹旸.内蒙古典型草原地区内陆湖面积变化研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古师范大学,2019. |
| 32 | 刘旭隆.岱海湖泊面积与水位动态变化及其驱动力分析[D]呼和浩特:内蒙古大学,2019. |
| 33 | 张光辉,费宇红,刘春华,等.华北滹滏平原地下水位下降与灌溉农业关系[J].水科学进展,2013,24(2):228-234. |
| 34 | Sahoo S, Russo T A, Elliott J,et al.Machine learning algorithms for modeling groundwater level changes in agricultural regions of the U.S.[J].Water Resources Research,2017,53(5):3878-3895. |
| 35 | 朱永华.变化环境下半干旱区农牧交错带水-植被相互作用关系及地下水反演模拟研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2019. |
| 36 | Feng W, Zhong M, Lemoine J-M,et al.Evaluation of groundwater depletion in North China using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) data and ground-based measurements[J].Water Resources Research,2013,49(4):2110-2118. |
| 37 | 丁元芳,李月宁,吴昊晨,等.西辽河流域地下水开发利用及问题成因分析[J].东北水利水电,2020,38(5):32-34. |
| 38 | 赵威,韦志刚,郑志远,等.1964-2013年中国北方农牧交错带温度和降水时空演变特征[J].高原气象,2016,35(4):979-988. |
| 39 | Working Group I Contribution to the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report.Climate Change 2013:The Physical Science Basis:Summary for Policymakers[R].IPCC,2013. |
| 40 | 闫冠华,李巧萍,吕冬红.中国北方农牧交错带气候变化特征及未来趋势[J].南京气象学院学报,2008,34(5):671-678. |
| 41 | 韩晓敏,延军平.东北农牧交错带旱涝特征对气候变化的响应[J].水土保持通报,2015,35(2):257-262. |
| 42 | 渠翠平,关德新,王安志,等.近56年来科尔沁沙地气候变化特征[J].生态学杂志,2009,28(11):2326-2332. |
| 43 | 陈永金,马胜兰,许婕,等.华北地区近65 a气候变化及其与相关因子关系分析[J].河北师范大学学报(自然科学版),2021,45(3):314-324. |
| 44 | 林长存,王堃,孙钰茗.中国北方农牧交错带中段近60年气温序列变化研究[J].草地学报,2016,24(4):747-753. |
| 45 | 李思慧.1961-2018年科尔沁沙地气候变化特征[J].内蒙古气象,2019,42(5):8-10. |
| 46 | 曾晟轩,顾娟,贺缠生.西北农牧交错带中部气候变化特征及其持续性[J].水土保持研究,2018,25(4):356-364. |
| 47 | 刘亚南,潘志华,李超,等.近50年北方农牧交错带气候月季变化和空间分布规律[J].中国农业大学学报,2012,17(4):96-102. |
| 48 | 刘晓琼,刘彦随,李同昇,等.高强度能源开发区气候变化的人文驱动力分析及对策研究:以陕西省榆林市为例[J].地域研究与开发,2014,33(2):159-164. |
| 49 | 李政,呼格吉勒图,李文通.阴山北麓农牧交错带1980年以来气候变化特征及对农作物产量的影响:以武川县为例[J].农技服务,2017,34(5):91-92. |
| 50 | 李敏敏,延军平,丁彩霞.北方农牧交错带气候变化与旱涝响应特征[J].水土保持通报,2014,34(5):304-308. |
| 51 | 裴宏伟,王飞枭,张红娟,等.中国北方农牧交错带水资源问题荟萃分析[J].河北建筑工程学院学报,2020,38(4):83-90. |
| 52 | 刘孟竹,张红娟,王彦芳,等.基于土地利用的北方农牧交错带生境质量研究[J].水土保持研究,2021,28(3):156-162. |
| 53 | 刘军会,高吉喜,耿斌,等.北方农牧交错带土地利用及景观格局变化特征[J].环境科学研究,2007,23(5):148-154. |
| 54 | 刘孟竹,王彦芳,裴宏伟.退耕还林(草)背景下中国北方农牧交错带土地利用及碳储量变化[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(1):174-182. |
| 55 | An W, Li Z, Shuai W,et al.Exploring the effects of the "Grain for Green" program on the differences in soil water in the semi-arid Loess Plateau of China[J].Ecological Engineering,2017,107(7):144-151. |
| 56 | 王金凤,武桃丽.气候变化影响下冶河流域径流变化特征分析[J].山西师范大学学报(自然科学版),2019,33(3):62-67. |
| 57 | 杨恒山,刘江,梁怀宇.西辽河平原气候及水资源变化特征[J].应用生态学报,2009,20(1):84-90. |
| 58 | 史晓亮,杨志勇,吕杰,等.滦河流域气候变化的水文响应研究[J].水土保持研究,2016,23(2):123-127. |
| 59 | 李鸿雁,王凡,刘莹莹,等.洮儿河流域平原区气候变化情景下浅层地下水水位动态响应分析[J].北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2021,57(3):345-352. |
| 60 | 秦欢欢,孙占学,高柏,等.气候变化影响下华北平原地下水可持续利用研究[J].灌溉排水学报,2020,39(1):106-114. |
| 61 | 王磊,刘亭亭,谢建治.基于SWAT模型的张家口清水河流域土地利用情景变化对径流影响研究[J].水土保持研究,2019,26(4):245-251. |
| 62 | 吴杰昭.土地利用变化对滦河流域水文生态过程影响研究[D].天津:天津大学,2018. |
| 63 | 王晓勇,朱立峰,董佳秋,等.干旱-半干旱区下垫面变化对地下水位的影响[J].西北地质,2019,52(2):227-235. |
| 64 | 孙标,朱永华,张生,等.通辽平原区近35年地下水埋深及土地利用变化响应关系研究[J].中国农村水利水电,2019,23(8):15-19. |
| 65 | Qi Y, Chang Q, Jia K,et al.Temporal-spatial variability of desertification in an agro-pastoral transitional zone of northern Shanxi Province,China[J].Catena,2012,88(1):37-45. |
| 66 | 吴立钰,张璇,李冲,等.气候变化和人类活动对伊逊河流域径流变化的影响[J].自然资源学报,2020,35(7):1744-1756. |
| 67 | 曾小凡,苏布达,姜彤,等.21世纪前半叶长江流域气候趋势的一种预估[J].气候变化研究进展,2007,34(5):293-298. |
| 68 | Croke B, Merritt W S, Jakeman A J.A dynamic model for predicting hydrologic response to land cover changes in gauged and ungauged catchments[J].Journal of Hydrology,2004,291(1/2):115-131. |
| 69 | Guo H, Hu Q, Jiang T.Annul and seasonal stream flow responses to climate and land-cover changes in the Poyang Lake basin,China[J].Journal of Hydrology,2008,35(1):104-122. |
| 70 | Barnett T P, Adam J C, Lettenmaier D P.Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions[J].Nature,2005,438(7066):303-309. |
| 71 | 雷鸣,孔祥斌,张雪靓,等.黄淮海平原区土地利用变化对地下水资源量变化的影响[J].资源科学,2017,39(6):1099-1116. |
| 72 | 宋小园.气候变化和人类活动影响下锡林河流域水文过程响应研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2016. |
| 73 | 李帅,魏虹,刘媛,等.气候与土地利用变化下宁夏清水河流域径流模拟[J].生态学报,2017,37(4):1252-1260. |
| 74 | Zhang L, Karthikeyan R, Bai Z,et al.Analysis of stream flow responses to climate variability and land use change in the Loess Plateau region of China[J].Catena,2017,154(7):1-11. |
| 75 | 朱永华,张生,赵胜男,等.气候变化与人类活动对地下水埋深变化的影响[J].农业机械学报,2017,48(9):199-205. |
| 76 | 王随继,闫云霞,颜明,等.皇甫川流域降水和人类活动对径流量变化的贡献率分析:累积量斜率变化率比较方法的提出及应用[J].地理学报,2012,67(3):388-397. |
| 77 | 黄俊雄,刘兆飞,张航,等.土地利用与气候变化对密云水库来水量变化的影响研究[J].水文,2021,41(1):1-6. |
| 78 | Wang G, Xia J, Chen J.Quantification of effects of climate variations and human activities on runoff by a monthly water balance model:a case study of the Chao Bai River basin in northern China[J].Water Resources Research,2009,45(2):324-335. |
| 79 | 曹钧恒.气候变化和人类活动对无定河流域径流量影响的定量研究[D].陕西杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2020. |
| 80 | 张利平,李凌程,夏军,等.气候波动和人类活动对滦河流域径流变化的定量影响分析[J].自然资源学报,2015,30(4):664-672. |
| 81 | 王威娜,高瑞忠,王喜喜,等.锡林河流域径流变化规律及气候波动和人类活动影响的定量分析[J].水土保持研究,2018,25(2):347-353. |
| 82 | 付金霞.小理河流域径流泥沙对气候和土地利用变化的响应研究[D].陕西杨凌:西北农林科技大学,2017. |
| 83 | 党素珍,董国涛,蒋晓辉,等.气候变化和人类活动对泾河上游径流的影响[J].南水北调与水利科技,2014,12(4):30-34. |
| 84 | 樊晶晶,黄强,刘登峰,等.人类活动和气候变化对北洛河径流变化的影响[J].西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2016,44(2):221-227. |
| 85 | 郑培龙,李云霞,赵阳,等.黄土高原泾河流域气候和土地利用变化对径流产沙的影响[J].水土保持研究,2015,22(5):20-24. |
| 86 | 李芳芳,梁文涛,尹航,等.气候变化和人类活动对塔布河流域径流变化的影响分析[J].内蒙古水利,2021,54(5):12-15. |
| 87 | 郭军庭,张志强,王盛萍,等.应用SWAT模型研究潮河流域土地利用和气候变化对径流的影响[J].生态学报,2014,34(6):1559-1567. |
| 88 | 黄斌斌,郝成元,李若男,等.气候变化及人类活动对地表径流改变的贡献率及其量化方法研究进展[J].自然资源学报,2018,33(5):899-910. |
| [1] | 宫毓来, 马绍休, 刘伟琦. 机器学习与统计模型在石羊河流域气候降尺度研究中的适用性对比[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 196-210. |
| [2] | 柳本立, 彭婉月, 刘树林, 杨婷. 2021年3月中旬东亚中部沙尘天气地面起尘量及源区贡献率估算[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 79-86. |
| [3] | 雷燕慧, 丁国栋, 李梓萌, 迟文峰, 高广磊, 赵媛媛. 京津风沙源治理工程区土地利用/覆盖变化及生态系统服务价值响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(6): 29-40. |
| [4] | 马晓慧, 庞奖励, 刘小槺, 丁丹, 岳晓晓, 贾飞飞. 瓦窑沟剖面记录的早中全新世毛乌素沙地东南缘气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 71-80. |
| [5] | 张小梅, 靳鹤龄, 刘冰. 末次盛冰期以来库布齐沙漠环境变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 81-93. |
| [6] | 马永桃, 任孝宗, 胡慧芳, 刘敏, 孟琪. 基于地理探测器的浑善达克沙地植被变化定量归因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 195-204. |
| [7] | 韩兰英, 张强, 马鹏里, 王有恒, 黄涛, 贾建英, 王鑫, 王小巍, 刘卫平, 李丹华, 卢国阳, 黄鹏程, 白冰. 气候变暖背景下黄河流域干旱灾害风险空间特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 225-234. |
| [8] | 王有恒, 谭丹, 韩兰英, 李丹华, 王鑫, 卢国阳, 林婧婧. 黄河流域气候变化研究综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 235-246. |
| [9] | 贺晓慧, 司建华, 赵春彦, 王春林, 周冬蒙. 西藏沙棘(Hippophae thibetana)潜在地理分布及其对未来气候变化的响应模拟[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 101-109. |
| [10] | 刘孟竹, 王彦芳, 裴宏伟. 退耕还林(草)背景下中国北方农牧交错带土地利用及碳储量变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 174-182. |
| [11] | 何远政, 黄文达, 赵昕, 吕朋, 王怀海. 气候变化对植物多样性的影响研究综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 59-66. |
| [12] | 邓迪, 赵泽斌, 马媛. 基于GIS的柠条锦鸡儿(Caragana korshinskii)分布模型[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(5): 74-80. |
| [13] | 韩超, 肖生春, 丁爱军, 滕泽宇. 腾格里沙漠南缘青海云杉(Picea crassifolia)和油松(Pinus tabulaeformis)年轮记录的气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 50-58. |
| [14] | 李想, 苏志珠, 马义娟, 张彩霞, 柳苗苗. 毛乌素沙地东南缘全新世气候不稳定性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 109-117. |
| [15] | 赵泽芳, 卫海燕, 郭彦龙, 栾文飞, 赵泽斌. 气候变化下的孑遗植物裸果木(Gymnocarpos przewalskii)适宜生境分布[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 125-133. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
