中国沙漠 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 110-121.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00064
尹振良1,2( ), 朱睿3, 方春爽3(
), 朱睿3, 方春爽3( ), 杨华庆3, 陈泽霞1
), 杨华庆3, 陈泽霞1
收稿日期:2024-04-29
修回日期:2024-05-22
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-12-06
通讯作者:
方春爽
作者简介:方春爽(E-mail: 12211915@stu.lzjtu.edu.cn)基金资助:
Zhenliang Yin1,2( ), Rui Zhu3, Chunshuang Fang3(
), Rui Zhu3, Chunshuang Fang3( ), Huaqing Yang3, Zexia Chen1
), Huaqing Yang3, Zexia Chen1
Received:2024-04-29
Revised:2024-05-22
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-12-06
Contact:
Chunshuang Fang
摘要:
昌马河是疏勒河的主要干流段,其径流变化对气候变化和下垫面变化极其敏感。以昌马河流域为研究对象,运用Budyko假设对径流变化进行归因分析。结果表明:(1)径流、气候和下垫面因子均具有明显的突变特征,气候特征总体上呈暖湿化趋势。(2)径流对降水量变化的敏感性最高,其次为下垫面和潜在蒸散发;气候变化和下垫面变化分别贡献径流量变化的37.31%和62.79%,下垫面变化是径流变化的主要原因,降水增加对径流变化起到次要作用。(3)叶面积指数是与径流变化最相关的影响因子,其次为降水量和土壤水分;气候变化引起下垫面变化能够在更大程度上解释径流变化。
中图分类号:
尹振良, 朱睿, 方春爽, 杨华庆, 陈泽霞. 基于Budyko假设的昌马河流域径流变化归因分析[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(6): 110-121.
Zhenliang Yin, Rui Zhu, Chunshuang Fang, Huaqing Yang, Zexia Chen. Attribution analysis of runoff variations in the Changma River Basin based on the Budyko hypothesis[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2024, 44(6): 110-121.
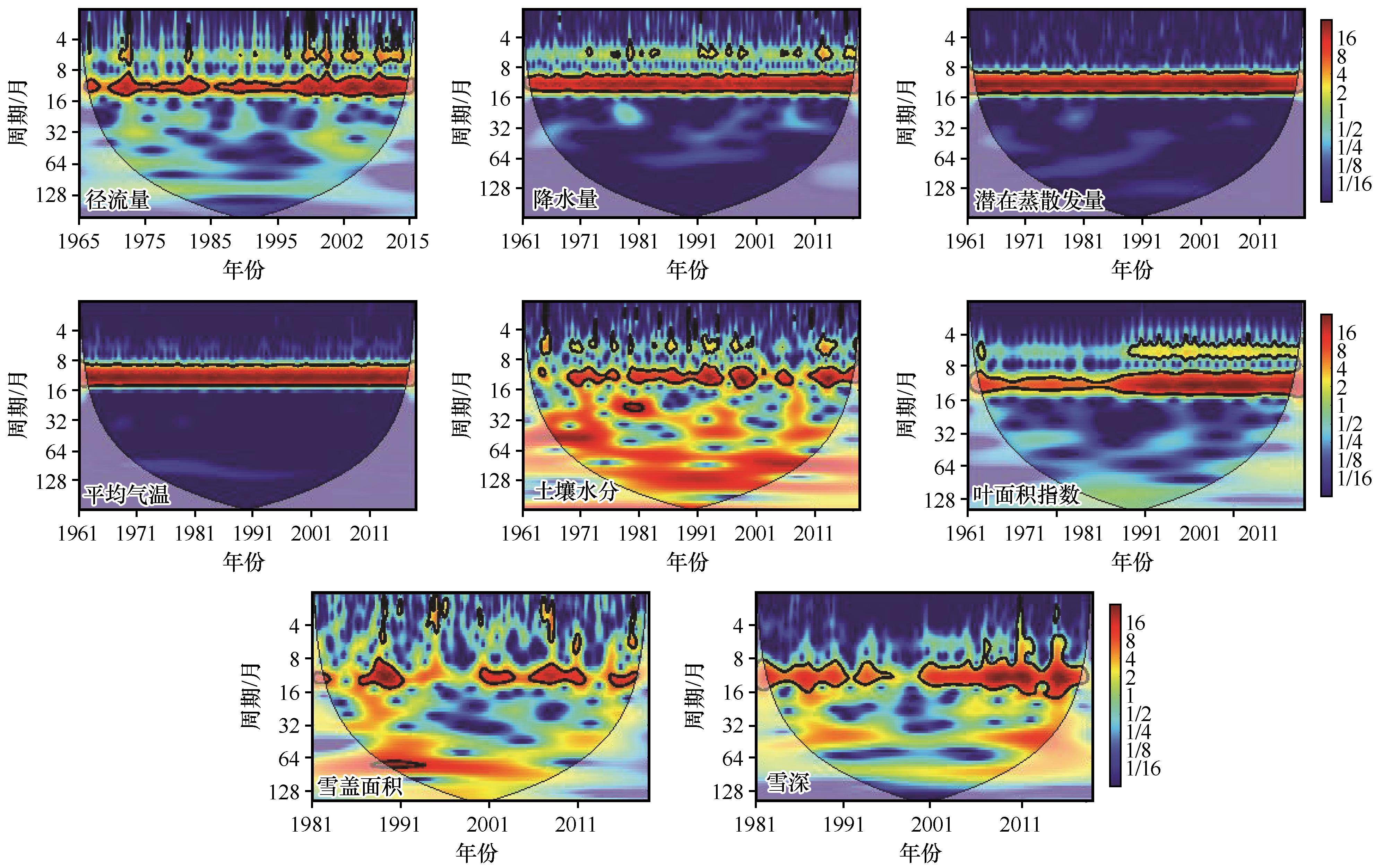
图4 径流和影响因子的连续小波谱注:粗实线表示相对于红噪声的5%显著性水平;浅色区域表示受边缘效应影响区域;颜色表示功率谱强弱
Fig.4 Continuous wavelet transforms of runoff and impact factors. Thick contours denote 5% significance levels against red noise; pale regions denote the cone of influence where edge effects might distort the results; the color denotes the strength of wavelet power
| 时期 | 弹性系数( | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基准期(1965—2000年) | 78.4 | 283.4 | 833.4 | 0.95 | 0.28 | 2.94 | 1.69 | -0.69 | -1.59 |
| 变化期(2001—2015年) | 113.5 | 309.6 | 858.0 | 0.80 | 0.367 | 2.78 | 1.53 | -0.53 | -1.33 |
| 差值 | 35.1 | 26.2 | 24.6 | -0.15 | 0.087 | -0.16 | -0.16 | 0.16 | 0.26 |
表1 基准期和变化期水文气象要素的特征值及弹性系数
Table 1 Statistics in hydro-climatic variables and elasticity coefficient of streamflow to P, ET0, and ω in two periods
| 时期 | 弹性系数( | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基准期(1965—2000年) | 78.4 | 283.4 | 833.4 | 0.95 | 0.28 | 2.94 | 1.69 | -0.69 | -1.59 |
| 变化期(2001—2015年) | 113.5 | 309.6 | 858.0 | 0.80 | 0.367 | 2.78 | 1.53 | -0.53 | -1.33 |
| 差值 | 35.1 | 26.2 | 24.6 | -0.15 | 0.087 | -0.16 | -0.16 | 0.16 | 0.26 |
| 基准期 | 变化期 | ΔRo/mm | ΔRP /mm | Δ | ΔRω /mm | ΔRc/mm | 贡献率/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CONp | CONw | ||||||||
| 1965—2000年 | 2000—2015年 | 35.10 | 14.68 | -1.72 | 27.66 | 40.62 | 33.31% | -3.90% | 62.79% |
表2 昌马河流域降水量、潜在蒸散发量和下垫面对径流变化的贡献率
Table 2 Contribution of P, ET0, and ω to runoff change
| 基准期 | 变化期 | ΔRo/mm | ΔRP /mm | Δ | ΔRω /mm | ΔRc/mm | 贡献率/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CONp | CONw | ||||||||
| 1965—2000年 | 2000—2015年 | 35.10 | 14.68 | -1.72 | 27.66 | 40.62 | 33.31% | -3.90% | 62.79% |
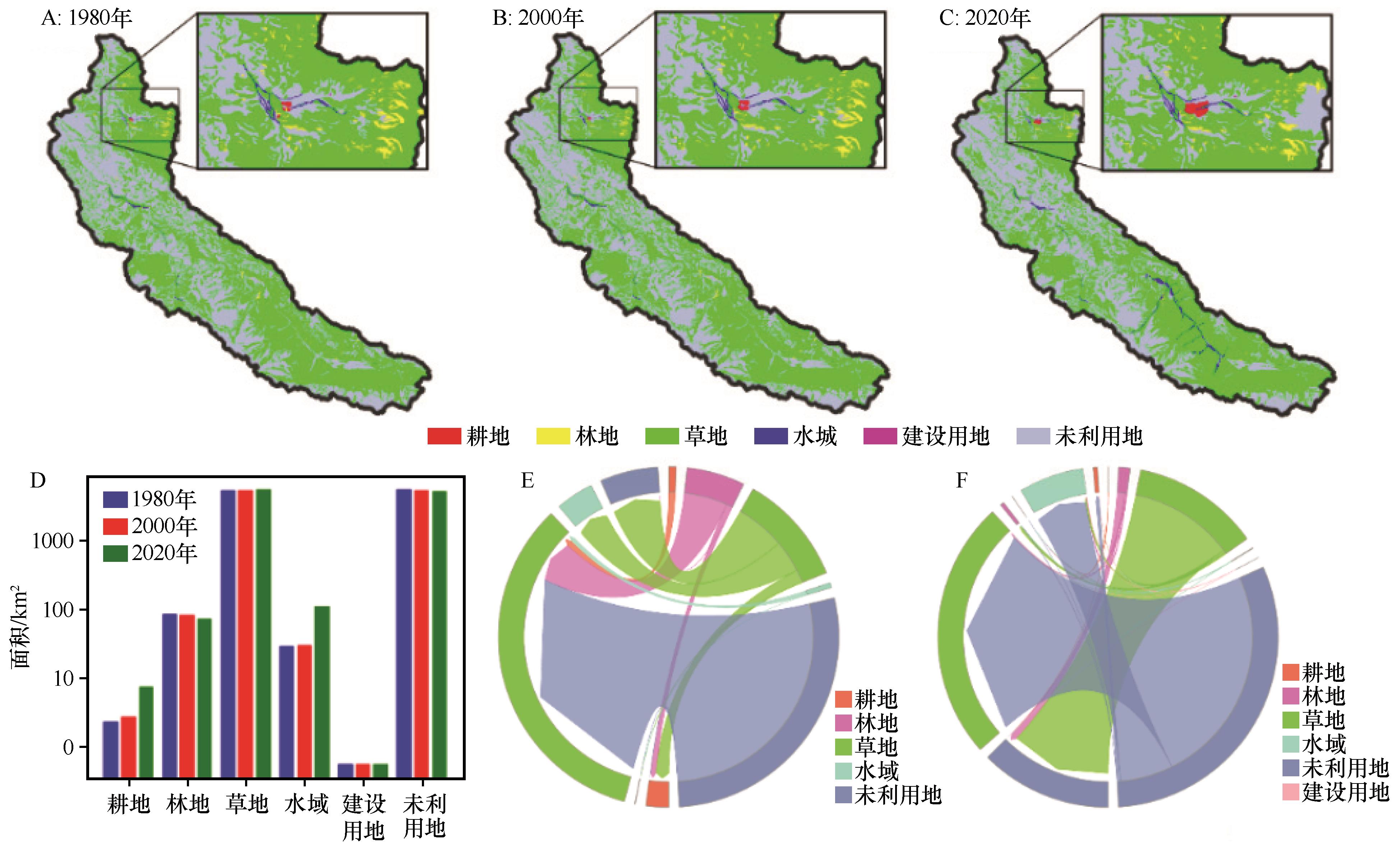
图5 1980(A)、2000(B)、2020年(C)昌马河流域土地利用类型空间分布;1980、2000年和2020年土地利用类型统计值(D);1980—2000年(E)和2000—2020年(F)年的地类转移状况
Fig.5 Land cover classification maps over the study area in 1980 (A), 2000 (B) and 2020 (C); Land cover classification proportions (D); Land use change over the study area between 1980 and 2000 (E) and between 2000 and 2020 (F)
| 时期 | 冰川面积 /km2 | 冰川数量 | 冰储量/km3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| FCGI(1960s—1970s) | 494.46[ | 505[ | 30.58[ |
| 1990年 | 481.07 | 503 | 28.07 |
| 1995年 | 456.28 | 506 | 26.64 |
| 2000年 | 437.39 | 505 | 25.51 |
| 2005年 | 421.24 | 505 | 24.57 |
| SCGI(2005—2010年) | 415.29[ | 501[ | 24.81[ |
| 2010年 | 414.12 | 506 | 24.13 |
| 2015年 | 401.14 | 520 | 23.31 |
| 2020年 | 384.05 | 519 | 22.80 |
表 3 1960s/1970s—2020年昌马河流域冰川变化特征
Table 3 Glacier change over the study area between 1970s and 2020
| 时期 | 冰川面积 /km2 | 冰川数量 | 冰储量/km3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| FCGI(1960s—1970s) | 494.46[ | 505[ | 30.58[ |
| 1990年 | 481.07 | 503 | 28.07 |
| 1995年 | 456.28 | 506 | 26.64 |
| 2000年 | 437.39 | 505 | 25.51 |
| 2005年 | 421.24 | 505 | 24.57 |
| SCGI(2005—2010年) | 415.29[ | 501[ | 24.81[ |
| 2010年 | 414.12 | 506 | 24.13 |
| 2015年 | 401.14 | 520 | 23.31 |
| 2020年 | 384.05 | 519 | 22.80 |
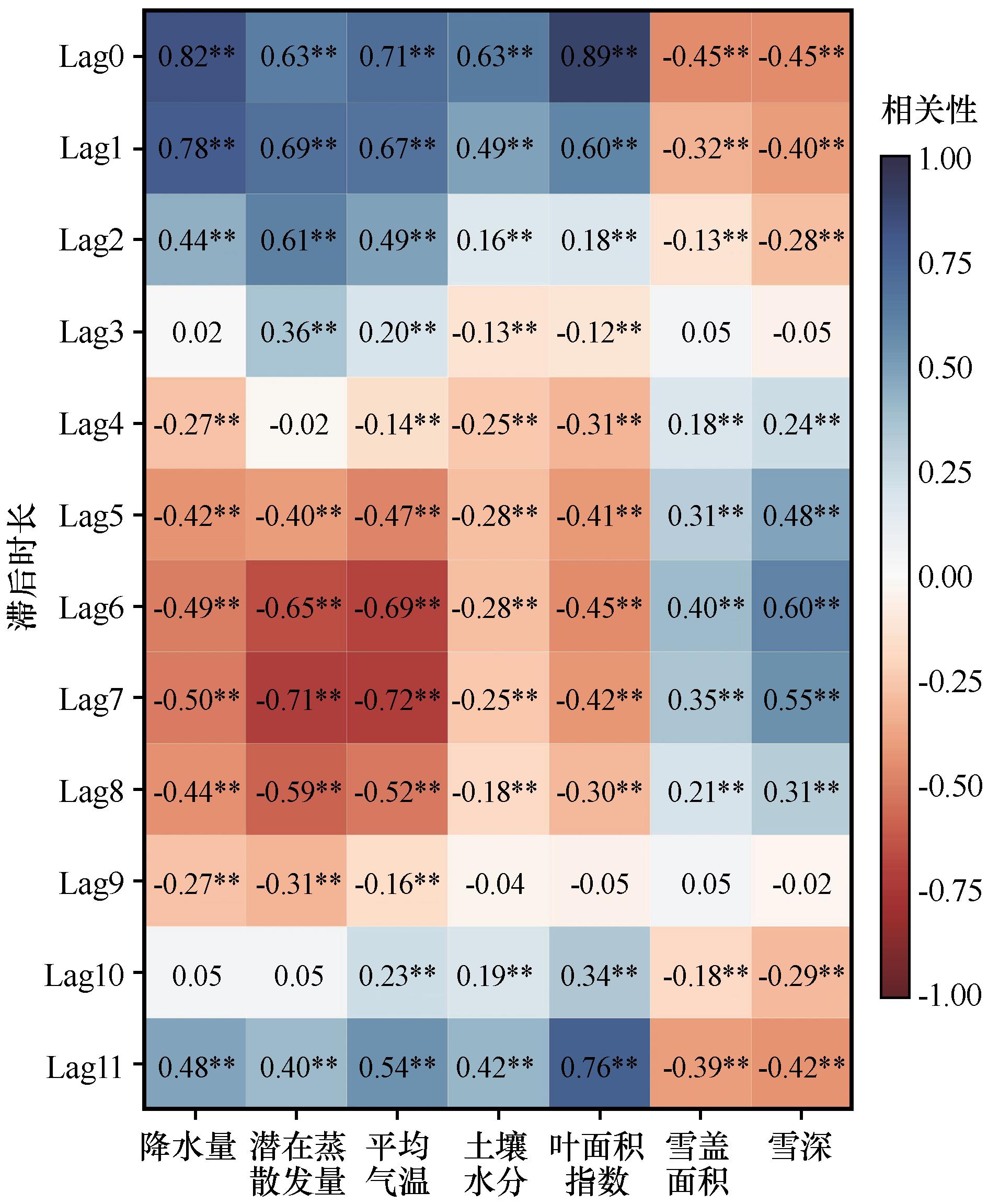
图6 径流与影响因子的交叉分析注:Lag0~Lag 11表示径流滞后影响因子0~11个月; 显著性P0.05,标记为**; 显著性P0.1,标记为*
Fig.6 The interrelation between runoff and influencing factors.Lag0-Lag 11 denotes the impact of runoff lagging behind influencing factors by 0 to 11 months. Significance P0.05, marked as **; significance P0.1, marked as *
| PCP | ET0 | TMP | SW | LAI | SCE | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WTC | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.85 | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.85 |
| PASC | 46.67% | 29.99% | 25.04% | 41.82% | 54.48% | 15.85 | 18.05 |
表 4 径流与单个影响因子之间的小波相干分析的统计值
Table 4 Coherence between runoff and individual influencing factor
| PCP | ET0 | TMP | SW | LAI | SCE | SD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WTC | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.91 | 0.85 | 0.89 | 0.83 | 0.85 |
| PASC | 46.67% | 29.99% | 25.04% | 41.82% | 54.48% | 15.85 | 18.05 |
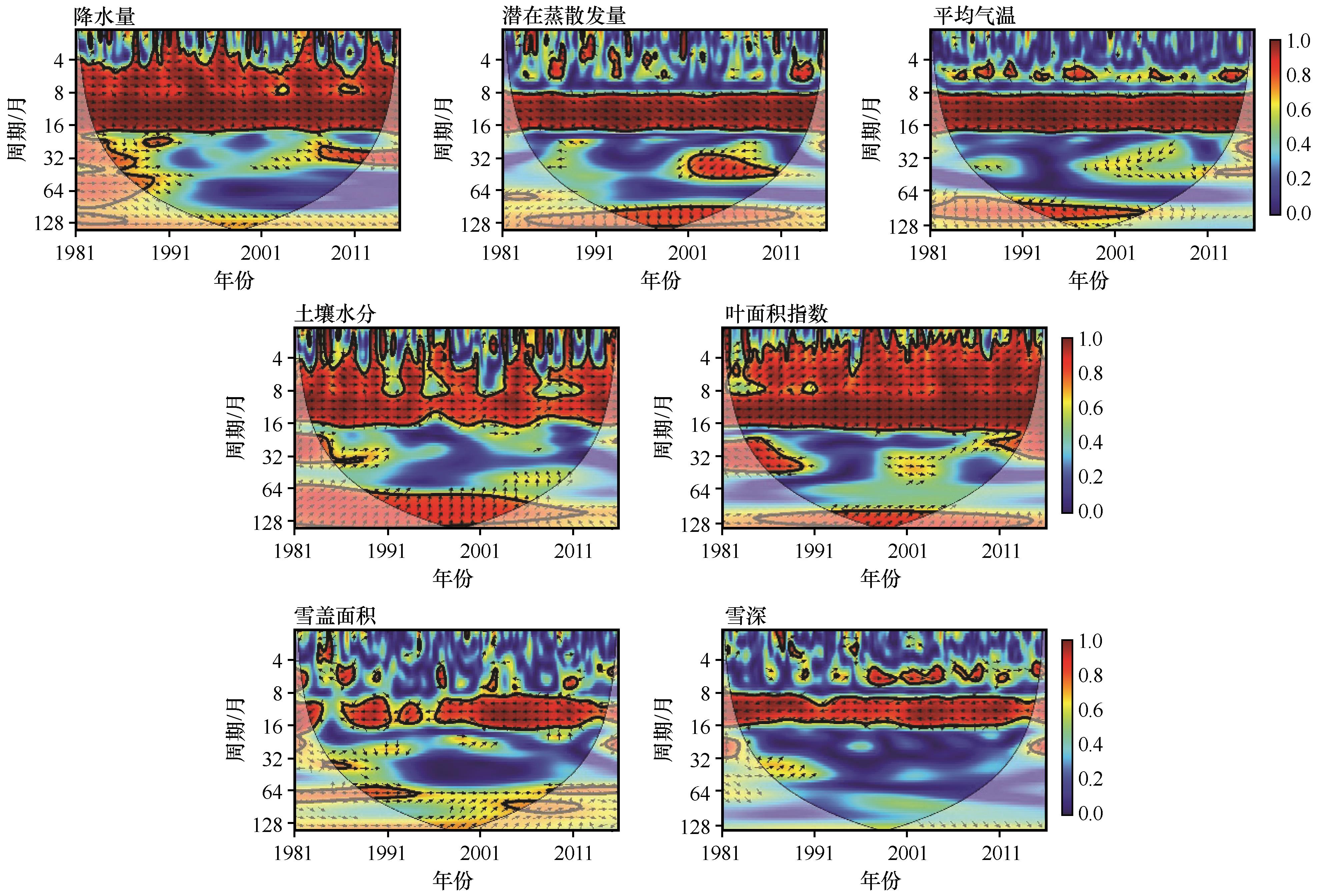
图7 径流与单个影响因子之间的小波相干谱注:粗实线表示相对于红噪声的5%显著性水平;灰色区域表示受边缘效应影响区域;颜色表示相干性强弱
Fig.7 Wavelet coherence between runoff and individual influencing factor. Thick contours denote 5% significance levels against red noise; pale regions denote the cone of influence where edge effects might distort the results; the color denotes the strength of coherence
| 双变量 | MWC2 | PASC/% | 三变量 | MWC3 | PASC/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAI-SW | 0.95 | 60.65 | LAI-SW-SCE | 0.98 | 58.87 |
| LAI-SCE | 0.94 | 55.23 | LAI-SW-PCP | 0.98 | 58.03 |
| LAI-PCP | 0.95 | 53.40 | LAI-SW-ET0 | 0.98 | 55.55 |
| LAI-ET0 | 0.95 | 51.75 | LAI-SCE-PCP | 0.98 | 54.60 |
| PCP-SW | 0.95 | 51.24 | LAI-SCE-ET0 | 0.97 | 54.31 |
| PCP-ET0 | 0.95 | 51.19 | LAI-SW-SD | 0.97 | 54.29 |
| LAI-SD | 0.94 | 50.03 | LAI-PCP-ET0 | 0.98 | 53.11 |
| LAI-TMP | 0.95 | 47.23 | LAI-SCE-TMP | 0.97 | 51.84 |
| PCP-SCE | 0.96 | 44.40 | LAI-PCP-SD | 0.98 | 51.78 |
| PCP-SD | 0.95 | 40.47 | LAI-SW-TMP | 0.98 | 51.38 |
| PCP-TMP | 0.95 | 39.30 | LAI-SCE-SD | 0.97 | 49.20 |
表5 径流与多个影响因子组合之间小波相干分析的统计值
Table 5 Coherence between runoff and multiple influencing factor
| 双变量 | MWC2 | PASC/% | 三变量 | MWC3 | PASC/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LAI-SW | 0.95 | 60.65 | LAI-SW-SCE | 0.98 | 58.87 |
| LAI-SCE | 0.94 | 55.23 | LAI-SW-PCP | 0.98 | 58.03 |
| LAI-PCP | 0.95 | 53.40 | LAI-SW-ET0 | 0.98 | 55.55 |
| LAI-ET0 | 0.95 | 51.75 | LAI-SCE-PCP | 0.98 | 54.60 |
| PCP-SW | 0.95 | 51.24 | LAI-SCE-ET0 | 0.97 | 54.31 |
| PCP-ET0 | 0.95 | 51.19 | LAI-SW-SD | 0.97 | 54.29 |
| LAI-SD | 0.94 | 50.03 | LAI-PCP-ET0 | 0.98 | 53.11 |
| LAI-TMP | 0.95 | 47.23 | LAI-SCE-TMP | 0.97 | 51.84 |
| PCP-SCE | 0.96 | 44.40 | LAI-PCP-SD | 0.98 | 51.78 |
| PCP-SD | 0.95 | 40.47 | LAI-SW-TMP | 0.98 | 51.38 |
| PCP-TMP | 0.95 | 39.30 | LAI-SCE-SD | 0.97 | 49.20 |
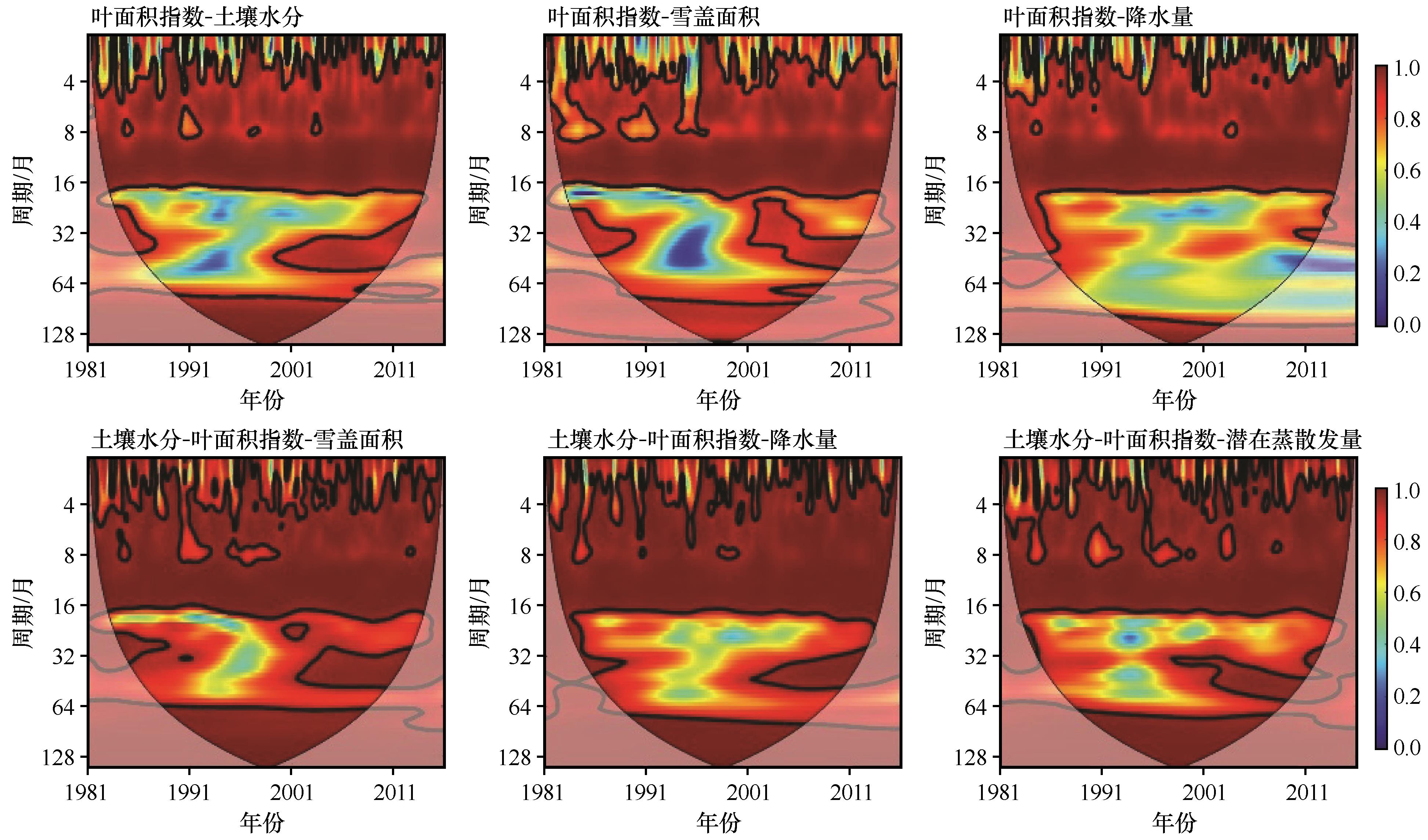
图8 径流与组合影响因子之间的小波相干谱注:双因子组合(上),三因子组合(下);粗实线表示相对于红噪声的5%显著性水平;灰色区域表示受边缘效应影响区域;颜色表示相干性强弱
Fig.8 Wavelet coherence between runoff and multiple influencing factors. Thick contours denote 5% significance levels against red noise; pale regions denote the cone of influence where edge effects might distort the results; the color denotes the strength of coherence
| 1 | 冯起,龙爱华,王宁练,等.西北内陆区水资源安全保障技术集成与应用[J].人民黄河,2019,41(10):103-108. |
| 2 | 丁永建,赵求东,吴锦奎,等.中国冰冻圈水文未来变化及其对干旱区水安全的影响[J].冰川冻土,2020,42(1):23-32. |
| 3 | Chen Y N, Li B F, Li Z,et al.Water resource formation and conversion and water security in arid region of Northwest China[J].Journal of Geographical Sciences,2016,26(7):939-952. |
| 4 | 汤秋鸿,兰措,苏凤阁,等.青藏高原河川径流变化及其影响研究进展[J].科学通报,2019,64(27):2807-2821. |
| 5 | 常启昕,孙自永,潘钊,等.高寒山区河道径流的形成与水文调节机制研究进展[J].地球科学,2022,47(11):4196-4209. |
| 6 | 王磊,刘虎,雍斌,等.陆地冰冻圈水文过程的研究现状及展望[J].北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),2023,59(3):489-496. |
| 7 | 余国安,岳蓬胜,张晨笛,等.藏东南地区的河流水文研究:进展与挑战[J].科学通报,2024,69(3):394-413. |
| 8 | Dey P, Mishra A.Separating the impacts of climate change and human activities on streamflow:a review of methodologies and critical assumptions[J].Journal of Hydrology,2017,548:278-290. |
| 9 | 宋晓猛,张建云,占车生,等.气候变化和人类活动对水文循环影响研究进展[J].水利学报,2013,44(7):779-790. |
| 10 | 董磊华,熊立华,于坤霞,等.气候变化与人类活动对水文影响的研究进展[J].水科学进展,2012,23(2):278-285. |
| 11 | 尹振良,冯起,刘时银,等.水文模型在估算冰川径流研究中的应用现状[J].冰川冻土,2016,38(1):248-258. |
| 12 | Choudhury B J.Evaluation of an empirical equation for annual evaporation using field observations and results from a biophysical model[J].Journal of Hydrology,1999,216(1/2):99-110. |
| 13 | Yang H B, Yang D W, Lei Z,et al.New analytical derivation of the mean annual water‐energy balance equation[J].Water Resources Research,2008,44(3):2007WR006135. |
| 14 | Konapala G, Mishra A K.Three-parameter-based streamflow elasticity model:application to MOPEX basins in the USA at annual and seasonal scales[J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2016,20(6):2545-2556. |
| 15 | 孙莉茹,毕华兴,马志瑾,等.1951-2020年黄河上中游径流变化特征及归因分析[J].北京林业大学学报,2024,46(1):82-92. |
| 16 | Xin J L, Sun X Y, Liu L,et al.Quantifying the contribution of climate and underlying surface changes to alpine runoff alterations associated with glacier melting[J].Hydrological Processes,2021,35(3):e14069. |
| 17 | 梁鹏飞,辛惠娟,李宗省,等.基于Budyko假设的党河径流变化归因[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(3):210-219. |
| 18 | 张晓晓,张钰,徐浩杰.疏勒河上游径流年内分配变化规律分析[J].人民黄河,2014,36(6):58-60. |
| 19 | 贾玲,张百祖,牛最荣,等.疏勒河上游径流变化与预测分析[J].干旱区研究,2022,39(5):1588-1597. |
| 20 | 王学良,陈仁升,刘俊峰,等.1956-2021年疏勒河流域主要河流出山径流变化及成因分析[J].干旱区研究,2022,39(6):1782-1792. |
| 21 | 孙美平,张磊,姚晓军,等.1954-2016年疏勒河上游径流变化特征及影响因素[J].冰川冻土,2022,44(2):657-666. |
| 22 | 李洪源,赵求东,吴锦奎,等.疏勒河上游径流组分及其变化特征定量模拟[J].冰川冻土,2019,41(4):907-917. |
| 23 | Zhang Z H, Deng S F, Zhao Q D,et al.Projected glacier meltwater and river run-off changes in the upper reach of the Shule River Basin,north-eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau[J].Hydrological Processes,2019,33(7):1059-1074. |
| 24 | Wu J K, Li H Y, Zhou J X,et al.Variation of runoff and runoff components of the upper Shule River in the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau under climate change[J].Water,2021,13(23):3357. |
| 25 | Zhou J X, Ding Y J, Wu J K,et al.Streamflow generation in semi-arid,glacier-coverd,montane catchments in the upper Shule River,Qilian Mountains,northeastern Tibetan plateau[J].Hydrological Processes,2021,35(8):e14276. |
| 26 | Guo W Q, Liu S Y, Xu J L,et al.The second Chinese glacier inventory:data,methods and results[J].Journal of Glaciology,2015,61(226):357-372. |
| 27 | 吴佳,高学杰.一套格点化的中国区域逐日观测资料及与其它资料的对比[J].地球物理学报,2013,56(4):1102-1111. |
| 28 | Allen Richard G, Pereira Luis S, Raes Dirk,et al.Crop Evapotranspiration-Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements[M].Rome,Italy: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations,1998. |
| 29 | Muñoz-Sabater J, Dutra E, Agustí-Panareda A,et al.ERA5-Land:a state-of-the-art global reanalysis dataset for land applications[J].Earth System Science Data,2021,13(9):4349-4383. |
| 30 | Che T, Li X, Jin R,et al.Snow depth derived from passive microwave remote-sensing data in China[J].Annals of Glaciology,2008,49:145-154. |
| 31 | Hao X H, Huang G H, Che T,et al.The NIEER AVHRR snow cover extent product over China:a long-term daily snow record for regional climate research[J].Earth System Science Data,2021,13(10):4711-4726. |
| 32 | Hamed K H.Trend detection in hydrologic data:the Mann-Kendall trend test under the scaling hypothesis[J].Journal of Hydrology,2008,349(3/4):350-363. |
| 33 | Li C Y, Hao J S, Zhang G T,et al.Runoff variations affected by climate change and human activities in Yarlung Zangbo River,southeastern Tibetan Plateau[J].Catena,2023,230:107184. |
| 34 | Zhang Q, Xu C Y, Jiang T,et al.Possible influence of ENSO on annual maximum streamflow of the Yangtze River,China[J].Journal of Hydrology,2007,333(2/4):265-274. |
| 35 | Su L, Miao C Y, Duan Q Y,et al.Multiple‐wavelet coherence of world's large rivers with meteorological factors and ocean signals[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Atmospheres,2019,124(9):4932-4954. |
| 36 | Ukasha M, Ramirez J A, Niemann J D.Temporal variations of NDVI and LAI and interactions with hydroclimatic variables in a large and agro‐ecologically diverse region[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Biogeosciences,2022,127(4):e2021JG006395. |
| 37 | Chen T, de Jeu R A M, Liu Y Y,et al.Using satellite based soil moisture to quantify the water driven variability in NDVI:a case study over mainland Australia[J].Remote Sensing of Environment,2014,140:330-338. |
| 38 | 陈亚宁,李忠勤,徐建华,等.中国西北干旱区水资源与生态环境变化及保护建议[J].中国科学院院刊,2023,38(3):385-393. |
| 39 | 张强,杨金虎,王朋岭,等.西北地区气候暖湿化的研究进展与展望[J].科学通报,2023,68(14):1814-1828. |
| 40 | Liu S Y, Sun W X, Shen Y P,et al.Glacier changes since the Little Ice Age maximum in the western Qilian Shan,Northwest China,and consequences of glacier runoff for water supply[J].Journal of Glaciology,2003,49(164):117-124. |
| 41 | Hu W, Si B C.Technical note:multiple wavelet coherence for untangling scale-specific and localized multivariate relationships in geosciences[J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2016,20(8):3183-3191. |
| 42 | Ng E K, Chan J.Geophysical applications of partial wavelet coherence and multiple wavelet coherence[J].Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology,2012,29(12):1845-1853. |
| 43 | 包文,段安民,游庆龙,等.青藏高原气候变化及其对水资源影响的研究进展[J].气候变化研究进展,2024,20(2):158-169. |
| 44 | Gu C J, Mu X M, Gao P,et al.Distinguishing the effects of vegetation restoration on runoff and sediment generation on simulated rainfall on the hillslopes of the loess plateau of China[J].Plant and Soil,2020,447(1/2):393-412. |
| 45 | Guo X X, Du M, Gao P,et al.Response of runoff-sediment processes to vegetation restoration patterns under different rainfall regimes on the Loess Plateau[J].Catena,2024,234:107647. |
| 46 | Tan X Y, Jia Y W, Yang D W,et al.Impact ways and their contributions to vegetation-induced runoff changes in the Loess Plateau[J].Journal of Hydrology:Regional Studies,2024,51:101630. |
| 47 | Shi P, Li P, Li Z B,et al.Effects of grass vegetation coverage and position on runoff and sediment yields on the slope of Loess Plateau,China[J].Agricultural Water Management,2022,259:107231. |
| [1] | 李森, 杨宗英, 赵鸿雁, 那仁图雅null, 安桂香, 谢家丽, 贾晓鹏, 颜长珍. 1975—2020年黄河“几字弯”沙漠化时空变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(5): 13-22. |
| [2] | 贺祯子, 徐冰鑫, 刘文静, 胡宜刚. 荒漠生物结皮碳交换对模拟增温和降雨变化的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(3): 269-278. |
| [3] | 葛健辉, 刘冰, 徐宇杰, 孙爱军, 汪克奇, 李冬雪, 赵晖. 末次冰消期以来黄河首曲流域气候变化与地表过程相互关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(2): 121-132. |
| [4] | 陈阳, 吕萍, 曹敏, 夏子书, 马芳, 余军林. 腾格里沙漠湖泊群小气候特征及其对气候变化的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(2): 231-238. |
| [5] | 李庆, 周娜, 王盛, 李童洲, 王仁德, 王金凤. 气候变化和人类活动对土壤风蚀影响的定量评估[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 178-188. |
| [6] | 冯筱, 屈建军, 丁新辉, 田琴, 范庆斌. 沙漠化逆转过程中榆林市植被净初级生产力时空格局及其影响因素[J]. 中国沙漠, 2024, 44(1): 22-32. |
| [7] | 赵延卓, 谢远云, 康春国, 迟云平, 孙磊, 吴鹏, 魏振宇. 呼伦贝尔沙地风成砂-古土壤剖面记录的全新世气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(5): 85-96. |
| [8] | 路建兵, 鞠珂, 廖伟斌. 2000—2020年甘肃省植被覆盖特征及其对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 118-127. |
| [9] | 尤其, 许宝荣, 邹松兵, 秦艺豪, 王铎, 于冬. 中国北方干旱半干旱区植被-气候响应关系特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 274-287. |
| [10] | 王耀宗, 岳新斌, 谢家丽, 刘志鹏, 马媛, 王亚晖, 宫燕. 2000—2020年宁夏河东沙区沙漠化演变[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 31-40. |
| [11] | 梁鹏飞, 辛惠娟, 李宗省, 南富森, 唐彪, 张文豹. 基于Budyko假设的党河径流变化归因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 210-219. |
| [12] | 段然, 李宗杰, 王昱, 刘晓颖, 桂娟, 梁鹏飞, 李玉辰, 薛健, 刘梦晴, 徐斌. 石羊河流域径流变化特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 57-68. |
| [13] | 韩子言, 蒙吉军, 邹易, 朱利凯. 1982—2017年黑河流域植被指数动态及其对气候变化与生态建设工程的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 96-106. |
| [14] | 辛春明, 何明珠, 李承义, 张力斌, 李新荣. 荒漠土壤氧化亚氮排放及其驱动因素研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 184-194. |
| [15] | 孙红, 段霁芸, 刘雨洁, 冉瑞兰, 李晓凤, 赵鹏善. 气候变化背景下沙蓬属( Agriophyllum )物种潜在地理分布[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 255-263. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
