中国沙漠 ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (5): 81-93.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00054
收稿日期:2021-03-28
修回日期:2021-04-26
出版日期:2021-09-20
发布日期:2021-09-23
通讯作者:
靳鹤龄
作者简介:靳鹤龄(E-mail: jinhl@lzb.ac.cn)基金资助:
Xiaomei Zhang1,2( ), Heling Jin1(
), Heling Jin1( ), Bing Liu1
), Bing Liu1
Received:2021-03-28
Revised:2021-04-26
Online:2021-09-20
Published:2021-09-23
Contact:
Heling Jin
摘要:
中国北方季风边缘区沙漠/沙地如何响应气候变化及其反馈研究对于理解干旱半干旱地区现代地表过程及其未来环境演变趋势有重要的科学意义。库布齐沙漠作为中国北方季风边缘区中东部唯一的以流动、半流动为主的沙漠,现代地表景观与周围沙地(如毛乌素沙地、浑善达克沙地、科尔沁沙地等)明显不同。晚第四纪以来库布齐沙漠与季风边缘区中东部沙地环境演化过程到底是否一致,其湿润期究竟发生于何时,尚存颇多争议。区域风成沉积和湖泊沉积记录研究得出的结论明显不同,存在中晚全新世和早中全新世湿度最优期的分歧。对库布齐沙漠风成沉积年代-岩性的概率密度分布(Probability Density Function,PDF)进行处理,与周边沙地风成沉积和湖泊沉积古环境记录进行了对比分析。结果表明:末次盛冰期以来库布齐沙漠与季风边缘区中东部沙地环境演化过程总体一致,27.6—10 ka和晚全新世(2—0 ka),风沙堆积强烈,气候相对干旱;早全新世(10—6 ka)古土壤渐次发育,沙丘逐渐被固定,湿度增加,环境状况有所改善;中全新世(6—2 ka)古土壤广泛发育,沙丘经历固定成壤,气候最为湿润。区域环境演变过程受控于低纬太阳辐射和高纬冰量变化的双重制约。
中图分类号:
张小梅, 靳鹤龄, 刘冰. 末次盛冰期以来库布齐沙漠环境变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 81-93.
Xiaomei Zhang, Heling Jin, Bing Liu. Environment changes in the Hobq Desert since the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(5): 81-93.
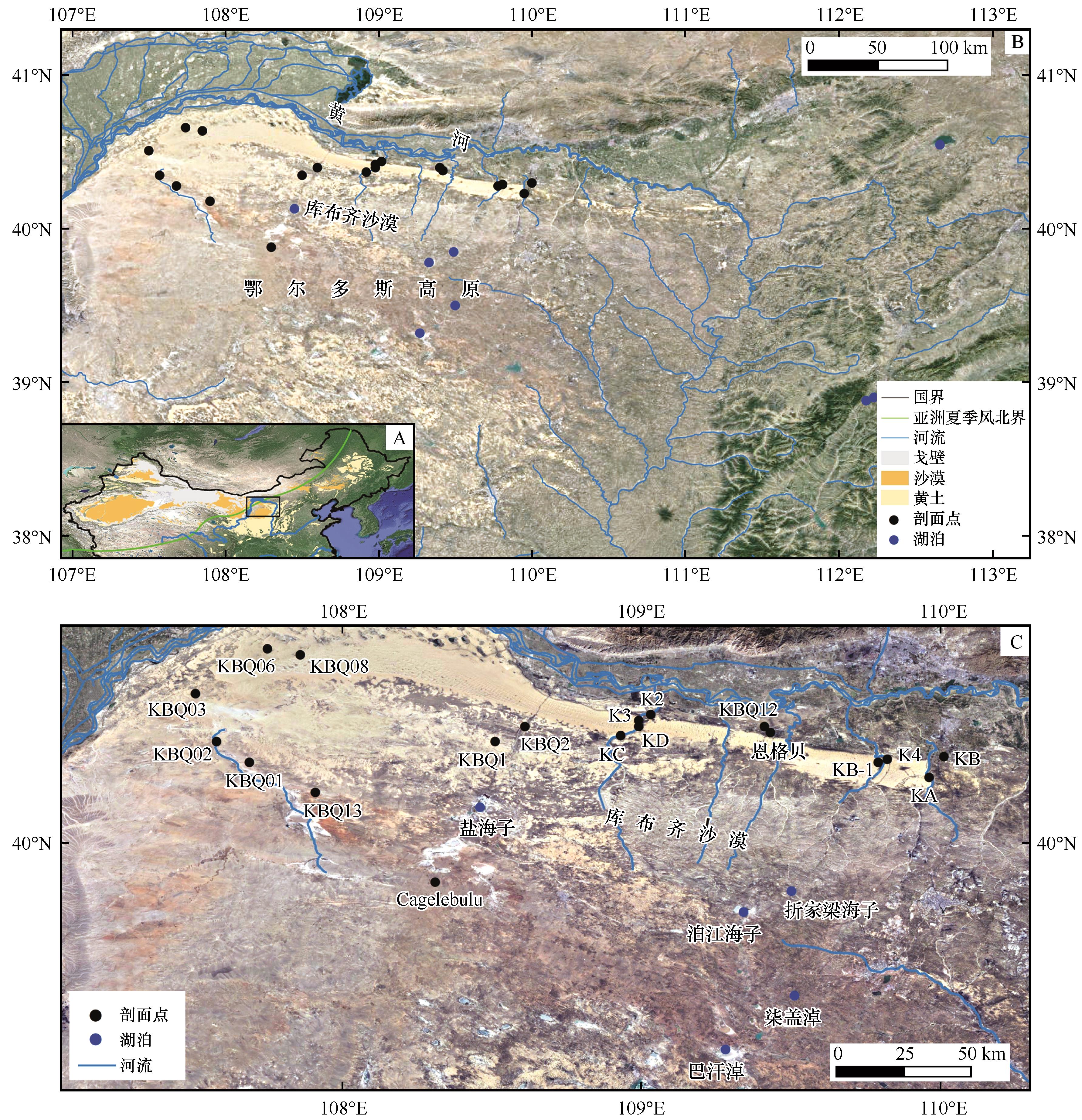
图1 中国北方沙漠/沙地分布及现代亚洲夏季风北界(A)、鄂尔多斯高原(B)与库布齐沙漠剖面点及周边湖泊分布(C)剖面KB位置据Sun等[2];剖面Cagelebulu位置据Zhou等[17];剖面KA、KB-1、KC、KD位置据杨小平等[24];剖面KBQ1、KBQ2、KBQ12、KBQ13位置据Xu等[33];剖面KBQ01、KBQ02、KBQ03、KBQ06、KBQ08、K2、K3、K4位置据Fan等[34];恩格贝剖面位置据杨利荣等[44]
Fig.1 Distribution of deserts/sandy lands in northern China and the northern boundary of modern Asian summer monsoon (A), profile points in the Ordos Plateau (B) and Hobq Desert and surrounding lakes (C)

图2 末次盛冰期以来库布齐沙漠地层沉积序列和年代剖面KB地层岩性及年代据Sun等[2];剖面Cagelebulu地层岩性及年代据Zhou等[17];剖面KA、KB-1和KC地层岩性及年代据杨小平等[24];剖面KBQ1、KBQ2、KBQ11、KBQ12、KBQ13和KBQ14地层岩性及年代据Xu等[33];剖面KBQ01、KBQ02、KBQ03、KBQ06、KBQ08、K2、K3、K4地层岩性及年代据Fan等[34];恩格贝剖面地层岩性及年代据杨利荣等[44]
Fig.2 Stratigraphic sedimentary sequence and chronological results in the Hobq Desert since the Last Glacial Maximum
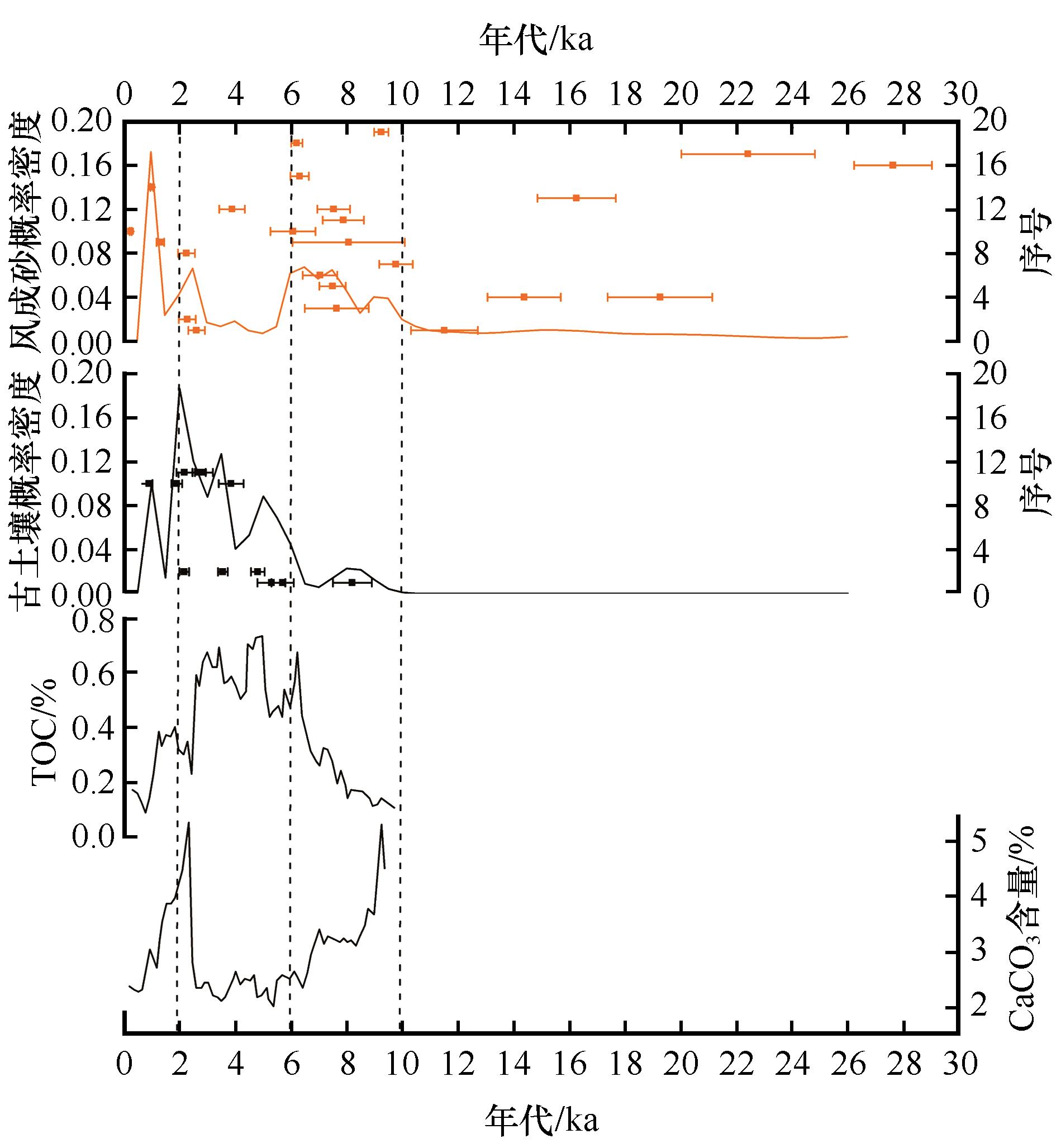
图3 末次盛冰期以来库布齐沙漠风成砂与古土壤OSL年代、概率密度曲线及环境指标变化环境指标TOC及CaCO3数据引自Yang等[35]
Fig.3 OSL chronology and probability density curve of aeolian sand and paleosol in the Hobq Desert and changes of palaeoenvironmental proxies since the Last Glacial Maximum
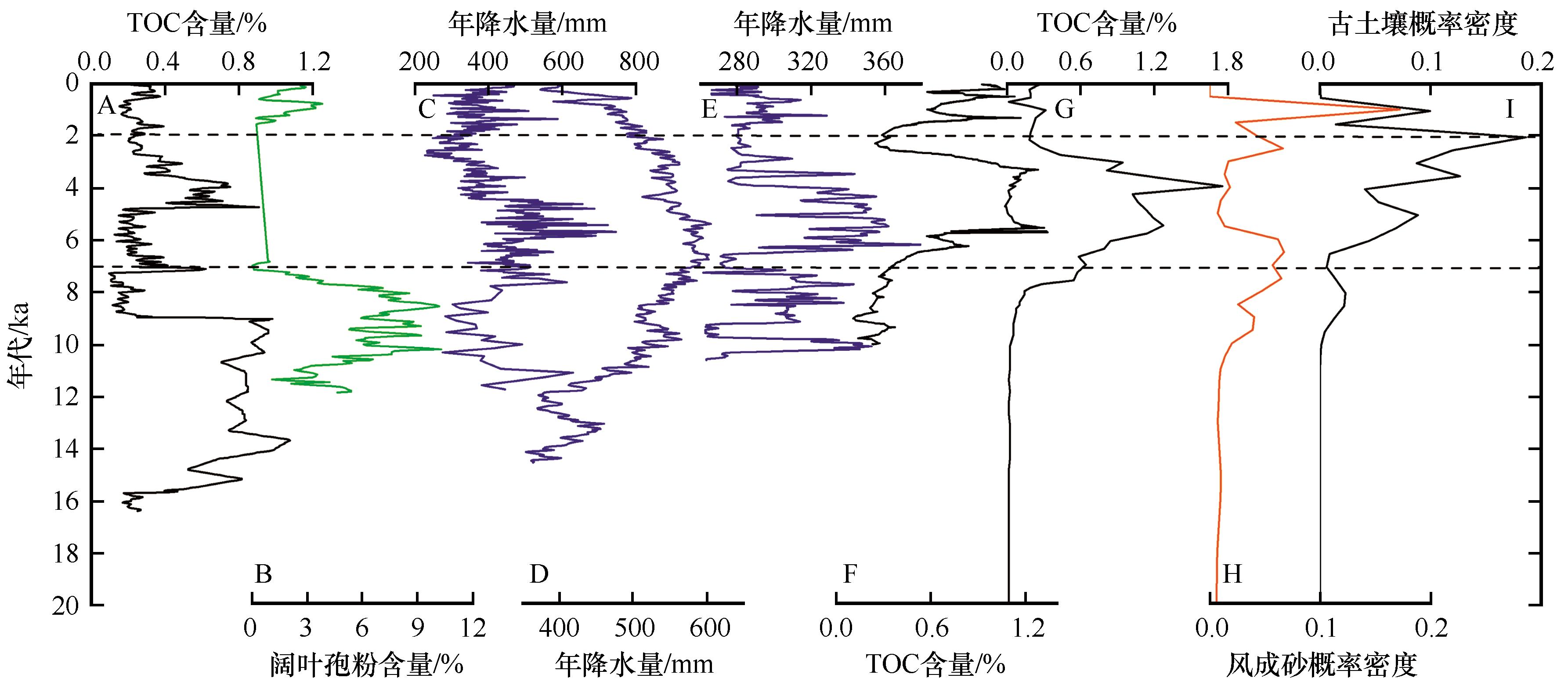
图5 盐海子、泊江海子与周边气候记录对比A:盐海子[36];B:泊江海子[37];C:岱海[49];D:公海[40];E:柒盖淖[53];F:沙漠黄土过渡带JB剖面[55];G:榆林剖面[56];H:库布齐沙漠风成砂概率密度曲线;I:库布齐沙漠古土壤概率密度曲线
Fig.5 Comparison of climate records between Yanhaizi, Bojianghaizi and surrounding areas

图6 末次盛冰期以来库布齐沙漠与季风边缘区中东部沙地环境演化过程的对比
Fig.6 Comparison of the environmental evolution process of the Hobq Desert and the sandy lands in the middle and east of the monsoonal margin region since the Last Glacial Maximum
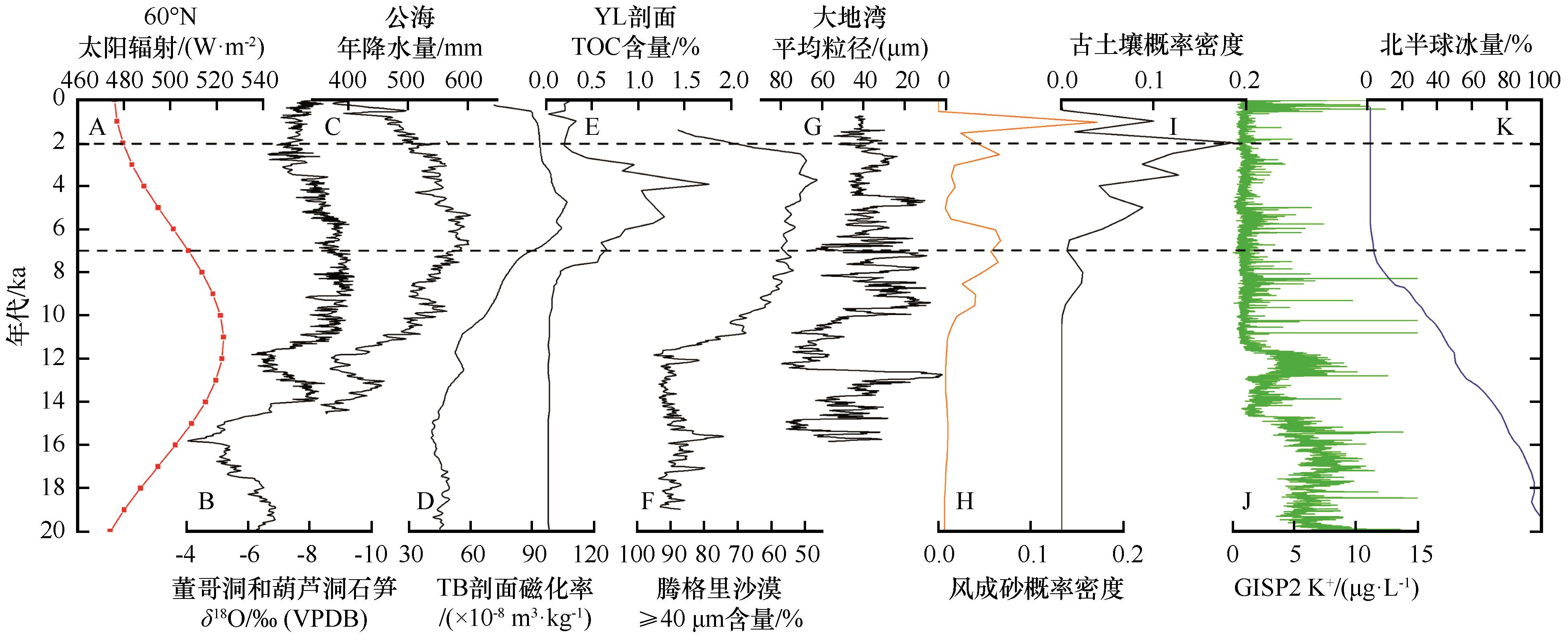
图7 末次盛冰期以来库布齐沙漠环境演变的驱动机制A:60°N太阳辐射[39];B:董哥洞和葫芦洞石笋[63,65];C:公海[40];D:TB剖面磁化率[67];E:YL剖面TOC含量[56];F:腾格里沙漠≥40μm含量[29];G:大地湾平均粒径[68];H:库布齐沙漠风成砂概率密度曲线;I:库布齐沙漠古土壤概率密度曲线;J:GISP2 K+浓度[74];K:北半球冰量[69,75]
Fig.7 Driving mechanisms of environmental evolution in the Hobq Desert since the Last Glacial Maximum
| 1 | Sun J M,Ding Z L,Liu T S.Desert distributions during the glacial maximum and climatic optimum:example of China[J].Episodes,1998,21(1):28-31. |
| 2 | Sun J M,Li S H,Han P,et al.Holocene environmental changes in the central Inner Monglia,based on the single-aliquot-quartz optical dating and multi-proxy study of dune sands[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2006,233(1/2):51-62. |
| 3 | Mason J A,Lu H Y,Zhou Y L,et al.Dune mobility and aridity at the desert margin of northern China at a time of peak monsoon strength[J].Geology,2009,37(10):947-950. |
| 4 | Yang X P,Scuderi L,Paillou P,et al.Quaternary environmental changes in the drylands of China:a critical review[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2011,30(23/24):3219-3233. |
| 5 | Yang X P,Wang X L,Liu Z T,et al.Initiation and variation of the dune fields in semi-arid China:with a special reference to the Hunshandake Sandy Land,Inner Mongolia[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2013,78:369-380. |
| 6 | Yang X P,Scuderib L A,Wang X L,et al.Groundwater sapping as the cause of irreversible desertification of Hunshandake Sandy Lands,Inner Mongolia,northern China[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2015, 112(3):702-706. |
| 7 | He Z,Zhou J,Yang L H,et al.Holocene dune mobility and forcing mechanisms at the northern margin of the East Asian monsoon[J].Acta Geological Sinica,2013,87(4):1168-1178. |
| 8 | Enzel Y,Ely L L,Mishra S,et al.High-resolution Holocene environmental changes in the Thar Desert,Northwestern India[J].Science,1999,284(5411):125-128. |
| 9 | Betancourt J L,Latorre C,Rech J A,et al.A 22,000-year record of monsoonal precipitation from Northern Chile’s Atacama Desert[J].Science,2000,289(5484):1542-1546. |
| 10 | Preusser F,Radies D,Matter A.A 160,000-year record of dune development and atmospheric circulation in Southern Arabia[J].Science,2002,296(5575):2018-2020. |
| 11 | Lu H Y,Miao X D,Zhou Y L,et al.Late Quaternary aeolian activity in the Mu Us and Otindag dune fields (north China) and lagged response to insolation forcing[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2005,32:365-370. |
| 12 | Lu H Y,Mason J A,Stevens T,et al.Response of surface processes to climatic change in the dunefields and Loess Plateau of North China during the late Quaternary[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2011,36(12):1590-1603. |
| 13 | Lu H Y,Zhao C F,Mason J,et al.Holocene climatic changes revealed by aeolian deposits from the Qinghai Lake area (northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau) and possible forcing mechanisms[J].The Holocene,2011,21(2):297-304. |
| 14 | Lu H Y,Yi S W,Xu Z W,et al.Chinese deserts and sand fields in Last Glacial Maximum and Holocene Optimum[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2013,58(23):2775-2783. |
| 15 | Zhang X Y,Gong S L,Zhao T L,et al.Sources of Asian dust and role of climate change versus desertification in Asian dust emission[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2003,30(24):2272-2275. |
| 16 | Wang T,Han P,Wu S,et al.Deserts and Aeolian Desertification in China[M].Beijing:Science Press,2011:1-819. |
| 17 | Zhou W J,Dodson J,Head M J,et al.Environmental variability within the Chinese desert-loess transition zone over the last 20,000 years[J].The Holocene,2002,12(1):107-112. |
| 18 | Bush A B G,Rokosh D,Rutter N W,et al.Desert margins near the Chinese Loess Plateau during the mid-Holocene and at the Last Glacial Maximum:a model-data intercomparison[J].Global and Planetary Change,2002,32(4):361-374. |
| 19 | Xu Z W,Mason J A,Xu C,et al.Critical transitions in Chinese dunes during the past 12000 years[J].Science Advances,2020,6(9):1-10. |
| 20 | Xu D Y,Li C L,Song X,et al.The dynamics of desertification in the farming-pastoral region of North China over the past 10 years and their relationship to climate change and human activity[J].Catena,2014,123:11-22. |
| 21 | De Baar H J W,De Jong J T M,Bakker D C E,et al.Importance of iron for plankton blooms and carbon dioxide drawdown in the Southern Ocean[J].Nature,1995,373(6513):412-415. |
| 22 | Uno I,Eguchi K,Yumimoto K,et al.Asian dust transported one full circuit around the globe[J].Nature Geoscience,2009,2(8):557-560. |
| 23 | 朱震达,吴正,刘恕,等.中国沙漠概论[M].北京:科学出版社,1980:46-55. |
| 24 | 杨小平,梁鹏,张德国,等.中国东部沙漠/沙地全新世地层序列及其古环境[J].中国科学(D辑):地球科学,2019,49(8):1293-1307. |
| 25 | Li S H,Sun J M.Optical dating of Holocene dunes sands from the HulunBuir desert,northeastern China[J].The Holocene,2006,16(3):457-462. |
| 26 | Zhao H,Lu Y C,Yin J H.Optical dating of Holocene sand dune activities in the Horqin sand-fields in Inner Mongolia,China,using the SAR protocol[J].Quaternary Geochronology,2007,2:29-33. |
| 27 | Jin H L,Sun L Y,Sun Z.Millennial-scale evolution of Hunshandake Desert and climate change during the Holocene in Inner Mongolia,northern China[J].Sciences in Cold and Arid Regions,2010,2(6):505-513. |
| 28 | Liu B,Jin H L,Sun L Y,et al.Holocene moisture change revealed by the Rb/Sr ratio of aeolian deposits in the southeastern Mu Us Desert,China[J].Aeolian Research,2014,13:109-119. |
| 29 | Qiang M R,Chen F H,Wang Z T,et al.Aeolian deposits at the southeastern margin of the Tengger Desert (China):implications for surface wind strength in the Asian dust source area over the past 20,000 years[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2010,286(1/2):66-80. |
| 30 | Lu R J,Jia F F,Gao S Y,et al.Holocene aeolian activity and climatic change in Qinghai Lake basin,northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2015,430:1-10. |
| 31 | Liu B,Zhao H,Jin H L,et al.Holocene moisture variation recorded by aeolian sand-palaeosol sequences of the Gonghe Basin,Northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau,China[J].Acta Geological Sinica,2020,94(3):668-681. |
| 32 | Yu L P,Lai Z P.OSL chronology and palaeoclimatic implications of aeolian sediments in the eastern Qaidam Basin of the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2012,337-338:120-129. |
| 33 | Xu Y T,Lai Z P,Chen T Y,et al.Late Quaternary optically stimulated luminescence (OSL) chronology and environmental changes in the Hobq Desert,northern China[J].Quaternary International,2018,470:1-8. |
| 34 | Fan Y X,Chen X L,Fan T L,et al.Sedimentary and OSL dating evidence for the development of the present Hobq desert landscape,Northern China[J].Science China (Seri.D):Earth Sciences,2013,56(12):2037-2044. |
| 35 | Yang X P,Forman S,Hu F G,et al.Initial insights into the age and origin of the Kubuqi sand sea of northern China[J].Geomorphology,2016,259:30-39. |
| 36 | Chen C T A,Lan H C,Lou J Y,et al.The dry Holocene Megathermal in Inner Mongolia[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2003,193(2):181-200. |
| 37 | 姜雅娟,王维,马玉贞,等.内蒙古鄂尔多斯高原泊江海子全新世气候变化初步研究[J].第四纪研究,2014,34(3):654-665. |
| 38 | 蒋复初,王书兵,傅建利,等.鄂尔多斯高原距今15ka以来环境演化[J].地质力学学报,2014,20(2):165-173. |
| 39 | Berger A,Louter M F.Insolation values for the climate of the last 10 million years[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,1991,10(4):297-317. |
| 40 | Chen F H,Xu Q H,Chen J H,et al.East Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability since the last deglaciation[J].Scientific Reports,2015,5:11186. |
| 41 | Wen R L,Xiao J L,Fan J W,et al.Pollen evidence for a mid-Holocene East Asian summer monsoon maximum in northern China[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2017,176:29-35. |
| 42 | Ma L.Geological Atlas of China[M].Beijing:Geological Press,2002:1-20. |
| 43 | 吴泽群.内蒙古河套地区晚第四纪库布齐沙漠的形成和演化[D].北京:中国地质大学,2017. |
| 44 | 杨利荣,邹宁,岳乐平,等.库布齐沙漠碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄组成及其物源分析[J].第四纪研究,2017,37(3):560 -569. |
| 45 | Zeng L,Yi S W,Lu H Y,et al.Response of dune mobility and pedogenesis to fluctuations in monsoon precipitation and human activity in the Hulunbuir dune field,northeastern China,since the last deglaciation[J].Global and Planetary Change,2018,168:1-14. |
| 46 | Venkatesan T R,Ramesh R.Consideration of analytical uncertainties while plotting histograms[J].Journal of Geological Society of India,1993,41:313-317. |
| 47 | 杜世松,伍永秋,李拓宇,等.基于年代数据的青藏高原东北部全新世风沙活动研究[J].北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2016,52(1):97-104. |
| 48 | Xu Z W,Lu H Y,Yi S W,et al.Climate-driven changes to dune activity during the Last Glacial Maximum and deglaciation in the Mu Us dune field,north-central China[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2015,427:149-159. |
| 49 | Xu Q H,Xiao J L,Li Y C,et al.Pollen-based quantitative reconstruction of Holocene climate changes in the Daihai Lake area,Inner Mongolia,China[J].Journal of Climate,2010,23(11):2856-2868. |
| 50 | Xiao J L,Xu Q H,Nakamura T,et al.Holocene vegetation variation in the Daihai Lake region of north-central China:a direct indication of the Asian monsoon climatic history[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2004,23(14):1669-1679. |
| 51 | Sun Q L,Zhou J,Shen J,et al.Environmental characteristics of Mid-Holocene recorded by lacustrine sediments from Lake Daihai,north environment sensitive zone,China[J].Science in China(Series D:Earth Sciences),2006,49(9):968-981. |
| 52 | Zhang S W,Yang Z Y,Cioppa M T,et al.A high-resolution Holocene record of the East Asian summer monsoon variability in sediments from Mountain Ganhai Lake,North China[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2018,508:17-34. |
| 53 | Sun A Z,Feng Z D.Holocene climatic reconstructions from the fossil pollen record at Qigai Nuur in the southern Mongolian Plateau[J].The Holocene,2013,23(10):1391-1402. |
| 54 | 郭兰兰,冯兆东,李心清,等.鄂尔多斯高原巴汗淖湖泊记录的全新世气候变化[J].科学通报,2007,52(5):584-590. |
| 55 | Xiao J L,Nakamura T,Lu H Y,et al.Holocene climate changes over the desert/loess transition of north-central China[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2002,197(1/2):11-18. |
| 56 | Lu H Y,Yi S W,Liu Z Y,et al.Variation of East Asian monsoon precipitation during the past 21 k.y. and potential CO2 forcing[J].Geology,2013,41(9):1023-1026. |
| 57 | Yang L H,Zhou J,Lai Z P,et al.Lateglacial and Holocene dune evolution in the Horqin dunefield of northeastern China based on luminescence dating[J].Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology,2010,296(1/2):44-51. |
| 58 | Gong Z J,Li S H,Sun J M,et al.Environmental changes in Hunshandake (Otindag) sandy land revealed by optical dating and multi-proxy study of dune sands[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences,2013,76:30-36. |
| 59 | Jia F F,Lu R J,Gao S Y,et al.Holocene aeolian activities in the southeastern Mu Us Desert,China[J].Aeolian Research,2015,19(B):267-274. |
| 60 | Yang X P,Zhu B Q,Wang X,et al.Late Quaternary environmental changes and organic carbon density in the Hunshandake Sandy Land,eastern Inner Mongolia,China[J].Global and Planetary Change,2008,61(1/2):70-78. |
| 61 | Yang L H,Wang T,Zhou J,et al.OSL chronology and possible forcing mechanism of dune evolution in the Horqin dunefiled in northern China since the Last Glacial Maximum[J].Quaternary Research,2012,78(2):185-196. |
| 62 | Hu C Y,Henderson G M,Huang J H,et al.Quantification of Holocene Asian monsoon rainfall from spatially separated cave records [J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2008,266(3/4):221-232. |
| 63 | Wang Y J,Cheng H,Edwards R L,et al.A high-resolution absolute-dated Late Pleistocene monsoon record from Hulu cave,China [J].Science,2001,294(29):2345-2348. |
| 64 | Wang Y J,Cheng H,Edwards R L,et al.Millennial-and orbital-scale changes in the East Asian monsoon over the past 224,000 years[J].Nature,2008,451(7182):1090-1093. |
| 65 | Dykoski C A,Edwards R L,Cheng H,et al.A high-resolution,absolute-dated Holocene and deglacial Asian monsoon record from Dongge Cave,China[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2005,233(1/2):71-86. |
| 66 | Jiang W Y,Guo Z T,Sun X J,et al.Reconstruction of climate and vegetation changes of Lake Bayanchagan (Inner Mongolia):Holocene variability of the East Asian monsoon[J].Quaternary Research,2006,65(3):411-420. |
| 67 | Zhou Y W,Han Z Y,Li X S,et al.Sandy loess records of precipitation changes and monsoon migrations in the Hunshandake Sandy Land since the Last Glacial Maximum[J].Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology,2018,33(9):945-957. |
| 68 | Liu X X,Sun Y B,Vandenberghe J,et al.Palaeoenvironmental implication of grain-size compositions of terrace deposits on the western Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Aeolian Research,2018,32:202-209. |
| 69 | Dyke A S.An outline of North American deglaciation with emphasis on central and northern Canada[J].Development Quaternary Sciences,2004,2(B):373-424. |
| 70 | Ding Z L,Liu T S,Rutter N W,et al.Ice-volume forcing of East Asian winter monsoon variations in the past 800,000 years[J].Quaternary Research,1995,44(2):149-159. |
| 71 | Ding Z L,Derbyshire E,Yang S L,et al.Stepwise expansion of desert environment across northern China in the past 3.5 Ma and implications for monsoon evolution[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2005,237(1/2):45-55. |
| 72 | Porter S C.Chinese loess record of monsoon climate during the last glacial-interglacial cycle[J].Earth-Science Reviews,2001,54(1/3):115-128. |
| 73 | Wang Y J,Cheng H,Edwards R L,et al.The Holocene Asian monsoon:link to solar changes and north Atlantic climate[J].Science,2005,308:854-857. |
| 74 | Mayewski P A,Meeker L D,Twickler M S,et al.Major features and forcing of high-latitude northern hemisphere atmospheric circulation using a 110,000-year-long glaciochemical series[J].Journal of Geophysical Research,1997,102(12):26345-26366. |
| 75 | Gowan E J,Zhang X,Khosravi S,et al.A new global ice sheet reconstruction for the past 80000 years[J].Nature Communications,2021,12:1199. |
| 76 | Chen F H,Chen S Q,Zhang X,et al.Asian dust-storm activity dominated by Chinese dynasty changes since 2000 BP[J].Nature Communications,2020,11(1):992. |
| [1] | 马启民, 王海兵, 贾晓鹏. 库布齐沙漠人工柠条(Caragana korshinskii)林地表辐射特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 43-50. |
| [2] | 马晓慧, 庞奖励, 刘小槺, 丁丹, 岳晓晓, 贾飞飞. 瓦窑沟剖面记录的早中全新世毛乌素沙地东南缘气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 71-80. |
| [3] | 马永桃, 任孝宗, 胡慧芳, 刘敏, 孟琪. 基于地理探测器的浑善达克沙地植被变化定量归因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 195-204. |
| [4] | 韩兰英, 张强, 马鹏里, 王有恒, 黄涛, 贾建英, 王鑫, 王小巍, 刘卫平, 李丹华, 卢国阳, 黄鹏程, 白冰. 气候变暖背景下黄河流域干旱灾害风险空间特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 225-234. |
| [5] | 王有恒, 谭丹, 韩兰英, 李丹华, 王鑫, 卢国阳, 林婧婧. 黄河流域气候变化研究综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 235-246. |
| [6] | 贺晓慧, 司建华, 赵春彦, 王春林, 周冬蒙. 西藏沙棘(Hippophae thibetana)潜在地理分布及其对未来气候变化的响应模拟[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 101-109. |
| [7] | 何远政, 黄文达, 赵昕, 吕朋, 王怀海. 气候变化对植物多样性的影响研究综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 59-66. |
| [8] | 林龙圳, 郑佳, 林震. 基于条件价值法(CVM)的库布齐沙漠治理支付意愿及影响因素研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(6): 190-200. |
| [9] | 邓迪, 赵泽斌, 马媛. 基于GIS的柠条锦鸡儿(Caragana korshinskii)分布模型[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(5): 74-80. |
| [10] | 韩超, 肖生春, 丁爱军, 滕泽宇. 腾格里沙漠南缘青海云杉(Picea crassifolia)和油松(Pinus tabulaeformis)年轮记录的气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 50-58. |
| [11] | 李想, 苏志珠, 马义娟, 张彩霞, 柳苗苗. 毛乌素沙地东南缘全新世气候不稳定性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 109-117. |
| [12] | 赵泽芳, 卫海燕, 郭彦龙, 栾文飞, 赵泽斌. 气候变化下的孑遗植物裸果木(Gymnocarpos przewalskii)适宜生境分布[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 125-133. |
| [13] | 魏巍, 张稳定, 陈焕盛, 任远哲, 皮冬勤, 吴剑斌, 陈婷婷, 肖林鸿, 罗保刚, 晏平仲. 库布齐沙漠治理对京津冀地区空气质量影响:2017年5月3-6日沙尘天气模拟[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(1): 77-87. |
| [14] | 马启民, 贾晓鹏, 王海兵, 李永山, 李劭宁. 气候和人为因素对植被变化影响的评价方法综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(6): 48-55. |
| [15] | 刘荔昀, 鲁瑞洁, 刘小槺. 风成沉积物色度记录的毛乌素沙漠全新世以来气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(6): 83-89. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
