中国沙漠 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 47-60.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00146
收稿日期:2024-08-22
修回日期:2024-10-30
出版日期:2025-03-20
发布日期:2025-03-26
通讯作者:
徐志伟
作者简介:程星雨(2000—),男,浙江杭州人,硕士研究生,研究方向为沙尘遥感。E-mail: 502022270005@smail.nju.edu.cn
基金资助:
Xingyu Cheng1( ), Zhiwei Xu1(
), Zhiwei Xu1( ), Yan Yu2, Xiaoxiao Zhang3
), Yan Yu2, Xiaoxiao Zhang3
Received:2024-08-22
Revised:2024-10-30
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-26
Contact:
Zhiwei Xu
摘要:
沙尘是地球表层系统的活跃媒介,对全球气候变化响应敏感,能够通过一系列反馈作用影响全球辐射、能量平衡和物质循环。近年来,越来越多的卫星遥感产品被用于监测沙尘活动,例如沙尘气溶胶光学厚度(DOD)。然而,包括DOD在内的基于遥感反演的多种沙尘指数与沙尘活动强度的关系仍然缺少量化表征。利用中国北方沙尘暴观测站点资料和《沙尘天气年鉴》等数据,对2001—2007年中国北方沙尘事件的强度和次数进行统计,并检验DOD的沙尘指示意义;在此基础上,对不同区域、不同强度的沙尘事件进行区分,进而探讨2001—2022年中蒙地区沙尘事件频次的时空变化特征及其原因。结果表明:(1)随着浮尘与扬沙、沙尘暴、强沙尘暴等沙尘活动强度的增加,DOD总体呈现增加趋势,但是不同区域沙尘事件对应的DOD阈值有明显差别,其中,西部地区DOD对于不同强度沙尘事件的区分效果较好,浮尘与扬沙的DOD阈值(0.2)低于中东部地区(0.4)。(2)年均沙尘事件频次(FoO)高值区主要分布在中国新疆、内蒙古北部和蒙古国南部的戈壁沙漠,以及柴达木盆地的部分地区,并且这些地区春夏季的沙尘事件频次普遍高于秋冬季。(3)近20年来,中国北方沙尘事件频次整体呈现下降趋势,尤其是中国北方中部的沙漠沙地和黄土高原地区显著下降,而蒙古国沙尘事件频次呈现出东南部下降、西南部升高的特征。(4)研究区沙尘事件频次变化与植被指数和春季风速在大部分地区显著相关,反映出在气候变化与生态修复工程广泛实施的背景下,区域近地面风速下降和植被增多抑制了地表沙尘活动。
中图分类号:
程星雨, 徐志伟, 俞妍, 张小啸. 卫星遥感揭示的2001年以来中蒙地区沙尘事件频次变化及其原因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(2): 47-60.
Xingyu Cheng, Zhiwei Xu, Yan Yu, Xiaoxiao Zhang. Changes in frequency and possible causes of dust occurrence in northern China and Mongolia since 2001 revealed by remote sensing[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(2): 47-60.
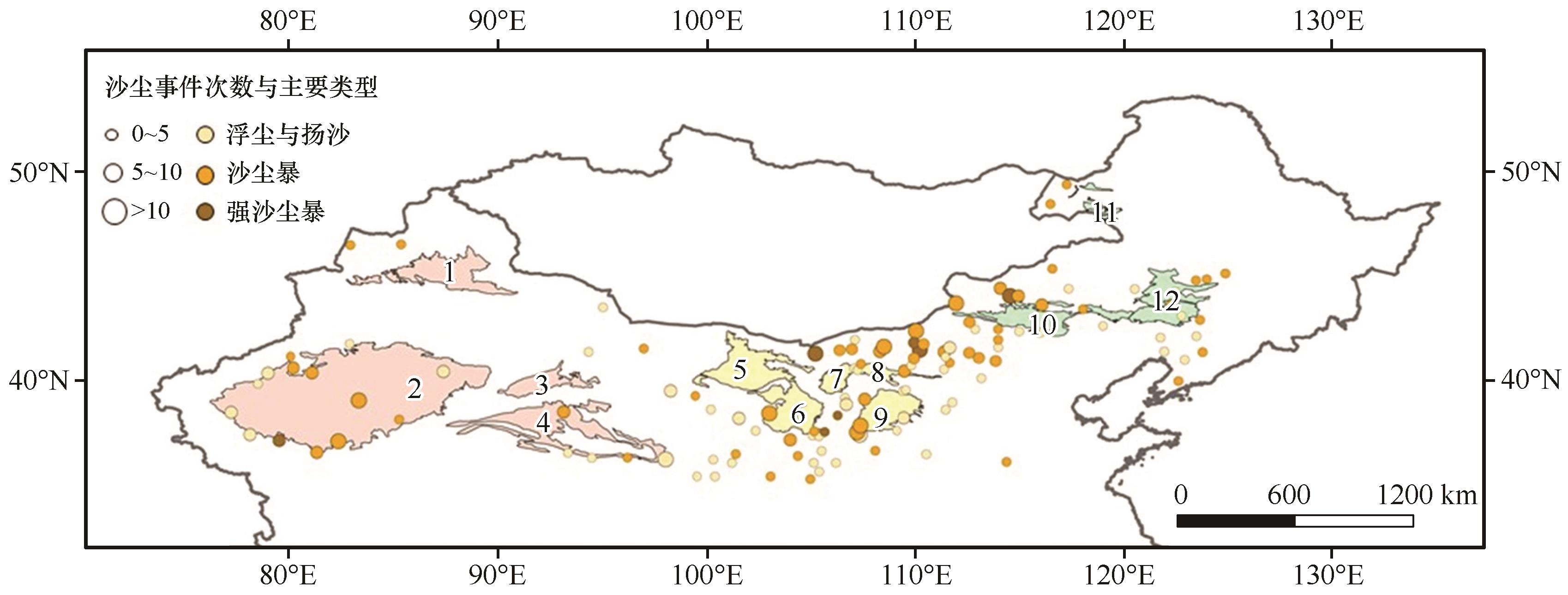
图1 2001—2007年中国北方气象站点观测的沙尘事件次数与主要类型注:圆圈大小代表该站点记录的沙尘事件总次数,颜色由浅到深代表该站点记录的沙尘事件中的主要类型,分别为浮尘与扬沙事件、沙尘暴事件或强沙尘暴事件。数字1~12分别代表各个沙漠和沙地。其中,西部地区沙漠包括:1.古尔班通古特沙漠,2.塔克拉玛干沙漠,3.库姆塔格沙漠,4.柴达木盆地沙漠;中部地区沙漠沙地包括:5.巴丹吉林沙漠,6.腾格里沙漠,7.乌兰布和沙漠,8.库布齐沙漠,9.毛乌素沙地;东部地区沙地包括:10.浑善达克沙地,11.呼伦贝尔沙地,12.科尔沁沙地。地图基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:GS(2024)0650号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.1 The number of sand and dust storms and their main types observed by meteorological stations in North China from 2001 to 2007
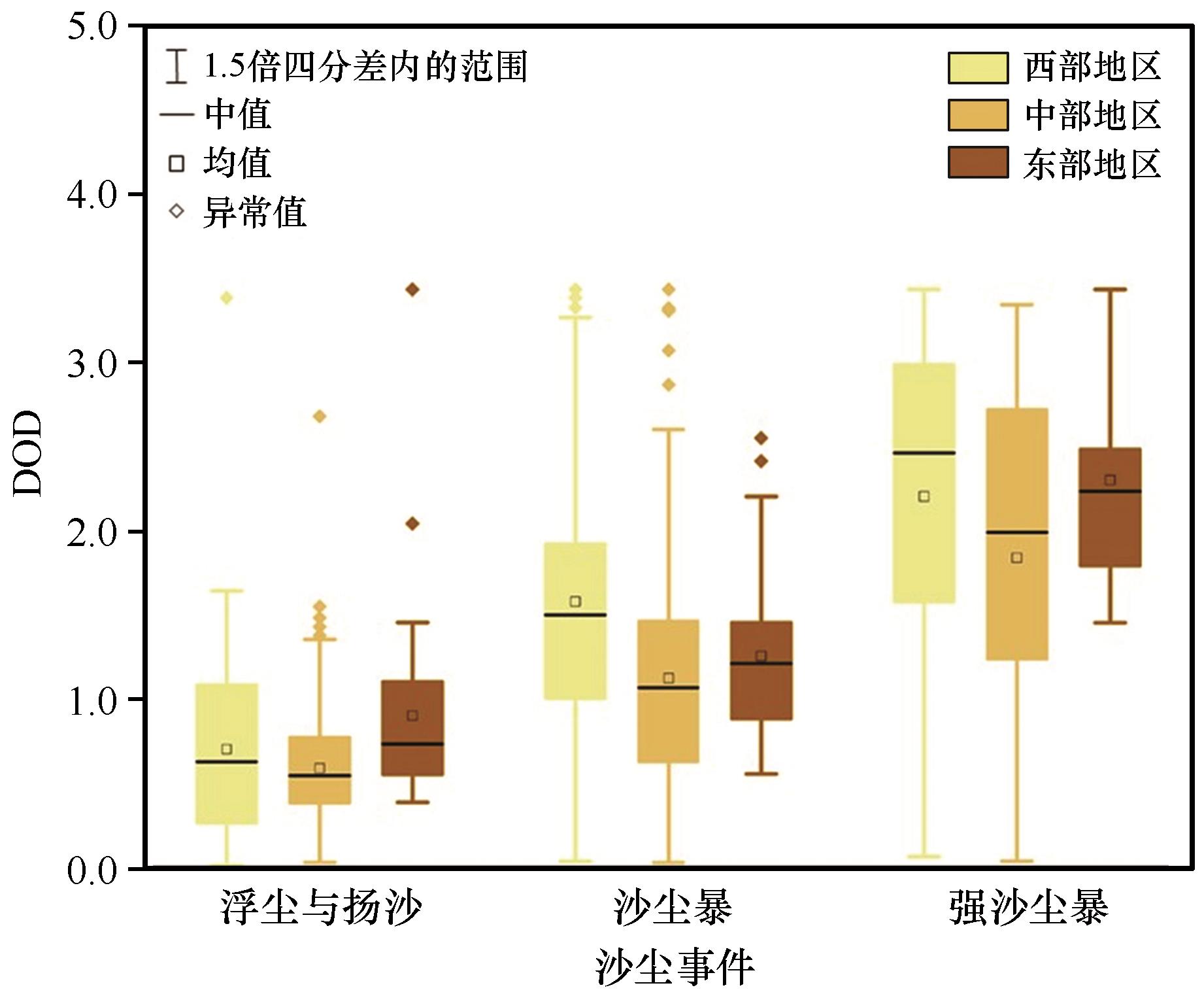
图2 中国北方西部、中部、东部不同区域沙尘事件DOD日值分布统计
Fig.2 Statistical distribution of daily DOD values for different sand and dust storms in western, central, and eastern parts of North China
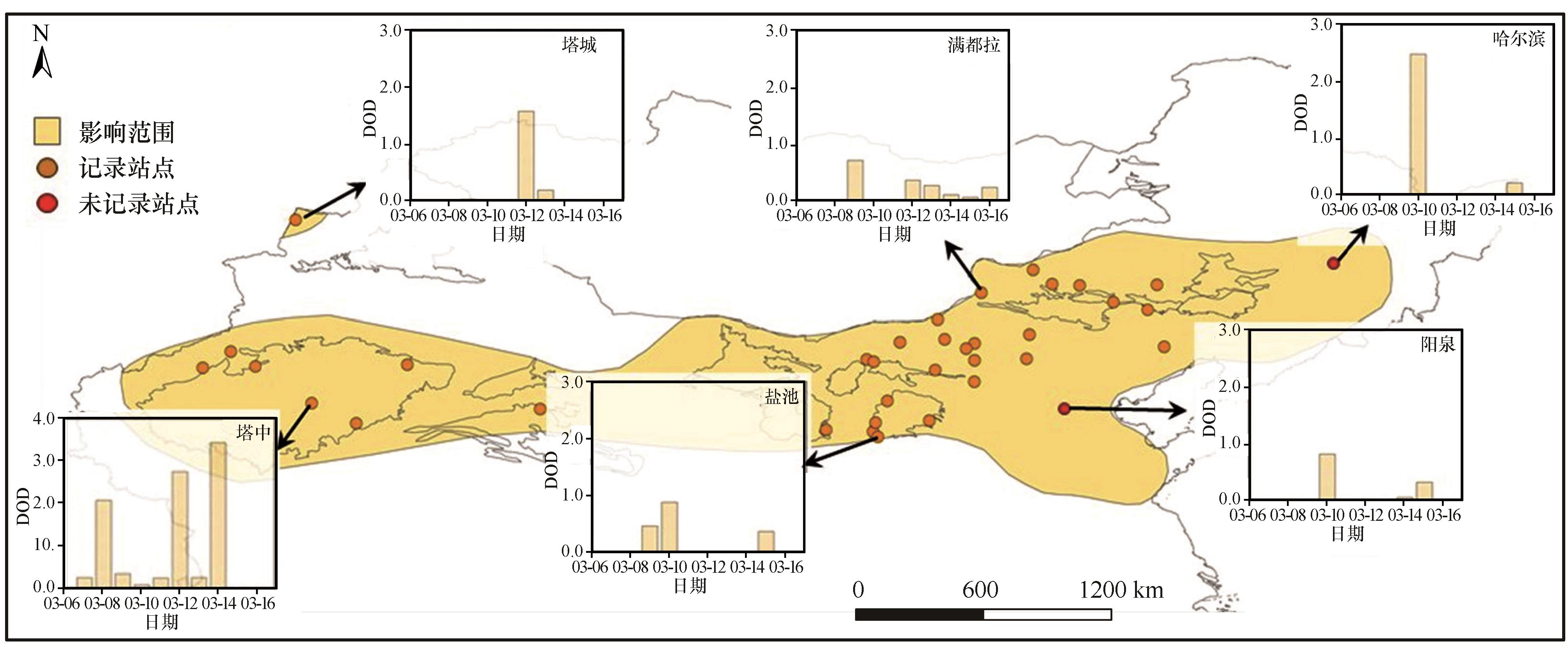
图3 2006年3月9—12日沙尘事件影响范围及典型站点DOD变化注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:GS(2024)0650号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.3 The influence area of a sand and dust storm in North China from March 9 to 12, 2006, and the variations in DOD at typical stations
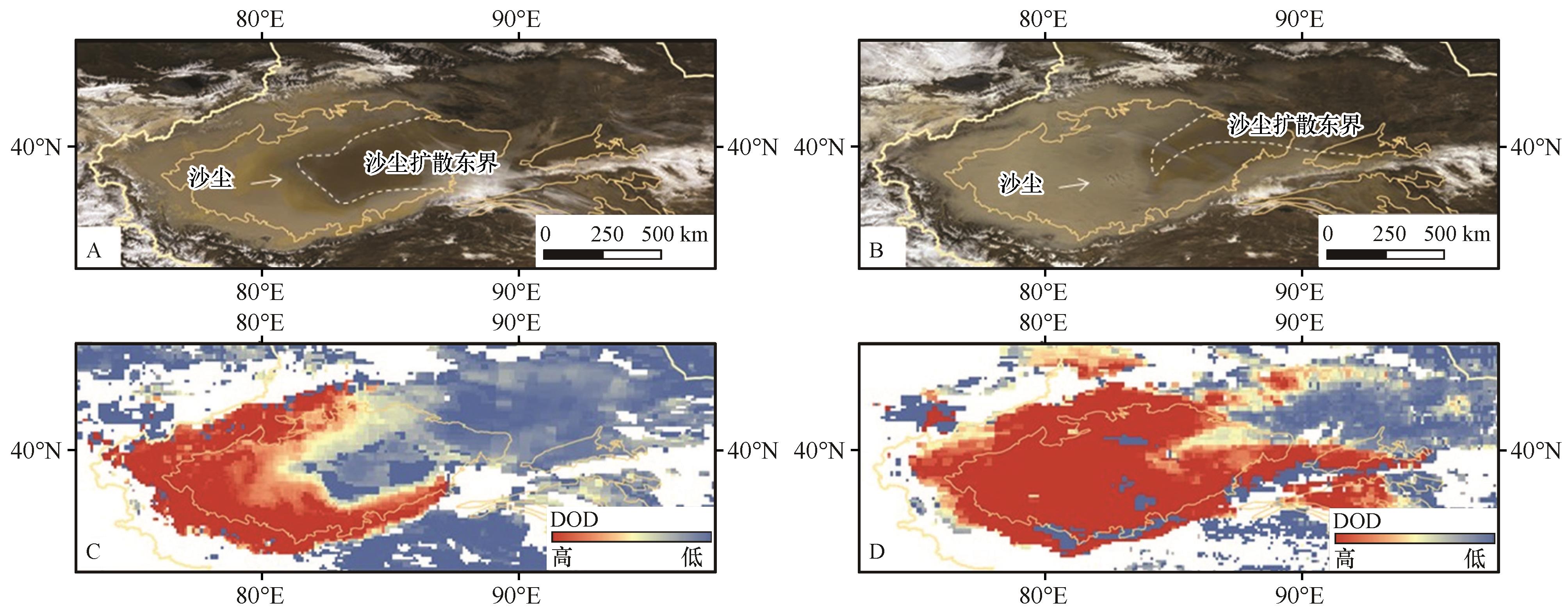
图4 2006年3月13日(A、C)、14日(B、D)MODIS可见光影像(A、B)和DOD分布(C、D)揭示的塔里木盆地沙尘活动和扩散情况注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:GS(2024)0650号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.4 Dust activity and its diffusion in Tarim Basin revealed by MODIS images (A, B) and DOD distribution (C, D) on March 13 (A, C) and March 14 (B, D) in the year 2006
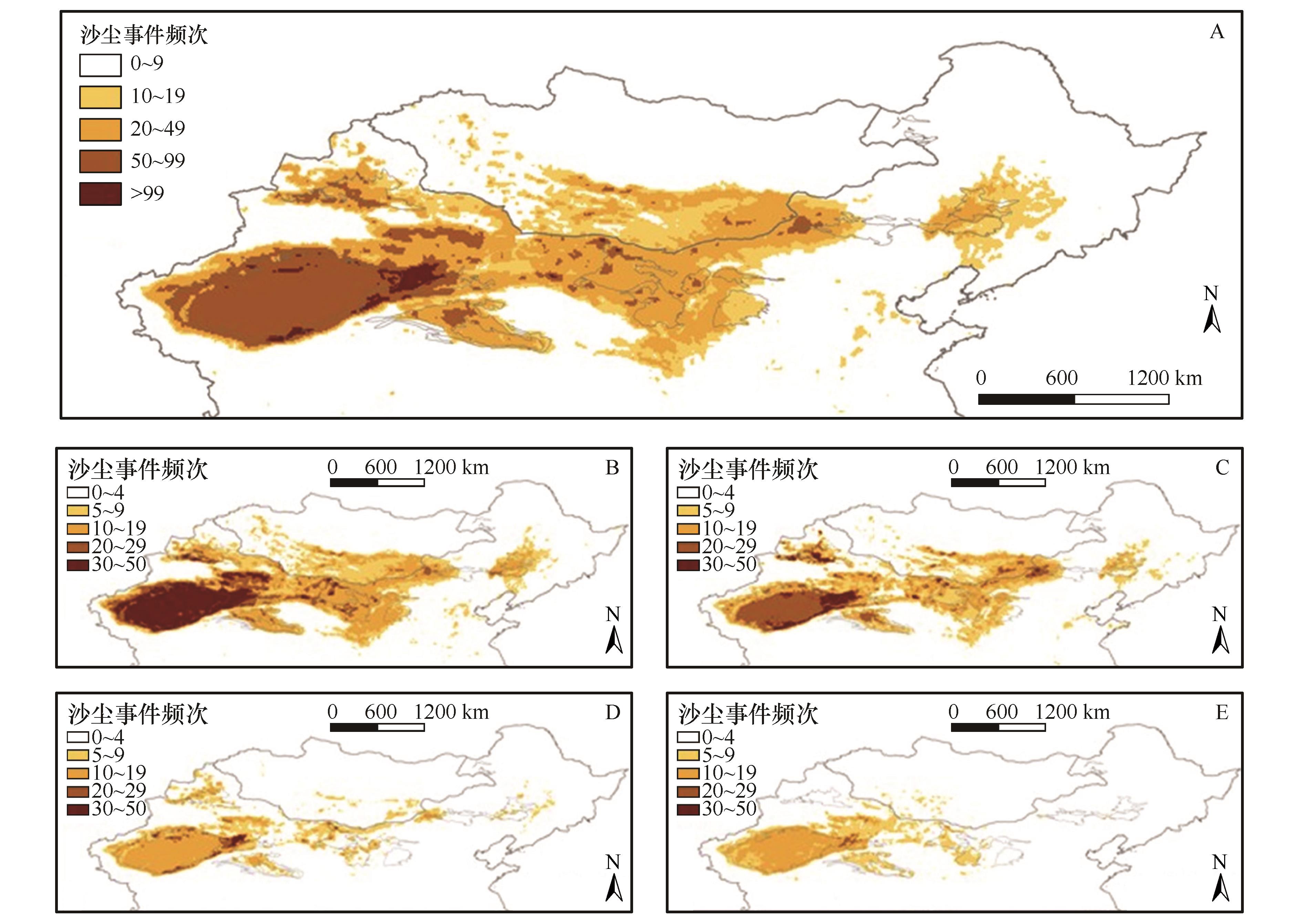
图5 2001—2022年中蒙地区多年平均(A)和春季(B)、夏季(C)、秋季(D)、冬季(E)季节平均沙尘事件频次(FoO)空间分布注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:GS(2024)0650号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.5 Spatial distribution of annual mean FoO (A) and seasonal mean FoO in spring (B), summer (C), autumn (D), and winter (E) in North China and Mongolia from 2001 to 2022
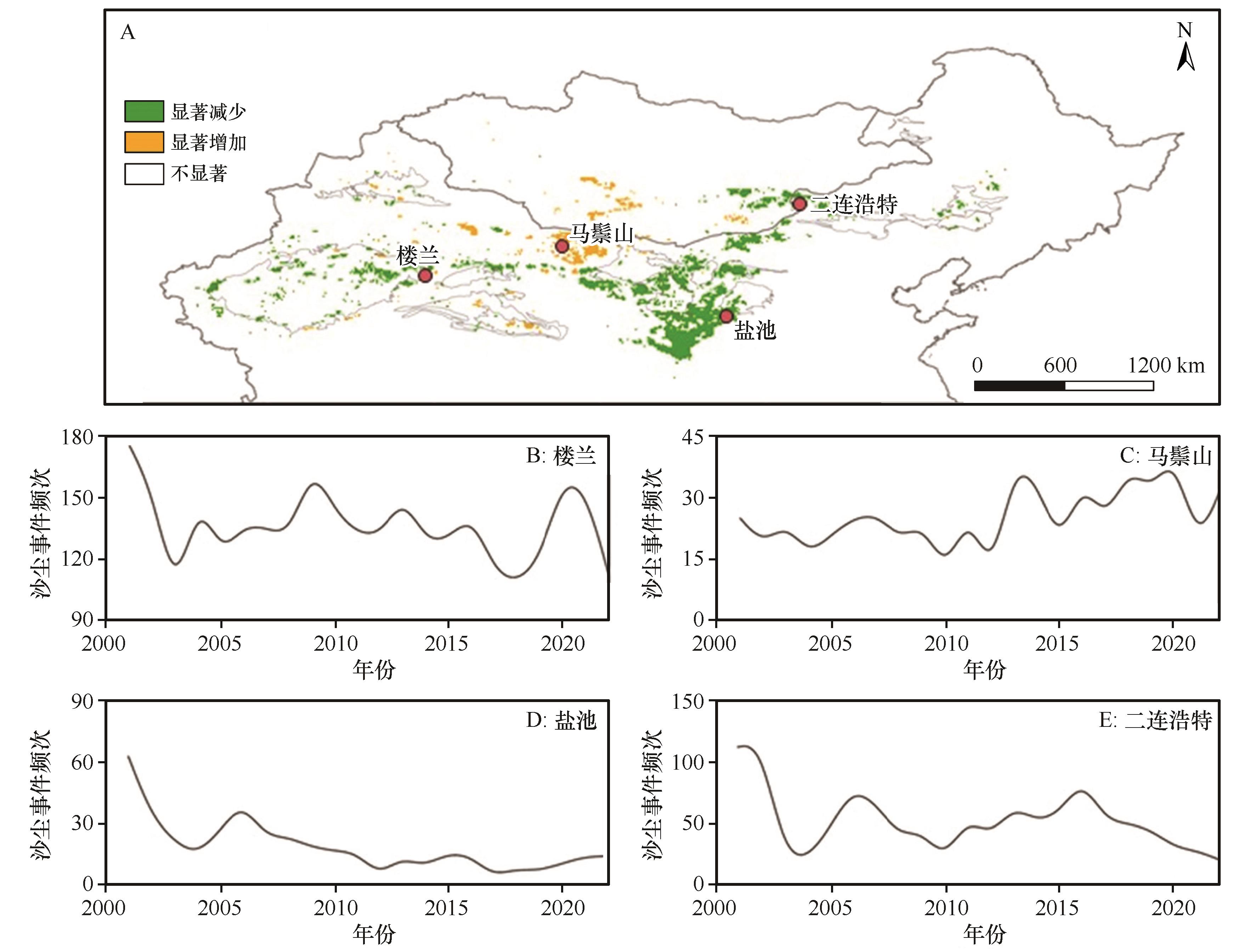
图6 2001—2022年中蒙地区沙尘活跃区(A)及典型站点(B~E)年沙尘事件频次(FoO)变化趋势注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:GS(2024)0650号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.6 Trend of annual FoO in the dust-active regions of North China and Mongolia (A) and variations in FoO at typical stations (B-E) from 2001 to 2022
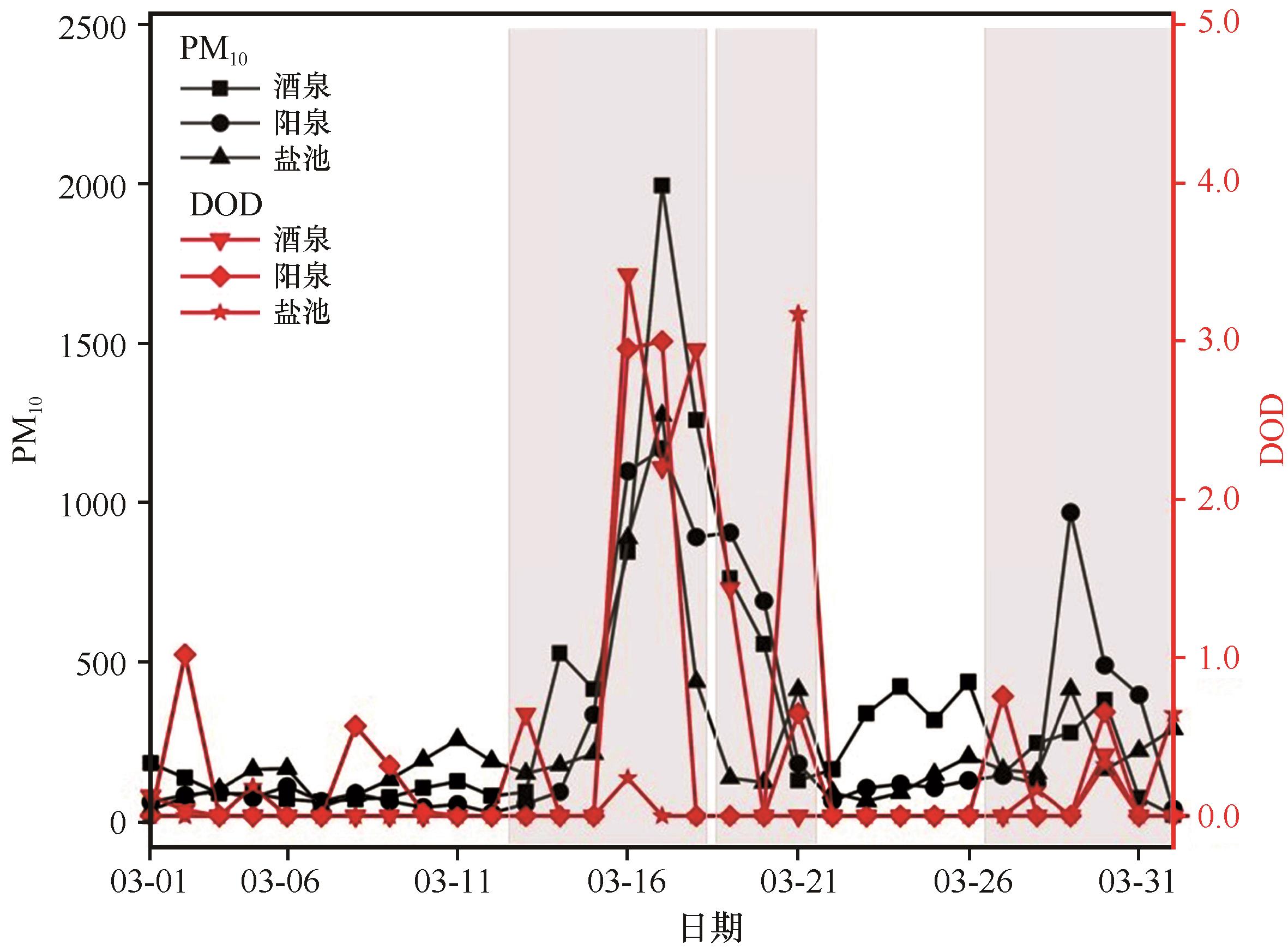
图7 2021年3月部分站点PM10浓度和DOD变化图(灰色阴影代表观测记录的沙尘事件发生时段)
Fig.7 Changes in PM10 and DOD at typical stations in March 2021 (the periods of observed sand and dust storms are indicated by gray shading)
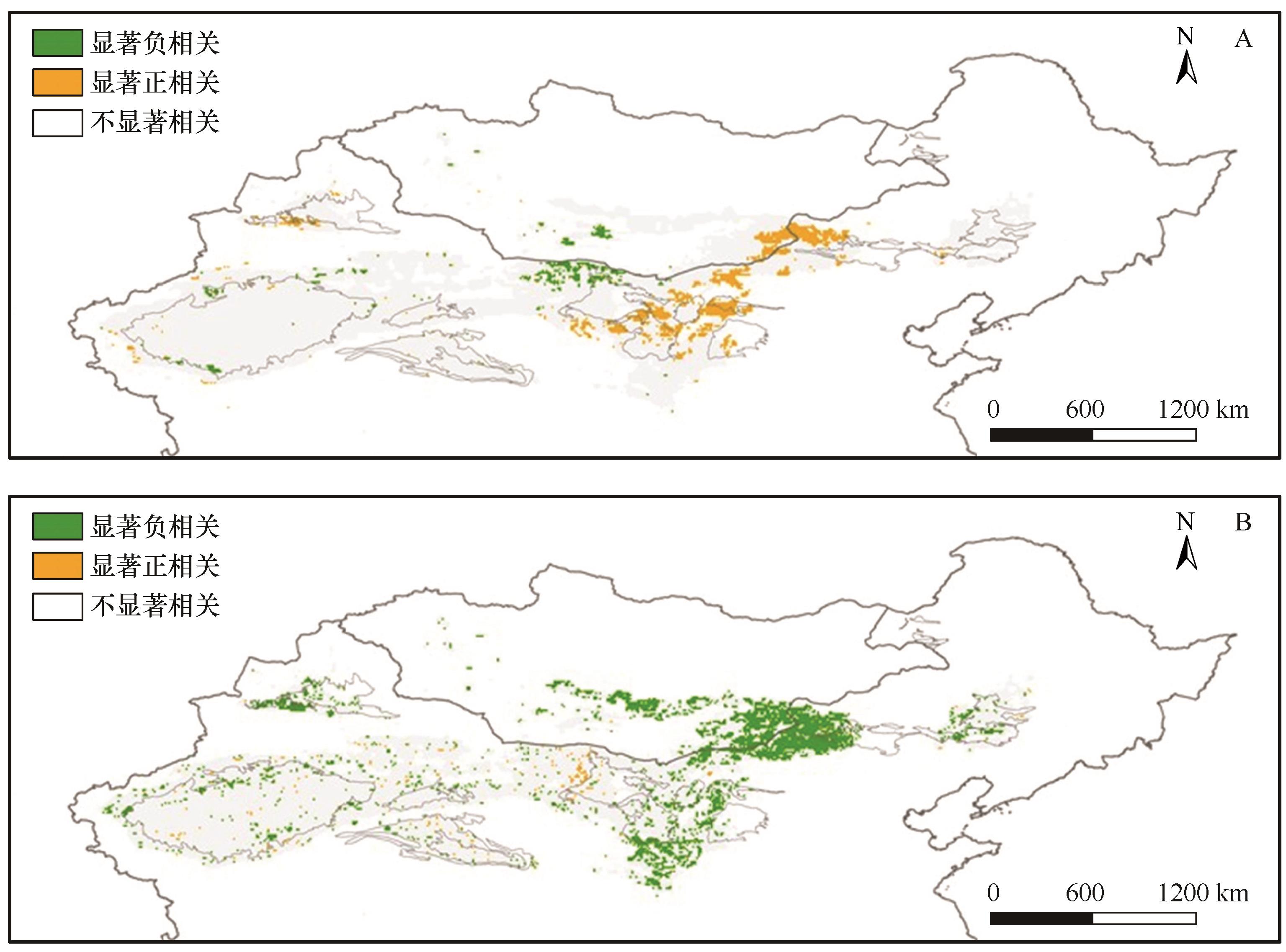
图8 中蒙沙尘活跃区2001—2022年沙尘事件频次(FoO)和春季风速(A)、生长季NDVI(B)的相关性注:基于自然资源部标准地图服务网站标准地图(审图号:GS(2024)0650号)制作,底图边界无修改
Fig.8 Correlation of FoO with spring wind speed (A) and growing season NDVI (B) in dust-active region of North China and Mongolia from 2001 to 2022
| 1 | 邱新法,曾燕,缪启龙.我国沙尘暴的时空分布规律及其源地和移动路径[J].地理学报,2001,56(3):316-322. |
| 2 | Liang P, Chen B, Yang X,et al.Revealing the dust transport processes of the 2021 mega dust storm event in northern China[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2022,67(1):21-24. |
| 3 | Tan S, Li J, Che H,et al.Transport of East Asian dust storms to the marginal seas of China and the southern North Pacific in spring 2010[J].Atmospheric Environment,2017,148:316-328. |
| 4 | Chen S, Zhao D, Huang J,et al.Mongolia contributed more than 42% of the dust concentrations in Northern China in March and April 2023[J].Advances in Atmospheric Sciences,2023,40(9):1549-1557. |
| 5 | 郭彩贇,韩致文,李爱敏.塔克拉玛干沙漠地区沙尘暴研究进展[J].中国沙漠,2016,36(6):1646-1652. |
| 6 | McGillicuddy D J, Sedwick P N, Dinniman M S,et al.Iron supply and demand in an Antarctic shelf ecosystem[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2015,42(19):8088-8097. |
| 7 | Zhang S, Yang S, Xiong S,et al.Origin and depositional background of the Holocene black soil in Northeast China:evidence from grain-size analysis and optically stimulated luminescence dating[J].Catena,2024,239:107963. |
| 8 | Yang F, Zhang G, Yang F,et al.Pedogenetic interpretations of particle-size distribution curves for an alpine environment[J].Geoderma,2016,282:9-15. |
| 9 | Xu Z, Hu R, Wang K,et al.Recent greening (1981-2013) in the Mu Us dune field,north-central China,and its potential causes[J].Land Degradation & Development,2018,29(5):1509-1520. |
| 10 | Wang L, Qiu Y, Han Z,et al.Climate,topography and anthropogenic effects on desert greening:a 40-year satellite monitoring in the Tengger Desert,northern China[J].Catena,2022,209:105851. |
| 11 | Wang S, Yu Y, Zhang X,et al.Weakened dust activity over China and Mongolia from 2001 to 2020 associated with climate change and land-use management[J].Environmental Research Letters,2021,16(12):124056. |
| 12 | Prospero J M, Nees R T.Dust concentration in the atmosphere of the equatorial North Atlantic; possible relationship to the Sahelian drought[J].Science,1977,196(4295):1196-1198. |
| 13 | Wu C, Lin Z, Shao Y,et al.Drivers of recent decline in dust activity over East Asia[J].Nature Communications,2022,13(1):7105. |
| 14 | Huang J, Lin B, Minnis P,et al.Satellite-based assessment of possible dust aerosols semi‐direct effect on cloud water path over East Asia[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2006,33(19):026561. |
| 15 | Wang T, Tang J, Sun M,et al.Identifying a transport mechanism of dust aerosols over South Asia to the Tibetan Plateau:a case study[J].Science of The Total Environment,2021,758:143714. |
| 16 | Yu Y, Kalashnikova O V, Garay M J,et al.Identification and characterization of dust source regions across North Africa and the Middle East using MISR satellite observations[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2018,45(13):6690-6701. |
| 17 | Minamoto Y, Nakamura K, Wang M,et al.Large-scale dust event in East Asia in May 2017:dust emission and transport from multiple source regions[J].SOLA,2018,14:33-38. |
| 18 | Li J, He Q, Jin L,et al.Three-dimensional distribution of dust aerosols over the Tarim Basin and the Tibet Plateau during 2007-2021 derived from CALIPSO lidar observations[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2023,400:136746. |
| 19 | Kaufman Y J, Tanre D, Boucher O.A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system[J].Nature,2002,419(6903):215-223. |
| 20 | Ginoux P, Prospero J M, Gill T E,et al.Global-scale attribution of anthropogenic and natural dust sources and their emission rates based on MODIS Deep Blue aerosol products[J].Reviews of Geophysics,2012,50(3):000388. |
| 21 | Prospero J M, Ginoux P, Torres O,et al.Environmental characterization of global sources of atmospheric soil dust identified with the nimbus 7 total ozone mapping spectrometer(TOMS) absorbing aerosol product[J].Reviews of Geophysics,2002,40(1):1-2. |
| 22 | Liu J, Ding J, Rexiding M,et al.Characteristics of dust aerosols and identification of dust sources in Xinjiang,China[J].Atmospheric Environment,2021,262:118651. |
| 23 | Tian X, Tang C, Wu X,et al.The global spatial-temporal distribution and EOF analysis of AOD based on MODIS data during 2003-2021[J].Atmospheric Environment,2023,302:119722. |
| 24 | Miller S D.A consolidated technique for enhancing desert dust storms with MODIS[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2003,30(20):018279. |
| 25 | King M D, Kaufman Y J, Menzel W P,et al.Remote sensing of cloud,aerosol,and water vapor properties from the moderate resolution imaging spectrometer (MODIS)[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,1992,30(1):2-27. |
| 26 | Levy R C, Mattoo S, Munchak L A,et al.The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean[J].Atmospheric Measurement Techniques,2013,6(11):2989-3034. |
| 27 | Hsu N C, Tsay S, King M D,et al.Aerosol properties over bright-reflecting source regions[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2004,42(3):557-569. |
| 28 | Pu B, Ginoux P.How reliable are CMIP5 models in simulating dust optical depth?[J].Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics,2018,18(16):12491-12510. |
| 29 | Anderson T L.Testing the MODIS satellite retrieval of aerosol fine-mode fraction[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2005,110(D18):18204. |
| 30 | Eck T F, Holben B N, Reid J S,et al.Wavelength dependence of the optical depth of biomass burning,urban,and desert dust aerosols[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,1999,104(D24):31333-31349. |
| 31 | 王式功,王金艳,周自江,等.中国沙尘天气的区域特征[J].地理学报,2003,58(2):193-200. |
| 32 | Hamed K H.Trend detection in hydrologic data:the Mann-Kendall trend test under the scaling hypothesis[J].Journal of Hydrology,2008,349(3/4):350-363. |
| 33 | Hamed K H, Ramachandra Rao A.A modified Mann-Kendall trend test for autocorrelated data[J].Journal of Hydrology,1998,204(1):182-196. |
| 34 | 张咪,段菁春,殷丽娜,等.北京市2018年春季一次沙尘回流过程的污染特征[J].中国环境科学,2021,41(11):4990-4998. |
| 35 | Wang L, Chen Y, Niu Y,et al.Analysis of atmospheric turbidity in clear skies at Wuhan,Central China[J].Journal of Earth Science,2017,28(4):729-738. |
| 36 | Zhang Y, Li Z, Bai K,et al.Satellite remote sensing of atmospheric particulate matter mass concentration:advances,challenges,and perspectives[J].Fundamental Research,2021,1(3):240-258. |
| 37 | Lin Q, Liu Y, Guo J,et al.Simulated dust activity in typical time periods of the past 250 million years[J/OL].Fundamental Research, 2024.DOI:10.1016/j.fmre.2024.02.00 . |
| 38 | Baddock M C, Ginoux P, Bullard J E,et al.Do MODIS‐defined dust sources have a geomorphological signature?[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2016,43(6):2606-2613. |
| 39 | Wang S, Wang J, Zhou Z,et al.Regional characteristics of three kinds of dust storm events in China[J].Atmospheric Environment,2005,39(3):509-520. |
| 40 | Liu X, Yin Z, Zhang X,et al.Analyses of the spring dust storm frequency of northern China in relation to antecedent and concurrent wind,precipitation,vegetation,and soil moisture conditions[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2004,109(D16):D16210-D16211. |
| 41 | Qian W, Quan L, Shi S.Variations of the dust storm in China and its climatic control[J].Journal of Climate,2002,15(10):1216-1229. |
| 42 | Goudie A S.Dust storms in space and time[J].Progress in Physical Geography,1983,7(4):502-530. |
| 43 | 张小曳.亚洲粉尘的源区分布、释放、输送、沉降与黄土堆积[J].第四纪研究,2001,21(1):29-40. |
| 44 | Zhang X, Arimoto R, An Z.Dust emission from Chinese desert sources linked to variations in atmospheric circulation[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,1997,102(D23):28041-28047. |
| 45 | 王伊蒙,范亚秋,龙川,等.基于文献记录的敦煌地区历史时期沙尘天气序列重建[J].中国沙漠,2024,44(2):162-171. |
| 46 | 李晋昌,董治宝,王训明,等.塔里木盆地沙尘天气的季节变化及成因分析[J].中国沙漠,2008,28(1):142-148. |
| 47 | Yin Z, Wan Y, Zhang Y,et al.Why super sandstorm 2021 in North China?[J].National Science Review,2022,9(3):nwab165. |
| 48 | Zhang X, Gong S, Zhao T,et al.Sources of Asian dust and role of climate change versus desertification in Asian dust emission[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2003,30(24):ASC1-ASC8. |
| 49 | Sun J, Zhang M, Liu T.Spatial and temporal characteristics of dust storms in China and its surrounding regions,1960-1999:Relations to source area and climate[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2001,106(D10):325-333. |
| 50 | Wang X, Dong Z, Zhang J,et al.Modern dust storms in China:an overview[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2004,58(4):559-574. |
| 51 | 古丽斯坦·阿卜杜克热木,丁建丽,马雯.南疆地区不同类型沙尘天气及相关因素对气溶胶光学厚度影响研究[J].环境科学学报,2024,44(6):259-269. |
| 52 | Cui M, Lu H, Wiggs G F S,et al.Quantifying the effect of geomorphology on aeolian dust emission potential in northern China[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,2019,44(14):2872-2884. |
| 53 | 侯承志,黄丹青,桂东伟,等.1961-2019年中国北方沙漠沙地极端气候变化特征及其影响因素[J].地理科学,2023,43(8):1495-1505. |
| 54 | Hou C, Huang D, Xu H,et al.Evaluation of ERA5 reanalysis over the deserts in northern China[J].Theoretical and Applied Climatology,2023,151(1/2):801-816. |
| 55 | Gou J, Xu H, Liu L,et al.The trend reversal of dust aerosol over East Asia and the North Pacific Ocean attributed to large-scale meteorology,deposition,and soil moisture[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2019,124(19):10450-10466. |
| 56 | Wang X, Zhang C.Sensitivity of soil dust emissions to driving factor variability in earth's main drylands[J].Geoderma,2024,445:116876. |
| 57 | Qiu Y, Xu Z, Xu C,et al.Can remotely sensed vegetation patterns signal dryland restoration success?[J].Restoration Ecology,2023,31(3):e13760. |
| 58 | Zhang L, Zhou B, Song B,et al.Significant carbon isotopic fractionation during early formation of biological soil crusts with indications for dryland carbon cycling[J].iScience,2024,27(3):109114. |
| 59 | Song B, Fang J, Yu Z,et al.The development of biological soil crust along the time series is mediated by archaeal communities[J].Geoderma,2024,449:117022. |
| 60 | Tian Q, Huang G, Hu K,et al.Observed and global climate model based changes in wind power potential over the Northern Hemisphere during 1979-2016[J].Energy,2019,167:1224-1235. |
| 61 | 卜凡蕊,刘颖,邹学勇.中国东部典型沙地植被覆盖度对降水变化的响应[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(3):9-20. |
| 62 | Zhao W, Liu B.The response of sap flow in shrubs to rainfall pulses in the desert region of China[J].Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2010,150(9):1297-1306. |
| 63 | 张强,杨金虎,王朋岭,等.西北地区气候暖湿化的研究进展与展望[J].科学通报,2023,68(14):1814-1828. |
| 64 | 董祝雷,姜学恭,衣娜娜,等.风速和植被对内蒙古地区沙尘天气影响的数值模拟[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(6):29-39. |
| 65 | Wang S, Li R, Wu Y,et al.Effects of multi-temporal scale drought on vegetation dynamics in Inner Mongolia from 1982 to 2015,China[J].Ecological Indicators,2022,136:108666. |
| 66 | Zhang H, Fan J, Cao W,et al.Response of wind erosion dynamics to climate change and human activity in Inner Mongolia,China during 1990 to 2015[J].Science of The Total Environment,2018,639:1038-1050. |
| [1] | 翟颖, 庞奖励, 黄春长, 查小春, 周亚利, 李瑜琴, 张玉柱, 孙雪晴, 赵晓康. 若尔盖盆地阿米欧拉-南剖面粒度端元特征及其记录的15 ka来气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(2): 111-118. |
| [2] | 胡昕, 买买提·沙吾提, 张峰, 崔锦涛, 艾尼玩·艾买尔, 阿斯娅·曼力克. 基于蒲公英优化随机森林模型的沙漠土壤Fe2O3 含量高光谱遥感反演[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(2): 191-204. |
| [3] | 王彦希, 屈建军, 沈城, 钟帅, 李君. 雷州半岛灯楼角砂质海岸的侵蚀及防治[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(1): 10-19. |
| [4] | 韩超信, 韩永翔, 李嘉欣. 弱风背景下阵风起沙对大气沙尘气溶胶总量的贡献[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(1): 259-265. |
| [5] | 李彬, 孙小龙, 赵悦晨, 江琪, 卢士庆, 唐家琦. 基于随机森林的局地起沙量预测评估模型[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(1): 292-303. |
| [6] | 胡荻, 黄宁, 裴斌斌, Pakzad Rezaali, 张洁. 沙尘暴环境中低矮建筑风压特性的数值研究[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(1): 32-43. |
| [7] | 尹振良, 朱睿, 方春爽, 杨华庆, 陈泽霞. 基于Budyko假设的昌马河流域径流变化归因分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 110-121. |
| [8] | 陈兵兵, 盖迎春, 宋忠航, 吴向楠, 艾宇, 杨映, 王生棠, 刘宇烁. 祁连山地区生态质量时空变化及驱动力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 258-267. |
| [9] | 王志刚, 贾若尘, 罗凤敏, 刘明虎, 刘芳, 巴超群, 刘志民. 沙尘热动力机制与农田防护林抑尘机理[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 116-122. |
| [10] | 李森, 杨宗英, 赵鸿雁, 那仁图雅null, 安桂香, 谢家丽, 贾晓鹏, 颜长珍. 1975—2020年黄河“几字弯”沙漠化时空变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 13-22. |
| [11] | 张浪, 党国锋, 鱼腾飞, 韩拓, 殷一丹, 陈勇. 基于无人机激光雷达的额济纳绿洲植被覆盖度监测及变化分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 170-181. |
| [12] | 张腾, 苗运法, 邹亚国, 张孜越, 冯国平. 极端干旱区苏干湖湿地植被分类与变化分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(4): 81-90. |
| [13] | 杜佳瑜, 刘宪锋, 孙高鹏, 李双双. 2003—2018年黄土高原植被光学厚度时空变化及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 222-230. |
| [14] | 贺祯子, 徐冰鑫, 刘文静, 胡宜刚. 荒漠生物结皮碳交换对模拟增温和降雨变化的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 269-278. |
| [15] | 葛健辉, 刘冰, 徐宇杰, 孙爱军, 汪克奇, 李冬雪, 赵晖. 末次冰消期以来黄河首曲流域气候变化与地表过程相互关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(2): 121-132. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
