中国沙漠 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 166-175.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2024.00105
• • 上一篇
收稿日期:2024-07-11
修回日期:2024-11-08
出版日期:2025-03-20
发布日期:2025-03-26
通讯作者:
张东梅
作者简介:康建军(1982—),男,甘肃张掖人,博士,研究方向为植物生理生态学。E-mail: kangjj14@lzb.ac.cn
基金资助:
Jianjun Kang1( ), Dongmei Zhang1(
), Dongmei Zhang1( ), Liwen Zhao1, Fan Yang2
), Liwen Zhao1, Fan Yang2
Received:2024-07-11
Revised:2024-11-08
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-26
Contact:
Dongmei Zhang
摘要:
荒漠绿洲芦苇(Phragmites australis)种群的发育特征和规律性受环境变化的显著影响,形成了独特的硅(Si)、氮(N)化学计量特征。本文以河西走廊荒漠绿洲5种芦苇景观生境(沙丘、草滩、丘间低地、盐化草地和湿地)为研究对象,探讨了芦苇Si、N化学计量学及内稳定性特征。结果表明:生境土壤Si含量和Si/N,芦苇各生育期和器官Si、N含量及Si/N存在显著差异。芦苇Si(SiO2)和土壤Si(SiO2)含量均较高,但土壤有效Si(H4SiO4)含量较低,导致芦苇Si/N较低,芦苇的生长受到Si素的限制。5种生境芦苇Si、N含量之间及其Si/N与土壤Si、N含量及Si/N,以及地下水埋深显著正相关,与地下水Si、N含量及Si/N无相关性,芦苇Si、N的相互耦合作用存在一定的协同性和稳定性。不同生境芦苇Si、N及其Si/N具有较高的内稳定性,并且芦苇Si/N的内稳定性要高于元素本身(HISi/N>HISi>HIN>4),相对于Si、N营养,芦苇Si/N受外界环境的影响较小,其生长过程是按照一定的Si、N吸收比例来调控自身的养分供应。
中图分类号:
康建军, 张东梅, 赵丽雯, 杨帆. 荒漠绿洲芦苇( Phragmites australis )硅氮化学计量学及内稳定性特征[J]. 中国沙漠, 2025, 45(2): 166-175.
Jianjun Kang, Dongmei Zhang, Liwen Zhao, Fan Yang. Si and N stoichiometry and homeostasis characteristics of Phragmites australis in desert oasis[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2025, 45(2): 166-175.
| 项目 | 生境 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
湿地W 0~0.2 m(泥炭层) | 盐化草地SM 0~1.0 m | 草滩DT 0~2.5 m | 丘间低地IL 0~2.5 m | 沙丘SD 0~2.5 m | |
| 地下水埋深/m | 0 | 0.90±0.06 | 1.70±0.24 | 2.30±0.28 | 6.00±0.37 |
| 土壤类型 | 积水、土壤泥炭发育 | 土壤表层盐分积累 | 沙质壤土 | 风沙土 | 风沙土 |
| 芦苇生态类型 | 水生芦苇 | 盐化芦苇 | 过渡带芦苇 | 过渡带芦苇 | 沙丘芦苇 |
表1 不同景观生境特征
Table 1 Habitat characteristics in different landscape habitats
| 项目 | 生境 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
湿地W 0~0.2 m(泥炭层) | 盐化草地SM 0~1.0 m | 草滩DT 0~2.5 m | 丘间低地IL 0~2.5 m | 沙丘SD 0~2.5 m | |
| 地下水埋深/m | 0 | 0.90±0.06 | 1.70±0.24 | 2.30±0.28 | 6.00±0.37 |
| 土壤类型 | 积水、土壤泥炭发育 | 土壤表层盐分积累 | 沙质壤土 | 风沙土 | 风沙土 |
| 芦苇生态类型 | 水生芦苇 | 盐化芦苇 | 过渡带芦苇 | 过渡带芦苇 | 沙丘芦苇 |
| 生 育 期 | 生境 | 器官 | 总量 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穗 | 叶 | 茎秆 | 地下垂直茎 | 地下水平茎 | 根系 | ||||||||||
| Si | N | Si | N | Si | N | Si | N | Si | N | Si | N | Si | N | ||
| 返 青 期 | 沙丘SD | — | — | 0.65c | 3.24c | 0.62a | 2.57c | 0.63c | 0.60b | 1.07a | 0.69a | 0.47bc | 1.10a | 3.44a | 8.20bc |
| 草滩DT | — | — | 0.94b | 2.99c | 0.37c | 2.60c | 1.03a | 0.30d | 0.82b | 0.53b | 0.51b | 0.94b | 3.67a | 7.36c | |
| 丘间低地IL | — | — | 0.24d | 3.69b | 0.29d | 3.41b | 0.61c | 0.42c | 0.73c | 0.54b | 0.59ab | 1.06a | 2.46c | 9.12b | |
| 盐化草地SM | — | — | 0.88b | 2.41d | 0.49b | 1.88d | 0.70b | 0.34d | 0.41d | 0.21c | 0.66a | 0.34c | 3.14ab | 5.18d | |
| 湿地W | — | — | 1.06a | 4.29a | 0.54b | 3.89a | 0.36d | 0.70a | 0.37de | 0.50b | 0.42c | 1.01ab | 2.75b | 10.39a | |
| 拔 节 期 | 沙丘SD | — | — | 1.01d | 2.69a | 1.04a | 1.42a | 0.51d | 0.69a | 1.29a | 0.42b | 0.52b | 0.49d | 4.37a | 5.71a |
| 草滩DT | — | — | 1.32bc | 2.55b | 0.83b | 0.77c | 1.09a | 0.29c | 0.82c | 0.21c | 0.56b | 0.62b | 4.62a | 4.44b | |
| 丘间低地IL | — | — | 0.67e | 2.15c | 0.54c | 0.44d | 0.62c | 0.17d | 0.94b | 0.17d | 0.63a | 0.52c | 3.40c | 3.45c | |
| 盐化草地SM | — | — | 1.43b | 2.66ab | 0.82b | 1.39a | 0.77b | 0.65a | 0.47d | 0.39b | 0.73a | 0.58bc | 4.22ab | 5.67a | |
| 湿地W | — | — | 1.81a | 2.82a | 0.79b | 0.98b | 0.42e | 0.57b | 0.36e | 0.76a | 0.51b | 0.87a | 3.89b | 6.00a | |
| 抽 穗 期 | 沙丘SD | 0.29c | 0.52a | 1.58b | 1.13a | 1.03b | 0.77b | 1.39a | 0.61b | 1.13b | 0.50c | 0.61c | 0.42b | 6.03a | 3.95a |
| 草滩DT | 0.25d | 0.43b | 1.17c | 1.03ab | 1.12b | 0.70c | 0.78c | 0.50c | 1.65a | 0.79a | 0.70b | 0.40b | 5.67a | 3.85ab | |
| 丘间低地IL | 0.30c | 0.45b | 0.91d | 0.95b | 0.70c | 0.53d | 0.85bc | 0.63b | 1.01b | 0.70b | 0.92a | 0.52a | 4.69b | 3.78b | |
| 盐化草地SM | 0.40b | 0.54a | 1.70b | 1.14a | 1.36a | 0.86a | 0.96b | 0.73a | 0.52c | 0.44d | 0.85ab | 0.49ab | 5.79a | 4.20a | |
| 湿地W | 0.47a | 0.50a | 2.47a | 1.18a | 1.09b | 0.67c | 0.31d | 0.33d | 0.41d | 0.36e | 0.61c | 0.55a | 5.36ab | 3.59c | |
| 枯 黄 期 | 沙丘SD | 1.42b | 1.41a | 1.23d | 1.53a | 1.37bc | 0.46b | 1.06a | 0.53a | 1.13a | 0.45a | 0.88a | 0.53b | 7.09b | 4.92a |
| 草滩DT | 1.54b | 0.96b | 1.36d | 1.17b | 1.23c | 0.34c | 0.98a | 0.31c | 0.89b | 0.36b | 0.77b | 0.62a | 6.77b | 3.77b | |
| 丘间低地IL | 1.09c | 0.82c | 1.88c | 1.47ab | 1.03d | 0.41bc | 0.36c | 0.42bc | 0.83b | 0.38b | 0.53c | 0.39c | 5.72c | 3.90b | |
| 盐化草地SM | 1.58ab | 1.31a | 2.44b | 1.52a | 1.80a | 0.52a | 0.62b | 0.45b | 0.51c | 0.47a | 0.78b | 0.62a | 7.73ab | 4.89a | |
| 湿地W | 1.75a | 0.73d | 3.59a | 1.58a | 1.48b | 0.36c | 0.38c | 0.35c | 0.38d | 0.34b | 0.54c | 0.53b | 8.12a | 3.89b | |
表2 不同景观生境芦苇各生育期各器官Si、N含量(%)
Table 2 Organ Si and N contents in different growth stage of Phragmites australis in different habitats
| 生 育 期 | 生境 | 器官 | 总量 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 穗 | 叶 | 茎秆 | 地下垂直茎 | 地下水平茎 | 根系 | ||||||||||
| Si | N | Si | N | Si | N | Si | N | Si | N | Si | N | Si | N | ||
| 返 青 期 | 沙丘SD | — | — | 0.65c | 3.24c | 0.62a | 2.57c | 0.63c | 0.60b | 1.07a | 0.69a | 0.47bc | 1.10a | 3.44a | 8.20bc |
| 草滩DT | — | — | 0.94b | 2.99c | 0.37c | 2.60c | 1.03a | 0.30d | 0.82b | 0.53b | 0.51b | 0.94b | 3.67a | 7.36c | |
| 丘间低地IL | — | — | 0.24d | 3.69b | 0.29d | 3.41b | 0.61c | 0.42c | 0.73c | 0.54b | 0.59ab | 1.06a | 2.46c | 9.12b | |
| 盐化草地SM | — | — | 0.88b | 2.41d | 0.49b | 1.88d | 0.70b | 0.34d | 0.41d | 0.21c | 0.66a | 0.34c | 3.14ab | 5.18d | |
| 湿地W | — | — | 1.06a | 4.29a | 0.54b | 3.89a | 0.36d | 0.70a | 0.37de | 0.50b | 0.42c | 1.01ab | 2.75b | 10.39a | |
| 拔 节 期 | 沙丘SD | — | — | 1.01d | 2.69a | 1.04a | 1.42a | 0.51d | 0.69a | 1.29a | 0.42b | 0.52b | 0.49d | 4.37a | 5.71a |
| 草滩DT | — | — | 1.32bc | 2.55b | 0.83b | 0.77c | 1.09a | 0.29c | 0.82c | 0.21c | 0.56b | 0.62b | 4.62a | 4.44b | |
| 丘间低地IL | — | — | 0.67e | 2.15c | 0.54c | 0.44d | 0.62c | 0.17d | 0.94b | 0.17d | 0.63a | 0.52c | 3.40c | 3.45c | |
| 盐化草地SM | — | — | 1.43b | 2.66ab | 0.82b | 1.39a | 0.77b | 0.65a | 0.47d | 0.39b | 0.73a | 0.58bc | 4.22ab | 5.67a | |
| 湿地W | — | — | 1.81a | 2.82a | 0.79b | 0.98b | 0.42e | 0.57b | 0.36e | 0.76a | 0.51b | 0.87a | 3.89b | 6.00a | |
| 抽 穗 期 | 沙丘SD | 0.29c | 0.52a | 1.58b | 1.13a | 1.03b | 0.77b | 1.39a | 0.61b | 1.13b | 0.50c | 0.61c | 0.42b | 6.03a | 3.95a |
| 草滩DT | 0.25d | 0.43b | 1.17c | 1.03ab | 1.12b | 0.70c | 0.78c | 0.50c | 1.65a | 0.79a | 0.70b | 0.40b | 5.67a | 3.85ab | |
| 丘间低地IL | 0.30c | 0.45b | 0.91d | 0.95b | 0.70c | 0.53d | 0.85bc | 0.63b | 1.01b | 0.70b | 0.92a | 0.52a | 4.69b | 3.78b | |
| 盐化草地SM | 0.40b | 0.54a | 1.70b | 1.14a | 1.36a | 0.86a | 0.96b | 0.73a | 0.52c | 0.44d | 0.85ab | 0.49ab | 5.79a | 4.20a | |
| 湿地W | 0.47a | 0.50a | 2.47a | 1.18a | 1.09b | 0.67c | 0.31d | 0.33d | 0.41d | 0.36e | 0.61c | 0.55a | 5.36ab | 3.59c | |
| 枯 黄 期 | 沙丘SD | 1.42b | 1.41a | 1.23d | 1.53a | 1.37bc | 0.46b | 1.06a | 0.53a | 1.13a | 0.45a | 0.88a | 0.53b | 7.09b | 4.92a |
| 草滩DT | 1.54b | 0.96b | 1.36d | 1.17b | 1.23c | 0.34c | 0.98a | 0.31c | 0.89b | 0.36b | 0.77b | 0.62a | 6.77b | 3.77b | |
| 丘间低地IL | 1.09c | 0.82c | 1.88c | 1.47ab | 1.03d | 0.41bc | 0.36c | 0.42bc | 0.83b | 0.38b | 0.53c | 0.39c | 5.72c | 3.90b | |
| 盐化草地SM | 1.58ab | 1.31a | 2.44b | 1.52a | 1.80a | 0.52a | 0.62b | 0.45b | 0.51c | 0.47a | 0.78b | 0.62a | 7.73ab | 4.89a | |
| 湿地W | 1.75a | 0.73d | 3.59a | 1.58a | 1.48b | 0.36c | 0.38c | 0.35c | 0.38d | 0.34b | 0.54c | 0.53b | 8.12a | 3.89b | |
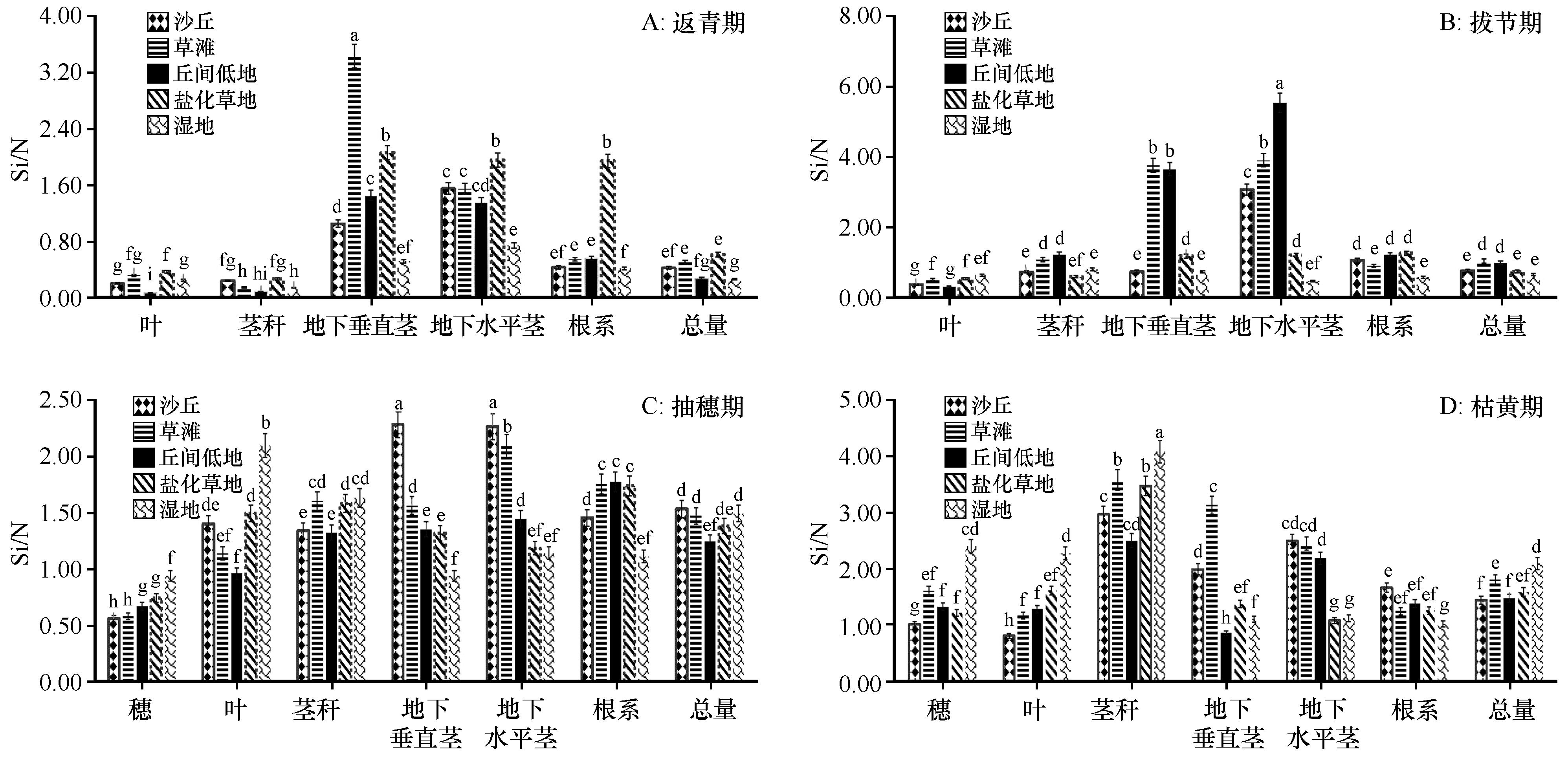
图2 不同景观生境芦苇各生育期、不同器官Si/N注:不同字母表示各处理间显著差异(P<0.05)
Fig.2 Si/N ratios in different organs and growth stages of Phragmites australis in different habitats
| 项目 | 效应 | 平方和 | 自由度df | 均方 | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | 截距 | 286.565 | 1 | 1 026.783 | 819.154 | 0.000** |
| 生境(A) | 155.651 | 1 | 153.254 | 96.254 | 0.000** | |
| 生育期(B) | 14.520 | 1 | 52.125 | 50.232 | 0.000** | |
| 器官(C) | 4.125 | 1 | 7.231 | 28.930 | 0.000** | |
| A×B | 24.512 | 2 | 24.532 | 24.542 | 0.000** | |
| A×C | 2.235 | 1 | 1.854 | 5.672 | 0.000** | |
| B×C | 12.254 | 1 | 12.500 | 10.468 | 0.000** | |
| A×B×C | 25.670 | 2 | 24.560 | 15.680 | 0.000** | |
| 误差 | 37.520 | 24 | 1.563 | |||
| 合计 | 1 548.000 | 32 | ||||
| N | 截距 | 212.256 | 1 | 678.776 | 417.180 | 0.000** |
| 生境(A) | 125.439 | 1 | 121.276 | 65.276 | 0.000** | |
| 生育期(B) | 10.531 | 1 | 35.170 | 25.234 | 0.000** | |
| 器官(C) | 3.165 | 2 | 5.225 | 21.965 | 0.000** | |
| A×B | 17.532 | 1 | 18.51 | 19.556 | 0.000** | |
| A×C | 2.265 | 2 | 1.450 | 4.630 | 0.000** | |
| B×C | 10.150 | 1 | 10.180 | 7.451 | 0.000** | |
| A×B×C | 20.361 | 1 | 16.512 | 11.663 | 0.000** | |
| 误差 | 30.558 | 16 | 1.340 | |||
| 合计 | 1 135.400 | 22 | ||||
| Si/N | 截距 | 367.835 | 1 | 788.796 | 312.150 | 0.000** |
| 生境(A) | 198.670 | 1 | 144.350 | 55.250 | 0.000** | |
| 生育期(B) | 20.650 | 2 | 49.148 | 29.279 | 0.000** | |
| 器官(C) | 6.120 | 1 | 6.280 | 20.663 | 0.000** | |
| A×B | 28.610 | 2 | 22.58 | 17.576 | 0.000** | |
| A×C | 2.851 | 2 | 1.865 | 5.750 | 0.000** | |
| B×C | 16.274 | 1 | 13.254 | 6.486 | 0.000** | |
| A×B×C | 27.685 | 1 | 19.750 | 10.691 | 0.000** | |
| 误差 | 34.512 | 27 | 1.680 | |||
| 合计 | 1 426.600 | 36 |
表3 生境、生育期和器官对芦苇Si、N含量及Si/N交互影响的方差分析结果
Table 3 Variance analysis of habitat, growth period and organ on Si, N content and Si/N interaction effects of reed
| 项目 | 效应 | 平方和 | 自由度df | 均方 | F | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Si | 截距 | 286.565 | 1 | 1 026.783 | 819.154 | 0.000** |
| 生境(A) | 155.651 | 1 | 153.254 | 96.254 | 0.000** | |
| 生育期(B) | 14.520 | 1 | 52.125 | 50.232 | 0.000** | |
| 器官(C) | 4.125 | 1 | 7.231 | 28.930 | 0.000** | |
| A×B | 24.512 | 2 | 24.532 | 24.542 | 0.000** | |
| A×C | 2.235 | 1 | 1.854 | 5.672 | 0.000** | |
| B×C | 12.254 | 1 | 12.500 | 10.468 | 0.000** | |
| A×B×C | 25.670 | 2 | 24.560 | 15.680 | 0.000** | |
| 误差 | 37.520 | 24 | 1.563 | |||
| 合计 | 1 548.000 | 32 | ||||
| N | 截距 | 212.256 | 1 | 678.776 | 417.180 | 0.000** |
| 生境(A) | 125.439 | 1 | 121.276 | 65.276 | 0.000** | |
| 生育期(B) | 10.531 | 1 | 35.170 | 25.234 | 0.000** | |
| 器官(C) | 3.165 | 2 | 5.225 | 21.965 | 0.000** | |
| A×B | 17.532 | 1 | 18.51 | 19.556 | 0.000** | |
| A×C | 2.265 | 2 | 1.450 | 4.630 | 0.000** | |
| B×C | 10.150 | 1 | 10.180 | 7.451 | 0.000** | |
| A×B×C | 20.361 | 1 | 16.512 | 11.663 | 0.000** | |
| 误差 | 30.558 | 16 | 1.340 | |||
| 合计 | 1 135.400 | 22 | ||||
| Si/N | 截距 | 367.835 | 1 | 788.796 | 312.150 | 0.000** |
| 生境(A) | 198.670 | 1 | 144.350 | 55.250 | 0.000** | |
| 生育期(B) | 20.650 | 2 | 49.148 | 29.279 | 0.000** | |
| 器官(C) | 6.120 | 1 | 6.280 | 20.663 | 0.000** | |
| A×B | 28.610 | 2 | 22.58 | 17.576 | 0.000** | |
| A×C | 2.851 | 2 | 1.865 | 5.750 | 0.000** | |
| B×C | 16.274 | 1 | 13.254 | 6.486 | 0.000** | |
| A×B×C | 27.685 | 1 | 19.750 | 10.691 | 0.000** | |
| 误差 | 34.512 | 27 | 1.680 | |||
| 合计 | 1 426.600 | 36 |
| 生境 | 土壤 | 地下水 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含水量/% | N含量/% | Si含量/% | Si/N | Si含量/% | N含量/% | Si/N | |
| 沙丘SD(0~2.5 m) | 3.2d | 0.0008a | 0.07cd | 87.50d | 0.00026ab | 0.00031ab | 0.84ab |
| 丘间低地IL(0~2.5 m) | 10.4c | 0.0005a | 0.09c | 185.71b | 0.00027a | 0.00030ab | 0.90a |
| 草滩DT(0~2.5 m) | 17.3b | 0.0007a | 0.13b | 180.00b | 0.00027a | 0.00036a | 0.75b |
| 盐化草地SM(0~1.0 m) | 22.7a | 0.0006a | 0.19a | 316.67a | 0.00029a | 0.00032a | 0.91a |
| 湿地W(0~0.2 m) | — | 0.0007a | 0.10bc | 142.86c | 0.00028a | 0.00033a | 0.85a |
表4 不同景观生境土壤及地下水Si、N含量
Table 4 Si and N contents of soil and groundwater in different landscape habitats
| 生境 | 土壤 | 地下水 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 含水量/% | N含量/% | Si含量/% | Si/N | Si含量/% | N含量/% | Si/N | |
| 沙丘SD(0~2.5 m) | 3.2d | 0.0008a | 0.07cd | 87.50d | 0.00026ab | 0.00031ab | 0.84ab |
| 丘间低地IL(0~2.5 m) | 10.4c | 0.0005a | 0.09c | 185.71b | 0.00027a | 0.00030ab | 0.90a |
| 草滩DT(0~2.5 m) | 17.3b | 0.0007a | 0.13b | 180.00b | 0.00027a | 0.00036a | 0.75b |
| 盐化草地SM(0~1.0 m) | 22.7a | 0.0006a | 0.19a | 316.67a | 0.00029a | 0.00032a | 0.91a |
| 湿地W(0~0.2 m) | — | 0.0007a | 0.10bc | 142.86c | 0.00028a | 0.00033a | 0.85a |
| 土壤Si | 土壤N | 土壤 Si/N | 地下水 埋深 | 芦苇 Si | 芦苇 N | 芦苇 Si/N | 地下水 Si | 地下水 N | 地下水 Si/N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤Si | — | |||||||||
| 土壤N | -0.32 | — | ||||||||
| 土壤Si/N | 0.90* | -0.58* | — | |||||||
| 地下水埋深 | -0.60* | 0.35 | -0.56* | — | ||||||
| 芦苇Si | 0.55* | 0.49* | 0.15 | 0.67* | — | |||||
| 芦苇N | 0.23 | 0.29 | 0.18 | 0.46* | 0.51* | — | ||||
| 芦苇Si/N | 0.09 | 0.22 | -0.06 | 0.54* | 0.61* | -0.56* | — | |||
| 地下水Si | 0.24 | -0.12 | 0.54* | -0.13 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.37 | — | ||
| 地下水N | -0.24 | -0.18 | 0.05 | -0.10 | -0.14 | -0.29 | -0.17 | 0.11 | — | |
| 地下水Si/N | 0.18 | 0.45 | 0.43 | -0.36 | 0.20 | 0.28 | 0.35 | 0.44* | -0.74* | — |
表5 芦苇Si、N化学计量特征与环境因素之间的相关性
Table 5 Correlation between Si, N stoichiometric characteristics of Phragmites australis and environmental factors
| 土壤Si | 土壤N | 土壤 Si/N | 地下水 埋深 | 芦苇 Si | 芦苇 N | 芦苇 Si/N | 地下水 Si | 地下水 N | 地下水 Si/N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤Si | — | |||||||||
| 土壤N | -0.32 | — | ||||||||
| 土壤Si/N | 0.90* | -0.58* | — | |||||||
| 地下水埋深 | -0.60* | 0.35 | -0.56* | — | ||||||
| 芦苇Si | 0.55* | 0.49* | 0.15 | 0.67* | — | |||||
| 芦苇N | 0.23 | 0.29 | 0.18 | 0.46* | 0.51* | — | ||||
| 芦苇Si/N | 0.09 | 0.22 | -0.06 | 0.54* | 0.61* | -0.56* | — | |||
| 地下水Si | 0.24 | -0.12 | 0.54* | -0.13 | 0.15 | 0.08 | 0.37 | — | ||
| 地下水N | -0.24 | -0.18 | 0.05 | -0.10 | -0.14 | -0.29 | -0.17 | 0.11 | — | |
| 地下水Si/N | 0.18 | 0.45 | 0.43 | -0.36 | 0.20 | 0.28 | 0.35 | 0.44* | -0.74* | — |
| 生境 | 指标 | 内稳定性 指数 | R2 | P | 是否 稳态 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沙丘 SD | Si | 6.55 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 稳态型 |
| N | 5.61 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 稳态型 | |
| Si/N | 7.79 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 稳态型 | |
| 草滩 DT | Si | 5.56 | 0.19 | 0.03 | 稳态型 |
| N | 4.94 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 稳态型 | |
| Si/N | 6.21 | 0.20 | 0.04 | 稳态型 | |
| 丘间 低地 IL | Si | 4.78 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 稳态型 |
| N | 5.36 | 0.27 | 0.02 | 稳态型 | |
| Si/N | 5.98 | 0.31 | 0.04 | 稳态型 | |
| 盐化 草地 SM | Si | 6.21 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 稳态型 |
| N | 5.05 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 稳态型 | |
| Si/N | 7.87 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 稳态型 | |
| 湿地 W | Si | 7.30 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 稳态型 |
| N | 6.23 | 0.29 | 0.04 | 稳态型 | |
| Si/N | 9.46 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 稳态型 |
表6 不同景观生境芦苇Si、N内稳定性
Table 6 Homeostasis of Si and N for Phragmitesaustralis in different habitats
| 生境 | 指标 | 内稳定性 指数 | R2 | P | 是否 稳态 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 沙丘 SD | Si | 6.55 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 稳态型 |
| N | 5.61 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 稳态型 | |
| Si/N | 7.79 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 稳态型 | |
| 草滩 DT | Si | 5.56 | 0.19 | 0.03 | 稳态型 |
| N | 4.94 | 0.10 | 0.03 | 稳态型 | |
| Si/N | 6.21 | 0.20 | 0.04 | 稳态型 | |
| 丘间 低地 IL | Si | 4.78 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 稳态型 |
| N | 5.36 | 0.27 | 0.02 | 稳态型 | |
| Si/N | 5.98 | 0.31 | 0.04 | 稳态型 | |
| 盐化 草地 SM | Si | 6.21 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 稳态型 |
| N | 5.05 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 稳态型 | |
| Si/N | 7.87 | 0.13 | 0.04 | 稳态型 | |
| 湿地 W | Si | 7.30 | 0.26 | 0.02 | 稳态型 |
| N | 6.23 | 0.29 | 0.04 | 稳态型 | |
| Si/N | 9.46 | 0.15 | 0.03 | 稳态型 |
| 1 | 南富森,李宗省,张小平,等.黄河北岸兰州段丘陵区土壤生态化学计量与空间变异[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(5):167-176. |
| 2 | 张志山,杨贵森,吕星宇,等.荒漠生态系统C、N、P生态化学计量研究进展[J].中国沙漠,2022,42(1):48-56. |
| 3 | 宁志英,李玉霖,杨红玲,等.科尔沁沙地优势固沙灌木叶片氮磷化学计量内稳性[J].植物生态学报,2019,43(1):46-54. |
| 4 | 阿里木·买买提,李翔,卡哈尔曼·恰依扎旦,等.天山云杉林下优势草本植物化学计量内稳性特征[J].西北林学院学报,2022,37(2):68-74. |
| 5 | Yu Q, Wilcox K, Pierre K L,et al.Stoichiometric homeostasis predicts plant species dominance,temporal stability,and responses to global change[J].Ecology,2015,96(9):2328-2335. |
| 6 | 贡璐,李红林,刘雨桐,等.N、P施肥对塔里木河上游绿洲棉花C、N、P生态化学计量特征的影响[J].生态学报,2017,37(22):7689-7697. |
| 7 | 金晓明,于良斌,张颖琪,等.群落演替对呼伦贝尔草地两种优势植物繁殖分配及生态化学计量的影响[J].应用生态学报,2020,31(3):787-793. |
| 8 | 赵睿,卜红梅,宋献方.再生水补水河道芦苇碳氮化学计量特征及其对环境的响应[J].生态学报,2021,41(6):2439-2450. |
| 9 | Xu H W, Qu Q, Yang J P,et al.Impact of drought on terrestrial ecosystem C-N-P stoichiometry and microbial nutrient limitation[J].Soil and tillage Research,2024,236:105951. |
| 10 | 杨恒,张丹,李桂芳,等.中国河湖岸带草本植物氮磷化学计量学及内稳性特征[J].生态科学,2024,43(2):78-86. |
| 11 | 海旭莹,董凌勃,汪晓珍,等.黄土高原退耕还草地C、N、P生态化学计量特征对植物多样性的影响[J].生态学报,2020,40(23):8570-8581. |
| 12 | Zhang Y W, Shang G, Zhou P.Interaction of soil water storage and stoichiometrical characteristics in the long-term natural vegetation restoration on the Loess Platea[J].Ecological Engineering,2018,116:7-13. |
| 13 | Rajman G, Rajendra K J, Ambuj M,et al.Treeline ecotone drives the soil physical,bio-chemical and stoichiometry properties in alpine ecosystems of the western Himalaya,India[J].Catena,2024,239:107950-107959. |
| 14 | 黄韵杰,李永刚,尹本丰,等.齿肋赤藓(Syntrichia caninervis)氮磷计量特征对降水量的响应[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(2):1-10. |
| 15 | Biju S, Fuentes S, Gupta D.Silicon improves seed germination and alleviates drought stress in lentil crops by regulating osmolytes,hydrolytic enzymes and antioxidant defense system[J].Plant Physiology and Biochemistry,2017,119:250-264. |
| 16 | 徐当会,高天鹏,李秋霞,等.硅的生物学功能及在草地生态系统中的应用研究进展[J].生态学报,2020,40(22):8347-8353. |
| 17 | Li Y T, Zhang W J, Cui J J,et al.Silicon nutrition alleviates the lipid peroxidation and ion imbalance of Glycyrrhiza uralensis seedlings under salt stress[J].Acta Physiologiae Plantarum,2016,38(4):96-105. |
| 18 | Zhang W J, Xie Z C, Wang L H,et al.Silicon alleviates salt and drought stress of Glycyrrhiza uralensis seedling by altering antioxidant metabolism and osmotic adjustment[J].Journal of Plant Research,2017,130(3):611-624. |
| 19 | Kang J J, Zhao W Z, Zhu X.Silicon improves photosynthesis and strengthens enzyme activities in the C3 succulent xerophyte Zygophyllum xanthoxylum [J].Journal of Plant Physiology,2016,199:76-86. |
| 20 | Kang J J, Zhao W Z, Wang Z W,et al.The features of main osmolytes,silicon and their coupling effects in improving drought resistance of the typical xerophytes in the desert areas of Northwest China[J].Land Degradation and Development,2020,31(17):2720-2733. |
| 21 | Cui G, Xiao X, Zhang W,et al.Exogenous Silicon relieve drought stress and salt stress of Glycyrrhiza uralensis seedlings by regulating proline metabolism and nitrogen assimilation[J].The Journal of Horticultural Science and Biotechnology,2021,96(6):728-737. |
| 22 | Cui J J, Zhang E H, Zhang X H,et al.Silicon alleviates salinity stress in licorice (Glycyrrhiza uralensis) by regulating carbon and nitrogen metabolism[J].Scientific Reports,2021,11(1):1115-1126. |
| 23 | Kang J J, Zhao W Z, Zhang C X,et al.Silicon accumulation by Phragmites australis positively responds to rise in groundwater depth in the desert oasis areas of the Hexi Corridor,China[J].Land Degradation and Development,2021,32(15):4350-4361. |
| 24 | Kang J J, Yang F, Zhang D M,et al.High ecostoichiometric stability and accumulating SiO2 and NO 3 - as main physiological adaptative mechanisms for reed to adverse environments[J].Research in Cold and Arid Regions,2024,16(5):250-258. |
| 25 | 邓晓红,宋玉琳,李宗省,等.河西地区生态敏感性演变格局及分区治理[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(5):232-240. |
| 26 | 李军,周发元,焦亮,等.1960-2022年河西走廊主要气候要素特征及气候生产潜力[J].中国沙漠,2024,44(6):14-25. |
| 27 | Persson J, Fink P, Goto A,et al.To be or not to be what you eat:regulation of stoichiometric homeostasis among autotrophs and heterotrophs[J].Oikos,2010,119(5):741-751. |
| 28 | 李合生.现代植物生理学[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2002. |
| 29 | 原雅楠,李正才,王斌,等.不同林龄榧树根、枝、叶的C、N、P化学计量及内稳性特征[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2021,45(6):135-142. |
| 30 | 王晶苑,王绍强,李纫兰,等.中国四种森林类型主要优势植物的 C∶N∶P化学计量学特征[J].植物生态学报,2011,35(6):587-595. |
| 31 | 秦遂初,马国瑞.植物营养与合理施肥[M]//孙羲.土壤养分.北京:农业出版社,1983:152-160. |
| 32 | 中国农业标准汇 编.土壤肥料卷[M].北京:中国标准出版社,1998:745-746. |
| 33 | 浙江农业大学.作物营养与施肥[M].北京:农业出版社,1992:123-138. |
| 34 | 李鸿博,陈诗,黄耀华,等.横断山脉亚高山带高山栎叶片生态化学计量及内稳性特征[J].植物研究,2023,43(6):923-931. |
| 35 | 中国土壤学会农业化学专业委员会.土壤农业化学常规分析法[M].北京:科学出版社,1983:274-288. |
| 36 | Chen Y H, Han W X, Tang L Y,et al.Leaf nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations of woody plants differ in responses to climate,soil and plant growth form[J].Ecography,2013,36(2):178-184. |
| 37 | 熊蔚,胡宇坤,宋垚彬,等.高等植物中硅元素的生态学作用[J].杭州师范大学学报(自然科学版),2017,16(2):164-172. |
| 38 | 李雨薇,王博,包玉海,等.草原风蚀坑发育对土壤生态化学计量的影响[J].中国沙漠,2023,43(5):166-175. |
| 39 | 张婷婷,刘文耀,黄俊彪,等.植物生态化学计量内稳性特征[J].广西植物,2019,39(5):701-712. |
| 40 | Xing W, Wu H, Shi Q,et al.Multielement stoichiometry of submerged macrophytes across Yunnan plateau lakes (China)[J].Scientific Reports,2015,5:10186-10194. |
| 41 | Li Y F, Li Q Y, Guo D Y,et al.Ecological stoichiometry homeostasis of Leymus chinensis in degraded grassland in western Jilin Province,NE China[J].Ecological Engineering,2016,90:387-391. |
| [1] | 胡广录, 陈海志, 麻进, 陶虎, 周成乾, 刘鹏. 黑河中游荒漠绿洲过渡带典型灌丛植物防风固沙效应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2023, 43(5): 31-40. |
| [2] | 赵颖, 刘冰, 赵文智, 温紫娟, 王宵. 荒漠绿洲湿地水分来源及植物水分利用策略[J]. 中国沙漠, 2022, 42(4): 151-162. |
| [3] | 张玲豫, 齐雅柯, 焦健, 李朝周. 河西走廊沙地芦苇(Phragmites australis)根际土壤微生物群落多样性[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(6): 1-9. |
| [4] | 宋冰, 王国华, 缑倩倩, 席璐璐. 沙埋对河西走廊荒漠绿洲过渡带一年生草本植物的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2021, 41(3): 185-194. |
| [5] | 常学礼, 李秀梅, 白雪莲, 季树新, 王理想. 荒漠绿洲交错区景观稳定性与维持机制[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(3): 43-50. |
| [6] | 王国华, 任亦君, 缑倩倩. 河西走廊荒漠绿洲过渡带封育对土壤和植被的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2020, 40(2): 222-231. |
| [7] | 孟阳阳, 刘冰, 刘婵. 荒漠绿洲湿地土壤水热盐动态过程及其影响机制[J]. 中国沙漠, 2019, 39(1): 149-160. |
| [8] | 孟阳阳, 刘冰, 刘婵. 水盐梯度下湿地柽柳(Tamarix ramosissima)光合响应特征和水分利用效率[J]. 中国沙漠, 2018, 38(3): 568-577. |
| [9] | 张勇勇, 富利, 赵文智, 闫加亮. 荒漠绿洲土壤优先流研究进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2017, 37(6): 1189-1195. |
| [10] | 张莹花, 刘世增, 纪永福, 刘虎俊, 李发明, 李银科. 石羊河中游河岸芦苇(Phragmites australis)群落空间格局[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(2): 342-348. |
| [11] | 张进虎, 唐进年, 李得禄, 魏林源, 满多清, 柴成武. 民勤荒漠绿洲过渡带灌丛沙堆形态特征及分布格局[J]. 中国沙漠, 2015, 35(5): 1141-1149. |
| [12] | 解婷婷1,2, 苏培玺1,3, 周紫鹃1,3, 李善家1,3, 张海娜1,3. 荒漠绿洲过渡带不同立地条件下物种多样性及其与土壤理化因子的关系[J]. 中国沙漠, 2013, 33(2): 508-514. |
| [13] | 彭 飞, 王 涛, 刘立超, 黄翠华. 民勤荒漠绿洲过渡带白刺灌丛沙堆演化阶段及其空间格局[J]. 中国沙漠, 2012, 32(3): 593-599. |
| [14] | 张恒嘉;赵文智. 有限灌溉对荒漠绿洲春玉米产量及产量性状的影响[J]. 中国沙漠, 2010, 30(4): 891-895. |
| [15] | 刘世增;孙保平;李银科;李发明. 微尺度下的荒漠绿洲景观结构数量分析与绿洲稳定性研究——以甘肃景泰县为例[J]. 中国沙漠, 2009, 29(6): 1148-1152. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
©2018中国沙漠 编辑部
地址: 兰州市天水中路8号 (730000)
电话:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
