中国沙漠 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 85-96.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2023.00021
赵延卓1( ), 谢远云1,2(
), 谢远云1,2( ), 康春国3, 迟云平2, 孙磊1, 吴鹏1, 魏振宇1
), 康春国3, 迟云平2, 孙磊1, 吴鹏1, 魏振宇1
收稿日期:2022-12-16
修回日期:2023-03-07
出版日期:2023-09-20
发布日期:2023-09-27
通讯作者:
谢远云
作者简介:谢远云(E-mail: xyy0451@hrbnu.edu.cn)基金资助:
Yanzhuo Zhao1( ), Yuanyun Xie1,2(
), Yuanyun Xie1,2( ), Chunguo Kang3, Yunping Chi2, Lei Sun1, Peng Wu1, Zhenyu Wei1
), Chunguo Kang3, Yunping Chi2, Lei Sun1, Peng Wu1, Zhenyu Wei1
Received:2022-12-16
Revised:2023-03-07
Online:2023-09-20
Published:2023-09-27
Contact:
Yuanyun Xie
摘要:
沙地和沙漠是干旱半干旱地区重要的地质档案载体,记录着丰富的气候演化和沙漠变化信息,尤其是位于东亚温带季风区的呼伦贝尔沙地,蕴含着丰富的东亚季风和人类活动信息。然而受沙丘流动性影响及研究手段的匮乏,目前对于呼伦贝尔沙地全新世以来的气候信息知之甚少。本研究针对呼伦贝尔沙地两个典型风成砂-古土壤沉积序列,进行了多指标如粒度、磁化率、色度、地球化学和总有机碳(TOC)分析,同时结合岩性特征重建了呼伦贝尔沙地全新世以来的气候演化历史。结果表明:两个剖面古土壤层的细颗粒组分、磁化率、化学蚀变指数(CIA)、Rb/Sr、TOC呈高值,而(CaO+Na2O+MgO)/TiO2和亮度呈低值。此外,在6 356±31~2 235±51 cal. a BP和1 620±42~498±17 cal. a BP年龄阶段出现两个明显的变化趋势,指示了呼伦贝尔沙地气候向暖湿方向的逆转,且风成砂层(气候干冷)向古土壤层(气候暖湿)过渡是逐渐进行的,而由古土壤层(气候暖湿)向风成砂层(气候干冷)过渡是骤然变化的。通过与呼伦贝尔沙地古土壤年龄汇编对比,当前研究的古土壤发育年代与邻区的气候暖湿期对应较好,表明呼伦贝尔沙地的正逆演化过程受区域气候演化控制。沙地古土壤发育时间与太阳辐射高值相对应,表明太阳辐射驱动的东亚夏季风变化是呼伦贝尔沙地气候逆转的主要因素。此外,近2000年来人类活动的增强可能对风沙活动加剧造成了一定影响。
中图分类号:
赵延卓, 谢远云, 康春国, 迟云平, 孙磊, 吴鹏, 魏振宇. 呼伦贝尔沙地风成砂-古土壤剖面记录的全新世气候变化[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(5): 85-96.
Yanzhuo Zhao, Yuanyun Xie, Chunguo Kang, Yunping Chi, Lei Sun, Peng Wu, Zhenyu Wei. Holocene climate change recorded by paleosoil profile in Hulun Buir Sandy Land[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(5): 85-96.
| 剖面 | 野外 编号 | 深度 /cm | 距今年代 /a BP | 树轮校正/cal. a BP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 区间 | 校正年龄 | ||||
| X | HL-67 | 55 | 430±20 | 512(68.2%)493 | 498±17 |
| X | HL-66 | 113 | 1 710±25 | 1 689(14.4%)1 672 cal. a BP 1 624(53.8%)1 566 | 1 620±42 |
| Y | HL-64 | 120 | 2 235±25 | 2 320(12.7%)2 302 cal. a BP 2 245(50.8%)2 178 2 169(4.7%)2 161 | 2 235±51 |
| Y | HL-63 | 292 | 5 575±30 | 6 396(31.1%)6 365 cal. a B P 6 353(37.1%)6 316 | 6 356±31 |
表1 呼伦贝尔沙地风成砂-古土壤剖面的 14C测年结果
Table 1 14C dating results of aeolian sand-paleosol profile in Hulun Buir Sandy Land
| 剖面 | 野外 编号 | 深度 /cm | 距今年代 /a BP | 树轮校正/cal. a BP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 区间 | 校正年龄 | ||||
| X | HL-67 | 55 | 430±20 | 512(68.2%)493 | 498±17 |
| X | HL-66 | 113 | 1 710±25 | 1 689(14.4%)1 672 cal. a BP 1 624(53.8%)1 566 | 1 620±42 |
| Y | HL-64 | 120 | 2 235±25 | 2 320(12.7%)2 302 cal. a BP 2 245(50.8%)2 178 2 169(4.7%)2 161 | 2 235±51 |
| Y | HL-63 | 292 | 5 575±30 | 6 396(31.1%)6 365 cal. a B P 6 353(37.1%)6 316 | 6 356±31 |
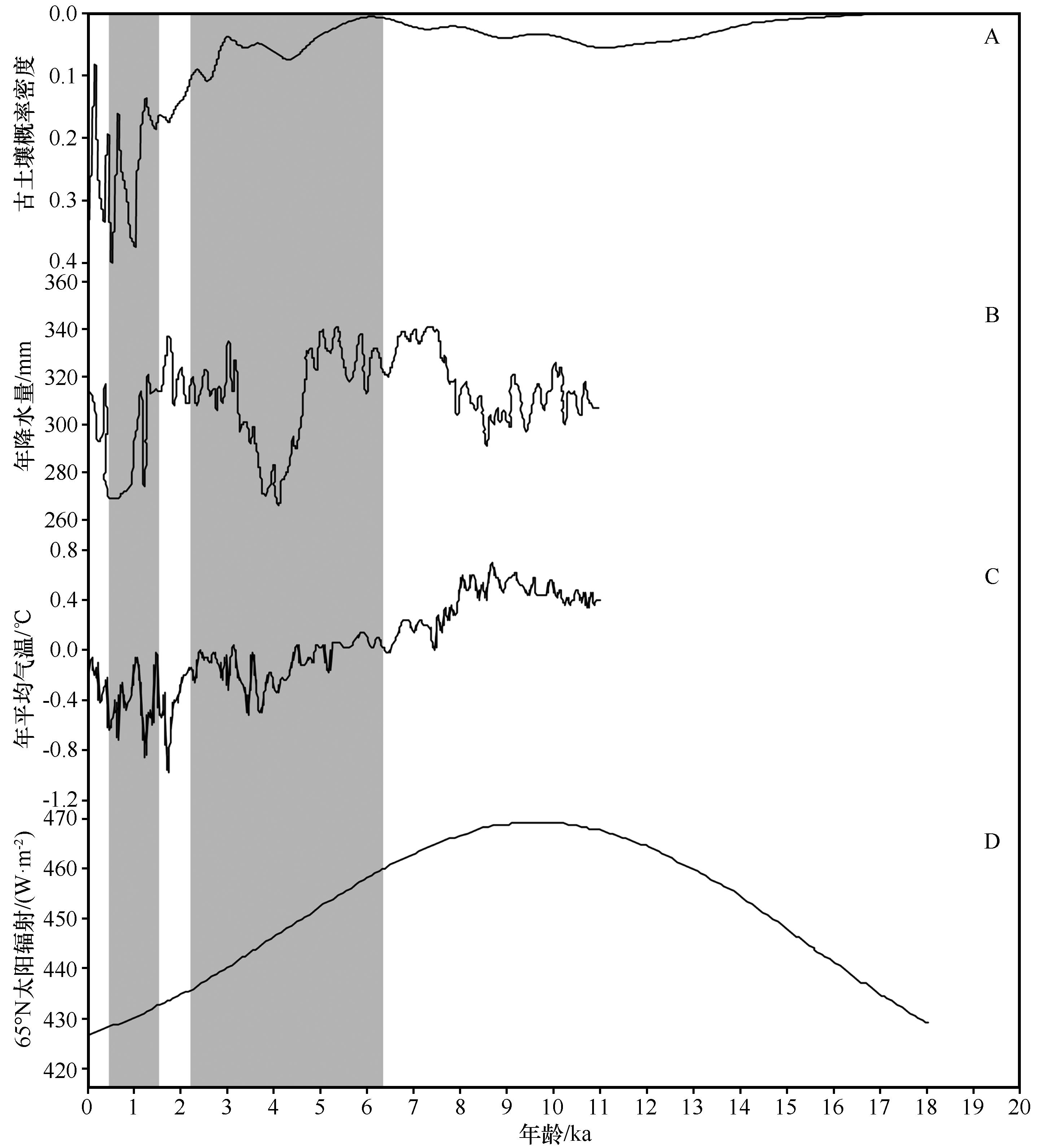
图5 呼伦贝尔沙地古土壤的概率密度曲线与邻区呼伦湖定量重建年降水量、年平均气温、65°N太阳辐射的对比[6,54]图中灰色条带代表了两个剖面古土壤发育阶段
Fig.5 Comparison of the probability density curve of paleosol in Hulun Buir Sandy Land with the quantitative reconstruction of annual mean precipitation,annual mean temperature and 65°N solar radiation in Hulun Lake[6,54]
| 1 | 赵爽,夏敦胜,靳鹤龄,等.科尔沁沙地过去近5000年高分辨率气候演变[J].第四纪研究,2013,33(2):283-292. |
| 2 | 冯晗,鹿化煜,弋双文,等.末次盛冰期和全新世大暖期中国季风区西北缘沙漠空间格局重建初探[J].第四纪研究,2013,33(2):252-259. |
| 3 | 杨小平,梁鹏,张德国,等.中国东部沙漠/沙地全新世地层序列及其古环境[J].中国科学:地球科学,2019,49(8):1293-1307. |
| 4 | 王思齐,魏东岚,张威.末次冰期以来辽东半岛风沙沉积的粒度端元特征与古气候演变研究[J].第四纪研究,2022,42(2):338-349. |
| 5 | 杨利荣,乐平.光释光测年揭示的科尔沁沙地末次晚冰期-全新世沙漠空间格局变化[J].第四纪研究,2013,33(2):260-268. |
| 6 | Zeng L, Yi S W, Lu H Y,et al.Response of dune mobility and pedogenesis to fluctuations in monsoon precipitation and human activity in the Hulunbuir dune field,northeastern China,since the last deglaciation[J].Global and Planetary Change,2018,168(2018):1-14. |
| 7 | 刘瑾,王永,姚培毅,等.末次冰消期以来内蒙古东部气候变化:基于风成砂-古土壤序列的地球化学记录[J].中国地质,2015,42(4):1103-1114. |
| 8 | 赵国永,刘秀铭,吕镔,等.全新世黄土记录的古气候演化及磁化率和粒度参数灵敏性探讨[J].第四纪研究,2012,32(4):777-784. |
| 9 | 李铮华,王玉海.黄土沉积的地球化学记录与古气候演化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质,1998,18(2):42-48. |
| 10 | 靳鹤龄,苏志珠,孙忠.浑善达克沙地全新世中晚期地层化学元素特征及其气候变化[J].中国沙漠,2003,23(4):32-37. |
| 11 | 赵锦慧,王丹,鹿化煜,等.西宁地区黄土地球化学元素所揭示的古气候变化[J].干旱区资源与环境,2006,20(5):104-108. |
| 12 | 张虎才,李吉均,马玉贞,等.腾格里沙漠南缘武威黄土沉积元素地球化学特征[J].沉积学报,1997,15(4):154-160. |
| 13 | 文启忠,刁桂仪,贾蓉芬,等.末次间冰期以来渭南黄土剖面地球化学指标所反映的古气候变化[J].地球化学,1996,25(6):529-535. |
| 14 | 曾琳,鹿化煜,弋双文,等.末次盛冰期和全新世大暖期呼伦贝尔沙地的环境变化[J].第四纪研究,2013,33(2):243-251. |
| 15 | Pye K, Tsoar H.Aeolian Sand and Sand Dunes[M].Berlin,Germany:Springer,2009. |
| 16 | UNDP,UNCCD.The Forgotten Billion:MDG Achievement in the Drylands[M].New York,USA:United Nations Office,2015. |
| 17 | 范育新,张青松,蔡青松,等.光释光年代学对腾格里沙漠化机制及风沙物源的指示[J].第四纪研究,2022,42(2):350-367. |
| 18 | 孙磊,谢远云,康春国,等.呼伦贝尔沙地重矿物、Sr-Nd同位素组成及其对亚洲风尘系统的指示[J].中国地质,2021,48(6):1965-1974. |
| 19 | 韩广,张桂芳,杨文斌.呼伦贝尔沙地沙丘砂来源的定量分析:逐步判别分析(SDA)在粒度分析方面的应用[J].地理学报,2004,59(2):189-196. |
| 20 | 尹金辉,郑勇刚,刘粤霞.古地震~(14)C年龄的日历年代校正[J].地震地质,2005,27(4):678-688. |
| 21 | 袁方,谢远云,詹涛,等.地球化学组成揭示的杜蒙沙地化学风化和沉积再循环特征及其对风尘物质贡献的指示[J].地理科学,2017,37(12):1885-1893. |
| 22 | Yang X P, Liu Y S, Li C Z,et al.Rare earth elements of acolian deposits in northerm China and their implications for determining the provenance of dust storms in Beijing[J].Geomorphology,2007,87(4):365-377. |
| 23 | 杜青松.黄土高原黄土-古土壤序列古气候代用指标综述[J].西北地质,2011,44(2):177-185. |
| 24 | 丁仲礼,孙继敏,刘东生.联系沙漠-黄土演变过程中耦合关系的沉积学指标[J].中国科学:D 辑,1999,29(1):82-87. |
| 25 | Lu H Y, Miao X D, Zhou Y L,et al.Late Quaternary aeolian activity in the Mu Us and Otindag dune fields (north China) and lagged response to insolation forcing[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2005,32(21):L21716. |
| 26 | An Z S, Kukla G J, S C Porter et al.Magnctic susceptibility evislence of monsoon variation on the Loess Plateau of central China during the last 130 000 yeras[J].Quaternary Researc,1991,361:29-36. |
| 27 | 鹿化煜,安芷生.黄土高原黄土粒度组成的古气候意义[J].中国科学:D辑,1998,28(3):278-283. |
| 28 | 刘秀铭,毛学刚,丁仲礼,等.黄土古气候变化趋势与青藏高原隆升关系初探[J].第四纪研究,2009,29(5):988-999. |
| 29 | Ding Z L, Sun J M, Rutter N W,et al.Changes in sand content of loess deposits along a north-south transect of the Chinese Loess Plateau and the implications for desert variations[J].Quaternary Research,1999,52(1):56-62. |
| 30 | Xiao J L, Porter S C, An Z S,et al.Grain size of quartz us an indicator of winter monsoon strength on the Loess Plateau of Central China during the last 130 000yr[J].Quaternary Research,1995,43(1):22-29. |
| 31 | Zhou L P, Oldfield F, Winale A G,et al.Parily pedogcic origin of magnclic varintions in Chinese Loess[J].Nature,1990,346:737-739. |
| 32 | 李明启,靳鹤龄,张洪,等.浑善达克沙地磁化率和有机质揭示的全新世气候变化[J].沉积学报,2005,23(4):683-689. |
| 33 | 靳鹤龄,苏志珠,孙良英,等.浑善达克沙地全新世气候变化[J].科学通报,2004,49(15):1532-1536. |
| 34 | Ding Z Y, Lu R J, Wang L D,et al.Early-Mid Holocene climatic changes inferred from colors of eolian deposits in the Mu Us Desert[J].Geoderma,2021,401:115172. |
| 35 | 彭淑贞,郭正堂.西峰晚第三纪红土记录的亮度学特征[J].第四纪研究,2003,23(1):110. |
| 36 | Kukla G, Heller F, Liu X M,et al.Pleistocene climates in China dated by magnetic susceptibility[J].Geology,1988,16(9):811-814. |
| 37 | 赵景波.黄土形成与演变模式[J].土壤学报,2002,39(4):459-466. |
| 38 | Nesbitt H W, Young G M.Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J].Nature,1982,299:715-717. |
| 39 | Fedo C M, Nesbitt W H, Young G M.Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols,with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance[J].Geology,1995,23(10):921-924. |
| 40 | Chen J, An Z S, Head J.Variation of Rb/Sr ratios in the loess-paleosol sequences of central China during the last 130,000 years and their implications for monsoon paleoclimatology[J].Quaternary Research,1999,51(3):215-219. |
| 41 | Dasch E J.Srontium isotopes in weathering profiles,deep-scasediments,and sedlimentary rocks[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Actn,1969,33(12):1521-1552. |
| 42 | 曾方明.西宁地区新近纪风尘堆积的元素组成特征及物源指示意义[J].第四纪研究,2017,37(6):1309-1319. |
| 43 | 刘硕,迟云平,郝冬梅,等.中更新世以来松嫩平原夏季风演化:来自哈尔滨黄土的磁化率、地球化学和总有机碳记录[J].地质科学,2021,56(4):1279-1298. |
| 44 | 冯力威,吴克宁,查理思,等.仰韶文化遗址区古土壤色度特征及其气候意义[J].生态环境学报,2015,24(5):892-897. |
| 45 | 石培宏,杨太保,田庆春,等.靖远黄土-古土壤色度变化特征分析及古气候意义[J].兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2012,48(2):15-23. |
| 46 | Bai Y F, Wu J G, Xing Q,et al.Primary production and rain use efficiency across a precipitation gradient on the Mongolia Plateau[J].Ecology,2008,89(8):2140-2153. |
| 47 | Li S H, Sun J M.Optical dating of Holocene dune sands from the Hulun Buir desert,North Eastern China[J].The Holocene,2006,16(3):457-462. |
| 48 | Yang L R, Ding Z L.Expansion and contraction of Hulun Buir dunefield in north-eastern China in the last late glacial and Holocene as revealed by OSL dating[J].Environmental Earth Sciences,2013,68(5):1305-1312. |
| 49 | Shen Q, Ao S, Xu Y,et al.Aeolian landform processes since the last deglaciation revealed by OSL chronology and stratigraphy in the Hulunbuir dune field in NE China[J].Quaternary Geochronology,2022,72:101352. |
| 50 | 张振克,王苏民.13 ka以来呼伦湖湖面波动与泥炭发育、风沙-古土壤序列的比较及其古气候意义[J].干旱区资源与环境,2000,14(3):56-59. |
| 51 | 羊向东,王苏民.呼伦湖、乌伦古湖全新世植物群发展与气候环境变化[J].海洋与湖沼,1996,27(1):67-72. |
| 52 | 王苏民,吉磊.呼伦湖晚第四纪湖相地层沉积学及湖面波动历史[J].湖泊科学,1995,7(4):297-306. |
| 53 | 汪佩芳.全新世呼伦贝尔沙地环境演变的初步研究[J].中国沙漠,1992,12(4):16-22. |
| 54 | Itoh Shigeru.Holocene precipitation and temperature variations in the East Asian Monsoonal Margin from pollen data from Hulun Lake in northeastern Inner Mongolia,China[C]//中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所第十届(2010年度)学术年会论文集(下).2011:874-884. |
| 55 | 刘子亭,杨小平,朱秉启.巴丹吉林沙漠全新世环境记录的年代校正与古气候重建[J].第四纪研究,2010,30(5):925-933. |
| 56 | Beer J, Mende W, Stellmacher R.The role of the sun in climate forcing[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2000,19(1):403-415. |
| 57 | Geel B V, Raspopov O M, Renssen H,et al.The role of solar forcing upon climate change[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,1999,18(3):331-338. |
| 58 | Davis B A S, Brewer S.Orbital forcing and role of the latitudinal insolation/temperature gradient[J].Climate Dynamics,2009,32(2/3):143-165. |
| 59 | Ganopolski A, Kubatzki C, Claussen M,et al.The influence of vegetation-atmosphere-ocean interaction on climate during the mid-Holocene[J].Science,1998,280(5371):1916-1919. |
| 60 | Minnis P, Harrison E F, Stowe L L,et al.Radiative climate forcing by the Mount Pinatubo eruption[J].Science,1993,259(5100):1411-1415. |
| 61 | Crowley T J, Criste T A, Smith N R.Reassessment of crete (Greenland) ice core acidity/volcanism link to climate change[J].Geophysical Research Letters,1993,20(3):209-212. |
| 62 | Neff U, Burns S J, Mangini A,et al.Strong coherence between solar variability and the monsoon in Oman between 9 and 6 kyr ago[J].Nature,2001,411(6835):290-293. |
| 63 | Wang Y J, Cheng H, Edwards R L,et al.The Holocene Asian monsoon: links to solar change sand north Atlantic climate[J].Science,2005,308(5723):854-857. |
| 64 | Liu X, Dong H, Yang X,et al.Late Holocene forcing of the Asian winter and summer monsoon as evidenced by proxy records from the northern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,2009,280(1/4):276-284. |
| 65 | Berger A M.Insolation values for the climate of the last 10 million years[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,1991,10(4):297-317. |
| 66 | Mason J, Swinehart J.Holocene climatic changes revealed by aeolian deposits from the Qinghai Lake area (northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau) and possible forcing mechanisms[J].The Holocene,2011,21(2):297-304. |
| 67 | Li P, Zhang C X, Wu H B,et al.Geochemical characteristics of Holocene loess-paleosol sequences in central Chinese Loess Plateau and their implications for East Asian monsoon evolution[J].Quaternary International,2022,33:616-623. |
| 68 | Zhang P, Cheng H, Edwards R,et al.A test of climate,sun,and culture relationships from an 1810-year Chinese cave record[J].Science,2008,322(5903):940-942. |
| 69 | Liu J, Wang B, Wang H,et al.Forced response of the East Asian summer rainfall over the past millennium: results from a coupled model simulation[J].Climate Dynamics,2011,36(1):323-336. |
| 70 | Chen F, Xu Q, Chen J,et al.East Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability since the last deglaciation[J].Scientific Reports,2015,5:11186. |
| 71 | 卓海昕,鹿化煜,贾鑫,等.全新世中国北方沙地人类活动与气候变化关系的初步研究[J].第四纪研究,2013,33(2):303-313. |
| 72 | Sun J.Origin of eolian sand mobilization during the past 2300 years in the Mu Us Desert,China[J].Quaternary Research,2000,53(1):78-88. |
| 73 | Lu H Y, Yi S W, Xu Z W,et al.Chinese deserts and sand fields in Last Glacial Maximum and Holocene Optimum[J].Chinese Science Bulletin,2013,58(23):19-27. |
| [1] | 路建兵, 鞠珂, 廖伟斌. 2000—2020年甘肃省植被覆盖特征及其对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 118-127. |
| [2] | 尤其, 许宝荣, 邹松兵, 秦艺豪, 王铎, 于冬. 中国北方干旱半干旱区植被-气候响应关系特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 274-287. |
| [3] | 王耀宗, 岳新斌, 谢家丽, 刘志鹏, 马媛, 王亚晖, 宫燕. 2000—2020年宁夏河东沙区沙漠化演变[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 31-40. |
| [4] | 梁鹏飞, 辛惠娟, 李宗省, 南富森, 唐彪, 张文豹. 基于Budyko假设的党河径流变化归因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 210-219. |
| [5] | 段然, 李宗杰, 王昱, 刘晓颖, 桂娟, 梁鹏飞, 李玉辰, 薛健, 刘梦晴, 徐斌. 石羊河流域径流变化特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 57-68. |
| [6] | 韩子言, 蒙吉军, 邹易, 朱利凯. 1982—2017年黑河流域植被指数动态及其对气候变化与生态建设工程的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 96-106. |
| [7] | 胡梦珺, 庄静, 孙文丽, 郑登友, 吉天琪, 许澳康. 青藏高原东北部全新世常量元素地球化学特征及环境演变[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 11-20. |
| [8] | 辛春明, 何明珠, 李承义, 张力斌, 李新荣. 荒漠土壤氧化亚氮排放及其驱动因素研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 184-194. |
| [9] | 孙红, 段霁芸, 刘雨洁, 冉瑞兰, 李晓凤, 赵鹏善. 气候变化背景下沙蓬属( Agriophyllum )物种潜在地理分布[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 255-263. |
| [10] | 杨宇哲, 岳大鹏, 赵景波, 刘怡婷, 李嘉宁, 杨天宇. 毛乌素沙地东南缘L3 、S3 黄土-古土壤色度特征及古气候意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 176-186. |
| [11] | 和海秀, 付爱红, 王川. 塔城地区西北部低山草甸植被指数变化及其驱动力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 187-196. |
| [12] | 秦豪君, 杨晓军, 马莉, 王一丞, 傅朝, 张君霞, 陆正奇. 2000—2020年中国西北地区区域性沙尘暴特征及成因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(6): 53-64. |
| [13] | 柳欣滢, 金明, 杨帆, 马亚鹏, 刘慧, 孙小云, 夏敦胜. 毛乌素沙地东缘中全新世以来环境变化及其对文明演化的影响初探[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 92-100. |
| [14] | 朱士华, 方霞, 杭鑫, 谢小萍, 孙良宵, 曹良中. 中亚草地植被指数( NDVI )对气候变化及人类活动的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 229-241. |
| [15] | 陈雪萍, 赵学勇, 王瑞雄, 宁志英, 卢建男, 赵思腾. 气候变化与土地利用/覆被变化对中国北方农牧交错带水资源影响研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(3): 170-177. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
