
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2020, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (5): 158-168.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2020.00088
Previous Articles Next Articles
Qianqian Liu1( ), Xiaoping Yang2(
), Xiaoping Yang2( )
)
Received:2020-07-16
Revised:2020-08-21
Online:2020-09-28
Published:2020-09-28
Contact:
Xiaoping Yang
CLC Number:
Qianqian Liu, Xiaoping Yang. Spatial variations of grain size parameters of dune sands in the Mu Us Sandy Land and Hobq Sand Sea, northern China and its potential causes[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(5): 158-168.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2020.00088

Fig.1 Location and sampling sites of the Mu Us Sandy Land and the Hobq Sand Sea. Sand roses are calculated following Fryberger et al[31] with data from the U.S. National Climatic Data Center (NCDC) from 1973 to 2016, and the measurement interval is 3 h
| 采样区域 | 沙丘类型 | 样品 数量 | 各粒级沙百分含量/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 极粗沙 (-1~0 Φ) | 粗沙 (0~1 Φ) | 中沙 (1~2 Φ) | 细沙 (2~3 Φ) | 极细沙 (3~4 Φ) | 粉沙及黏土 (4~5 Φ) | ||||
| 毛乌素沙地东部 | 固定-半固定沙丘 | 6 | 最大值 | 0.33 | 12.73 | 69.55 | 50.96 | 4.83 | 0.19 |
| 最小值 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 47.06 | 26.23 | 0.73 | 0.03 | |||
| 平均值 | 0.05 | 2.65 | 57.72 | 36.52 | 2.93 | 0.12 | |||
| 流动沙丘 | 5 | 最大值 | 0.00 | 5.89 | 64.36 | 72.98 | 25.72 | 0.91 | |
| 最小值 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 15.35 | 26.86 | 2.79 | 0.05 | |||
| 平均值 | 0.00 | 1.54 | 42.78 | 45.69 | 9.56 | 0.42 | |||
| 毛乌素沙地西部 | 固定-半固定沙丘 | 3 | 最大值 | 0.23 | 2.56 | 12.00 | 86.03 | 25.19 | 6.40 |
| 最小值 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.40 | 53.62 | 8.48 | 0.39 | |||
| 平均值 | 0.08 | 0.89 | 6.99 | 74.03 | 15.22 | 2.79 | |||
| 流动沙丘 | 10 | 最大值 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 38.00 | 95.85 | 8.98 | 0.25 | |
| 最小值 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 54.90 | 2.33 | 0.00 | |||
| 平均值 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 10.34 | 84.85 | 4.71 | 0.08 | |||
| 库布齐沙漠 | 流动沙丘 | 13 | 最大值 | 0.00 | 1.46 | 27.73 | 93.51 | 42.34 | 3.55 |
| 最小值 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 50.85 | 3.63 | 0.02 | |||
| 平均值 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 5.09 | 76.83 | 17.50 | 0.46 | |||
| 河漫滩 | 1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.65 | 38.11 | 54.64 | 6.60 | ||
Table 1 Grain size composition of aeolian sands in the Mu Us Sandy Land and the Hobq Sand Sea
| 采样区域 | 沙丘类型 | 样品 数量 | 各粒级沙百分含量/% | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 极粗沙 (-1~0 Φ) | 粗沙 (0~1 Φ) | 中沙 (1~2 Φ) | 细沙 (2~3 Φ) | 极细沙 (3~4 Φ) | 粉沙及黏土 (4~5 Φ) | ||||
| 毛乌素沙地东部 | 固定-半固定沙丘 | 6 | 最大值 | 0.33 | 12.73 | 69.55 | 50.96 | 4.83 | 0.19 |
| 最小值 | 0.00 | 0.15 | 47.06 | 26.23 | 0.73 | 0.03 | |||
| 平均值 | 0.05 | 2.65 | 57.72 | 36.52 | 2.93 | 0.12 | |||
| 流动沙丘 | 5 | 最大值 | 0.00 | 5.89 | 64.36 | 72.98 | 25.72 | 0.91 | |
| 最小值 | 0.00 | 0.01 | 15.35 | 26.86 | 2.79 | 0.05 | |||
| 平均值 | 0.00 | 1.54 | 42.78 | 45.69 | 9.56 | 0.42 | |||
| 毛乌素沙地西部 | 固定-半固定沙丘 | 3 | 最大值 | 0.23 | 2.56 | 12.00 | 86.03 | 25.19 | 6.40 |
| 最小值 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.40 | 53.62 | 8.48 | 0.39 | |||
| 平均值 | 0.08 | 0.89 | 6.99 | 74.03 | 15.22 | 2.79 | |||
| 流动沙丘 | 10 | 最大值 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 38.00 | 95.85 | 8.98 | 0.25 | |
| 最小值 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.17 | 54.90 | 2.33 | 0.00 | |||
| 平均值 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 10.34 | 84.85 | 4.71 | 0.08 | |||
| 库布齐沙漠 | 流动沙丘 | 13 | 最大值 | 0.00 | 1.46 | 27.73 | 93.51 | 42.34 | 3.55 |
| 最小值 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.20 | 50.85 | 3.63 | 0.02 | |||
| 平均值 | 0.00 | 0.12 | 5.09 | 76.83 | 17.50 | 0.46 | |||
| 河漫滩 | 1 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.65 | 38.11 | 54.64 | 6.60 | ||
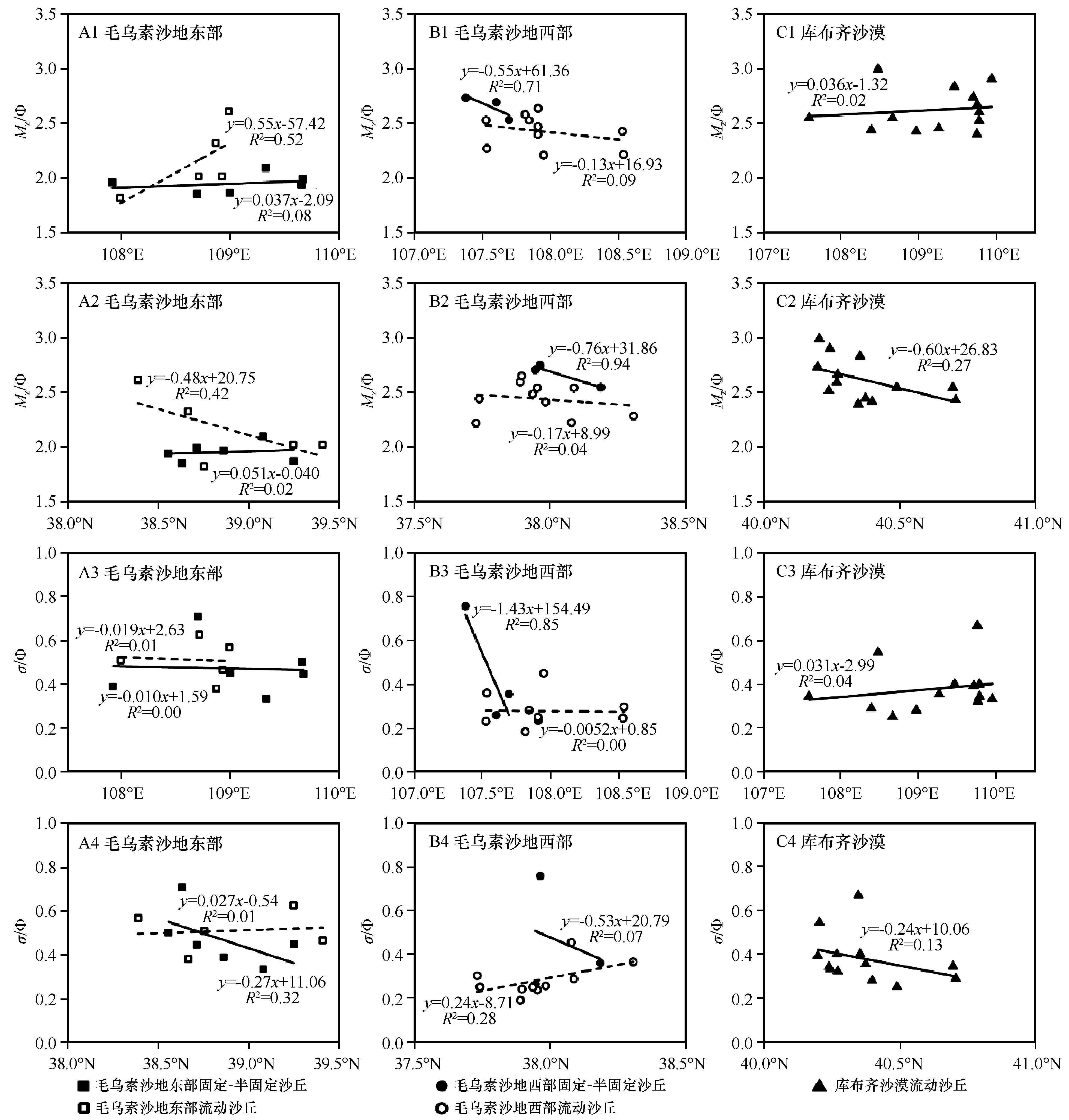
Fig.6 Variation of the mean grain size (Mz) and sorting coefficient (σ) of aeolian sands in the Mu Us Sandy Land and the Hobq Sand Sea with longitudes and latitudes.
| 1 | Pye K,Tsoar H.Aeolian Sand and Sand Dunes[M].Berlin,Germany:Springer,2002. |
| 2 | 朱震达,吴正,刘恕,等.中国沙漠概论[M].北京:科学出版社,1980. |
| 3 | Muhs D R,Stafford T W,Cowherd S D,et al.Origin of the late Quaternary dune fields of northeastern Colorado[J].Geomorphology,1996,17(1/3):129-149. |
| 4 | Williams M.Climate Change in Deserts[M].Cambridge,UK:Cambridge University Press,2014. |
| 5 | Goudie A S.Great Warm Deserts of the World:Landscapes and Evolution[M].New York,USA:Oxford University Press,2002. |
| 6 | Visher G S.Grain-size distributions and depositional processes[J].Journal of Sedimentary Petrology,1969,39(3):1074-1106. |
| 7 | 吉启慧.粒度分析在塔克拉玛干沙漠研究中的应用[J].中国沙漠,1996,16(2):173-179. |
| 8 | 杨转玲,钱广强,董治宝,等.库姆塔格沙漠北部三垄沙地区风成沉积物粒度特征[J].中国沙漠,2016,36(3):589-596. |
| 9 | 梁爱民,屈建军,董治宝,等.库姆塔格沙漠沉积物粒度端元特征及其物源启示[J].中国沙漠,2020,40(2):33-42. |
| 10 | Wang X M,Dong Z B,Zhang J W,et al.Grain size characteristics of dune sands in the central Taklimakan Sand Sea[J].Sedimentary Geology,2003,161(1/2):1-14. |
| 11 | 陈渭南.塔克拉玛干沙漠84 ºE沿线沙物质的粒度特征[J].地理学报,1993,48(1):33-46. |
| 12 | 毕志伟,杨振京,徐建明,等.塔里木盆地腹地第四纪沉积物粒度特征及其沉积环境[J].干旱区地理,2009,32(3):335-339. |
| 13 | Liu B L,Qu J J,Ning D H,et al.Grain-size study of aeolian sediments found east of Kumtagh Desert[J].Aeolian Research,2014,13:1-6. |
| 14 | 何清,杨兴华,霍文,等.库姆塔格沙漠粒度分布特征及环境意义[J].中国沙漠,2009,29(1):18-22. |
| 15 | 钱广强,董治宝,罗万银,等.巴丹吉林沙漠地表沉积物粒度特征及区域差异[J].中国沙漠,2011,31(6):1357-1364. |
| 16 | 宁凯,李卓仑,王乃昂,等.巴丹吉林沙漠地表风积砂粒度空间分布及其环境意义[J].中国沙漠,2013,33(3):642-648. |
| 17 | 钱亦兵,周兴佳,吴兆宁.准噶尔盆地沙物质粒度特征研究[J].干旱区研究,2000,17(2):34-41. |
| 18 | 黄杏珍,潘中海.应用粒度资料探讨毛乌素沙漠西南部的风砂特征[J].地理学报,1981,36(1):70-78. |
| 19 | 舒培仙,牛东风,李保生,等.毛乌素沙地现代沙丘沙的粒度特征及其意义[J].中国沙漠,2016,36(1):158-166. |
| 20 | 陈国祥,董治宝,崔徐甲,等.毛乌素沙地中部风成沙的组成与微形态特征[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(3):473-483. |
| 21 | 哈斯.腾格里沙漠东南缘格状沙丘粒度特征与成因探讨[J].地理研究,1998,17(2):178-184. |
| 22 | 哈斯,王贵勇.沙坡头地区新月形沙丘粒度特征[J].中国沙漠,2001,21(3):271-275. |
| 23 | 李超,董治宝,崔徐甲.腾格里沙漠东南缘不同发育阶段横向沙丘粒度特征[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(1):129-135. |
| 24 | 张正偲,董治宝,管梦鸾.腾格里沙漠东南缘反向沙丘形态演化过程[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(4):709-715. |
| 25 | 哈斯,庄燕美,王蕾,等.毛乌素沙地南缘横向沙丘粒度分布及其对风向变化的响应[J].地理科学进展,2006,25(6):42-51. |
| 26 | 刘海霞,李晋昌,苏志珠,等.毛乌素沙地西南缘灌丛沙丘沉积物的粒度和元素特征[J].中国沙漠,2015,35(1):24-31. |
| 27 | 李智佩,岳乐平,薛祥煦,等.毛乌素沙地东南部边缘不同地质成因类型土地沙漠化粒度特征及其地质意义[J].沉积学报,2016,24(2):267-275. |
| 28 | 李占宏,海春兴,丛艳静.毛乌素沙地表土粒度特征及其空间变异[J].中国水土保持科学,2009,7(2):74-79. |
| 29 | 吴霞,哈斯,杜会石,等.库布齐沙漠南缘抛物线形沙丘表面粒度特征[J].沉积学报,2012,30(5):937-944. |
| 30 | 庞营军,吴波,贾晓红,等.毛乌素沙地风况及输沙势特征[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(1):62-67. |
| 31 | Fryberger S G,Dean G.Dune forms and wind regime[M]//McKee E D. A Study of Global Sand Seas.Washington,USA:Government Printing Office,1979. |
| 32 | Yang X P,Li H W,Conache A.Large-scale controls on the development of sand seas in northern China[J].Quaternary International,2012,250:74-83. |
| 33 | Stevens T,Carter A,Watson T P,et al.Genetic linkage between the Yellow River,the Mu Us Desert and the Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Quaternary Science Reviews,2013,78:355-368. |
| 34 | Liu Q Q,Yang X P.Geochemical composition and provenance of aeolian sands in the Ordos Deserts,northern China[J].Geomorphology,2018,318:354-374. |
| 35 | Wang Z Y,Wu Y Q,Tan L H,et al.Provenance studies of aeolian sand in Mu Us Desert based on heavy-mineral analysis[J].Aeolian Research,2019,40:15-22. |
| 36 | Krumbein W C.Application of logarithmic moments to size frequency distributions of sediments[J].Journal of Sedimentary Petrology,1936,6(1):35-41. |
| 37 | Folk R L,Ward W.Brazos River bar:a study in the significance of grain size parameters[J].Journal of Sedimentary Petrology,1957,27(1):3-26. |
| 38 | 杨利荣,邹宁,岳乐平,等.库布齐沙漠碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄组成及其物源分析[J].第四纪研究,2017,37(3):560-569. |
| 39 | Langford R P,Gill T E,Jones S B.Transport and mixing of eolian sand from local sources resulting in variations in grain size in a gypsum dune field,White Sands,New Mexico,USA[J].Sedimentary Geology,2016,333(1):184-197. |
| 40 | Glennie K W.Desert Sedimentary Environments[M].Amsterdam,Netherlands:Elsevier,1970. |
| 41 | Bagnold R A.The Physics of Blown Sand and Desert Dunes[M].London,UK:Methuen,1941. |
| 42 | Lancaster N,Nickling W G,Neuman C M.Particle size and sorting characteristics of sand in transport on the stoss slope of a small reversing dune[J].Geomorphology,2002,43(3/4):233-242. |
| 43 | Wasson R J,Nanninga P M.Estimating wind transport of sand on vegetated surfaces[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms,1986,11(5):505-514. |
| 44 | Wolf S A,Nickling W G.The protective role of sparse vegetation in wind erosion[J].Progress in Physical Geography,1993,17(1):50-68. |
| 45 | Wiggs G F S,Livingstone I,Thomas D S G,et al.Effect of vegetation removal on airflow patterns and dune dynamics in the southwest Kalahari Desert[J].Land Degradation and Rehabilitation,1994,5(1):13-24. |
| 46 | Van de Ven T,Frypear D W,Spaan W P.Vegetation characteristics and soil loss by wind[J].Journal of Soil and Water Conservation,1989,44(4):347-349. |
| 47 | Fan D Q,Qin S G,Zhang Y Q,et al.Effects of sand-fixing vegetation on topsoil properties in the Mu Us Desert,northwest China[J].Nature Environment and Pollution Technology,2015,14(4):749-756. |
| 48 | Chepil W S.Dynamics of wind erosion:1.Nature of movement of soil by wind[J].Soil Science,1945,60(4):305-320. |
| 49 | Chepil W S.Influence of moisture on erodibility of soil by wind[J].Proceedings of Soil Science Society of America,1956,20(2):288-292. |
| 50 | Dong Z B,Liu X P,Wang X M.Wind initiation thresholds of the moistened sands[J].Geophysical Research Letters,2002,29(12):GL013128. |
| 51 | Wiggs G F S,Baird A J,Atherton R J.The dynamic effects of moisture on the entrainment and transport of sand by wind[J].Geomorphology,2004,59(1/4):13-30. |
| 52 | McKenna-Neuman C,Gilbert R.Aeolian processes and landforms in glaciofluvial environments of southeastern Baffin Island,NWT,Canada[M]//Nickling W G.Aeolian Geomorphology.Boston,USA:Allen and Unwin,1986:213-235. |
| 53 | Li Z S,Feng D J,Wu S L,et al.Grain size and transport characteristics of non-uniform sand in aeolian saltation[J].Geomorphology,2008,100(3/4):484-493. |
| 54 | 管超,哈斯额尔敦,周炎广,等.库布齐沙漠南缘风水交互特征及其对抛物线形沙丘发育的影响[J].中国沙漠,2018,38(5):899-908. |
| 55 | 李小妹,严平.干旱区沙漠与河流复合地貌过程研究进展[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(5):97-104. |
| [1] | Kaijia Pan, Zhengcai Zhang, Aimin Lang. The characteristics of inner boundary layer airflow over reversing dunes and its effect on dune morphological evolution [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 1-8. |
| [2] | Ying Yang, Lü Ping, Fang Ma, Zhun Liang, Mingjing Xu. Characteristics of wind regime in the southwest edge of the Ulan Buh Desert and their influence on the formation of dome dune [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 19-26. |
| [3] | Sarina, Zhibao Dong, Weige Nan. The Aesthetic Value of Mega-dune Lines in the Badain Jaran Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 221-230. |
| [4] | Chunming Zhu, Zhibao Dong, Zhengyao Liu, Nan Xiao, Junhuai Yang, Miaoyan Feng. Grain size and micro-morphology characteristics of the surface ediments of dendritic sand dunes in the Gurbantunggut Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 9-18. |
| [5] | Min Cao, Lupeng Yu, Ping An, Zhibao Dong, Junxiang Zhao, Zhongping Lai, Changsheng Wang. Luminescence chronology and environmental implications of palaeolacustrine sediments beneath linear dunes in northern Qarhan Salt Lake region [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 101-110. |
| [6] | Xiaoxu Wang, Ping Yan, Yong Wang, Miao Dong, Yijiao Wang, Xiao Zhang. Effects of slope gradient and shape on climbing dunes: a wind tunnel experiment [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(6): 118-126. |
| [7] | Di Deng, Zebin Zhao, Yuan Ma. Modeling of species distribution with GIS in arid regions: take Caragana korshinskii for example [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(5): 74-80. |
| [8] | Suchao Li, Man Qiu, Xiaoze Li, Jingde Liu, Limin Wang, Yang Hu, Zhigang Li, Gaihong Niu. Characteristics, age and process of Mohetai alluvial fan gobi in the upper reaches of Baiyang River in the western margin of Junggar Basin, NW China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 1-9. |
| [9] | Fang Chen, Quanlin Ma, Linyuan Wei, Dekui Zhang, Hongbo Yuan, Feng Ding, Xiaoke Hu, Zhong Zhang. Soil seed bank characteristics of Agriophyllum squarrosum [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 190-196. |
| [10] | Mingjing Xu, Lü Ping, Nan Xiao, Junhuai Yang, Zhengyao Liu, Miaoyan Feng, Zhun Liang. Effect of vegetation cover on dune migration in northwest Mu Us Sandy Land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 71-80. |
| [11] | Keqi Wang, Hui Zhao, Yongwei Sheng, Shengan Zhang, Xingfan Wang, Hongyu Yang, Qian Chao. Distribution and morphological parameters of dunes in the Badain Jaran Desert based on DEM [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 81-94. |
| [12] | Liu Hui, Li Xiaoying, Xia Cuizhen, Yao Zhengyi. Formation of dunes in Gyaca-Mainling section of Yarlung Zangbo River Valley of China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(3): 16-26. |
| [13] | Li Zhixing, Li Zhizhong, Jin Jianhui, Zheng Fei, Zhang Wenjing, Bai Li. Spatial-temporal variation of drift potential and dune morphology evolution during 2008-2018 in Changli coast of Hebei, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(3): 94-105. |
| [14] | Shi Weikang, Dong Zhibao, Chen Guoxiang, Ma Fang, Li Chao, Yang Junhuai. Discussion on the symbiosis of barchan dune and linear dune: a case study from Sahara Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(3): 135-144. |
| [15] | Shao Mei, Luo Wanyin, Che Xuehua. Preliminary application and accuracy assessment of COSI-Corr in the study of aeolian geomorphology [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(3): 151-158. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech