
- CN 62-1070/P
- ISSN 1000-694X
- Bimonthly 1981

Journal of Desert Research ›› 2021, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (5): 183-191.DOI: 10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00061
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yingying He1( ), Minghan Yu1(
), Minghan Yu1( ), Guodong Ding1, Guanglei Gao1, Wei Liu2, Ziyuan Zhou1
), Guodong Ding1, Guanglei Gao1, Wei Liu2, Ziyuan Zhou1
Received:2021-04-05
Revised:2021-04-27
Online:2021-09-20
Published:2021-09-23
Contact:
Minghan Yu
CLC Number:
Yingying He, Minghan Yu, Guodong Ding, Guanglei Gao, Wei Liu, Ziyuan Zhou. Responses of seedling growth and biomass allocation of Artemisia ordosica to precipitation and precipitation interval[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(5): 183-191.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.desert.ac.cn/EN/10.7522/j.issn.1000-694X.2021.00061
| 处理 时间 | 月平均 降雨量/mm | 降雨 间隔 | 平均每次降雨量/mm | 月降雨频次 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W- | W | W+ | ||||
| 7月 | 69.75 | T | 8.14 | 11.63 | 15.11 | 6 |
| T+ | 16.2 | 23.25 | 30.23 | 3 | ||
| T++ | 24.41 | 34.88 | 45.34 | 2 | ||
| 8月 | 63.33 | T | 7.39 | 10.56 | 13.72 | 6 |
| T+ | 14.70 | 21.11 | 27.44 | 3 | ||
| T++ | 22.17 | 31.67 | 41.18 | 2 | ||
| 9月 | 52.76 | T | 6.16 | 8.79 | 11.43 | 6 |
| T+ | 12.30 | 17.59 | 22.86 | 3 | ||
| T++ | 18.40 | 26.38 | 34.29 | 2 | ||
Table 1 Total precipitation and precipitation interval setting in experiment
| 处理 时间 | 月平均 降雨量/mm | 降雨 间隔 | 平均每次降雨量/mm | 月降雨频次 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W- | W | W+ | ||||
| 7月 | 69.75 | T | 8.14 | 11.63 | 15.11 | 6 |
| T+ | 16.2 | 23.25 | 30.23 | 3 | ||
| T++ | 24.41 | 34.88 | 45.34 | 2 | ||
| 8月 | 63.33 | T | 7.39 | 10.56 | 13.72 | 6 |
| T+ | 14.70 | 21.11 | 27.44 | 3 | ||
| T++ | 22.17 | 31.67 | 41.18 | 2 | ||
| 9月 | 52.76 | T | 6.16 | 8.79 | 11.43 | 6 |
| T+ | 12.30 | 17.59 | 22.86 | 3 | ||
| T++ | 18.40 | 26.38 | 34.29 | 2 | ||
| 变量 | 株高 | 冠幅 |
|---|---|---|
| W | 26.532*** | 0.028 |
| T | 8.191** | 76.380*** |
| W×T | 0.625 | 2.791 |
Table 2 Results(F-values)based on Two-way ANOVA of the effects of precipitation and precipitation interval on tree height and crown of Artemisia ordosica seedlings
| 变量 | 株高 | 冠幅 |
|---|---|---|
| W | 26.532*** | 0.028 |
| T | 8.191** | 76.380*** |
| W×T | 0.625 | 2.791 |
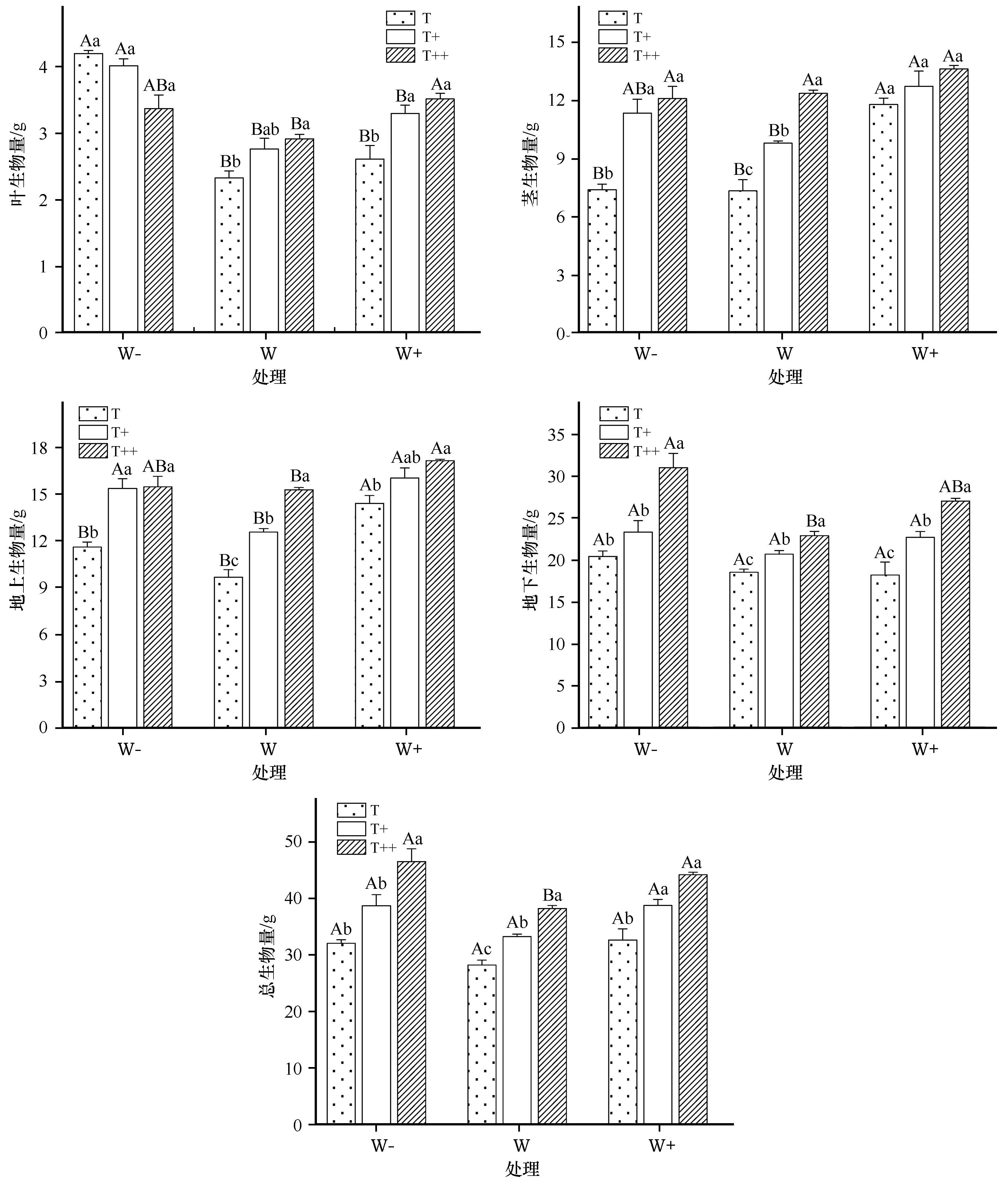
Fig.2 Dynamics of leaf biomass,stem biomass,aboveground biomass, underground biomass, total biomass of Artemisia ordosica seedlings in different precipitation patterns (Mean±SE)
| 变量 | 地上生物量 | 地下生物量 | 总生物量 | 根冠比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | 39.199*** | 13.780*** | 17.772*** | 36.496*** |
| T | 60.052*** | 49.249*** | 61.273*** | 23.001*** |
| W×T | 3.860** | 3.319** | 0.775 | 13.186*** |
Table 3 Results(F-values)based on Two-way ANOVA of the effects of precipitation and precipitation interval on aboveground biomass,belowground biomass and root/shoot ratio of Artemisia ordosica seedlings
| 变量 | 地上生物量 | 地下生物量 | 总生物量 | 根冠比 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W | 39.199*** | 13.780*** | 17.772*** | 36.496*** |
| T | 60.052*** | 49.249*** | 61.273*** | 23.001*** |
| W×T | 3.860** | 3.319** | 0.775 | 13.186*** |
| 1 | Gong D,Shi P,Wang J.Daily precipitation changes in the semi-arid region over northern China[J].Journal of Arid Environments,2004,59(4):771-784. |
| 2 | IPCC.Climate Change 2013:The Physical Science Basis[M].Cambridge,UK: Cambridge University Press,2013. |
| 3 | Yao S,Zhao C.Impact of Different Yearly Rainfall Patterns on Dynamic Changes of Soil Moisture of Fixed Sand Dune in the Horqin Sandy Land[R].IOP Conference Series Earth and Environmental Science,2019:12-20. |
| 4 | 段桂芳.模拟降水格局变化对红砂种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[D].兰州:甘肃农业大学,2016. |
| 5 | 岳永寰,靳瑰丽,宫珂,等.人工模拟降水格局变化对醉马草种子萌发和幼苗生长的影响[J].生态学杂志,2020,39(3):838-846. |
| 6 | Piper F I,Viegla B,Linares J C,et al.Mediterranean and temperate tree lines are controlled by different environmental drivers[J].Journal of Ecology,2016,104(3):691-702. |
| 7 | 于明含.典型固沙植物冠层温度和气孔导度特征及其对土壤水分的响应[D].北京:北京林业大学,2016. |
| 8 | Weltzin J F,Loik M E,Susanne S,et al.Assessing the response of terrestrial ecosystems to potential changes in precipitation[J].Bioence,2003,53(10):941-952. |
| 9 | 及利,韩姣,王芳,等.干旱胁迫对不同土壤基质下核桃楸幼苗的生理特性的影响[J].植物研究,2019,39(5):722-732. |
| 10 | Liu Y,Pan Q,Zheng S,et al.Intra-seasonal precipitation amount and pattern differentially affect primary production of two dominant species of Inner Mongolia grassland[J].Acta Oecologica,2012,44:2-10. |
| 11 | 白蕾,单立山,李毅,等.降雨格局变化对红砂幼苗根系生长和生物量分配的影响[J].西北植物学报,2017,37(1):163-170. |
| 12 | 赵文智,刘鹄.干旱、半干旱环境降水脉动对生态系统的影响[J].应用生态学报,2011,22(1):243-249. |
| 13 | 董雪,辛智鸣,鲍芳,等.模拟降雨格局变化下白刺(Nitraria tangutorum)表型变异[J].中国沙漠,2019,39(1):127-134. |
| 14 | 张金屯.数量生态学[M].北京:科学出版社,2011. |
| 15 | 温琦,赵文博,张幽静,等.植物干旱胁迫响应的研究进展[J].江苏农业科学,2020,48(12):11-15. |
| 16 | 单立山,李毅,段桂芳,等.模拟降雨变化对两种荒漠植物幼苗生长及生物量分配的影响[J].干旱区地理,2016,39(6):1267-1274. |
| 17 | Carrión-Prieto P,Hernández-Navarro S,Martín-Ramos P,et al.Mediterranean shrublands as carbon sinks for climate change mitigation:new root-to-shoot ratios[J].Carbon Management,2017,8(1):67-77. |
| 18 | Walch J L,Hidayati S N,Dixon K W,et al.Climate change and plant regeneration from seed[J].Global Change Biology,2011,17(6):2145-2161. |
| 19 | Vile D,Pervent M,Belluau M,et al.Arabidopsis growth under prolonged high temperature and water deficit: independent or interactive effects?[J].Plant Cell & Environment,2012,35:702-718. |
| 20 | 马赟花,张铜会,刘新平,等.极端降水事件对科尔沁沙地一年生植被的影响[J].中国沙漠,2016,36(1):52-58. |
| 21 | 周双喜,吴冬秀,张琳,等.降雨格局变化对内蒙古典型草原优势种大针茅幼苗的影响[J].植物生态学报,2010,34(10):1155-1164. |
| 22 | 何莹莹,于明含,丁国栋,等.基于冠层温度的典型沙生植物土壤水分状况诊断[J].中国水土保持科学,2018,16(4):89-96. |
| 23 | 姜江.中国季风区及干旱区变化与预估[D].北京:中国科学院大学,2015. |
| 24 | 王佳佳.夜间增温和改变降雨对三种温带草原类型根系生长和死亡的影响[D].开封:河南大学,2019. |
| 25 | 杨石岭,董欣欣,肖举乐.末次冰盛期以来东亚季风变化历史中国北方的地质记录[J].中国科学:地球科学,2019,49(8):1169-1181. |
| 26 | Cheng X,An S,Li B,et al.Summer rain pulse size and rainwater uptake by three dominant desert plants in a desertified grassland ecosystem in northwestern China[J].Plant Ecology,2006,184(1):1-12. |
| 27 | Bai Y F,Wu J G,Xing Q,et al.Primary production and rain use efficiency across a precipitation gradient on the Mongolia Plateau[J].Ecology,2008,89:2140-2153. |
| 28 | 张浩,王新平,张亚峰,等.干旱荒漠区不同生活型植物生长对降雨量变化的响应[J].生态学杂志,2015,34(7):1847-1853. |
| 29 | 何季,吴波,鲍芳,等.人工模拟增雨对乌兰布和沙漠白刺生物量分配的影响[J].林业科学,2016,52(5):81-91. |
| 30 | Chou W W,Silver W L,Jackson R D,et al.The sensitivity of annual grassland carbon cycling to the quantity and timing of rainfall[J].Global Change Biology,2008,14:1382-1394. |
| 31 | Loik M E.Sensitivity of water relations and photosynthesis to summer precipitation pulses for Artemisia tridentata and Purshia tridentata[J].Plant Ecology,2007,191:95-108. |
| 32 | 金成功.增雨和竞争对大豆和反枝苋的生长和氮素吸收的影响[D].哈尔滨:东北农业大学,2017. |
| 33 | 李文娆,张岁岐,丁圣彦,等.干旱胁迫下紫花苜蓿根系形态变化及与水分利用的关系[J].生态学报,2010,30(19):5140-5150. |
| 34 | Kir L P,Weisbach A N,Weiner J.Root and shoot competition: a meta-analysis[J].Journal of Ecology,2013,101:1298-1312. |
| 35 | Yu M H,Ding G D,Gao G L,et al.Double effects of age and environment on resource allocation trade-offs of Salix psammophila in different microtopographic habitats of a sand dune[J].Journal of Plant Growth Regulation,2020,39:544-552. |
| 36 | Robertson T R,Bell C W,Zak J C,et al.Precipitation timing and magnitude differentially affect aboveground annual net primary productivity in three perennial species in a Chihuahuan Desert grassland[J].New Phytologist,2009,181(1):230-242. |
| 37 | 代烁.降雨格局对羊草生物量、雨水利用效率和土壤性质的影响[D].吉林:东北师范大学,2020. |
| 38 | Golodets C,Sternberg M,Kigel J,et al.From desert to Mediterranean rangelands:will increasing drought and inter-annual rainfall variability affect herbaceous annual primary productivity?[J].Climatic Change,2013,119(3/4):785-798. |
| 39 | 张宇航,杨默远,潘兴瑶,等.降雨场次划分方法对降雨控制率的影响分析[J].中国给水排水,2019,35(13):122-127. |
| 40 | 张嘉嘉.不同时期降雨变化对中国北方半干旱草地生态系统物种丰富度和地上净初级生产力的影响[D].开封:河南大学,2018. |
| 41 | 丁红,张智猛,戴良香,等.水分胁迫和氮肥对花生根系形态发育及叶片生理活性的影响[J].应用生态学报,2015,26(2):450-456. |
| 42 | 孙百生,钱金平,赵欢蕊.西北典型荒漠植物红砂生物量及根系形态特征对降水格局的响应[J].生态环境学报,2018,27(11):1993-1999. |
| 43 | 张荣.人工模拟降雨格局变化对白刺幼苗生长及根系形态特征的影响[D].兰州:甘肃农业大学,2016. |
| 44 | 张景波,李新乐,吴波,等.长期模拟增雨对荒漠植物形态特征及空间分布格局的影响[J].应用生态学报,2019,30(10):3367-3375. |
| 45 | 盛军.模拟降雨格局变化与延迟萌发对两种一年生植物表型可塑性的影响[D].长春:东北师范大学,2019. |
| 46 | 王博,段玉玺,王伟峰,等.油蒿灌丛群落浅层土壤水分对不同降雨格局的响应[J].应用生态学报,2020,31(5):1571-1578. |
| 47 | 李新乐,吴波,张建平,等.白刺沙包浅层土壤水分动态及其对不同降雨量的响应[J].生态学报,2019,39(15):5701-5708. |
| 48 | 单立山,李毅,张荣,等.降雨格局变化对白刺幼苗根系形态特征的影响[J].生态学报,2017,37(21):7324-7332. |
| 49 | 段桂芳,单立山,李毅,等.降水格局变化对红砂幼苗生长的影响[J].生态学报,2016,36(20):6457-6464. |
| 50 | Heisler-White J L,Knapp A K,Kelly E F.Increasing precipitation event size increases aboveground net primary productivity in a semi-arid grassland[J].Oecologia,2008,158(1):129-140. |
| 51 | Fay P A,Blair J M,Smith M D,et al.Relative effects of precipitation variability and warming on tallgrass prairie ecosystem function[J].Biogeosciences,2011,11:3053-3068. |
| 52 | Knapp A K,Fay P A,Blair J M,et al.Rainfall variability,carbon cycling,and plant species diversity in a mesic grassland[J].Science,2002,298(5601):2202-2205. |
| [1] | Yanli Tian, Peifang Chong, Wentao Lu, Xiangyang Jia. Effects of simulated nitrogen settlement and precipitation changes on physiological characteristics of Reaumuria soongorica and Salsola passerina [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(3): 165-173. |
| [2] | Shengxia Wang, Fei Wang. Response of oasis area to the surface runoff in Hexi inland river basin of China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(2): 231-241. |
| [3] | Xinxin Guo, Xiaoan Zuo, Ping Yue, Xiangyun Li, Shenglong Zhao, Peng Lv, Ya Hu. Responses of leaf morphological traits of three dominant plants to water and nitrogen in desert steppe of Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 137-144. |
| [4] | Jun Lei, Xiaohu Yang, Hongmei Liu, Yuhong Zhao, Juping Fan, Caixia Guo. The characteristics of desert vegetation biomass and its influencing factors in the middle reaches of the Heihe River [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 203-208. |
| [5] | Yuanzheng He, Wenda Huang, Xin Zhao, Peng Lv, Huaihai Wang. Review on the impact of climate change on plant diversity [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2021, 41(1): 59-66. |
| [6] | Yimei Sun, Qing Tian, Aixia Guo, Xiaoan Zuo, Peng Lv, Senxi Zhang. Effects of water and nitrogen changes on vegetation characteristics and leaf traits in Horqin Sandy land, Northern China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(6): 223-232. |
| [7] | Xianzhi Yin, Yirong Wang, Han Luo, Yulong Ren, Tiantian Wang, Yanfeng Wang. The relationship between atmospheric water renewal and the spatial distribution of surface precipitation in Gansu Province from 1960 to 2019 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(6): 61-70. |
| [8] | Jin Zhan, Yulin Li, Dan Han, Hongling Yang. Biomass allocation and its ecological significance of three dominant sand-fixing shrubs in the semi-arid desert area [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(5): 149-157. |
| [9] | Bingyao Wang, Xingchen Liu, Lichao Liu. Characteristics of precipitation in the surrounding area of Tengger Desert in 1957-2017 [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(4): 163-170. |
| [10] | Yue Yanpeng, Sun Yingtao, Pang Yingjun, Cheng Long, Zhou Hong, Jia Xiaohong, Zhao Yuxing, Zhao Heju, Wu Bo. Root characteristics of Artemisia ordosica in the process of sand dunes activation in Mu Us Sandland [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(3): 177-184. |
| [11] | Wu Lili, Liu Danyi, Yang Wenbin, Wang Tao, Li Wei, Feng Jinchao, Feng Wei. Relationship between precipitation and soil water storage and soil deep percolation in mobile sand land [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(3): 210-218. |
| [12] | Li Xiangyun, Yue Ping, Guo Xinxin, Zhang Rui, Zhao Shenglong, Zhang Senxi, Wang Shaokun, Zuo Xiaoan. Response of photosynthetic rate of plant community to water and nitrogen addition in desert steppe of Inner Mongolia [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2020, 40(1): 116-124. |
| [13] | Ma Xiaojun, Li Yunfei. Soil Microbial Biomass and Enzyme Activities during Revegetation Process in the Southeastern Fringe of the Tengger Desert [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(6): 159-166. |
| [14] | Lai Chimin, Lai Riwen, Xue Xian, Li Chengyang, You Quangang, Huang Cuihua, Peng Fei. Estimation of Aboveground Biomass of Different Degraded Alpine Grassland Based on Vegetation Coverage and Height [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(5): 127-134. |
| [15] | Chen Juanli, Zhao Xueyong, Liu Xinping, Zhang Yaqiu, Luo Yongqing, Zhang Rui, Zhang Runxia, Yu Hailun. Effects of Precipitation on Growth and Physiology of Three Psammophytes in the Horqin Sandy Land, China [J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2019, 39(5): 163-173. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
©2018Journal of Desert Research
Tel:0931-8267545
Email:caiedit@lzb.ac.cn;desert@lzb.ac.cn
Support:Magtech