中国沙漠 ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (6): 29-40.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00085
雷燕慧1( ), 丁国栋1, 李梓萌1, 迟文峰2, 高广磊1, 赵媛媛1(
), 丁国栋1, 李梓萌1, 迟文峰2, 高广磊1, 赵媛媛1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-02-10
修回日期:2021-06-28
出版日期:2021-11-20
发布日期:2021-12-17
通讯作者:
赵媛媛
作者简介:赵媛媛(E-mail: yuanyuan0402@bjfu.edu.cn)基金资助:
Yanhui Lei1( ), Guodong Ding1, Zimeng Li1, Wenfeng Chi2, Guanglei Gao1, Yuanyuan Zhao1(
), Guodong Ding1, Zimeng Li1, Wenfeng Chi2, Guanglei Gao1, Yuanyuan Zhao1( )
)
Received:2021-02-10
Revised:2021-06-28
Online:2021-11-20
Published:2021-12-17
Contact:
Yuanyuan Zhao
摘要:
监测土地利用/覆盖及生态系统服务价值变化是评估生态工程效益最直接有效的方式。以京津风沙源治理工程区为研究区,基于土地利用/覆盖变化面积和植被覆盖度等指标,从土地利用/覆盖类型转换和土地覆盖渐变两个角度揭示区域土地利用/覆盖变化过程;并运用改进的当量因子法,评估同期生态系统服务价值的变化。结果表明:区域草地面积超过总面积的一半,总体上呈现草地和耕地集中分布,林地、沙丘零散镶嵌的格局。1990—2018年,区域沙地、草地面积减少,耕地、林地面积增加;同时,沙地上表现出植被覆盖增加的渐变特征,增速为每10年约增长4.22%。同期区域生态系统服务价值呈现出先减少后增加的趋势,生态工程实施后,2010—2018年生态系统服务价值增加明显。1990—2018年,生态系统服务价值总体上增加了3 655.21亿元,其中,由土地利用/覆盖类型变化导致的价值增加量为120.53亿元,而由土地覆盖渐变导致的增加量为5 355.04亿元。土地覆盖渐变对生态系统服务价值的影响不容忽视,我们建议在生态建设过程中,不仅要重视退耕还林、未利用地造林种草等土地利用/覆盖方式的改变,更要关注草地和林地的修复和恢复,注重生态工程成果的维持和质量的提升。
中图分类号:
雷燕慧, 丁国栋, 李梓萌, 迟文峰, 高广磊, 赵媛媛. 京津风沙源治理工程区土地利用/覆盖变化及生态系统服务价值响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(6): 29-40.
Yanhui Lei, Guodong Ding, Zimeng Li, Wenfeng Chi, Guanglei Gao, Yuanyuan Zhao. Land use/cover change and its ecosystem service value response in the Beijing-Tianjin sandstorm source control project area[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(6): 29-40.
| 一级类型 | 二级类型 | 森林 | 草地 | 农田 | 水域 | 沙地 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高覆盖度 | 中覆盖度 | 低覆盖度 | 高流动性 | 低流动性 | |||||
| 供给服务 | 食物生产 | 0.33 | 0.68 | 0.43 | 0.18 | 1 | 0.53 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| 原材料生产 | 2.98 | 0.57 | 0.36 | 0.15 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.02 | |
| 调节服务 | 气体调节 | 4.32 | 2.39 | 1.5 | 0.62 | 0.72 | 0.51 | 0.07 | 0.03 |
| 气候调节 | 4.07 | 2.48 | 1.56 | 0.64 | 0.97 | 2.06 | 0.16 | 0.07 | |
| 水文调节 | 4.09 | 2.42 | 1.52 | 0.62 | 0.77 | 18.77 | 0.09 | 0.04 | |
| 废物处理 | 1.72 | 2.10 | 1.32 | 0.54 | 1.39 | 14.85 | 0.32 | 0.14 | |
| 支持服务 | 保持土壤 | 4.02 | 3.56 | 2.24 | 0.92 | 1.47 | 0.41 | 0.21 | 0.09 |
| 文化服务 | 维持生物多样性 | 4.51 | 2.97 | 1.87 | 0.77 | 1.02 | 3.43 | 0.49 | 0.22 |
| 提供美学景观 | 2.08 | 1.38 | 0.87 | 0.36 | 0.17 | 4.44 | 0.30 | 0.13 | |
| 合计 | 28.12 | 18.56 | 11.67 | 4.78 | 7.9 | 45.35 | 1.71 | 0.75 | |
表1 单位面积生态系统服务当量
Table 1 Ecosystem service equivalent per unit area
| 一级类型 | 二级类型 | 森林 | 草地 | 农田 | 水域 | 沙地 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高覆盖度 | 中覆盖度 | 低覆盖度 | 高流动性 | 低流动性 | |||||
| 供给服务 | 食物生产 | 0.33 | 0.68 | 0.43 | 0.18 | 1 | 0.53 | 0.02 | 0.01 |
| 原材料生产 | 2.98 | 0.57 | 0.36 | 0.15 | 0.39 | 0.35 | 0.05 | 0.02 | |
| 调节服务 | 气体调节 | 4.32 | 2.39 | 1.5 | 0.62 | 0.72 | 0.51 | 0.07 | 0.03 |
| 气候调节 | 4.07 | 2.48 | 1.56 | 0.64 | 0.97 | 2.06 | 0.16 | 0.07 | |
| 水文调节 | 4.09 | 2.42 | 1.52 | 0.62 | 0.77 | 18.77 | 0.09 | 0.04 | |
| 废物处理 | 1.72 | 2.10 | 1.32 | 0.54 | 1.39 | 14.85 | 0.32 | 0.14 | |
| 支持服务 | 保持土壤 | 4.02 | 3.56 | 2.24 | 0.92 | 1.47 | 0.41 | 0.21 | 0.09 |
| 文化服务 | 维持生物多样性 | 4.51 | 2.97 | 1.87 | 0.77 | 1.02 | 3.43 | 0.49 | 0.22 |
| 提供美学景观 | 2.08 | 1.38 | 0.87 | 0.36 | 0.17 | 4.44 | 0.30 | 0.13 | |
| 合计 | 28.12 | 18.56 | 11.67 | 4.78 | 7.9 | 45.35 | 1.71 | 0.75 | |
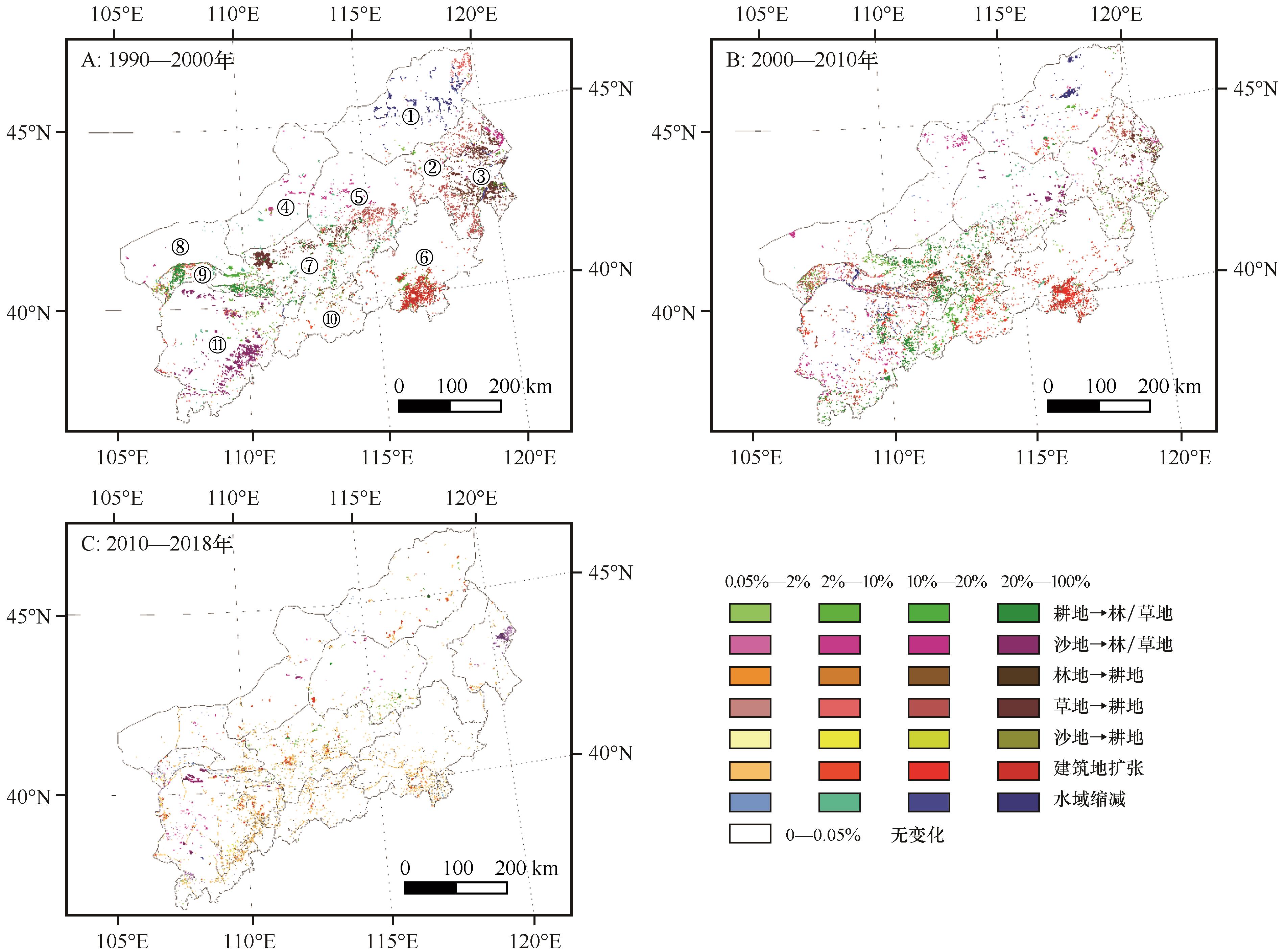
图3 京津风沙源治理工程区1990—2018年土地利用/覆盖类型变化
Fig.3 Changes in land use/cover types in the Beijing-Tianjin sandstorm source control project area from 1990 to 2018
| 地类 | 沙地 | 草地 | 耕地 | 林地 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全区 | 10.96* | 1.10 | 7.65 | -2.95 |
| 大兴安岭南部区 | -29.77** | -17.92* | -17.31* | -21.89** |
| 典型草原东区 | -31.05** | -5.18 | -4.72 | -20.67 |
| 典型草原西区 | 2.23 | 4.90 | 17.10** | 13.48* |
| 典型草原中区 | -6.83 | -1.79 | -11.05 | |
| 科尔沁沙地 | -8.14* | -14.38 | -6.86 | -6.94 |
| 浑善达克沙地 | 5.10 | -3.40 | 2.74 | 8.66 |
| 黄河灌溉区 | 11.13 | 29.48** | 22.71** | -11.28 |
| 燕山丘陵山地水源保护区 | -7.83 | 5.30 | 6.00 | 1.06 |
| 鄂尔多斯高原 | 19.48** | 24.28** | 46.20** | 34.43** |
| 晋北山地丘陵区 | 28.31** | 25.28** | 20.57** | |
| 农牧交错带区 | -38.43** | -3.60 | -3.02 | -12.01 |
表2 1990—2018年京津风沙源治理工程区及各亚区不同地类植被覆盖变化斜率(%)
Table 2 The slope of vegetation cover change of different land types in the Beijing-Tianjin sandstorm source control project area and each sub-region from 1990 to 2018
| 地类 | 沙地 | 草地 | 耕地 | 林地 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全区 | 10.96* | 1.10 | 7.65 | -2.95 |
| 大兴安岭南部区 | -29.77** | -17.92* | -17.31* | -21.89** |
| 典型草原东区 | -31.05** | -5.18 | -4.72 | -20.67 |
| 典型草原西区 | 2.23 | 4.90 | 17.10** | 13.48* |
| 典型草原中区 | -6.83 | -1.79 | -11.05 | |
| 科尔沁沙地 | -8.14* | -14.38 | -6.86 | -6.94 |
| 浑善达克沙地 | 5.10 | -3.40 | 2.74 | 8.66 |
| 黄河灌溉区 | 11.13 | 29.48** | 22.71** | -11.28 |
| 燕山丘陵山地水源保护区 | -7.83 | 5.30 | 6.00 | 1.06 |
| 鄂尔多斯高原 | 19.48** | 24.28** | 46.20** | 34.43** |
| 晋北山地丘陵区 | 28.31** | 25.28** | 20.57** | |
| 农牧交错带区 | -38.43** | -3.60 | -3.02 | -12.01 |
| 生态系统 服务价值 | 年份 | 森林 | 草地 | 农田 | 水域 | 沙地 | 总计 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高覆盖度 | 中覆盖度 | 低覆盖度 | 高流动性 | 低流动性 | ||||||
| ESV/亿元 | 1990 | 6 387.25 | 8 449.63 | 10 390.41 | 827.84 | 3 315.51 | 1 714.54 | 185.40 | 47.87 | 31 318.45 |
| 2000 | 6 405.30 | 5 644.79 | 11 729.61 | 946.75 | 3 368.87 | 1 789.86 | 163.73 | 48.40 | 30 097.31 | |
| 2010 | 7 235.87 | 5 540.25 | 10 176.80 | 1 335.99 | 3 374.98 | 1 600.82 | 190.61 | 42.77 | 29 498.09 | |
| 2018 | 7 315.39 | 20 438.16 | 1 540.79 | 479.76 | 3 349.75 | 1 667.06 | 127.18 | 55.57 | 34 973.66 | |
| 贡献率/% | 1990 | 20.39 | 26.98 | 33.18 | 2.64 | 10.59 | 5.47 | 0.59 | 0.15 | 100.00 |
| 2000 | 21.28 | 18.76 | 38.97 | 3.15 | 11.19 | 5.95 | 0.54 | 0.16 | 100.00 | |
| 2010 | 24.53 | 18.78 | 34.50 | 4.53 | 11.44 | 5.43 | 0.65 | 0.14 | 100.00 | |
| 2018 | 20.92 | 58.44 | 4.41 | 1.37 | 9.58 | 4.77 | 0.36 | 0.16 | 100.00 | |
| 变化量/亿元 | 1990—2000 | 18.05 | -2 804.84 | 1 339.20 | 118.91 | 53.36 | 75.32 | -21.67 | 0.53 | -1 221.14 |
| 2000—2010 | 830.57 | -104.54 | -1 552.81 | 389.24 | 6.11 | -189.04 | 26.88 | -5.63 | -599.22 | |
| 2010—2018 | 79.52 | 14 897.91 | -8 636.01 | -856.23 | -25.23 | 66.24 | -63.43 | 12.80 | 5 475.57 | |
| 1990—2018 | 928.14 | 11 988.53 | -8 849.62 | -348.08 | 34.24 | -47.48 | -58.22 | 7.70 | 3 655.21 | |
| 变化率/% | 1990—2000 | 0.28 | -33.19 | 12.89 | 14.36 | 1.61 | 4.39 | -11.69 | 1.11 | -3.90 |
| 2000—2010 | 12.97 | -1.85 | -13.24 | 41.11 | 0.18 | -10.56 | 16.42 | -11.63 | -1.99 | |
| 2010—2018 | 1.10 | 268.90 | -84.86 | -64.09 | -0.75 | 4.14 | -33.28 | 29.93 | 18.56 | |
| 1990—2018 | 14.53 | 141.88 | -85.17 | -42.05 | 1.03 | -2.77 | -31.40 | 16.09 | 11.67 | |
表3 各类土地利用/覆盖生态系统服务价值变化
Table 3 Changes in the ecosysterm services value of different land use/covers
| 生态系统 服务价值 | 年份 | 森林 | 草地 | 农田 | 水域 | 沙地 | 总计 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高覆盖度 | 中覆盖度 | 低覆盖度 | 高流动性 | 低流动性 | ||||||
| ESV/亿元 | 1990 | 6 387.25 | 8 449.63 | 10 390.41 | 827.84 | 3 315.51 | 1 714.54 | 185.40 | 47.87 | 31 318.45 |
| 2000 | 6 405.30 | 5 644.79 | 11 729.61 | 946.75 | 3 368.87 | 1 789.86 | 163.73 | 48.40 | 30 097.31 | |
| 2010 | 7 235.87 | 5 540.25 | 10 176.80 | 1 335.99 | 3 374.98 | 1 600.82 | 190.61 | 42.77 | 29 498.09 | |
| 2018 | 7 315.39 | 20 438.16 | 1 540.79 | 479.76 | 3 349.75 | 1 667.06 | 127.18 | 55.57 | 34 973.66 | |
| 贡献率/% | 1990 | 20.39 | 26.98 | 33.18 | 2.64 | 10.59 | 5.47 | 0.59 | 0.15 | 100.00 |
| 2000 | 21.28 | 18.76 | 38.97 | 3.15 | 11.19 | 5.95 | 0.54 | 0.16 | 100.00 | |
| 2010 | 24.53 | 18.78 | 34.50 | 4.53 | 11.44 | 5.43 | 0.65 | 0.14 | 100.00 | |
| 2018 | 20.92 | 58.44 | 4.41 | 1.37 | 9.58 | 4.77 | 0.36 | 0.16 | 100.00 | |
| 变化量/亿元 | 1990—2000 | 18.05 | -2 804.84 | 1 339.20 | 118.91 | 53.36 | 75.32 | -21.67 | 0.53 | -1 221.14 |
| 2000—2010 | 830.57 | -104.54 | -1 552.81 | 389.24 | 6.11 | -189.04 | 26.88 | -5.63 | -599.22 | |
| 2010—2018 | 79.52 | 14 897.91 | -8 636.01 | -856.23 | -25.23 | 66.24 | -63.43 | 12.80 | 5 475.57 | |
| 1990—2018 | 928.14 | 11 988.53 | -8 849.62 | -348.08 | 34.24 | -47.48 | -58.22 | 7.70 | 3 655.21 | |
| 变化率/% | 1990—2000 | 0.28 | -33.19 | 12.89 | 14.36 | 1.61 | 4.39 | -11.69 | 1.11 | -3.90 |
| 2000—2010 | 12.97 | -1.85 | -13.24 | 41.11 | 0.18 | -10.56 | 16.42 | -11.63 | -1.99 | |
| 2010—2018 | 1.10 | 268.90 | -84.86 | -64.09 | -0.75 | 4.14 | -33.28 | 29.93 | 18.56 | |
| 1990—2018 | 14.53 | 141.88 | -85.17 | -42.05 | 1.03 | -2.77 | -31.40 | 16.09 | 11.67 | |
| 生态系统 服务价值 | 年份 | 草地 | 沙地 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 原系数 | 系数修订后 | 原系数 | 系数修订后 | ||
| ESV | 1990 | 16 265.98 | 19 667.88 | 223.72 | 233.27 |
| 2000 | 16 167.62 | 18 321.15 | 219.12 | 1 212.13 | |
| 2010 | 15 631.10 | 17 053.04 | 212.78 | 233.38 | |
| 2018 | 15 562.90 | 22 458.71 | 206.36 | 182.75 | |
| 变化量 | 1990—2000 | -98.36 | -1 346.73 | -4.6 | -21.14 |
| 2000—2010 | -536.52 | -1 268.11 | -6.34 | 21.25 | |
| 2010—2018 | -68.20 | 5 405.67 | -6.42 | -50.63 | |
| 1990—2018 | -703.08 | 2 790.83 | -17.36 | -50.52 | |
表4 系数修订前后区域草地和沙地生态系统服务价值(亿元)
Table 4 The ecosystem service value of grasslands and sand dunes before and after the coefficient revision
| 生态系统 服务价值 | 年份 | 草地 | 沙地 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 原系数 | 系数修订后 | 原系数 | 系数修订后 | ||
| ESV | 1990 | 16 265.98 | 19 667.88 | 223.72 | 233.27 |
| 2000 | 16 167.62 | 18 321.15 | 219.12 | 1 212.13 | |
| 2010 | 15 631.10 | 17 053.04 | 212.78 | 233.38 | |
| 2018 | 15 562.90 | 22 458.71 | 206.36 | 182.75 | |
| 变化量 | 1990—2000 | -98.36 | -1 346.73 | -4.6 | -21.14 |
| 2000—2010 | -536.52 | -1 268.11 | -6.34 | 21.25 | |
| 2010—2018 | -68.20 | 5 405.67 | -6.42 | -50.63 | |
| 1990—2018 | -703.08 | 2 790.83 | -17.36 | -50.52 | |
| 年份 | 类型变化 | 土地覆盖渐变 | 净变化 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1990—2000 | 146.73 | -1 367.87 | -221.14 |
| 2000—2010 | 647.64 | -1 246.86 | -599.22 |
| 2010—2018 | 120.53 | 5 355.04 | 5 475.57 |
| 1990—2018 | 914.90 | 2 740.31 | 3 655.21 |
表5 土地利用/覆盖变化导致的生态系统服务价值(亿元)变化
Table 5 Changes in the ecosystem service value caused by land use/cover type conversion and land cover modification
| 年份 | 类型变化 | 土地覆盖渐变 | 净变化 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1990—2000 | 146.73 | -1 367.87 | -221.14 |
| 2000—2010 | 647.64 | -1 246.86 | -599.22 |
| 2010—2018 | 120.53 | 5 355.04 | 5 475.57 |
| 1990—2018 | 914.90 | 2 740.31 | 3 655.21 |
| 年份 | 措施 | 区域 | 目标 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000—2005 | 封沙育林、农防林、荒山荒地造林 | 内蒙古克什克腾旗 | 治理沙源 | http://www.nmg.gov.cn/ |
| 2013 | 人工造林、飞播造林、飞播牧草,工程固沙 | 陕西省 | 加强林草植被保护 | http://www.shaanxi.gov.cn/ |
| 2015 | “植树造林绿化”工程 | 山西省 | 构筑京津绿色屏障 | http://lcj.shanxi.gov.cn/ |
| 2018 | “人工造林”项目 | 内蒙古鄂尔多斯市 | 提高贫困农牧民在生态建设中的参与度、受益度 | http://www.ordos.gov.cn/ |
| 2020 | 探索建立“草长制” | 河北省 | 加强草原生态保护,构筑生态安全屏障 | http://lycy.hebei.gov.cn/ |
表6 京津风沙源治理工程区生态工程措施
Table 6 Ecological engineering measures in the Beijing-Tianjin sandstorm source control project area
| 年份 | 措施 | 区域 | 目标 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000—2005 | 封沙育林、农防林、荒山荒地造林 | 内蒙古克什克腾旗 | 治理沙源 | http://www.nmg.gov.cn/ |
| 2013 | 人工造林、飞播造林、飞播牧草,工程固沙 | 陕西省 | 加强林草植被保护 | http://www.shaanxi.gov.cn/ |
| 2015 | “植树造林绿化”工程 | 山西省 | 构筑京津绿色屏障 | http://lcj.shanxi.gov.cn/ |
| 2018 | “人工造林”项目 | 内蒙古鄂尔多斯市 | 提高贫困农牧民在生态建设中的参与度、受益度 | http://www.ordos.gov.cn/ |
| 2020 | 探索建立“草长制” | 河北省 | 加强草原生态保护,构筑生态安全屏障 | http://lycy.hebei.gov.cn/ |
| 1 | 陈杰,赵素平,殷代英,等.沙尘天气过程对中国北方城市空气质量的影响[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(2):423-430. |
| 2 | Zhao Y,Xin Z,Ding G,et al.Spatiotemporal variation in the occurrence of sand-dust events and its influencing factors in the Beijing-Tianjin Sand Source Region,China,1982-2013[J].Regional Environmental Change,2018,18(8):2433-2444. |
| 3 | 魏巍,张稳定,陈焕盛,等.库布齐沙漠治理对京津冀地区空气质量影响:2017年5月3-6日沙尘天气模拟[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(1):77-87. |
| 4 | Bryan B A,Gao L,Ye Y,et al.China's response to a national land-system sustainability emergency[J].Nature,2018,559(12):193-204. |
| 5 | 吴丹,巩国丽,邵全琴,等.京津风沙源治理工程生态效应评估[J].干旱区资源与环境,2016,30(11):117-123. |
| 6 | 黄麟,吴丹,孙朝阳.基于规划目标的京津风沙源治理区生态保护与修复效应[J].生态学报,2020,40(6):1923-1932. |
| 7 | Lambin E,Geist Helmut J.Land-Use and Land-Cover Change:Local Processes and Global Impacts[M].Switzerland:Springer,2006:11-25. |
| 8 | Steffen W,Sanderson A,Tyson P D,et al.Global Change and the Earth System:A Planet under Pressure[M].Berlin,Germany:Springer,2004:32-36. |
| 9 | 盛晓雯,曹银贵,周伟,等.京津冀地区土地利用变化对生态系统服务价值的影响[J].中国农业资源与区划,2018,39(6):79-86. |
| 10 | Costanza R,d’Arge R,de Groot R,et al.The value of the world’s ecosystem services and nature[J].Nature,1997,387(15):253-260. |
| 11 | 欧阳志云,王效科,苗鸿.中国陆地生态系统服务功能及其生态经济价值的初步研究[J].生态学报,1999,19(5):19-25. |
| 12 | 欧阳志云,王如松,赵景柱.生态系统服务功能及其生态经济价值评价[J].应用生态学报,1999,10(5):635-640. |
| 13 | 谢高地,张钇锂,鲁春霞,等.中国自然草地生态系统服务价值[J].自然资源学报,2001,16(1):47-53. |
| 14 | 谢高地,鲁春霞,冷允法,等.青藏高原生态资产的价值评估[J].自然资源学报, 2003,18(2):189-196. |
| 15 | 谢高地,肖玉.农田生态系统服务及其价值的研究进展[J].中国生态农业学报,2013,21(6):645-651. |
| 16 | 谢高地,张彩霞,张雷明,等.基于单位面积价值当量因子的生态系统服务价值化方法改进[J].自然资源学报,2015,30(8):1243-1254. |
| 17 | 郝林华,何帅,陈尚,等.海洋生态系统调节服务价值评估方法及应用:以温州市为例[J].生态学报,2020,40(13):4264-4278. |
| 18 | 严恩萍,林辉,党永峰,等.2000-2012年京津风沙源治理区植被覆盖时空演变特征[J].生态学报,2014,34(17):5007-5020. |
| 19 | 崔晓,赵媛媛,丁国栋,等.京津风沙源治理工程区植被对沙尘天气的时空影响[J].农业工程学报,2018,34(12):171-179. |
| 20 | 迟文峰,匡文慧,贾静,等.京津风沙源治理工程区LUCC及土壤风蚀强度动态遥感监测研究[J].遥感技术与应用,2018,33(5):965-974. |
| 21 | 李愈哲,樊江文,于海玲.京津风沙源治理工程不同恢复措施对草地恢复过程的差异性影响[J].草业学报,2018,27(5):1-14. |
| 22 | Zhao Y,Chi W,Kuang W,et al.Ecological and environmental consequences of ecological projects in the Beijing-Tianjin sand source region[J].Ecological Indicators,2020,11(2):106-111. |
| 23 | Wu Z,Wu J,Liu J,et al.Increasing terrestrial vegetation activity of ecological restoration program in the Beijing-Tianjin Sand Source Region of China[J].Ecological Engineering,2013,5(2):37-50. |
| 24 | Yang X,Xu B,Jin Y,et al.Remote sensing monitoring of grassland vegetation growth in the Beijing-Tianjin sandstorm source project area from 2000 to 2010[J].Ecological Indicators,2014,44(4):244-252. |
| 25 | 李屹峰,罗跃初,刘纲,等.土地利用变化对生态系统服务功能的影响:以密云水库流域为例[J].生态学报,2013,33(3):726-736. |
| 26 | 江凌,肖燚,饶恩明,等.内蒙古土地利用变化对生态系统防风固沙功能的影响[J].生态学报,2016,36(12):3734-3747. |
| 27 | 吴波,李晓松,刘文,等.京津风沙源工程区沙漠化防治区划与治理对策研究[J].林业科学,2006,52(10):65-70. |
| 28 | Liu J,Kuang W,Zhang Z,et al.Spatiotemporal characteristics,patterns,and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s[J].Journal of Geography Sinica,2014,24(2):195-210. |
| 29 | Liu J,Ning J,Kuang W,et al.Spatiotemporal patterns and characteristics of land-use change in China during 2010-2015[J].Acta Geography Sinica,2018,73(5):789-802. |
| 30 | Tucker C J,Pinzon J E,Brown M E,et al.An extended AVHRR 8-km NDVI dataset compatible with MODIS and SPOT vegetation NDVI data[J].International Journal of Remote Sensing,2005,26(20):4485-4498. |
| 31 | Holben B N.Characteristics of maximum value composite images from temporal AVHRR data[J].International Journal of Remote Sensing,1986,7(11):1417-1434. |
| 32 | Gutman G,Ignatov A.The derivation of the green vegetation fraction from NOAA/AVHRR data for use in numerical weather prediction models[J].International Journal of Remote Sensing,1998,19(8):1533-1543. |
| 33 | 何立恒,周寅康,杨强.延安市2000—2013年植被覆盖时空变化及特征分析[J].干旱区资源与环境,2015,29(11):174-179. |
| 34 | 史培军,陈晋,潘耀忠.深圳市土地利用变化机制分析[J].地理学报,2000,67(2):151-160. |
| 35 | Zhao Y,He C,Zhang Q.Monitoring vegetation dynamics by coupling linear trend analysis with change vector analysis:a case study in the Xilingol steppe in northern China[J].International Journal of Remote Sensing,2012,33(1):287-308. |
| 36 | Millennium Ecosystem Assessment.Ecosystems and Human Well-being:Synthesis[M].Washington DC,USA:Island Press,2005:5-10. |
| 37 | 王希义,彭淑贞,徐海量,等.基于生物量的塔里木河下游胡杨(Populus euphratica)生态服务价值评估[J].生态学报,2019,39(4):1441-1451. |
| 38 | 赖炽敏,赖日文,薛娴,等.基于植被盖度和高度的不同退化程度高寒草地地上生物量估算[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(5):127-134. |
| 39 | 刘纪远,邵全琴,樊江文.三江源区草地生态系统综合评估指标体系[J].地理研究,2009,28(2):273-283. |
| 40 | 董治宝,陈渭南,李振山,等.植被对土壤风蚀影响作用的实验研究[J].土壤侵蚀与水土保持学报,1996,10(2):1-8. |
| 41 | 谢高地,甄霖,鲁春霞,等.一个基于专家知识的生态系统服务价值化方法[J].自然资源学报,2008,23(5):911-919. |
| 42 | 傅伯杰,张立伟.土地利用变化与生态系统服务:概念、方法与进展[J].地理科学进展,2014,33(4):441-446. |
| 43 | 邹欣怡,赵伟,蒲海霞.三峡库区重庆段土地利用转型及生态服务功能价值时空分异特征[J].水土保持研究,2021,28(2):267-275. |
| 44 | 孙斌,高志海,王红岩,等.近30年京津风沙源区气候干湿变化分析[J].干旱区资源与环境,2014,28(11):164-170. |
| 45 | 汪滨,张志强.黄土高原典型流域退耕还林土地利用变化及其合理性评价[J].农业工程学报,2017,33(7):235-245. |
| 46 | 黄露,周伟,李浩然,等.土地利用/覆被变化对鄂尔多斯市草地生态系统净初级生产力的影响[J].水土保持通报,2018,38(4):46-52. |
| [1] | 杨洁, 谢保鹏, 张德罡. 黄河流域生态系统服务权衡协同关系时空异质性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(6): 78-87. |
| [2] | 马晓慧, 庞奖励, 刘小槺, 丁丹, 岳晓晓, 贾飞飞. 瓦窑沟剖面记录的早中全新世毛乌素沙地东南缘气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 71-80. |
| [3] | 张小梅, 靳鹤龄, 刘冰. 末次盛冰期以来库布齐沙漠环境变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 81-93. |
| [4] | 韩梦涛, 涂建军, 徐桂萍, 姜莉. 黄河流域水域生态系统服务与经济发展时空协调性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 167-176. |
| [5] | 马永桃, 任孝宗, 胡慧芳, 刘敏, 孟琪. 基于地理探测器的浑善达克沙地植被变化定量归因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 195-204. |
| [6] | 韩兰英, 张强, 马鹏里, 王有恒, 黄涛, 贾建英, 王鑫, 王小巍, 刘卫平, 李丹华, 卢国阳, 黄鹏程, 白冰. 气候变暖背景下黄河流域干旱灾害风险空间特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 225-234. |
| [7] | 王有恒, 谭丹, 韩兰英, 李丹华, 王鑫, 卢国阳, 林婧婧. 黄河流域气候变化研究综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(4): 235-246. |
| [8] | 贺晓慧, 司建华, 赵春彦, 王春林, 周冬蒙. 西藏沙棘(Hippophae thibetana)潜在地理分布及其对未来气候变化的响应模拟[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 101-109. |
| [9] | 张亦然, 刘廷玺, 童新, 段利民, 王昕. 基于U型神经网络的沙丘-草甸相间地区无人机影像植被覆盖度提取及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 16-24. |
| [10] | 李骊, 张青青, 王雅梅, 李宏, 赵新风. 2000—2018年克孜河流域生态系统脆弱性、服务功能价值及风险评价[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(2): 164-172. |
| [11] | 王旭洋, 李玉霖, 连杰, 段育龙, 王立龙. 半干旱典型风沙区植被覆盖度演变与气候变化的关系及其对生态建设的意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 183-194. |
| [12] | 何远政, 黄文达, 赵昕, 吕朋, 王怀海. 气候变化对植物多样性的影响研究综述[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(1): 59-66. |
| [13] | 曹永香, 毛东雷, 蔡富艳, 王雪梅, 开买尔古丽·阿不来提null, 苏松领. 新疆策勒绿洲化进程中典型下垫面的小气候空间差异[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(6): 180-189. |
| [14] | 邓迪, 赵泽斌, 马媛. 基于GIS的柠条锦鸡儿(Caragana korshinskii)分布模型[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(5): 74-80. |
| [15] | 韩超, 肖生春, 丁爱军, 滕泽宇. 腾格里沙漠南缘青海云杉(Picea crassifolia)和油松(Pinus tabulaeformis)年轮记录的气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 50-58. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
