中国沙漠 ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 274-287.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2022.00137
• • 上一篇
尤其1( ), 许宝荣1(
), 许宝荣1( ), 邹松兵1, 秦艺豪1, 王铎2, 于冬3
), 邹松兵1, 秦艺豪1, 王铎2, 于冬3
收稿日期:2022-07-23
修回日期:2022-11-23
出版日期:2023-07-20
发布日期:2023-08-14
通讯作者:
许宝荣
作者简介:许宝荣(E-mail: brxu@lzu.edu.cn)基金资助:
Qi You1( ), Baorong Xu1(
), Baorong Xu1( ), Songbing Zou1, Yihao Qin1, Duo Wang2, Dong Yu3
), Songbing Zou1, Yihao Qin1, Duo Wang2, Dong Yu3
Received:2022-07-23
Revised:2022-11-23
Online:2023-07-20
Published:2023-08-14
Contact:
Baorong Xu
摘要:
气候变化背景下干旱区植被的时空分布及变化特征,是区域植被恢复和国家自然保护区建设等亟需研究的关键生态环境问题。在建立中国北方干旱半干旱区潜在植被分类及对Holdridge生命地带模型进行修正和拓展的基础上,结合中国气象模拟数据(1981—2020年),引入植被面积转移矩阵、Kappa系数和平均中心模型等方法,对中国北方干旱半干旱区气候要素进行分析并实现了潜在植被定量识别和空间分布格局模拟。结果显示:40年间年降水量、年平均生物温度和可能蒸散率总体均呈上升趋势,研究区存在暖干化现象;研究区共出现6种潜在植被类型,在不同年代际均呈地带性分布;温带荒漠植被、温带草本植被和温带森林植被是主要植被类型,共占总覆盖面积约71%;温带森林植被的面积总体增长最快,平均每10年增加1.1%,温带荒漠植被减少最快,平均每10年减少1.3%;相邻年代际间,各类潜在植被的面积转换关系较为稳定,差别在于转换程度;山地森林植被、温带荒漠植被和温带森林植被的平均中心总体偏移距离大于50 km,除温带荒漠植被,其他植被的平均中心总体均往西移。
中图分类号:
尤其, 许宝荣, 邹松兵, 秦艺豪, 王铎, 于冬. 中国北方干旱半干旱区植被-气候响应关系特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 274-287.
Qi You, Baorong Xu, Songbing Zou, Yihao Qin, Duo Wang, Dong Yu. The vegetation-climate quantitative relationship and characteristics in arid and semi-arid region of northern China[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2023, 43(4): 274-287.
| 编码 | 合并后潜在植被类型 | 1:100万中国植被图植被型 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 高山冻原与稀疏植被 | 高山苔原,高山稀疏植被,高山垫状植被,垫状矮半灌木高寒荒漠 |
| 2 | 高山草本植被 | 禾草、薹草高寒草原,嵩草、杂类草高寒草甸,亚高山落叶阔叶灌丛,亚高山革质常绿阔叶灌丛 |
| 3 | 山地森林植被 | 寒温带和温带山地针叶林,亚热带山地针叶、常绿阔叶、落叶阔叶混交林,亚热带和热带山地针叶林 |
| 4 | 温带荒漠植被 | 矮半乔木荒漠,半灌木、矮半灌木荒漠,草原化灌木荒漠,多汁盐生矮半灌木荒漠,灌木荒漠,一年生草本荒漠,温带丛生矮禾草、矮半灌木荒漠草原 |
| 5 | 温带草本植被 | 禾草、杂类草草甸,温带禾草、杂类草草甸草原,温带丛生禾草草原 |
| 6 | 温带森林植被 | 亚热带常绿、落叶阔叶混交林,亚热带常绿阔叶林,亚热带和热带竹林及竹丛,亚热带针叶林,温带落叶阔叶林,温带针叶林,温带针叶、落叶阔叶混交林,温带落叶灌丛 |
表1 中国北方干旱半干旱区潜在自然植被分类
Table 1 Potential vegetation classification of arid and semi-arid region of northern China
| 编码 | 合并后潜在植被类型 | 1:100万中国植被图植被型 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 高山冻原与稀疏植被 | 高山苔原,高山稀疏植被,高山垫状植被,垫状矮半灌木高寒荒漠 |
| 2 | 高山草本植被 | 禾草、薹草高寒草原,嵩草、杂类草高寒草甸,亚高山落叶阔叶灌丛,亚高山革质常绿阔叶灌丛 |
| 3 | 山地森林植被 | 寒温带和温带山地针叶林,亚热带山地针叶、常绿阔叶、落叶阔叶混交林,亚热带和热带山地针叶林 |
| 4 | 温带荒漠植被 | 矮半乔木荒漠,半灌木、矮半灌木荒漠,草原化灌木荒漠,多汁盐生矮半灌木荒漠,灌木荒漠,一年生草本荒漠,温带丛生矮禾草、矮半灌木荒漠草原 |
| 5 | 温带草本植被 | 禾草、杂类草草甸,温带禾草、杂类草草甸草原,温带丛生禾草草原 |
| 6 | 温带森林植被 | 亚热带常绿、落叶阔叶混交林,亚热带常绿阔叶林,亚热带和热带竹林及竹丛,亚热带针叶林,温带落叶阔叶林,温带针叶林,温带针叶、落叶阔叶混交林,温带落叶灌丛 |
| 潜在植被类型 | 年降水量(P)/mm | 年平均生物温度(ABT)/°C | 可能蒸散率(PER) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高山冻原与稀疏植被 | 13.0 | 338.5 | 0.2 | 2.3 | -3.9 | 8.2 |
| 高山草本植被 | 201.5 | 563.3 | 0.9 | 3.3 | -2.8 | 4.7 |
| 山地森林植被 | 355.0 | 584.8 | 3.8 | 6.0 | 0.1 | 1.3 |
| 温带荒漠植被 | 42.6 | 193.7 | 7.2 | 12.2 | 0.3 | 17.8 |
| 温带草本植被 | 236.5 | 433.0 | 5.5 | 9.6 | -0.4 | 3.5 |
| 温带森林植被 | 349.9 | 709.5 | 6.9 | 11.6 | -1.3 | 4.4 |
表2 各植被类型气候指标参考值
Table 2 Reference value of climate indicators relevant to different types of potential vegetation
| 潜在植被类型 | 年降水量(P)/mm | 年平均生物温度(ABT)/°C | 可能蒸散率(PER) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高山冻原与稀疏植被 | 13.0 | 338.5 | 0.2 | 2.3 | -3.9 | 8.2 |
| 高山草本植被 | 201.5 | 563.3 | 0.9 | 3.3 | -2.8 | 4.7 |
| 山地森林植被 | 355.0 | 584.8 | 3.8 | 6.0 | 0.1 | 1.3 |
| 温带荒漠植被 | 42.6 | 193.7 | 7.2 | 12.2 | 0.3 | 17.8 |
| 温带草本植被 | 236.5 | 433.0 | 5.5 | 9.6 | -0.4 | 3.5 |
| 温带森林植被 | 349.9 | 709.5 | 6.9 | 11.6 | -1.3 | 4.4 |
| 潜在植被类型 | 年降水量(P)模拟值/mm | 年平均生物温度(ABT)模拟值/°C | 可能蒸散率(PER)模拟值 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 最大值 | |
| 高山冻原与稀疏植被 | 20 | 320 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 8 |
| 高山草本植被 | 160 | 640 | 0.75 | 3 | 0 | 4 |
| 山地森林植被 | 320 | 640 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 1 |
| 温带荒漠植被 | 40 | 160 | 6 | 12 | 0.5 | 16 |
| 温带草本植被 | 160 | 320 | 6 | 12 | 0 | 4 |
| 温带森林植被 | 320 | 640 | 6 | 12 | 0 | 4 |
表3 各植被类型气候指标模拟值
Table 3 Analog value of climate indicators relevant to different types of potential vegetation
| 潜在植被类型 | 年降水量(P)模拟值/mm | 年平均生物温度(ABT)模拟值/°C | 可能蒸散率(PER)模拟值 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 最大值 | |
| 高山冻原与稀疏植被 | 20 | 320 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 8 |
| 高山草本植被 | 160 | 640 | 0.75 | 3 | 0 | 4 |
| 山地森林植被 | 320 | 640 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 1 |
| 温带荒漠植被 | 40 | 160 | 6 | 12 | 0.5 | 16 |
| 温带草本植被 | 160 | 320 | 6 | 12 | 0 | 4 |
| 温带森林植被 | 320 | 640 | 6 | 12 | 0 | 4 |
| 潜在植被类型 | 年降水量(P)模拟值/mm | 年平均生物温度(ABT)模拟值/℃ | 可能蒸散率(PER)模拟值 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 最大值 | |
| 高山冻原与稀疏植被 | 20 | 240 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 8 |
| 高山草本植被 | 240 | 640 | 0.75 | 3 | 0 | 4 |
| 山地森林植被 | 320 | 640 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 1.5 |
| 温带荒漠植被 | 40 | 160 | 3 | 12 | 0.5 | 16 |
| 温带草本植被 | 160 | 320 | 3 | 12 | 0 | 6 |
| 温带森林植被 | 320 | 640 | 6 | 12 | 0 | 4 |
表4 中国北方干旱半干旱区各生命地带参数
Table 4 Parameters of life zones of arid and semi-arid region of northern China
| 潜在植被类型 | 年降水量(P)模拟值/mm | 年平均生物温度(ABT)模拟值/℃ | 可能蒸散率(PER)模拟值 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 最小值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 最大值 | |
| 高山冻原与稀疏植被 | 20 | 240 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 8 |
| 高山草本植被 | 240 | 640 | 0.75 | 3 | 0 | 4 |
| 山地森林植被 | 320 | 640 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 1.5 |
| 温带荒漠植被 | 40 | 160 | 3 | 12 | 0.5 | 16 |
| 温带草本植被 | 160 | 320 | 3 | 12 | 0 | 6 |
| 温带森林植被 | 320 | 640 | 6 | 12 | 0 | 4 |
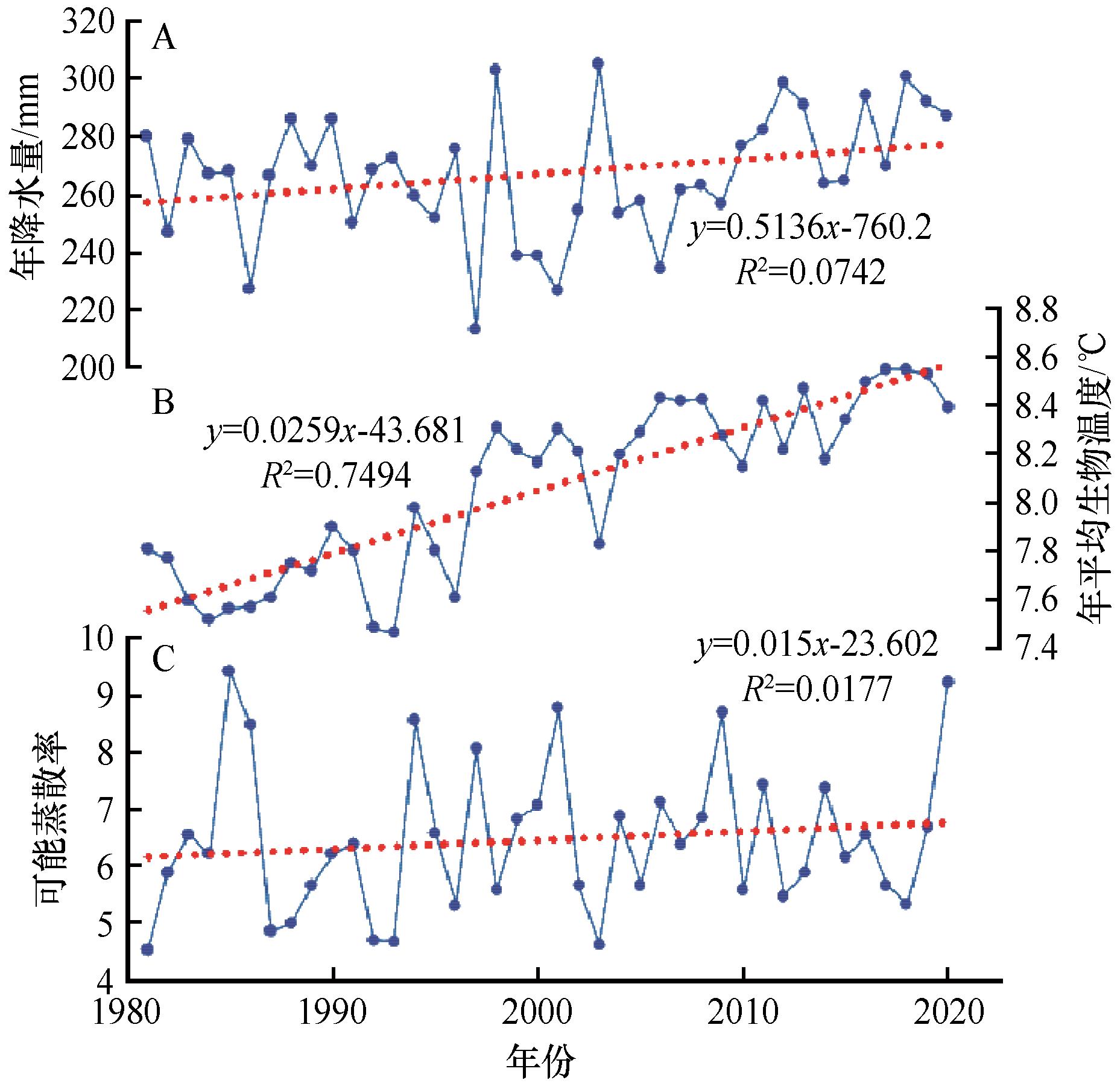
图4 1981—2020年中国北方干旱半干旱区年降水量、年平均生物温度和可能蒸散率变化趋势
Fig.4 Trends of mean annual precipitation, mean annual bio-temperature and potential evapotranspiration rate in arid and semi-arid region of northern China from 1981 to 2010
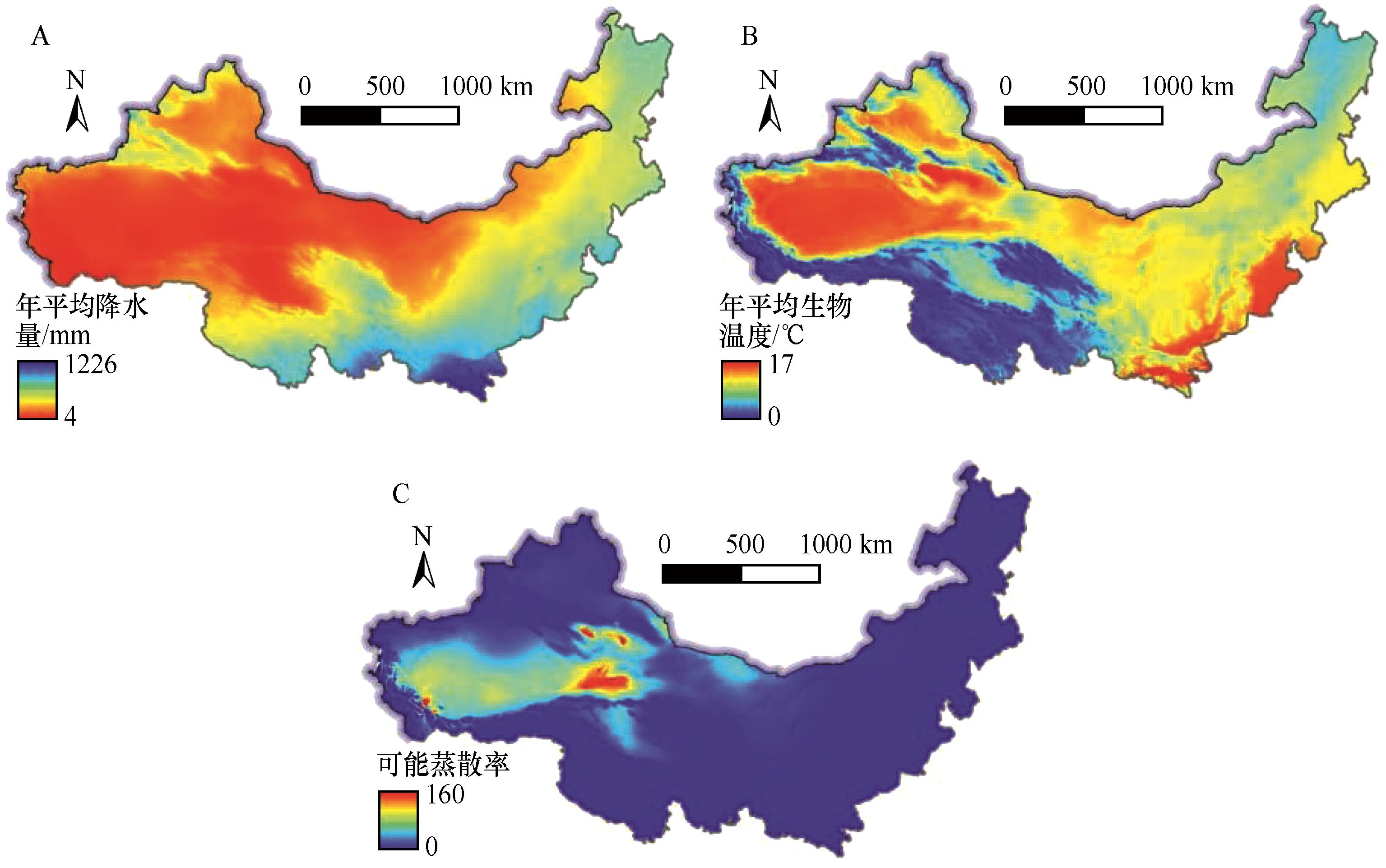
图5 1981—2020年中国北方干旱半干旱区气候指标平均空间分布
Fig.5 Average spatial distribution of climate indicators in arid and semi-arid region of northern China from 1981 to 2010
| 现状植被 编码 | 潜在植被编码 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 总面积 | |
| 1 | 108 585 | 34 599 | 165 | 6 733 | 1 118 | 0 | 151 200 |
| 2 | 66 914 | 245 353 | 32 589 | 9 506 | 19 922 | 1 667 | 375 951 |
| 3 | 659 | 4 120 | 55 867 | 316 | 7 375 | 6 868 | 75 205 |
| 4 | 13 583 | 2 252 | 3 210 | 399 314 | 221 649 | 9 323 | 649 331 |
| 5 | 8 035 | 7 376 | 43 432 | 6 407 | 171 750 | 187 604 | 424 604 |
| 6 | 224 | 316 | 13 456 | 1 947 | 11 547 | 117 581 | 145 071 |
| 总面积 | 198 000 | 294 016 | 148 719 | 424 223 | 433 361 | 323 043 | 1 821 362 |
表5 现状植被与潜在植被面积转移矩阵(km2 )
Table 5 Area transition matrix between real vegetation and potential vegetation
| 现状植被 编码 | 潜在植被编码 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 总面积 | |
| 1 | 108 585 | 34 599 | 165 | 6 733 | 1 118 | 0 | 151 200 |
| 2 | 66 914 | 245 353 | 32 589 | 9 506 | 19 922 | 1 667 | 375 951 |
| 3 | 659 | 4 120 | 55 867 | 316 | 7 375 | 6 868 | 75 205 |
| 4 | 13 583 | 2 252 | 3 210 | 399 314 | 221 649 | 9 323 | 649 331 |
| 5 | 8 035 | 7 376 | 43 432 | 6 407 | 171 750 | 187 604 | 424 604 |
| 6 | 224 | 316 | 13 456 | 1 947 | 11 547 | 117 581 | 145 071 |
| 总面积 | 198 000 | 294 016 | 148 719 | 424 223 | 433 361 | 323 043 | 1 821 362 |
| 编码 | 1980s | 1990s | 2000s | 2010s | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | |
| 1 | 306 418 | 9.6 | 306 982 | 9.5 | 245 855 | 7.8 | 256 271 | 8.5 |
| 2 | 385 305 | 12.1 | 384 409 | 11.8 | 427 788 | 13.6 | 398 840 | 13.3 |
| 3 | 262 931 | 8.2 | 247 997 | 7.6 | 227 995 | 7.3 | 210 144 | 7.0 |
| 4 | 741 024 | 23.2 | 717 130 | 22.1 | 665 232 | 21.2 | 584 254 | 19.4 |
| 5 | 696 307 | 21.8 | 736 866 | 22.7 | 800 784 | 25.5 | 699 750 | 23.3 |
| 6 | 801 769 | 25.1 | 853 222 | 26.3 | 776 848 | 24.7 | 858 314 | 28.5 |
表6 各年代潜在植被面积及占比
Table 6 Interdecadal area and proportion of potential vegetation
| 编码 | 1980s | 1990s | 2000s | 2010s | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | 面积/km2 | 比例/% | |
| 1 | 306 418 | 9.6 | 306 982 | 9.5 | 245 855 | 7.8 | 256 271 | 8.5 |
| 2 | 385 305 | 12.1 | 384 409 | 11.8 | 427 788 | 13.6 | 398 840 | 13.3 |
| 3 | 262 931 | 8.2 | 247 997 | 7.6 | 227 995 | 7.3 | 210 144 | 7.0 |
| 4 | 741 024 | 23.2 | 717 130 | 22.1 | 665 232 | 21.2 | 584 254 | 19.4 |
| 5 | 696 307 | 21.8 | 736 866 | 22.7 | 800 784 | 25.5 | 699 750 | 23.3 |
| 6 | 801 769 | 25.1 | 853 222 | 26.3 | 776 848 | 24.7 | 858 314 | 28.5 |
| 1980s | 1990s | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 总面积 | |
| 1 | 289 155 | 1 681 | 0 | 8 764 | 1 799 | 0 | 301 399 |
| 2 | 10 629 | 365 229 | 3 346 | 0 | 3 319 | 0 | 382 523 |
| 3 | 0 | 1 086 | 232 957 | 0 | 3 068 | 25 820 | 262 931 |
| 4 | 56 | 0 | 0 | 659 494 | 43 713 | 0 | 703 263 |
| 5 | 3 | 0 | 1 943 | 12 903 | 660 260 | 17 274 | 692 383 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 46 | 0 | 24 707 | 768 207 | 792 960 |
| 总面积 | 299 843 | 367 996 | 238 292 | 681 161 | 736 866 | 811 301 | 3 135 459 |
表7 1980s与1990s潜在植被面积转移矩阵(km2 )
Table 7 Area transition matrix of potential vegetation between 1980s and 1990s
| 1980s | 1990s | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 总面积 | |
| 1 | 289 155 | 1 681 | 0 | 8 764 | 1 799 | 0 | 301 399 |
| 2 | 10 629 | 365 229 | 3 346 | 0 | 3 319 | 0 | 382 523 |
| 3 | 0 | 1 086 | 232 957 | 0 | 3 068 | 25 820 | 262 931 |
| 4 | 56 | 0 | 0 | 659 494 | 43 713 | 0 | 703 263 |
| 5 | 3 | 0 | 1 943 | 12 903 | 660 260 | 17 274 | 692 383 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 46 | 0 | 24 707 | 768 207 | 792 960 |
| 总面积 | 299 843 | 367 996 | 238 292 | 681 161 | 736 866 | 811 301 | 3 135 459 |
| 1990s | 2000s | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 总面积 | |
| 1 | 240 585 | 42 013 | 0 | 8 708 | 3 812 | 0 | 295 118 |
| 2 | 1 887 | 365 218 | 7 857 | 0 | 3 013 | 0 | 377 975 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 213 883 | 0 | 1 916 | 28 425 | 244 224 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 612 152 | 30 525 | 0 | 642 677 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 6 247 | 27 608 | 662 706 | 28 317 | 724 878 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 98 812 | 720 098 | 818 910 |
| 总面积 | 242 472 | 407 231 | 227 987 | 648 468 | 800 784 | 776 840 | 3 103 782 |
表8 1990s与2000s潜在植被面积转移矩阵(km2 )
Table 8 Area transition matrix of potential vegetation between 1990s and 2000s
| 1990s | 2000s | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 总面积 | |
| 1 | 240 585 | 42 013 | 0 | 8 708 | 3 812 | 0 | 295 118 |
| 2 | 1 887 | 365 218 | 7 857 | 0 | 3 013 | 0 | 377 975 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 213 883 | 0 | 1 916 | 28 425 | 244 224 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 612 152 | 30 525 | 0 | 642 677 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 6 247 | 27 608 | 662 706 | 28 317 | 724 878 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 98 812 | 720 098 | 818 910 |
| 总面积 | 242 472 | 407 231 | 227 987 | 648 468 | 800 784 | 776 840 | 3 103 782 |
| 2000s | 2010s | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 总面积 | |
| 1 | 234 418 | 2 562 | 0 | 1 927 | 1 834 | 0 | 240 741 |
| 2 | 9 689 | 380 644 | 7 294 | 0 | 2 169 | 0 | 399 796 |
| 3 | 0 | 2 304 | 193 999 | 0 | 99 | 10 313 | 206 715 |
| 4 | 4 594 | 0 | 0 | 568 692 | 67 480 | 0 | 640 766 |
| 5 | 1 025 | 1 331 | 6 990 | 1 973 | 627 768 | 151 047 | 790 134 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 1 772 | 0 | 316 | 696 617 | 698 705 |
| 总面积 | 249 726 | 386 841 | 210 055 | 572 592 | 699 666 | 857 977 | 2 976 857 |
表9 2000s与2010s潜在植被面积转移矩阵(km2 )
Table 9 Area transition matrix of potential vegetation between 2000s and 2010s
| 2000s | 2010s | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 总面积 | |
| 1 | 234 418 | 2 562 | 0 | 1 927 | 1 834 | 0 | 240 741 |
| 2 | 9 689 | 380 644 | 7 294 | 0 | 2 169 | 0 | 399 796 |
| 3 | 0 | 2 304 | 193 999 | 0 | 99 | 10 313 | 206 715 |
| 4 | 4 594 | 0 | 0 | 568 692 | 67 480 | 0 | 640 766 |
| 5 | 1 025 | 1 331 | 6 990 | 1 973 | 627 768 | 151 047 | 790 134 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 1 772 | 0 | 316 | 696 617 | 698 705 |
| 总面积 | 249 726 | 386 841 | 210 055 | 572 592 | 699 666 | 857 977 | 2 976 857 |
| 编码 | 1980s―1990s | 1990s―2000s | 2000s―2010s | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 偏移距离/km | 偏移方向 | 偏移距离/km | 偏移方向 | 偏移距离/km | 偏移方向 | |
| 1 | 36.0 | 东 | 97.0 | 西 | 34.2 | 东南 |
| 2 | 12.0 | 东南 | 19.4 | 西南 | 26.8 | 西北 |
| 3 | 110.8 | 西南 | 119.4 | 西南 | 46.6 | 西南 |
| 4 | 56.0 | 东南 | 29.6 | 东南 | 87.5 | 西北 |
| 5 | 35.1 | 西 | 147.7 | 东 | 144.9 | 西 |
| 6 | 12.4 | 西南 | 64.0 | 西 | 100.2 | 东北 |
表10 相邻年代际潜在植被平均中心时空偏移
Table 10 Adjacent interdecadal shift trends of potential vegetation's mean center
| 编码 | 1980s―1990s | 1990s―2000s | 2000s―2010s | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 偏移距离/km | 偏移方向 | 偏移距离/km | 偏移方向 | 偏移距离/km | 偏移方向 | |
| 1 | 36.0 | 东 | 97.0 | 西 | 34.2 | 东南 |
| 2 | 12.0 | 东南 | 19.4 | 西南 | 26.8 | 西北 |
| 3 | 110.8 | 西南 | 119.4 | 西南 | 46.6 | 西南 |
| 4 | 56.0 | 东南 | 29.6 | 东南 | 87.5 | 西北 |
| 5 | 35.1 | 西 | 147.7 | 东 | 144.9 | 西 |
| 6 | 12.4 | 西南 | 64.0 | 西 | 100.2 | 东北 |
| 1 | 魏一鸣,袁潇晨,吴刚,等.气候变化风险评估研究现状与热点:基于Web of Science的文献计量分析[J].中国科学基金,2014,28(5):347-356. |
| 2 | IPCC.Climate Change 2021:The Physical Science Basis.Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[R].Cambridge,UK:Cambridge University Press,2021. |
| 3 | IPCC.Climate Change 2022:Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability.Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[R].Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press,2022. |
| 4 | 倪健.植被-气候分类指标及其应用[J].生态学杂志,1998(5):34-45. |
| 5 | 陈亚宁.干旱区科学概论[M].北京:科学出版社,2021. |
| 6 | 陈亚宁,李玉朋,李稚,等.全球气候变化对干旱区影响分析[J].地球科学进展,2022(2):111-119. |
| 7 | 李飞,赵军,赵传燕,等.中国北方干旱半干旱区潜在植被演替[J].生态学报,2011,31(3):689-697. |
| 8 | 陈曦,胡汝骥,姜逢清,等.中国干旱区自然地理[M].北京:科学出版社,2015. |
| 9 | 杨思遥,孟丹,李小娟,等.华北地区2001-2014年植被变化对SPEI气象干旱指数多尺度的响应[J].生态学报,2018,38(3):1028-1039. |
| 10 | 安洁,付博,李玮,等.东亚地区典型极端气候指标未来预估及高温下人口暴露度研究[J].北京大学学报(自然科学版),2020,56(5):884-892. |
| 11 | 杨舒畅,杨恒山.1982-2013年内蒙古地区干旱变化及植被响应[J].自然灾害学报,2019,28(1):175-183. |
| 12 | 韩兰英,张强,马鹏里,等.气候变暖背景下黄河流域干旱灾害风险空间特征[J].中国沙漠,2021,41(4):225-234. |
| 13 | 张华,徐存刚,王浩.2001-2018年西北地区植被变化对气象干旱的响应[J].地理科学,2020,40(6):1029-1038. |
| 14 | 刘华民,吴绍洪,郑度,等.潜在自然植被研究与展望[J].地理科学进展,2004(1):62-70. |
| 15 | 赵传燕,冯兆东,南忠仁,等.黄土高原祖厉河流域潜在植被分布模拟研究[J].地理学报,2007,62(1):52-61. |
| 16 | 张新时.中国植被及其地理格局中华人民共和国植被图集(1∶100万)说明书(上卷)[M].北京:地质出版社,2007. |
| 17 | Tüxen R.Die heutige potentielle natürliche vegetation als gegenstand der vegetationskartierung: mit 10 Tabellen[J]. Berichte zur deutschen Landeskunde,1956,13. |
| 18 | Holdridge L R.Determination of world plant formations from simple climatic data[J].Science,1947,105(2727):367. |
| 19 | Fan Z, Fan B.Shifts of the mean centers of potential vegetation ecosystems under future climate change in Eurasia[J].Forests,2019,10(10):873. |
| 20 | Zou S B, Cheng G D, Xiao H L,et al.Holocene natural rhythms of vegetation and present potential ecology in the Western Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Quaternary International,2009,194:55-67. |
| 21 | 范泽孟.中国生态过渡带分布的空间识别及情景模拟[J].地理学报,2021,76(3):626-644. |
| 22 | 范泽孟,范斌,岳天祥.欧亚大陆植被生态系统潜在分布情景及其对气候变化的响应[J].中国科学:地球科学,2019,49(11):1817-1830. |
| 23 | Fan Z, Bai X.Scenarios of potential vegetation distribution in the different gradient zones of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau under future climate change[J].Science of The Total Environment,2021,796(2):148918. |
| 24 | Bourque P A.Ecological life zones of Saint Lucia.[J].Global Ecology & Biogeography,2001,10(5):549-566. |
| 25 | 程姗岭,于海鹏,任钰,等.中国干旱半干旱区气候异常影响机理研究进展[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(3):21-35. |
| 26 | 尹云鹤,马丹阳,邓浩宇,等.中国北方干湿过渡区生态系统生产力的气候变化风险评估[J].地理学报,2021,76(7):1605-1617. |
| 27 | 侯学煜.中国的植被[M].北京:人民教育出版社,1960. |
| 28 | 张新时.研究全球变化的植被-气候分类系统[J].第四纪研究,1993(2):157-169. |
| 29 | MacMahon J A, Wieboldt T F.Applying biogeographic principles to resource management: a case study evaluating holdridge's life zone model[J].Great Basin Naturalist Memoirs,1978(2):245-257. |
| 30 | 郭柯,方精云,王国宏,等.中国植被分类系统修订方案[J].植物生态学报,2020,44(2):111-127. |
| 31 | 高萌.基于Holdridge生命地带模型的我国南北过渡带潜在植被分布模拟[D].兰州:兰州大学,2019. |
| 32 | 李玉,牛路,赵泉华.抚顺矿区1989-2019年土地利用/覆盖变化分析[J].测绘科学,2021,46(8):96-104. |
| 33 | 郝君明.中国Holdridge生命地带与潜在植被空间格局研究[D].兰州:西北师范大学,2009. |
| 34 | 修丽娜.基于CSCS模型的中国潜在自然植被时空分布特征研究[D].兰州:兰州大学,2014. |
| 35 | 车彦军,赵军,张明军,等.不同气候变化情景下2070-2099年中国潜在植被及其敏感性[J].生态学报,2016,36(10):2885-2895. |
| 36 | 杜怀玉,赵军,师银芳,等.气候变化下中国潜在植被演替及其敏感性[J].生态学杂志,2018,37(5):1459-1466. |
| [1] | 路建兵, 鞠珂, 廖伟斌. 2000—2020年甘肃省植被覆盖特征及其对气候变化和人类活动的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 118-127. |
| [2] | 冯永忠, 尹振良, 王凌阁, 毛龙, 邱晓峄, 陶卓琳, 吴翠霞. 1980—2020年气候和土地利用变化对甘肃省陆地生态系统碳储量的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(4): 168-179. |
| [3] | 程姗岭, 于海鹏, 任钰, 周洁, 罗红羽, 刘晨汐, 龚咏琪. 中国干旱半干旱区气候异常影响机理研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 21-35. |
| [4] | 梁鹏飞, 辛惠娟, 李宗省, 南富森, 唐彪, 张文豹. 基于Budyko假设的党河径流变化归因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 210-219. |
| [5] | 赵亚洲, 李生宇, 王世杰, 范敬龙, 吴燕. 2001—2020年新疆风沙环境致灾潜力特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 274-283. |
| [6] | 段然, 李宗杰, 王昱, 刘晓颖, 桂娟, 梁鹏飞, 李玉辰, 薛健, 刘梦晴, 徐斌. 石羊河流域径流变化特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 57-68. |
| [7] | 韩子言, 蒙吉军, 邹易, 朱利凯. 1982—2017年黑河流域植被指数动态及其对气候变化与生态建设工程的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(3): 96-106. |
| [8] | 辛春明, 何明珠, 李承义, 张力斌, 李新荣. 荒漠土壤氧化亚氮排放及其驱动因素研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 184-194. |
| [9] | 孙红, 段霁芸, 刘雨洁, 冉瑞兰, 李晓凤, 赵鹏善. 气候变化背景下沙蓬属( Agriophyllum )物种潜在地理分布[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(2): 255-263. |
| [10] | 杨宇哲, 岳大鹏, 赵景波, 刘怡婷, 李嘉宁, 杨天宇. 毛乌素沙地东南缘L3 、S3 黄土-古土壤色度特征及古气候意义[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 176-186. |
| [11] | 和海秀, 付爱红, 王川. 塔城地区西北部低山草甸植被指数变化及其驱动力[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(1): 187-196. |
| [12] | 李琳, 刘鹄, 孙程鹏, 赵文智. 基于地下水位与土壤含水量的地下水蒸散发估算[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(6): 277-287. |
| [13] | 秦豪君, 杨晓军, 马莉, 王一丞, 傅朝, 张君霞, 陆正奇. 2000—2020年中国西北地区区域性沙尘暴特征及成因[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(6): 53-64. |
| [14] | 赵康, 张磊, 李凯凯, 王斐, 张丙昌. 干旱区土壤自养微生物研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 177-186. |
| [15] | 柳欣滢, 金明, 杨帆, 马亚鹏, 刘慧, 孙小云, 夏敦胜. 毛乌素沙地东缘中全新世以来环境变化及其对文明演化的影响初探[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(5): 92-100. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
