中国沙漠 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 32-43.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00090
胡荻1,2a( ), 黄宁2a,2b, 裴斌斌2a,2b, Pakzad Rezaali2a,2b, 张洁2a,2b(
), 黄宁2a,2b, 裴斌斌2a,2b, Pakzad Rezaali2a,2b, 张洁2a,2b( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-20
修回日期:2024-07-10
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2025-01-13
通讯作者:
张洁
作者简介:张洁(E-mail: zhang-j@lzu.edu.cn)基金资助:
Di Hu1,2a( ), Ning Huang2a,2b, Binbin Pei2a,2b, Pakzad Rezaali2a,2b, Jie Zhang2a,2b(
), Ning Huang2a,2b, Binbin Pei2a,2b, Pakzad Rezaali2a,2b, Jie Zhang2a,2b( )
)
Received:2024-05-20
Revised:2024-07-10
Online:2025-01-20
Published:2025-01-13
Contact:
Jie Zhang
摘要:
基于欧拉-拉格朗日模型研究了风沙环境中低矮建筑的风压分布特征。结果表明:风场中沙颗粒的存在减小了平均风速,增大脉动风速,沙粒运动使小尺度涡的能量增加;与净风场相比,挟沙风场中的平均风压系数无明显变化,脉动风压系数增大显著;沙粒的扰动使湍流脉动增强、气流不稳定性增加,屋面的极值风压系数增大6%~10%,且屋面测点间的风压相关性有增大趋势,局部联动出现负压极值而造成围护结构破坏的概率增加;0°和45°风向角模型的非高斯区域均增大50%以上,因此沙尘暴环境中有更多区域的围护结构易发生局部撕裂破坏。
中图分类号:
胡荻, 黄宁, 裴斌斌, Pakzad Rezaali, 张洁. 沙尘暴环境中低矮建筑风压特性的数值研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(1): 32-43.
Di Hu, Ning Huang, Binbin Pei, Pakzad Rezaali, Jie Zhang. Numerical simulation study on the wind pressure characteristics of low-rise buildings in sandstorm environment[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(1): 32-43.
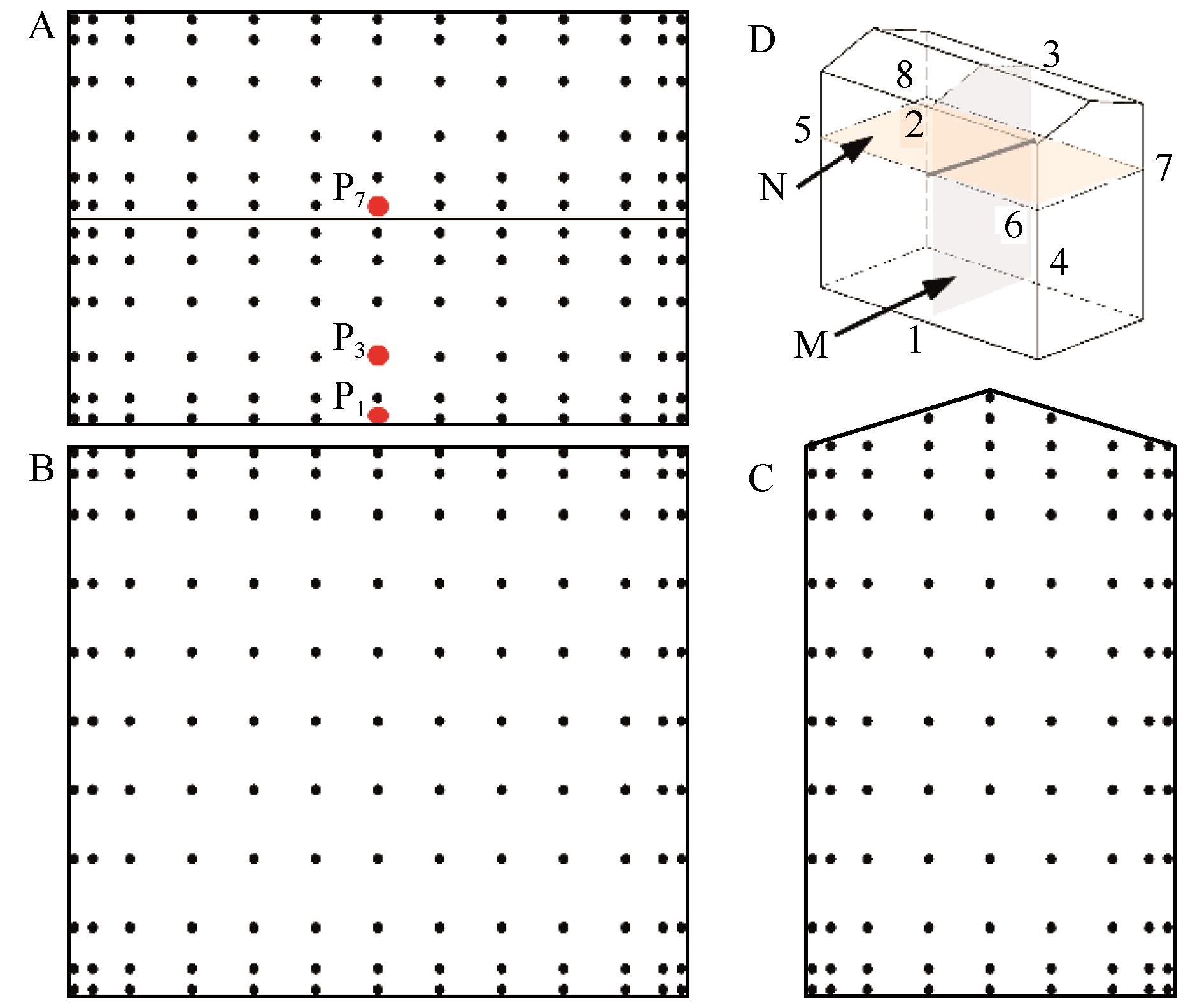
图3 屋面(A)、迎(背)风面(B)、两侧面(C)的测点布置及M截面(1-2-3-4)、N截面(5-6-7-8)定义(D)
Fig.3 Survey point layout on the roof (A), windward side and leeward side (B), and two sides (C), and two sections are defined for the ensuing analyses (D): section M (1-2-3-4) and section N (5-6-7-8)
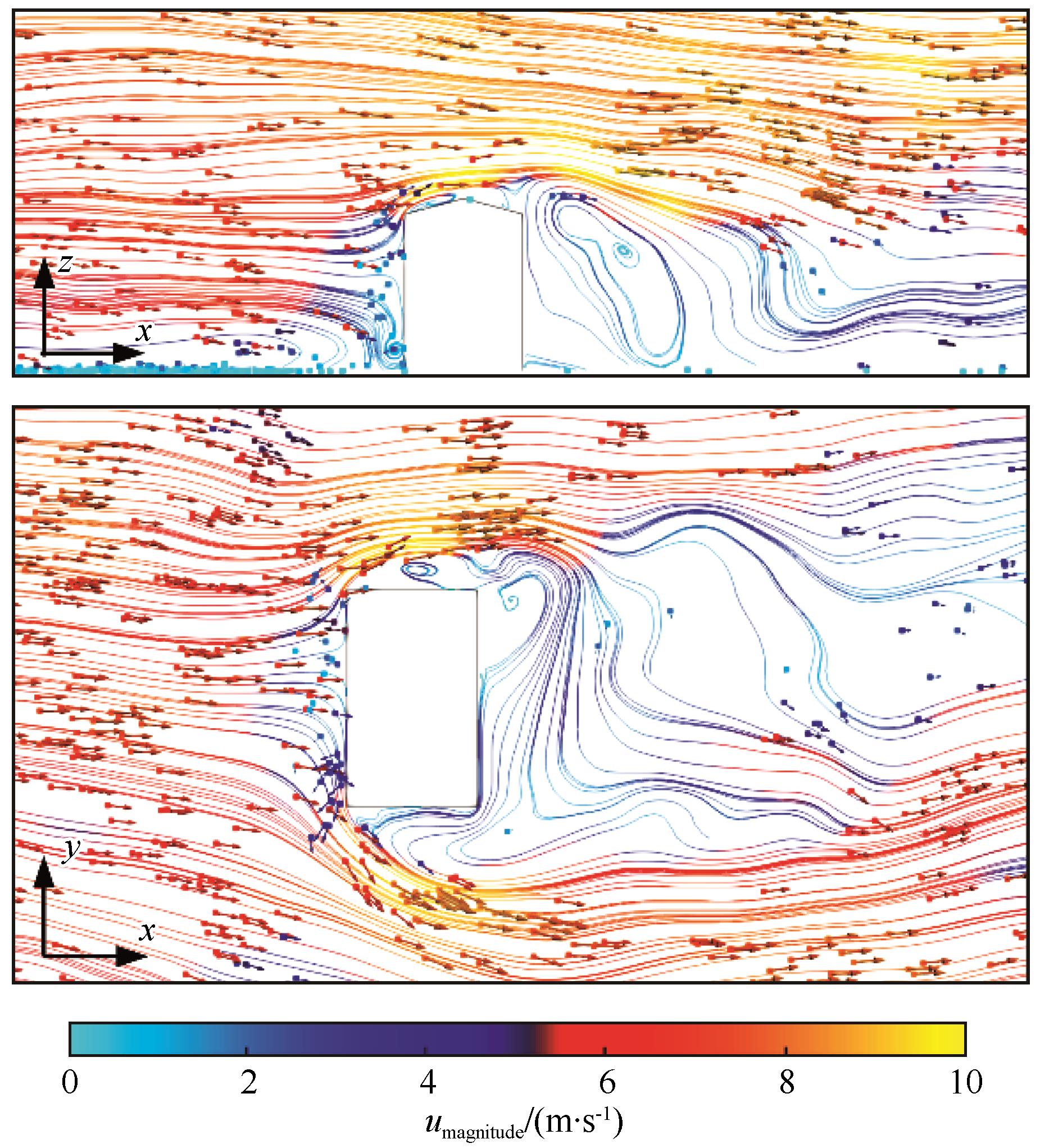
图8 0°风向角模型立面(A)、0.6L高水平面(B)瞬时风场速度流线和颗粒速度矢量图
Fig.8 Instantaneous streamlines and particle velocity vector diagrams on symmetric (A) and 0.6L horizontal plane (B) at 0° wind angle
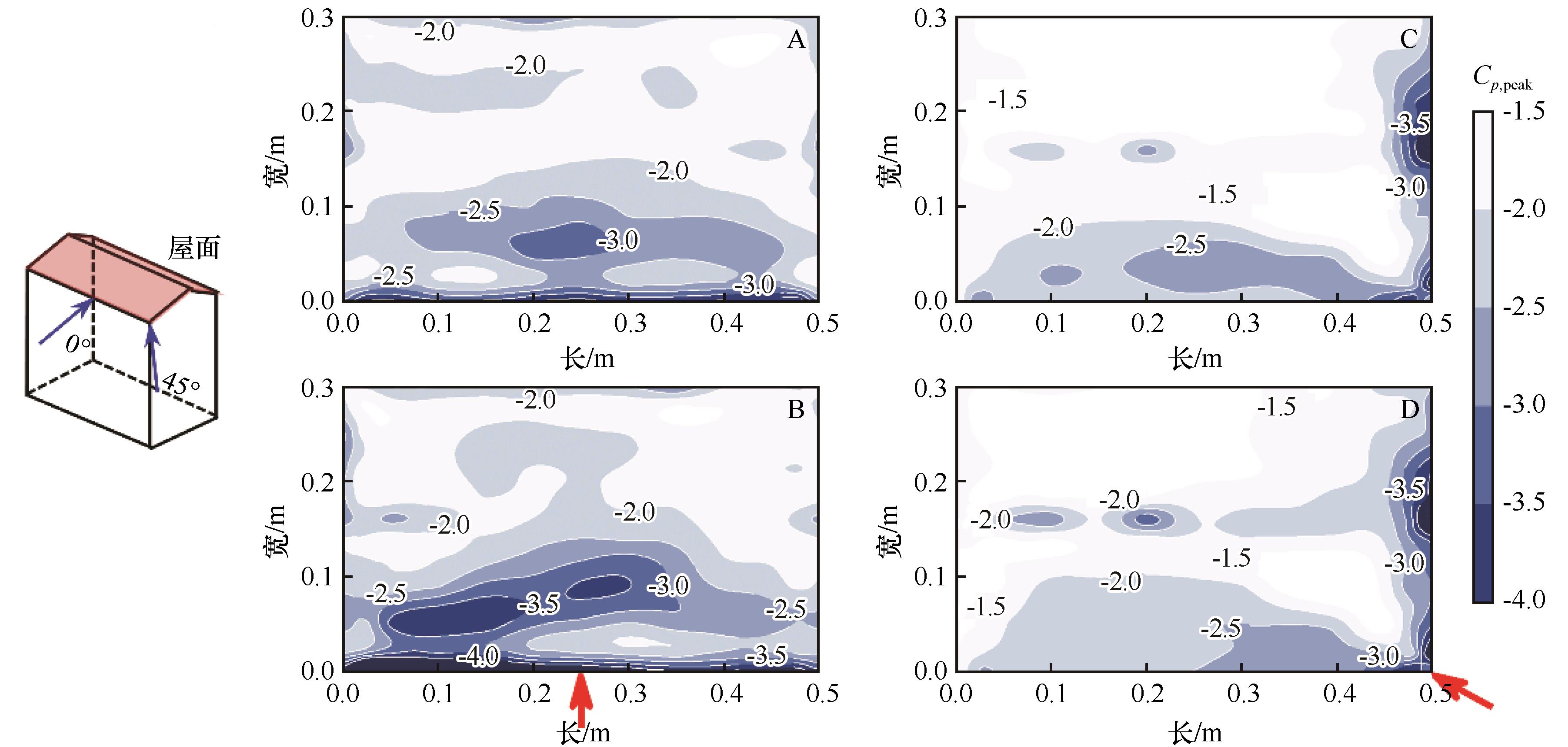
图9 7.98 I(A,0°)、7.98 S(B,0°)、12.65 I(C,45°)、12.65 S(D,45°)下屋面极值风压系数
Fig.9 The peak wind pressure coefficients of the roof at 7.98 I (A,0°), 7.98 S (B,0°), 12.65 I (C,45°) and 12.65 S (D,45°)
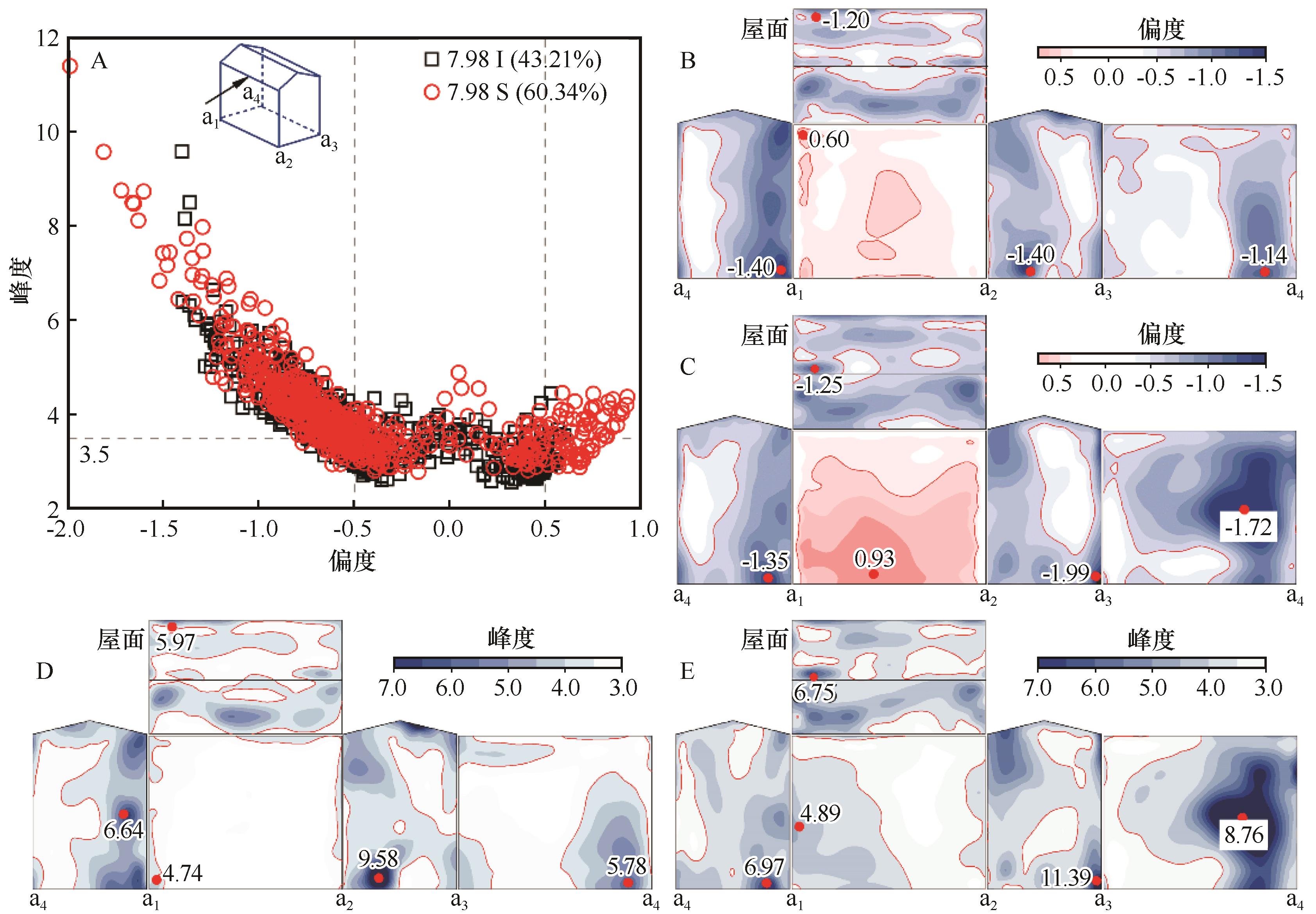
图11 0°风向角偏度峰度(A)、7.98 I偏度(B)、7.98 S偏度(C)、7.98 I峰度(D)、7.98 S峰度(E)统计
Fig.11 Statistical results of Skewness and Kurtosis (A), Skewness for 7.98 I (B), Skewness for 7.98 S (C), Kurtosis for 7.98 I (D), and Kurtosis for 7.98 S (E) at 0° wind angle
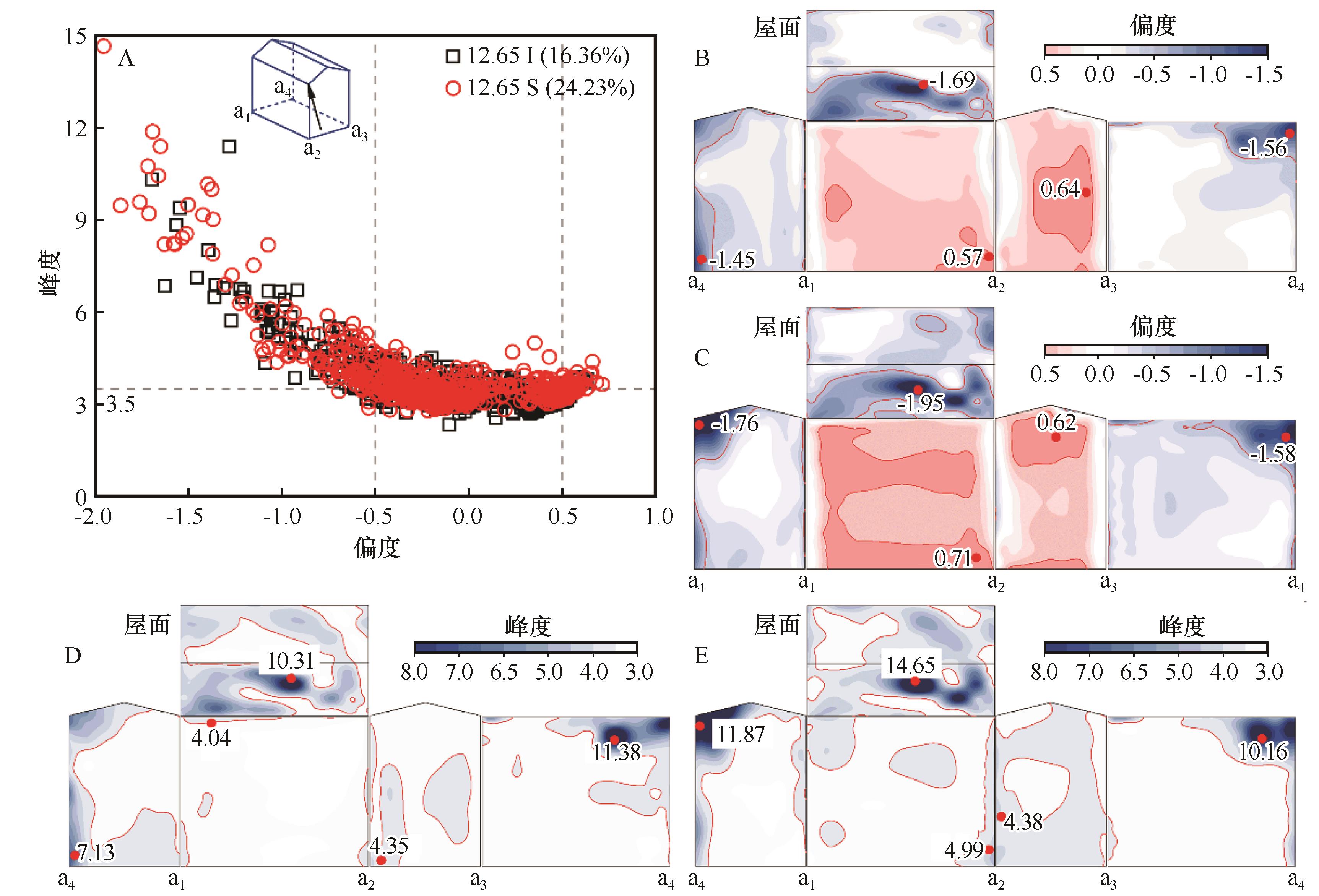
图12 45°风向角偏度峰度(A)、12.65 I偏度(B)、12.65 S偏度(C)、12.65 I峰度(D)、12.65 S峰度(E)统计
Fig.12 Statistical results of Skewness and Kurtosis (A), Skewness for 12.65 I (B), Skewness for 12.65 S (C), Kurtosis for 12.65 I (D), and Kurtosis for 12.65 S (E) at 45° wind angle
| 风向角 | 偏度 | 峰度 |
|---|---|---|
| 0° | 0.004 | 3.75×10-15 |
| 45° | 3.29×10-6 | 7.72×10-9 |
表1 显著性检验的 P 值结果
Table 1 P-values of significance test
| 风向角 | 偏度 | 峰度 |
|---|---|---|
| 0° | 0.004 | 3.75×10-15 |
| 45° | 3.29×10-6 | 7.72×10-9 |
| 1 | Saracoglu B O, Ohunakin O S, Adelekan D S,et al.A framework for selecting the location of very large photovoltaic solar power plants on a global/supergrid[J].Energy Reports,2018,4:586-602. |
| 2 | 国家发展改革委,国家能源局.以沙漠、戈壁、荒漠地区为重点的大型风电光伏基地规划布局方案[EB/OL].[2022-03-07].. |
| 3 | Cao S, Wang J.Statistical summary and case studies of strong wind damage in China[J].Journal of Disaster Research,2013,8(6):1096-1102. |
| 4 | 贺沅平,张云伟,顾兆林.特强沙尘暴灾害性天气的研究及展望[J].中国环境科学,2021,41(8):3511-3522. |
| 5 | Cao S.Typhoon and tornado induced damages in China[J].Wind Engineers,JAWE,2015,40(3):261-265. |
| 6 | Banks D, Meroney R N, Sarkar P P,et al.Flow visualization of conical vortices on flat roofs with simultaneous surface pressure measurement[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2000,84(1):65-85. |
| 7 | Huang P, Tao L, Gu M,et al.Wind effects of architectural details on gable-roofed low-rise buildings in southeastern coast of China[J].Advances in Structural Engineering,2014,17(11):1551-1565. |
| 8 | Razavi A, Sarkar P P.Tornado-induced wind loads on a low-rise building:influence of swirl ratio,translation speed and building parameters[J].Engineering Structures,2018,167:1-12. |
| 9 | Haines M, Taylor I.Numerical investigation of the flow field around low-rise buildings due to a downburst event using large eddy simulation[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2018,172:12-30. |
| 10 | Huang B, Li Z, Zhao Z,et al.Near-ground impurity-free wind and wind-driven sand of photovoltaic power stations in a desert area[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2018,179:483-502. |
| 11 | Huang B, Li Z, Zhang Z,et al.Study on flow field characteristics in sandstorm conditions using wind tunnel test[J].Atmosphere,2022,13(3):446. |
| 12 | Huang B, Li Z, Gong B,et al.Study on the sandstorm load of low-rise buildings via wind tunnel testing[J].Journal of Building Engineering,2023,65:105821. |
| 13 | Versteeg H K, Malalasekera W.An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics:The Finite Volume Method[M].London,UK:Pearson Education,2007. |
| 14 | 张默.基于FLUENT的建筑物风沙两相流场数值模拟[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2008. |
| 15 | 白江涛.风沙两相流绕圆柱工程结构的数值模拟[D].兰州:兰州大学,2020. |
| 16 | Valentine J R, Decker R A.A Lagrangian-Eulerian scheme for flow around an airfoil in rain[J].International Journal of Multiphase Flow,1995,21(4):639-648. |
| 17 | 陈峥,许晨豪,蒋崇文.建筑表面沙粒撞击压计算方法研究[C]//中国力学学会,北京理工大学.中国力学大会暨庆祝中国力学学会成立60周年大会论文集,2017:597-604. |
| 18 | Zhang Z, Chen Q.Comparison of the Eulerian and Lagrangian methods for predicting particle transport in enclosed spaces[J].Atmospheric Environment,2007,41(25):5236-5248. |
| 19 | Kaufmann A, Moreau M, Simonin O,et al.Comparison between Lagrangian and mesoscopic Eulerian modelling approaches for inertial particles suspended in decaying isotropic turbulence[J].Journal of Computational Physics,2008,227(13):6448-6472. |
| 20 | Zheng X, Feng S, Wang P.Modulation of turbulence by saltating particles on erodible bed surface[J].Journal of Fluid Mechanics,2021,918:A16. |
| 21 | Xu B, Zhang J, Huang N,et al.Characteristics of turbulent aeolian sand movement over straw checkerboard barriers and formation mechanisms of their internal erosion form[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2018,123(13):6907-6919. |
| 22 | Yamamoto Y, Potthoff M, Tanaka T,et al.Large-eddy simulation of turbulent gas-particle flow in a vertical channel:effect of considering inter-particle collisions[J].Journal of Fluid Mechanics,2001,442:303-334. |
| 23 | Kok J F, Renno N O.A comprehensive numerical model of steady state saltation (COMSALT)[J].Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres,2009,114(D17):17204. |
| 24 | Elghobashi S.On predicting particle-laden turbulent flows[J].Applied Scientific Research,1994,52:309-329. |
| 25 | Clift R, Grace J R, Weber M E.Bubbles,drops,and particles[M].New York,USA:Academic Press,1978. |
| 26 | Liu H, He X, Zheng X.Amplitude modulation in particle-laden atmospheric surface layers[J].Journal of Fluid Mechanics,2023,957:A14. |
| 27 | Blott S J, Pye K.Particle size distribution analysis of sand-sized particles by laser diffraction:an experimental investigation of instrument sensitivity and the effects of particle shape[J].Sedimentology,2006,53(3):671-685. |
| 28 | Tominaga Y, Mochida A, Yoshie R,et al.AIJ guidelines for practical applications of CFD to pedestrian wind environment around buildings[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2008,96(10/11):1749-1761. |
| 29 | Melaku A F, Bitsuamlak G T.A divergence-free inflow turbulence generator using spectral representation method for large-eddy simulation of ABL flows[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2021,212:104580. |
| 30 | Cabot W, Moin P.Approximate wall boundary conditions in the large-eddy simulation of high Reynolds number flow[J].Flow,Turbulence and Combustion,2000,63:269-291. |
| 31 | 陶文铨.数值传热学[M].西安:西安交通大学出版社,2001. |
| 32 | Hu D, Zhang J, Pakzad R,et al.A numerical study on load effects of low-rise buildings in a wind-blown sand environment[J].Journal of Building Engineering,2024:108610. |
| 33 | Spalart P R, Deck S, Shur M L,et al.A new version of detached-eddy simulation,resistant to ambiguous grid densities[J].Theoretical and Computational Fluid Dynamics,2006,20:181-195. |
| 34 | Levitan M L, Mehta K C, Vann W P,et al.Field measurements of pressures on the Texas Tech building[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,1991,38(2/3):227-234. |
| 35 | Ko N H, You K P, Kim Y M.The effect of non-Gaussian local wind pressures on a side face of a square building[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2005,93(5):383-397. |
| 36 | Wang G, Gu H, Zheng X.Large scale structures of turbulent flows in the atmospheric surface layer with and without sand[J].Physics of Fluids,2020,32(10):106604. |
| 37 | Zhang W, Wang Y, Lee S J.Simultaneous PIV and PTV measurements of wind and sand particle velocities[J].Experiments in Fluids,2008,45(2):241-256. |
| 38 | Li B, McKenna Neuman C.Boundary-layer turbulence characteristics during aeolian saltation[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2012,39(11):L052234. |
| 39 | Balachandar S, Eaton J K.Turbulent dispersed multiphase flow[J].Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics,2010,42:111-133. |
| 40 | Vasaturo R, Kalkman I, Blocken B,et al.Large eddy simulation of the neutral atmospheric boundary layer:performance evaluation of three inflow methods for terrains with different roughness[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2018,173:241-261. |
| 41 | Baskaran B A, Molleti S, Roodvoets D.Understanding low-sloped roofs under hurricane charley from field to practice[J].Journal of ASTM International,2007,4(10):1-13. |
| 42 | Mahmood M.Experiments to study turbulence and flow past a low-rise building at oblique incidence[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,2011,99(5):560-572. |
| 43 | Kumar K S, Stathopoulos T.Power spectra of wind pressures on low building roofs[J].Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics,1998,74:665-674. |
| 44 | Kumar K S, Stathopoulos T.Wind loads on low building roofs:a stochastic perspective[J].Journal of Structural Engineering,2000,126(8):944-956. |
| [1] | 韩超信, 韩永翔, 李嘉欣. 弱风背景下阵风起沙对大气沙尘气溶胶总量的贡献[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(1): 259-265. |
| [2] | 王志刚, 贾若尘, 罗凤敏, 刘明虎, 刘芳, 巴超群, 刘志民. 沙尘热动力机制与农田防护林抑尘机理[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 116-122. |
| [3] | 王伊蒙, 范亚秋, 龙川, 柳本立. 基于文献记录的敦煌地区历史时期沙尘天气序列重建[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(2): 162-171. |
| [4] | 丁涵泳, 康汉青, 吕晶晶. 土壤湿度产品对2021年3月华北强沙尘暴模拟结果的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(2): 172-184. |
| [5] | 廖承贤, 王海兵, 刘茜雅, 李悦. 以计算流体动力学模型(CFD)模拟的戈壁地表风沙两相流运动特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(6): 71-78. |
| [6] | 李亚云, 成巍, 王宁, 李欣, 高睿. 塔克拉玛干沙漠和戈壁沙漠春季沙尘暴特征及其气象影响因素对比[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 1-9. |
| [7] | 常凡, 胡伟伟, 李兴财. 无砟轨道防沙挡板减沙效果的数值模拟研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 98-106. |
| [8] | 张正偲, 潘凯佳, 张焱, 韩兰英. 中国西北戈壁区沙尘暴过程中近地层风沙运动特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 130-138. |
| [9] | 陈京平, 余子莹, 杨帆, 王蜜, 胡涵, 倪观忠, 高鑫, 王鑫. 塔克拉玛干沙漠腹地沙尘暴和地表沙物质粒度特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 150-158. |
| [10] | 秦豪君, 杨晓军, 马莉, 王一丞, 傅朝, 张君霞, 陆正奇. 2000—2020年中国西北地区区域性沙尘暴特征及成因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(6): 53-64. |
| [11] | 史忠林, 张信宝, 张润川. 2021年“3·15”沙尘暴沙尘来源核素示踪研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(2): 1-5. |
| [12] | 柳本立, 彭婉月, 刘树林, 杨婷. 2021年3月中旬东亚中部沙尘天气地面起尘量及源区贡献率估算[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(1): 79-86. |
| [13] | 李玲萍, 李岩瑛, 李晓京, 王博, 胡丽莉. 河西走廊不同强度冷锋型沙尘暴环流和动力特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(5): 219-228. |
| [14] | 王娟, 李兴财. 沙尘暴过程中5~7 000 m高度大气电场及其对颗粒带电量影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(1): 23-28. |
| [15] | 蒋盈沙, 高艳红, 潘永洁, 李霞. 青藏高原及其周边区域沙尘天气的时空分布特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(4): 83-91. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
